Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
AC Three-Phase Induction Motor
Încărcat de
Nayef AlrehayelTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AC Three-Phase Induction Motor
Încărcat de
Nayef AlrehayelDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Ch6. INDUCTION MOTOR
Prepared by: Dr. Hani Muhsen
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
INDUCTION MOTOR CONSTRUCTION
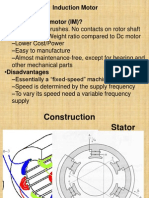
Induction motors can be classified based on rotor structure to two types:
1. Squirrel Cage Induction Motor
The three phases of the rotor windings are usually Y-connected, and the ends of the three
rotor wires are tied to slip rings on the rotor's shaft. The rotor windings are shorted
through brushes riding on the slip rings.
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
INDUCTION MOTOR CONSTRUCTION
2. Slip Ring Induction Motor (Wound Rotor)
A cage induction motor rotor consists of a series of conducting bars laid into slots
carved in the face of the rotor and shorted at either end by large shorting rings.
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Slip Ring I.M Vs. Squirrel Cage I.M
Slip Ring I.M:
Rotor currents accessible at the stator brushes.
Extra resistance call be inserted into the rotor circuit
Torque-speed characteristics and starting current can be controlled by external resistors
Squirrel Cage I.M:
Less expensive.
Less maintenance efforts
Frequently used
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
Basic Induction Motor Concepts
Induced Torque in an Induction Motor
1. 3 voltages applied to the stator 3 currents stator magnetic field
The magnetic field's rotates at speed known as synchronous speed
where: fs is the system frequency, P is the number of poles
2. passes over the rotor bars induces a voltage on the bars = ( )
Rotor current Rotor Magnetic field BR Counter clock wise induced torque on
the Rotor = .
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
Basic Induction Motor Concepts
Induced Torque Steps
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
Basic Induction Motor Concepts
What will happen to the induced torque if the rotor speed reached
the synchronous speed in induction motor ?
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
Basic Induction Motor Concepts
Note that in normal operation both the rotor and stator magnetic fields BR and BS
rotate together at synchronous speed ,while the rotor itself turns at a slower speed.
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Rotor Slip
The induced voltage and current in a rotor bar depends on the speed of the rotor
relative to the magnetic fields it is easier to use the speed of the rotor
relative to the stator magnetic field.
Slip (s) as percentage is given by =
Rotor speed (n) can be found by
% or by =
= ( ) or by
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
= ( )
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Rotor Slip
The rotor frequency can be expressed as
= .
or by substituting s
Note: at n = ns fr = 0 and at n = 0 (Locked) fr = fs
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Example 6.1: A 208-V, 10-hp, four-pole, 60Hz, Y-connected induction motor has a full-load
slip of 5 percent.
(a) What is the synchronous speed of this motor?
(b) What is the rotor speed of this motor at the rated load?
(c) What is the rotor frequency of this motor at the rated load?
(d) What is the shaft torque of this motor at the rated load?
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Solution Ex 6.1:
(a) The synchronous speed of this motor is
=
=
=
(d) The shaft load torque
=
=
= . .
(b) The rotor speed of the motor is
= = . =
(c) The rotor frequency
= . = . =
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
The Final Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor
To produce the final per-phase equivalent circuit for an induction motor, it is necessary to
refer the rotor part of the model over to the stator side.
The per-phase equivalent circuit of an induction motor
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
The Final Equivalent Circuit of Induction Motor
=
where : the rotor resistance,
: The effective turns ratio for a wound-rotor motor-it is basically the ratio of the
conductors per phase on the stator to the conductors per phase on the rotor, modified by any
pitch and distribution factor differences.
where 0 : the locked rotor reactance,
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Power And Torque In Induction Motors
Air Gap Power
=
Developed Power
=
= ( )
=
Output Power
Input Power
(SCL)
Stator Copper Losses
=
Core Losses
(RCL)
Rotor Copper Losses
=
Friction &
Windage
Losses
The power-flow diagram of an induction motor
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
Stray
Losses
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Power And Torque In Induction Motors
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Example 6.3: A 460-V, 25-hp, 60-Hz, four-pole, Y-connected induction motor has the
following impedances in ohms per phase referred to the stator circuit:.
1 = 0.641 , 2 = 0.332 , 1 = 1.106 , 2 = 0.464 , = 26.3 .
The total rotational losses are 1100 W and are assumed to be constant. The core loss is Jumped
in with the rotational losses. For a rotor slip of 2.2 percent at the rated voltage and rated
frequency, find the motor's:
(a) Speed (b) Stator current (c) Power factor (d) Pconv and Pout (e) Tin and Tload (f) Efficiency
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Solution Ex 6.3:
(a) The speed
= =
= . /
= = . = = . /
(b) Stator current
=
=
= + , = + , =
4600
3
2660
..
