Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
BSN 3 NSG Course Outlines Topics
Încărcat de
Allene Paderanga0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
75 vizualizări9 paginisdfsdfsd
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentsdfsdfsd
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
75 vizualizări9 paginiBSN 3 NSG Course Outlines Topics
Încărcat de
Allene Paderangasdfsdfsd
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 9
NCM 104.
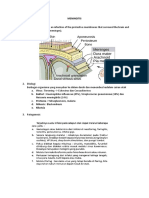
1 Care of Clients with Problems in Inflammatory, Immunologic Responses, Perception
and Coordination and those undergoing surgery
A. Alterations in Inflammatory and Immunologic Responses
a. Infectious and Inflammatory Reactions
i. Inflammatory and Emerging Viral Conditions
1. SARS
2. West Nile Virus/ Dengue/ Zika
3. Legionnaires Disease
4. Hantavirus Pulmonary Syndrome
5. Ebola Virus
6. AH1N1
7. Lyme disease
ii. Bacterial Conditions
iii. Bullous diseases
iv. Infestation and parasitic diseases
v. Vaccine preventable infectious diseases
b. Immunologic Reactions
i. Hypersensitivity and Allergic Reactions
1. Food Allergy
2. Urticaria
3. Anaphylaxis
4. Insect sting
5. Latex Allergy
ii. Immunodeficiency and HIV-AIDS
1. Primary
a. Phagocytic dysfunctions
b. B & T-cell deficiency
c. Combined B & T cell deficiency
d. Deficiencies of the Complement System
2. Secondary
3. HIV-AIDS
iii. Autoimmune disorders
1. Rheumatic Arthritis
2. Systemic Lupus Erythematosus
3. Systemic Sclerosis
4. Spondyloarthropathies
5. Fibromyalgia Syndrome
B. Alterations in Perception and Coordination
a. Alterations in Neural Regulation
i. Altered level of consciousness
ii. Headache & Pain
iii. Seizures
1. Epilepsy & Status Epilepticus
iv. Cerebrovascular disorders
1. Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIA)
2. Ischemic stroke
3. Hemorrhagic stroke
v. Neurologic Trauma & Infections
1. Head Injuries
2. Brain Injuries
3. Spinal Cord Injuries
4. Bacterial Meningitis
5. Encephalitis
6. Brain Abscess
vi. Autoimmune disorders and neuropathies
1. Multiple sclerosis
2. Myasthenia Gravis
3. Guillain-Barre Syndrome
4. Cranial nerve disorders
5. Trigeminal neuralgia
6. Bells palsy
7. Peripheral neuropathy
vii. Degenerative Neurologic Disorders
1. Parkinsons disease
2. Huntingtons disease
3. Alzheimers disease
b. Disturbances in Visual perception
i. Impaired Vision and blindness
1. Refractive errors
2. Low vision and blindness
3. Glaucoma
4. Cataract
ii. Corneal and Retinal disorders
1. Corneal dystrophies
2. Keratoconus
3. Retinal detachment
4. Retinal vascular disorders
5. Macular degeneration
iii. Infections and inflammatory conditions
1. Dry eye syndrome
2. Conjunctivitis
3. Uveitis
4. Orbital cellulitis
iv. Traumatic interferences
1. Orbital trauma
2. Ocular trauma
v. Orbital and ocular tumors
1. Benign tumor of the
a. Orbit
b. Eyelids
c. Conjunctiva
2. Malignant tumor of the orbit
c. Disturbances in Auditory perception
i. Deafness and loss of hearing
ii. Inflammatory, infection and trauma
1. External ear
a. Cerumen impaction
b. Foreign bodies
c. External otitis
d. Malignant external otitis
e. Masses of the external ear
f. Gapping Ear Puncture
2. Middle ear
a. Tympanic membrane perforation
b. Otitis media
i. Acute
ii. Serous
iii. Chronic
c. Otosclerosis
d. Middle ear masses
3. Inner ear
a. Motion sickness
b. Menieres disease
c. Tinnitus
d. Labyrinthitis
e. Benign paroxysmal positional vertigo
f. Ototoxicity
g. Acoustic neuroma
d. Alterations in Locomotion
i. Infections & inflammatory disorders
1. Osteomyelitis
2. Septic Arthritis
ii. Abnormalities of the Spine, Upper Extremities and foot
1. Acute low back pain
2. Bursitis and tendinitis
3. Loose bodies
4. Impingement syndrome
5. Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
6. Ganglion
7. Dupuytrens disease
8. Plantar fascitis
9. Corn
10. Callus
11. Ingrown toenail
12. Hammer toe
13. Pes Cavus
14. Mortons Neuroma
15. Flatfoot
iii. Degenerative and Metabolic disorders
1. Osteoporosis
2. Osteomalacia
3. Pagets disease
iv. Traumatic injuries
1. Contusion, strains and sprains
