Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Plan Is Ferio Celeste
Încărcat de
Anaitz BeHappyDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Plan Is Ferio Celeste
Încărcat de
Anaitz BeHappyDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Rotating Star Chart (section 1)
12 10
Canon Science Papercraft Mini-book
1 19
(1) Turn the star disk to
the current date and time,
as shown at right.
ar
c
13
11
7:0
PM 0
97
5 3
1 28
2
6 24
Directions
Example:
align to March 1, 7:00 PM
22 20 1
8
16 14 12
h
ut
Eastern sky
So
or
Print out pages 1 through 5 and cut out each individual part along their cut lines.
(2) Let's say you want to
observe the stars in the east.
Hold the star chart so that the
"East" marking is facing you,
as shown in the figure.
Now you're ready to match the
stars you see in the sky with
the constellations displayed on
your star chart!
We
st
*Cut out the card above and save it. You can collect the cards from each of the Papercraft
projects to make your own mini-book!
th
1. Align front pieces 1 and 2
15
17
You can use this handy rotating star chart
to help locate constellations when looking
at the night sky.
Turning the inner disk lets you know when
what constellation will appear, and where.
Let's do some stargazing!
6:
P 00
M
23 2
* How to use
your rotating star chart
Rotating Star Chart
7 25
Natural Science Series
92
31 2
4 2
8 6
Science Papercraft Natural Science Series
East
2. Fold over the tabs and glue in place
front piece 1
* observing the eastern sky
* The Zenith
star disk
align the top
and bottom
of the front
and back pieces
back
piece
* Region where your
star chart may be used
This star chart is designed to
be used within the region
shown on the map at right
(from about 26 to 48 north
latitude).
As this is a very simple star
chart, there may be some
error in the position of the
zenith and the constellations
shown in the window.
apply glue to the back piece
and press together
North
4. Insert the star disk
zenith
es
W
st
3. Attach back piece
fold the tabs back and glue in place
zenith
Ea
front piece 2
The point in the sky directly
above an observer is called the
zenith. On your star chart, the
zenith is indicated by the point
on the orange dotted line that
intersects an imaginary line
between the "North" and
"South" markings.
South
region where the star chart
may be used
10 8 6 4 2 31 29 27
1:00
12:00
0
2:0M
0:
3:
AM 00
00
9: PM
Canon Science Papercraft
Natural Science
Rotating Star Chart
0
8:0M
4:0
AM 0
for use at 35 north latitude
As this is a very simple star chart,
there may be some error in the position of
the constellations shown in the window.
PM
7:00
North
5:00
AM
6:00
here
AM
PM
7:00
5:00
es
W
Ea
s
6:00
AM
PM
Front piece 1
PM00
AM
mountain fold line
11:0
0
AM
(midnight)
cut line
Rotating Star Chart (section 2)
PM
Science Papercraft Natural Science Series
glue
cut out
gl
re
glu
ere
eh
eh
glu
ere
glue
here
he
ue
re
glu
he
glu
re
he
ue
re
gl
glu
South
eh
ere
ere
eh
glu
glue
here
glue he
re
glue here
re
glue he
here
glue
he
Science Papercraft Natural Science Series
Rotating Star Chart (section 3)
cut line
Front piece 2
* Region in which this star chart may be used
region where the star chart
may be used
align front
piece 1 with
this line and
glue together
This star chart is designed
to be used within the
region shown on the map
at right (from about 26 to
48 north latitude).