= . .
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
+ ,
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Solution Ex 6.3:
(c) Power Factor
= . = .
(d) Pconv and Pout
= , =
= . . = . and
= =
= = .
. =
=11.585 kW.
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
= .
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Solution Ex 6.3:
(e) Tin and Tload
=
. /
= . . , =
. /
(f) Motor Efficiency
=
% =
% = . %
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
= . .
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
6.11: Determining Circuit Model Parameters
The No-Load Test ( =? , =?)
(. )
= + + & +
= 312 1 +
= + & +
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
6.11: Determining Circuit Model Parameters
The No-Load Test ( =? , =?)
=
+
,
With the large lagging current, most of the
voltage drop will be across the inductive
components in the circuit. The equivalent
input impedance is thus approximately
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
The DC Test for Stator Resistance ( =? )
The inductance in DC is equivalent to S.C
=
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
The Locked-Rotor Test ( =? , =?)
= +
=
= +
=
=
= +
= cos + sin
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Example 6.8: The following test data were taken on a 7.5-hp, four-pole, 208-V,
60-Hz, design A, Y-connected induction motor having a rated current of 28 A.
DC test: = 13.6 , = 28
No-load test: = 208 , = 8.12 , = 8.20 , = 8.18 , = 420 , = 60
Locked-rotor test: = 25 , = 28.1 , = 28 , = 27.6 , = 920 , = 15
(a) Sketch the per-phase equivalent circuit for this motor.
(b) Find the slip at the pullout torque, and find the value of the pullout torque itself.
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Solution Ex 6.8:
(a) Sketch the per-phase equivalent circuit for this motor.
From DC-Test =
From noload Test , =
.
.
= .
.+.+.
= . ,
=
=
= . +
, .
From Locked-rotor Test =
(. )
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
= .
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Solution Ex 6.8:
=
920
3 (25 ) (27.9 )
= 1 0.762 = .
= = 0.517 40.4 = 0.394 = = .
= sin = 0.517 40.4 = 0.335
=
60
15
0.335 = . = +
= = . and from no-load test = 1 = .
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Solution Ex 6.8:
Per-phase Equivalent Circuit For This Motor
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
6.5: Induction Motor Torque-speed Characteristics
Comments
1. Tind = 0 at synchronous speed ns .
2. Torque- speed curve is nearly linear between no load
and full load. In this range, the induced torque increase
linearly (with increasing slip).
3. Breakdown torque, is 2 to 3 times the rated full-load torque
of the motor.
4. The starting torque on the motor is slightly larger than its
full-load torque. So this motor will start carrying any load.
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
6.6: Variations In Induction Motor Torque-speed Characteristics
Control of Motor Characteristics by Rotor Design
Rotor resistance R2 Starting torque
starting current
For a specific TL, if Rotor resistance R2
Slip and n Pout
Remember:
= ( )
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
AC Three-phase Induction Motor
Typical torque-speed curves for different rotor designs
National Electrical Manufacturers Association (NEMA)
Electric Machine Course ME331, Dr. Hani Muhsen
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Electrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseDe la EverandElectrical Machines: Lecture Notes for Electrical Machines CourseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument32 paginiSingle Phase Induction MotorDeep PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Single Phase Induction MotorDocument5 paginiSingle Phase Induction MotorSridhar SridharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationDe la EverandStudy of a reluctance magnetic gearbox for energy storage system applicationEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Chap1 Special MachinesDocument23 paginiChap1 Special MachinesHell Maax100% (2)
- Some Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDe la EverandSome Power Electronics Case Studies Using Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three-Phase Induction Motor PerformanceDocument10 paginiThree-Phase Induction Motor PerformanceMohamed Meeran100% (1)
- Simulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetDe la EverandSimulation of Some Power Electronics Case Studies in Matlab Simpowersystem BlocksetEvaluare: 2 din 5 stele2/5 (1)
- AlternatorDocument24 paginiAlternatorJoseEduardoSantaCruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial EDDocument10 paginiTutorial EDPavan KhetrapalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous MotorsDocument27 paginiSynchronous MotorsSyed Muhammad Munavvar Hussain50% (2)
- Armature WindingDocument17 paginiArmature Windingvasu_koneti5124Încă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motor Electric BrakingDocument12 paginiInduction Motor Electric Brakingmastanamma.Y100% (1)