2. Joint dislocation
3. Sports-related injuries
4. Occupation-related injuries
5. Specific musculoskeletal injuries
a. Tennis elbow
b. Rupture of Achilles tendon
c. Lateral and medial collateral ligament injury
d. Anterior and posterior cruciate ligament injury
6. Fractures
7. Amputations
NCM 105.1 Care of Clients with Maladaptive Patterns of Behavior
I. Overview of Psychiatric Nursing
A. Evolution of Mental Health - Psychiatric Nursing Practice
B. The Mental Health Nurse - Roles & Essential Qualities
C. The Interdisciplinary team
D. The Mental Health Illness Continuum
II. Mental Health Psychiatric Nursing Practice
A. Personality Theories and determinants of psychopathology
1. Psychoanalytic, behavioral, interpersonal, cognitive, humanistic
2. Psychobiologic, psychosocial, psychospiritual, eclectic
B. General Assessment Considerations
1. Principles & technique of Psychiatric Nursing Interview
2. Mental Status Examination
3. Diagnostic Examinations specific to psychiatric patients
C. Nurse-client relationship
1. Nurse-client interaction VS Nurse-client relationship
2. Therapeutic use of self
3. Therapeutic communication - Characteristics and techniques
4. Goals and phases in building nurse-client relationship
D. Therapeutic modalities, psychosocial skills and nursing strategies
1. Biophysical/ somatic intervention
a) Electroconvulsive and other somatic therapies
b) Psychopharmacology
2. Supportive psychotherapy
a) Nurse-pt relationship therapy
b) Group therapy, family therapy
3. Counseling
4. Mental health teaching/ client education
5. Self-enhancement, growth/ therapeutic groups
6. Assertiveness training, stress management
7. Behavior modification, cognitive restructuring
8. Milieu therapy, play therapy
9. Psychosocial support interventions
10. Psychospiritual inetrventions
11. Alternative medicine/ therapies
E. Concept of anxiety
1. Defining characteristics of anxiety
2. Levels of anxiety
3. Manifestations of levels of anxiety - physiologic and psychologic
4. Ego-defense mechanism - 4 levels of defense
F. Crisis
1. Characteristics and types of crisis
2. Phases of crisis development
3. Crisis intervention
III. Care of Clients with Maladaptive Patterns of Behavior Across the Lifespan
A. The Nursing Process Applied to Psychiatric Nursing Practice (MSA form)
1. Assessing Human Responses to Maladaptive Patterns of Behavior
a) Self-awareness and use of self
b) Bio-psycho-social and behavioral data
2. Nursing Diagnosis and Outcome Identification
3. Planning and implementing nursing intervention
4. Evaluation and treatment outcome
B. Maladaptive Patterns of Behavior
1. Anxiety-related disorders
a) Anxiety disorders
b) Somatoform disorders
c) Dissociative disorders
2. Psycho-physiologic response and sleep disorders
3. Personality disorders
a) Childhood personality disorder
b) Odd/ eccentric behavior
c) Dramatic, emotional and erratic behaviors
d) Anxious, fearful behavior
e) Passive, aggressive behaviors
4. Substance-related behaviors: substance abuse, dependence, intoxication,
withdrawal and polysubstance dependence
a) CNS depressants
b) CNS stimulants
c) Hallucinogens, cannabis, inhalants
5. Mood disorders
a) Reactive attachment, Bipolar I & II
b) Cyclothymic and dysthmic, Major depressive disorders
c) Clients at risk for suicidal and self-destructive behavior
6. Schizophrenia and other psychoses
a) Types of schizophrenia
b) Other psychotic disorders
7. Cognitive disorders
a) Fetal alcohol syndrome
b) Delirium, dementia
c) Alzheimers disease, Diffuse Lewy Body disease
d) Korsakoffs disease, Huntingtons and Picks disease
e) Vascular and Multi-infarct dementia
8. Eating disorders
a) Pica, rumination
b) Feeding disorders
c) Anorexia and bulimia nervosa
9. Psychosexual disorders
a) Gender identity
b) Sexual dysfunction
c) Paraphilia
10. Abuse and violence
a) Victims of violent behavior
b) Torture and ritual abuse
c) Rape and sexual assault
11. Age-related Maladaptive Patterns
a) Developmental disorders of childhood - MR, ASD
b) Disruptive Disorder - ADHD
c) Other childhood disorder - Tic, Tourette, Asperger