align front
piece 1 with
this line and
glue together
Rotating Star Chart (section 4)
Science Papercraft Natural Science Series
December
Ara
9 17
23 2
11
27 2
Sagittariu
s
Pa
vo
42
3
12
9
s
8
rpiu
Sco
10
12
14 r
8 16 be
20 1 em
24 22 Nov
28 26
2 30
8 6 4
14 1
16
20 18
ico
24 22
Se
Aqu
ila
Ca
r pe
ns
us
he
Cep
us
Ap 4 12 10
ril
Pho
Ar
ie
Cet
ng
ulu
m
eda
iopeia
Cass
us
Pisce
Tri
a
enix
ac
Dr
se
Androm
Bo
lis
Cy
ga
Pe
a
on
a
re
gn
us
sus
Aqu
Pe
r
inus
ustr
is A
Pisc
ariu
el
p
r
Co
Lyra
hi
nu
s
16 1
20 18
4 22
s
nu
Orion
Er
26 2
ino
r
ida
0 28
er
us
is M
23
4
pis
5 23
Canis
Pup
Major
08
Lepus
6 14
Columb
21 1
9 17
15 13
Ju
ly
o
rad
Do
Carina
11 9
Grus
ules
Herc
nc
Ca
Auriga
02
3 13
5
7 5 3
7
9
1 29 27 25 23 21 19 17 15 13 11
June
2
26 24
81
20 1
1
12
ay
March
s
iuchu
Mino
nx
Ly
i
28 26
8 6 4
3 1
5
7
2 31 29 27 25 23 21 19 17 15 13 11 9
Oph
rn
us
pr
pu
Serpens
Ursa
Ursa Maj
or
s Ven
atic
min
Ve
la
27 2
ua
0
21
In
Cane
Leo
Ge
Can
23
br
Fe
Lu
es
ot
Bo
Polaris
(North Star)
r
Tau
1 29
ry
du
s
ra
Lib
Virgo
r
Septembe
9 7 5
3
r
Corvus
Hyd
4
8
Ce
2
nt
10
a
13 2
u
r
u
9
4 12
s
2
7 25
16 1 t
2
3
0 18 us
2
1
22 2 Aug
1
9
1
26 24
Oc 7 15 13
Southern Cross
0 28
1
t
1
o
9
b
3 13
7 5 3
er
1 29 27 25 23 21 19 17 15 13 11 9 7 5
15
J
a
nu 13 11
ar y
Star disk
1 30 28 26 24 22 20 18 16 14 12 10
cut line
Rotating Star Chart (section 5)
Science Papercraft Natural Science Series
12 10
How to use your rotating star chart
6:
P 00
M
5 23
27 2
21 1
9 17
(1) Turn the star disk to
the current date and time,
as shown at right.
15
13
ar
11
ch
7:0
PM 0
97
5 3
1 28
26 24
22 20 1
8
Example:
align to March 1, 7:00 PM
(2) Let's say you want to
observe the stars in the east.
Hold the star chart so that the
"East" marking is facing you,
as shown in the figure.
Now you're ready to match the
stars you see in the sky with
the constellations displayed on
your star chart!
Eastern sky
The Zenith
zenith
t
es
W
zenith
Ea
st
The point in the sky directly
above an observer is called the
zenith. On your star chart, the
zenith is indicated by the point
on the orange dotted line that
intersects an imaginary line
between the "North" and
"South" markings.
North
Back piece
4 2
8 6
cut line
South
14 12 10
8 6 4 2 31 29 27
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- How To Use The Sun and StarDocument7 paginiHow To Use The Sun and StarCondor7tÎncă nu există evaluări
- Night Sky: A Field Guide to the ConstellationsDe la EverandNight Sky: A Field Guide to the ConstellationsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (6)
- How To Use An AstrolabeDocument37 paginiHow To Use An AstrolabeAmir KaracicÎncă nu există evaluări
- PlanisphereDocument8 paginiPlanisphereJohnny NoobodyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Half-Hours with the Stars: A Plain and Easy Guide to the Knowledge of the ConstellationsDe la EverandHalf-Hours with the Stars: A Plain and Easy Guide to the Knowledge of the ConstellationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Half-Hours with the Stars A Plain and Easy Guide to the Knowledge of the ConstellationsDe la EverandHalf-Hours with the Stars A Plain and Easy Guide to the Knowledge of the ConstellationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Book of Stars: Being a Simple Explanation of the Stars and Their Uses to Boy LifeDe la EverandThe Book of Stars: Being a Simple Explanation of the Stars and Their Uses to Boy LifeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celestial Sphere Star ChartsDocument3 paginiCelestial Sphere Star ChartsLonn ConleyÎncă nu există evaluări
- PLNT PosDocument15 paginiPLNT PosRavi K NÎncă nu există evaluări
- IOAA 2014, Romania (Problems)Document30 paginiIOAA 2014, Romania (Problems)Science Olympiad Blog70% (10)
- Rude Starfinder 2102Document4 paginiRude Starfinder 2102indumarnicaraguaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Cadet Publication: NavigationDocument52 paginiAir Cadet Publication: NavigationMarcus DragoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advertisement: Calendar NotesDocument2 paginiAdvertisement: Calendar NotesbirbiburbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Binoculars March 2024Document12 paginiBinoculars March 2024ageluz00Încă nu există evaluări
- Technique To Remember-NakshatrasDocument4 paginiTechnique To Remember-NakshatrasNarayanan Kallapiran67% (3)
- Astro 2Document4 paginiAstro 2Farkhan RaflesiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astro 13-15Document7 paginiAstro 13-15Celeste EspinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AstroCompass Solar AccessDocument8 paginiAstroCompass Solar AccessEnrico959100% (1)
- Moon Phase CalendarDocument4 paginiMoon Phase CalendarJoseph Stanovsky100% (1)
- Using A 90Document5 paginiUsing A 90Jorge Mario SpinelliÎncă nu există evaluări
- NavigationDocument9 paginiNavigationcasalecastavi47Încă nu există evaluări