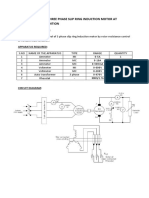
- Speed Control of Three Phase Slip Ring Induction Motor at Variable Load ConditionDocument3 paginiSpeed Control of Three Phase Slip Ring Induction Motor at Variable Load Conditionhi100% (1)
- 3 Phase Induction Motor - Lecture PDFDocument101 pagini3 Phase Induction Motor - Lecture PDFQuang TiênÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3Document5 paginiUnit 3Narasimman DonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Synchronous Machines - 2015Document93 paginiThree Phase Synchronous Machines - 2015आश्विन मरहट्टाÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motor PPT Part1Document20 paginiInduction Motor PPT Part1debipraasad100% (2)
- CH 3 - Induction MotorsDocument46 paginiCH 3 - Induction MotorsMiz AelyfhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC-Choppers Class A B C D EDocument18 paginiDC-Choppers Class A B C D EAnonymous iTJLpNVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction GeneratorDocument12 paginiInduction GeneratorSumaira SaifÎncă nu există evaluări
- ALTERNATOR TITLEDocument23 paginiALTERNATOR TITLEpremameÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why Induction Motors Are Commonly Used in IndustryDocument65 paginiWhy Induction Motors Are Commonly Used in IndustryAhmad Nawawi Ngah100% (1)
- Electrical BrakingDocument19 paginiElectrical BrakingAnilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Single Phase Induction MotorDocument12 paginiTypes of Single Phase Induction Motorkarthikeyan249Încă nu există evaluări
- Three Phase Induction MotorDocument11 paginiThree Phase Induction MotorMohamed Ashraf Abd Elaazem Ali ٢٠١٥٠١٣٨٣Încă nu există evaluări
- DC MachinesDocument48 paginiDC Machineskhed100% (1)
- Three Phase Induction Motor Interview Questions 2 1Document24 paginiThree Phase Induction Motor Interview Questions 2 1Kulshresth Joshi100% (1)
- DC MachinesDocument43 paginiDC Machinessupriyaditi100% (1)
- Week 71Document25 paginiWeek 71Raphael SebucÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motor Construction and OperationDocument36 paginiInduction Motor Construction and Operationkyaw winÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fractional Kilowatt MotorsDocument37 paginiFractional Kilowatt MotorsPavan Kumar100% (1)
- Chapter 6 Induction Motor ConstructionDocument42 paginiChapter 6 Induction Motor Constructionupendra35Încă nu există evaluări
- Special Electrical Machines Ee2403 PDFDocument16 paginiSpecial Electrical Machines Ee2403 PDFsamyramu100% (3)
- (4-2) Synchronous GeneratorDocument35 pagini(4-2) Synchronous Generatorfarah haniÎncă nu există evaluări
- PX7203-Special Electrical Machines PDFDocument11 paginiPX7203-Special Electrical Machines PDFvaishnavisriÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC MotorsDocument50 paginiAC MotorsDanzel SepilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Synchronous MotorsDocument25 paginiSynchronous MotorsParvesh NainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Drives: An Introduction to Power Electronics and Variable Speed AC and DC Motor DrivesDocument37 paginiElectrical Drives: An Introduction to Power Electronics and Variable Speed AC and DC Motor DrivesDawit Shimeles TesfayeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syncgronous Generator UpdatedDocument78 paginiSyncgronous Generator UpdatedarsalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Stability - Unit 4 PSOCDocument57 paginiPower System Stability - Unit 4 PSOChareesh.makesuÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Machine FundamentalsDocument53 paginiDC Machine FundamentalsK04Anoushka TripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes 1Document68 paginiNotes 1Vo SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 Most Important 3-Phase Induction Motor MCQ With Explanation 2Document13 pagini100 Most Important 3-Phase Induction Motor MCQ With Explanation 2NaveedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt-3 Various Methods of Braking of 3-Ph IMDocument6 paginiExpt-3 Various Methods of Braking of 3-Ph IMAnwesha pradhan50% (2)
- DC Machine Example ProblemsDocument4 paginiDC Machine Example ProblemsFemi Prince0% (1)
- Double Cage Rotor Motor StructureDocument2 paginiDouble Cage Rotor Motor Structuresalma100% (1)
- E M II: Synchronous MachineDocument10 paginiE M II: Synchronous MachineAkashman ShakyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines-II QuestionsDocument2 paginiElectrical Machines-II QuestionsHari Reddy0% (1)
- DC MotorDocument9 paginiDC MotorSayan DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TransformerDocument20 paginiTransformerKarthikeyanKarunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motor BrakingDocument26 paginiInduction Motor BrakingAshwini Singh100% (3)
- Induction Motors ExplainedDocument165 paginiInduction Motors ExplainedMillion GebretsadikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Induction Motor Power StagesDocument40 paginiInduction Motor Power StagesJaniel MalitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question Bank: DEPARTMENT OF EEE/Electrical Machines-II/III YEARDocument22 paginiQuestion Bank: DEPARTMENT OF EEE/Electrical Machines-II/III YEARPartha Roy100% (1)