C. Legal Issues Affecting Mental Health Nursing
D. Future Trends and Issues in Mental Health Nursing Practice
E. Community Based Mental Health Programs
ELEC 1: Hospice Palliative Care
I. Introduction to Palliative Care
A. Definition and comparison between palliative and hospice care
B. History of palliative care
C. Goals and philosophy of palliative care
D. Principles of palliative care
E. Essential components of palliative care
II. Promoting Quality of life in palliative care
A. Palliative care models
B. Palliative care for children
C. Palliative care at home
D. Members of the Interdisciplinary Palliative Care Team
E. Nurses role in the Interdisciplinary Team
F. Competencies necessary for nurses
G. Instruments used to assess quality of palliative care
III. Death and dying
A. Concept of death and dying
B. Theories of death and dying
C. Stages of death and dying
D. Signs and symptoms of impending death
E. Nursing interventions before death and at the time of death
F. Nursing process for grieving and dying patients and families
IV. Physical Aspects in Palliative Care
A. Symptom Management
1. Dyspnea, fatigue, anorexia, constipation, terminal dehydration,
depression, delirium, altered cognition and pain
B. Pain Management
1. Pain Assessment
2. Pharmacological Interventions
3. Pain management of special population
4. Non-drug pain interventions
V. Psychosocial Considerations in Palliative Care
A. Communication and its phases
B. Loss, suffering, bereavement and grief
1. Theories
2. Dimensions, stages
3. Assessment
4. Childs experience
5. Normal, dysfunctional and complicated grief
6. Caregiving and related interventions
7. Care for the families
VI. Ethical Considerations
A. Ethical theories and principles
B. Conceptual confusion and difficult decisions in end-of-life care
C. Active euthanasia and assisted suicide
VII. Legal aspects
A. Dying Persons Bill of Rights - Right to die
B. Advance directives
C. DNR/ No Code Orders
D. Comfort Measures Only and other special orders
E. Terminal Weaning
F. Informed consent
G. Patient self-determination
H. Death certificate
I. Organ donation
J. Actual location
VIII. Spiritual and Cultural Considerations
A. Spiritual care of the chronically ill
B. Spiritual well-being and quality of life at the end of life
C. Spiritual needs in death and bereavement
D. Considering culture competence
E. Religious and cultural rituals, ceremonies and funeral
IX. Holistic and complementary therapies
A. Healing modalities
B. Herbology
C. Homeopathy
D. Prayer
E. Other integrative therapies
X. Contemporary issues in palliative care
A. Generalist and specialist palliative care
B. Changes in health care economics
C. Professional organizations and certification hospice and palliative care
D. Continuing education in palliative care
E. Use of information and communications technology
F. Research in palliative care
NSG 40.1: Nursing research 1
I. Overview of Nursing Research
A. Purposes of conducting nursing research
B. Goals of nursing research
C. Sources of human knowledge
D. Roles of the nurse in research
E. Evolution of nursing research
F. Developing positive attitude towards nursing research
II. Ethics in Research
A. Code of Ethics
B. Ethical Principles
C. Procedures for protecting study participants
III. Types of Research
A. Level of Investigation
B. Motive
C. Time element
D. Approach
IV. The Research Process in Quantitative and Qualitative Studies
A. Phase 1: Conceptual phase
1. Problem Identification
a) Source of problems
b) Criteria in selecting a good research problem
c) Characteristics of a well stated problem
d) Significance of the problem
e) Scope and limitation
2. Review of Related Literature
a) Purpose of Literature Review
b) Categories of references
c) Locating relevant literature for research review
3. Defining the framework and developing conceptual definitions
a) Theoretical and conceptual framework
b) Formulation of hypothesis
(1) Purposes
(2) Types
(3) Criteria in stating hypothesis
c) Variables
(1) Types
d) Definition of terms
(1) Operational
(2) Conceptual
B. Phase II: Design and Planning phase
1. Selection of the research design