- Linking LabDocument8 paginiLinking Labsavannah0% (2)
- The Little Astronomer: Astronomy Training for Children With HandicraftsDe la EverandThe Little Astronomer: Astronomy Training for Children With HandicraftsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Ways To Use An Astrolabe - WikihowDocument5 pagini3 Ways To Use An Astrolabe - WikihowextraboomÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Return of Mars: Celestial CalendarDocument5 paginiThe Return of Mars: Celestial CalendarbirbiburbiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Where did That Number Come From?: Chronological Histories and Derivations of Numbers Important in ScienceDe la EverandWhere did That Number Come From?: Chronological Histories and Derivations of Numbers Important in ScienceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Star Finder and IdentifierDocument8 paginiStar Finder and IdentifierSandunMigaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divining Declination in Solar FireDocument6 paginiDivining Declination in Solar Firelettina2Încă nu există evaluări
- Astrology - A FortuneDocument7 paginiAstrology - A Fortunemeochauphi100% (1)
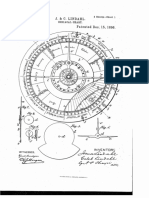
- US573091 Zodiacal Charts or PlanetographsDocument4 paginiUS573091 Zodiacal Charts or PlanetographsJohn StoufferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Where Are The Planets?: S Tar MapsDocument16 paginiWhere Are The Planets?: S Tar MapsgiannistrgrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daniel Min en Planetary Awareness TechniqueDocument150 paginiDaniel Min en Planetary Awareness TechniquenubunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stereo Nets How To PlotDocument12 paginiStereo Nets How To Plotoli659Încă nu există evaluări
- Extra Credit Project Telling Time by The Stars Due May 5Document4 paginiExtra Credit Project Telling Time by The Stars Due May 5mehedi2636Încă nu există evaluări
- The Earth-Sun Orientation: Activity 6Document4 paginiThe Earth-Sun Orientation: Activity 6IVIYI3r41nÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lunar Map Will TirionDocument7 paginiLunar Map Will TirionFellipy SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EtM Telescope V4 1Document12 paginiEtM Telescope V4 1Alexandroiu RaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Planetary Motion WorksheetDocument3 paginiPlanetary Motion WorksheetketchupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Using The Astro-Compass To Study Solar AccessDocument7 paginiUsing The Astro-Compass To Study Solar AccesslaeionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hot Degrees 2016Document3 paginiHot Degrees 2016Pravin YeluriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astronomy Laboratory: The Moon and Its Phases 1Document6 paginiAstronomy Laboratory: The Moon and Its Phases 1Pradeep Kumar SukumaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParallelsDocument30 paginiParallelsaries25th3100% (1)
- Planetary Orbits Worksheet: NameDocument6 paginiPlanetary Orbits Worksheet: NametabilinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stronomy Asics: T C C SDocument7 paginiStronomy Asics: T C C SWc KnirsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skymaps Com 2015 03Document2 paginiSkymaps Com 2015 033582Încă nu există evaluări
- Moons of Uranus - Astrophysics LabDocument6 paginiMoons of Uranus - Astrophysics Labmohammed qasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sun Dial PDFDocument2 paginiSun Dial PDFBoban ButrićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nama: Fajar Santoso NPM: 17315043 Kelas: TE17A: N Value For January 2Document6 paginiNama: Fajar Santoso NPM: 17315043 Kelas: TE17A: N Value For January 2Fajar SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Almanac 2011Document2 paginiAlmanac 2011dkalatzisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exploring Maps - Navigation: How Do We Know Where We're Going?Document5 paginiExploring Maps - Navigation: How Do We Know Where We're Going?Leonte ȘtirbuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9 OrienteeringDocument4 pagini9 Orienteeringdiego.murgarproÎncă nu există evaluări
- Half-hours with the Telescope Being a Popular Guide to the Use of the Telescope as a Means of Amusement and Instruction.De la EverandHalf-hours with the Telescope Being a Popular Guide to the Use of the Telescope as a Means of Amusement and Instruction.Încă nu există evaluări