- 21EE44-Module 3Document18 pagini21EE44-Module 3AshwiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- EMII - Lecture 14 - Synchronous MachinesDocument10 paginiEMII - Lecture 14 - Synchronous MachinesHassan Al BaityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Systems AssignmentDocument12 paginiPower Systems AssignmentJbmulindwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Braking Schemes of TractionDocument7 paginiBraking Schemes of TractionSuraj BhushanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ideal and Practical TransformerDocument8 paginiIdeal and Practical TransformerChintal.vinodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines Lab-II ManualDocument41 paginiElectrical Machines Lab-II Manualsuresh270Încă nu există evaluări
- 07-Squirrel Cage Induction Motor-Experiments ManualDocument25 pagini07-Squirrel Cage Induction Motor-Experiments ManualN. iManÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everything You Need to Know About AC Motor TheoryDocument22 paginiEverything You Need to Know About AC Motor TheoryRM HaroonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ele3209 Assignment 2018Document1 paginăEle3209 Assignment 2018aisha nakatoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DC Motor ChartsDocument8 paginiDC Motor ChartsMeredith M. AndersonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magneto TypesDocument1 paginăMagneto TypesDaniel MkandawireÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric GeneratorDocument7 paginiElectric GeneratorRahul ShivuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines Kuestion PDFDocument61 paginiElectrical Machines Kuestion PDFVijay Yadav BahoodurÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Proceedings of The Institution of Electrical Engineers: December 1962Document9 paginiThe Proceedings of The Institution of Electrical Engineers: December 1962DEEPTHI NAIRÎncă nu există evaluări
- Main EB Transformer - 33KV/11KV (8000KVA) ReadingsDocument30 paginiMain EB Transformer - 33KV/11KV (8000KVA) Readingsiotaathi tÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 +Ok+Direct+Axis+and+Quadrature+Axis+Subtransient+ReactancesDocument2 pagini3 +Ok+Direct+Axis+and+Quadrature+Axis+Subtransient+Reactancesnainesh goteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Starting of DC MotorDocument7 paginiStarting of DC Motorabbas bilalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To Motor & StartingDocument26 paginiGuide To Motor & Startingnooruddinkhan1100% (2)
- BLDC Motors: Easwari Engineering College (Autonomous) Department of Electrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument17 paginiBLDC Motors: Easwari Engineering College (Autonomous) Department of Electrical and Electronics Engineering52 Vikas VÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee8002 - Dem - Question Bank - Unit4Document4 paginiEe8002 - Dem - Question Bank - Unit4DEVIÎncă nu există evaluări
- SACE RCQ Residual Current Relay Installation GuideDocument16 paginiSACE RCQ Residual Current Relay Installation GuideGary MokÎncă nu există evaluări
- (A-12, A-13) Plan Armature AB Ploce +100Document14 pagini(A-12, A-13) Plan Armature AB Ploce +100Vladan ĆirovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Electrical Apparatus - Question PaperDocument12 paginiDesign of Electrical Apparatus - Question PaperVIGNESH T AÎncă nu există evaluări
- GTU Advanced Electrical Machines CourseDocument2 paginiGTU Advanced Electrical Machines Coursejijo123408Încă nu există evaluări
- EMEC Important QuestionsDocument3 paginiEMEC Important QuestionsHarish KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brushless DC Motor ReportDocument6 paginiBrushless DC Motor ReportSaumik HeronÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15ee210 Electrical Machines IIDocument2 pagini15ee210 Electrical Machines IIShivaji YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rotary and Linear Switched Reluctance MotorsDocument12 paginiRotary and Linear Switched Reluctance Motorskarthikeyan249100% (2)
- Ac Generators: Compiled and Presented by Doren NedrickDocument20 paginiAc Generators: Compiled and Presented by Doren Nedrickadamwaiz100% (1)
- DC MotorDocument84 paginiDC MotorMuhammad Fajar PrakasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Direct-Current Dynamos: Construction & Armature WindingsDocument43 paginiDirect-Current Dynamos: Construction & Armature WindingsHane MinasalbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Machines and Drives Course Outline 2010Document2 paginiElectrical Machines and Drives Course Outline 2010talohole2Încă nu există evaluări
- DC Machines-Top Interview Questions With Answers - OnlinemcqDocument3 paginiDC Machines-Top Interview Questions With Answers - OnlinemcqAmirSaeedÎncă nu există evaluări