a) Major categories of research design
(1) Experimental
(2) Non-experimental
(3) Qualitative
b) Characteristics of research design
c) Developing intervention protocols for experimental design
2. Sampling and sampling technique
a) Identifying the population to be studied
(1) Differentiate total, target population
b) Determining the sample
c) Designing the sampling plan
d) Methods of sampling
(1) Probability
(2) Non-probability
3. Instrumentation
a) Data collection methods
b) Types of instruments
c) Advantages and disadvantages of the different data collection
methods
d) Validity and reliability
4. Steps in Writing Good Research Proposal
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Schizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFDocument19 paginiSchizophrenia Mood Disorders Grief Loss MENTAL HEALTH NURSING PDFnursing concept mapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imagination in Kant's Critical PhilosophyDocument232 paginiImagination in Kant's Critical PhilosophyIdrilÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ On Human Resource ManagementDocument12 paginiMCQ On Human Resource ManagementAman Kumar satapathy50% (14)
- Module 4-2 Principal Components AnalysisDocument18 paginiModule 4-2 Principal Components AnalysisRubayat IslamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurocognitive Disorders RevisedDocument60 paginiNeurocognitive Disorders RevisedVincent De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Industry Perspective FDA Draft ValidationDocument6 paginiIndustry Perspective FDA Draft ValidationOluwasegun ModupeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Risk For InjuryDocument5 paginiRisk For InjuryAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gaint Cell Lesions UPLOADDocument176 paginiGaint Cell Lesions UPLOADAkshayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complications in Treatment of LYMEDocument131 paginiComplications in Treatment of LYMECharles Mitchell100% (1)
- Introduction To Reconstructive and Aesthetic Plastic SurgeryDocument15 paginiIntroduction To Reconstructive and Aesthetic Plastic SurgeryAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dahnert Radiology Review ManualDocument1.202 paginiDahnert Radiology Review Manualrvancura100% (11)
- Organization Structure of Maruti Suzuki Business EssayDocument14 paginiOrganization Structure of Maruti Suzuki Business EssayRohan PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research CritiqueDocument5 paginiResearch CritiqueAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advances in Shock Management and Fluid Resuscitation in ChildrenDocument9 paginiAdvances in Shock Management and Fluid Resuscitation in ChildrenErico Marcel Cieza MoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supply Chain Design and Analysis: Models and MethodsDocument22 paginiSupply Chain Design and Analysis: Models and MethodssankofakanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus 112Document9 paginiSyllabus 112Hassen Zabala100% (2)
- Ca2 Prefinal Exam Pointers To ReviewDocument3 paginiCa2 Prefinal Exam Pointers To ReviewlittlejynxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peripheral Nerve DiseaseDocument1 paginăPeripheral Nerve DiseaseerickÎncă nu există evaluări
- LECTURE 1 (August 4, 2022) - AM SESSION: Dopamine - Can Help Contract The HeartDocument344 paginiLECTURE 1 (August 4, 2022) - AM SESSION: Dopamine - Can Help Contract The HeartMeanie ManszÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Frank Pagdunzulan: Diseases of The Immune SystemDocument41 paginiDr. Frank Pagdunzulan: Diseases of The Immune SystemFu Xiao ShanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anki Checklists For 5th YearDocument7 paginiAnki Checklists For 5th YearDanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taking An Adult HistoryDocument5 paginiTaking An Adult HistorySharon ChiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NURS 336-Fall-2020-OutlineDocument5 paginiNURS 336-Fall-2020-OutlineyuddÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline Nurs 65Document5 paginiCourse Outline Nurs 65Louis RoderosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline Nurs 65Document5 paginiCourse Outline Nurs 65Louis RoderosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertigo-An Overview: PG Dhanya, VG Pradeep KumarDocument4 paginiVertigo-An Overview: PG Dhanya, VG Pradeep KumarDebby Mulya Rahmy100% (1)