- KAS Visual One - KAS AstrologyDocument5 paginiKAS Visual One - KAS AstrologyGauriGanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celestial NavigationDocument11 paginiCelestial NavigationCarlos DiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pingree - A Greek Ephemeris For 796Document4 paginiPingree - A Greek Ephemeris For 796Homo ByzantinusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reading Star ChartsDocument2 paginiReading Star ChartsadfhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sun OrientationDocument6 paginiSun Orientationzohaib nasirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annual Edition 2016Document63 paginiAnnual Edition 2016Raju Gopinathan NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus MineDocument8 paginiSyllabus MineJeremiah Miko LepasanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UTM To Latitude and Longitude ConverterDocument1 paginăUTM To Latitude and Longitude ConverterAnonymous QZwgOjEx3Încă nu există evaluări
- 17 NOV 2011 ENR 6-1 Romania AIP: Enroute Chart - Upper AirspaceDocument1 pagină17 NOV 2011 ENR 6-1 Romania AIP: Enroute Chart - Upper AirspaceIsac RobertÎncă nu există evaluări
- GN Divisions - P Codes: LegendDocument1 paginăGN Divisions - P Codes: LegendRavindra KumaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposed Topographic Survey of Panal River at TaysanDocument15 paginiProposed Topographic Survey of Panal River at TaysanRhea CelzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Draconic Chart (Data Sheet) Natal ChartDocument1 paginăDraconic Chart (Data Sheet) Natal ChartAMarijanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Processes and Landforms Along Plate Boundaries PDFDocument39 paginiProcesses and Landforms Along Plate Boundaries PDFRenDenverL.DequiñaIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- History and Development of Regional GeographyDocument2 paginiHistory and Development of Regional GeographyJamal MollaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geography Helps Us Understand Basic Physical Systems That Affect Everyday LifeDocument2 paginiGeography Helps Us Understand Basic Physical Systems That Affect Everyday LifeJessa Mae SusonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taal Affected Area Map - 280 PDFDocument1 paginăTaal Affected Area Map - 280 PDFRjo CabadingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Challenger 605 FMS Operators Guide (V4.0) PDFDocument874 paginiChallenger 605 FMS Operators Guide (V4.0) PDFJuan100% (4)
- Year 11 IGCSE Geography Fieldwork - Changes To The Urban Area-2Document2 paginiYear 11 IGCSE Geography Fieldwork - Changes To The Urban Area-2SpaghettiOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atkinson Deadman Dudycha Traynor 2005 Multi-Criteria Evaluation and Least Cost Path Analysis For An Arctic All-Weather RoadDocument21 paginiAtkinson Deadman Dudycha Traynor 2005 Multi-Criteria Evaluation and Least Cost Path Analysis For An Arctic All-Weather RoadbegzahlebzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differen T Types of MapsDocument25 paginiDifferen T Types of Mapsfatima de guzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Detail For The Year 19-20Document3 paginiCourse Detail For The Year 19-20nini PatnaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedon Description Form SOI-232 PDFDocument2 paginiPedon Description Form SOI-232 PDFJorris ArdhianÎncă nu există evaluări
- RTCA - An Expanded Description of The CPR AlgorithmDocument47 paginiRTCA - An Expanded Description of The CPR AlgorithmalgentileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tsunami Inundation Map: MontereyDocument1 paginăTsunami Inundation Map: MontereyAmy LarsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mapinfo Professional: InternalDocument88 paginiMapinfo Professional: InternalgargmanishgargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Guided Reading Lesson 2 Key 126gkj9Document4 paginiChapter 2 Guided Reading Lesson 2 Key 126gkj9mariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Landmark in British CartographyDocument30 paginiLandmark in British CartographyMuanfun Sirikorn-KunawongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geodetic Datum 2Document8 paginiGeodetic Datum 2wyath14Încă nu există evaluări
- Sem 1: EVS ProjectDocument22 paginiSem 1: EVS Projectmetalwihen50% (4)
- Small Greek WorldDocument308 paginiSmall Greek WorlddanielweizmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- NAV2 Module2 LuzonDocument18 paginiNAV2 Module2 LuzonRyan Brylle Luzon100% (1)
- Flooding Berrinba Flood Flag MapDocument1 paginăFlooding Berrinba Flood Flag MapNgaire TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peran Dan Fungsi IPCNDocument36 paginiPeran Dan Fungsi IPCNFahiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Europe Countries - Map Quiz GameDocument1 paginăEurope Countries - Map Quiz GamedanielalexgriffithsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geography's Empire: Histories of Geographical Knowledge: F DriverDocument18 paginiGeography's Empire: Histories of Geographical Knowledge: F Driveraaron_s_projÎncă nu există evaluări