- Paralytic SquintDocument3 paginiParalytic Squintapi-3756649100% (2)
- Oral - Internal 3rd YearDocument68 paginiOral - Internal 3rd Yearps886rd6chÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment For March 20 To April 102024Document3 paginiAssignment For March 20 To April 102024Diwata BuenviajeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Nursing Course OutlineDocument4 paginiMS Nursing Course OutlineKen Pulanco100% (1)
- Klasifikasi Berdasarkan Workshop American Academy of PeriodontologyDocument6 paginiKlasifikasi Berdasarkan Workshop American Academy of PeriodontologyDimasRadityaBahwonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Why Do We Fall IllDocument4 paginiBio Why Do We Fall IllDheer AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Syllabus NCM 104Document7 paginiRevised Syllabus NCM 104aby50% (4)
- Inflammatory and Immune ResponseDocument13 paginiInflammatory and Immune Responsemimie23100% (1)
- 06.30.17 Autism and Developmental Disorders (Cascio) - NotesDocument3 pagini06.30.17 Autism and Developmental Disorders (Cascio) - NotesDan WuiytÎncă nu există evaluări
- GOOD ANSWERS 1 Past Paper Answers Sem 1Document77 paginiGOOD ANSWERS 1 Past Paper Answers Sem 1abdulÎncă nu există evaluări
- COVERAGE 3rd Quarter Final Exam LECTURE RLEDocument1 paginăCOVERAGE 3rd Quarter Final Exam LECTURE RLECARLOS JOSETON PAOLO SANTIAGO TORREÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final DDDocument56 paginiFinal DDNehal Shabrawy0% (1)
- NCM 116 Midterms Topic 6 Cognitive Disorders NotesDocument4 paginiNCM 116 Midterms Topic 6 Cognitive Disorders NotesMyat LluvidoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abnormal Psychology 6Th Edition Nolen Hoeksema Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFDocument36 paginiAbnormal Psychology 6Th Edition Nolen Hoeksema Solutions Manual Full Chapter PDFdustin.washington425100% (18)
- Abnormal Psychology 6th Edition Nolen-Hoeksema Solutions Manual 1Document36 paginiAbnormal Psychology 6th Edition Nolen-Hoeksema Solutions Manual 1jonathanjohnsongfbykwatdc100% (23)
- Abnormal Psychology 6th Edition Nolen-Hoeksema Solutions Manual 1Document26 paginiAbnormal Psychology 6th Edition Nolen-Hoeksema Solutions Manual 1jamie100% (31)
- Biology and Diversity of InsectsDocument6 paginiBiology and Diversity of InsectsMuddassar ZafarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus of Second Professional M.B.B.S.: (A) General PathologyDocument41 paginiSyllabus of Second Professional M.B.B.S.: (A) General PathologyMOTIRAM PAWARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Krause, L., & Roth, E. (2019, September) - Healthline. Retrieved From Xiong, G. L. (2019, September) - Medscape. Retrieved FromDocument2 paginiKrause, L., & Roth, E. (2019, September) - Healthline. Retrieved From Xiong, G. L. (2019, September) - Medscape. Retrieved Fromandrés ramírezÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUMMARYDocument8 paginiSUMMARYSJane FeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 Sensory Perception SummaryDocument13 pagini15 Sensory Perception SummaryenggridÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Pathology I Lecture OutlineDocument18 paginiBone Pathology I Lecture OutlineAbinayaBÎncă nu există evaluări
- College of Our Lady of Mt. Carmel (Pampanga) : Course SyllabusDocument4 paginiCollege of Our Lady of Mt. Carmel (Pampanga) : Course Syllabus;'SiLeNt';Încă nu există evaluări
- Peripheral Nervous System (PNS) : 1. Anatomical ClassificationDocument4 paginiPeripheral Nervous System (PNS) : 1. Anatomical ClassificationShafiq ZahariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases of Nerve, Muscle and Neuromuscular JunctionDocument50 paginiDiseases of Nerve, Muscle and Neuromuscular JunctionMalueth AnguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Johannes H. SaingDocument67 paginiJohannes H. SaingRomMy WiEn MicKhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurologic System Disorders: Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityDocument2 paginiNeurologic System Disorders: Ateneo de Zamboanga UniversityNur SanaaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Star of LifeDocument16 paginiStar of Lifeerickestacio58Încă nu există evaluări
- NUR 413 Course GuideDocument3 paginiNUR 413 Course GuideCherry Joyce BascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meningitis: Prepared By: Mark Jansen Q. Abero Abby Pearl A. Allagadan Bsn-IiibDocument17 paginiMeningitis: Prepared By: Mark Jansen Q. Abero Abby Pearl A. Allagadan Bsn-IiibRodelyn Sequerra DariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurologic Disorders: 1 Anatomy & Physiology of The Nervous SystemDocument19 paginiNeurologic Disorders: 1 Anatomy & Physiology of The Nervous SystemJazzy Kathlene DumableÎncă nu există evaluări
- RNC Content and Study GuideDocument11 paginiRNC Content and Study GuideNicole CanadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MENINGITISDocument5 paginiMENINGITISFerrel CaderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Afp For MbbsDocument65 paginiAfp For MbbsShyam Sundar SÎncă nu există evaluări
- ncm116 TopicoutlineDocument3 paginincm116 TopicoutlineLuke SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.L: Microbiology Unit Open Ended QuestionsDocument18 pagini8.L: Microbiology Unit Open Ended QuestionsMoira Kelly SolangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qworld USMLE Step1 Course 2019Document91 paginiQworld USMLE Step1 Course 2019Qworld0% (1)
- CNS Pathology-Degeneration and DementiaDocument7 paginiCNS Pathology-Degeneration and DementiaShunqing ZhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tetanus Disease ProjectDocument3 paginiTetanus Disease ProjectTrabant P601Încă nu există evaluări
- Encyclopedia of Infectious Diseases: Modern MethodologiesDe la EverandEncyclopedia of Infectious Diseases: Modern MethodologiesMichel TibayrencÎncă nu există evaluări
- FAM MED COVID 19 by SC Rana RojoDocument112 paginiFAM MED COVID 19 by SC Rana RojoAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pedia Case ProtocolDocument5 paginiPedia Case ProtocolAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric DosageDocument2 paginiPediatric DosageAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.27 (FCM) Strategies For COVID-19Document9 pagini2.27 (FCM) Strategies For COVID-19Allene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.43 (FCM) Logic ModelsDocument6 pagini2.43 (FCM) Logic ModelsAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Attitude Evaluation 1Document1 paginăAttitude Evaluation 1Allene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.07 (OB-CK) Second Stage of LaborDocument9 pagini1.07 (OB-CK) Second Stage of LaborAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shalai Catering ServicesDocument4 paginiShalai Catering ServicesAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.63 Gyne Abnormal Uterine Bleeding 1Document6 pagini1.63 Gyne Abnormal Uterine Bleeding 1Allene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Galing Pook Awards Research ResultsDocument5 paginiThe Galing Pook Awards Research ResultsAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Repro HistoDocument26 paginiFemale Repro HistoAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Ear: OutlineDocument12 paginiAnatomy of The Ear: OutlineAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- UGI Sphincter: UES LES Pyloric SphincterDocument4 paginiUGI Sphincter: UES LES Pyloric SphincterAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Super Final BibliographyDocument17 paginiSuper Final BibliographyAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trigger 1: What Elements of Negligence Are Present in This AforementionedDocument3 paginiTrigger 1: What Elements of Negligence Are Present in This AforementionedAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrganizingDocument2 paginiOrganizingAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acapella Song ArrangementDocument2 paginiAcapella Song ArrangementAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paderanga Lt4 Case StudyDocument5 paginiPaderanga Lt4 Case StudyAllene PaderangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Position PaperDocument2 paginiPosition PaperAllene Paderanga0% (1)
- 11 1513322662 - 15-12-2017Document5 pagini11 1513322662 - 15-12-2017Editor IJRITCCÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scope of Agriculture ExtensionDocument3 paginiScope of Agriculture Extensionhasnain183533Încă nu există evaluări
- Metacognitive Skills, Academic Success and Exam Anxiety As The Predictors of Psychological Well-BeingDocument8 paginiMetacognitive Skills, Academic Success and Exam Anxiety As The Predictors of Psychological Well-Being9 PsychologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Safety and Accident Investigation Short Courses 2020Document21 paginiSafety and Accident Investigation Short Courses 2020Jose A. HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 343snowdenl Essay3Document5 pagini343snowdenl Essay3api-414035660Încă nu există evaluări
- Iimk Adam BrochureDocument15 paginiIimk Adam BrochureMudit SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 - Chase R (1989) Total Quality-Fact or Fiction The TQM MagazineDocument42 pagini8 - Chase R (1989) Total Quality-Fact or Fiction The TQM MagazineGK TiwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- R ProjectDocument82 paginiR Projecteldhoseoa35Încă nu există evaluări
- HPP Brochure 10 12 PDFDocument31 paginiHPP Brochure 10 12 PDFIndianhoshi HoshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name Nida Afzal KhanDocument23 paginiName Nida Afzal KhanSuresh ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Borrero 2008, Extincion MegafaunaDocument6 paginiBorrero 2008, Extincion MegafaunaHernanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Effectiveness of Performance Appraisal of An Employee'S in Loyal Textile Mills LTD, KovilpattiDocument20 paginiStudy On Effectiveness of Performance Appraisal of An Employee'S in Loyal Textile Mills LTD, KovilpattiJohn AjishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Insta Histo Utilizing Instagram AsDocument8 paginiInsta Histo Utilizing Instagram AsAlexander Morel RoyalÎncă nu există evaluări
- # Question Type Accuracy: View Player DataDocument13 pagini# Question Type Accuracy: View Player DataMoezi DamdustÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eruption! Discussion GuideDocument5 paginiEruption! Discussion GuideHoughton Mifflin HarcourtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of The BIM Method in Sustainable ConstructionDocument72 paginiApplication of The BIM Method in Sustainable ConstructionAnge Basile Diawara TshivumdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIA1 - 23 AugustDocument7 paginiCIA1 - 23 AugustALAKA RAJEEV 1930317Încă nu există evaluări
- STAT8017 Assignment 1Document6 paginiSTAT8017 Assignment 1Thompson Daphnis LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teacher-Competency-Checklist HHD AdjunctsDocument7 paginiTeacher-Competency-Checklist HHD AdjunctsMa. Kristel OrbocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Research Methodology MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - JavaTpointDocument17 paginiResearch Methodology MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - JavaTpointManjunath SPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Skill AssesmentDocument110 paginiGeneric Skill Assesmentkang-aipÎncă nu există evaluări
- BullyingDocument19 paginiBullyingPia SottoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set 8Document3 paginiProblem Set 8JonahJunior0% (1)
- Air Change Effectiveness Theory and Calculation Methods PDFDocument10 paginiAir Change Effectiveness Theory and Calculation Methods PDFClifford Allen CooperÎncă nu există evaluări