Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Female Pelvis Protocol r16 1
Încărcat de
api-349402240Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Female Pelvis Protocol r16 1
Încărcat de
api-349402240Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
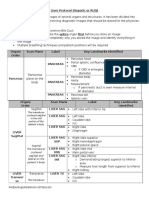
Pelvic Protocol
Use same protocol for Transvaginal
Protocol
Patient should have a full bladder for transabdominal & empty bladder for transvaginal
If transvaginal examination order, do a brief survey of the pelvis with a transabdominal approach first
Scan through the entire pelvis in both planes prior to storing any images:
Begin in the transverse plane starting at the symphysis pubis
Scan upward through the fundus, evaluating the uterus and surroundings
DO NOT ANGLE the probe while scanning up, your transducer should move up the body
Return to the mid body of the uterus and turn into the sagittal plane
Scan right to left and evaluate the uterus and surrounding structures fluid.
Structure Scan Plane Label Landmarks Identified
UT SAG ML Vaginal Canal (not included on endovaginal exam)
Uterus-cervix, body (with endometrium) and fundus
Vaginal Canal (not included on endovaginal exam)
UT SAG ML Uterus-cervix, body (with endometrium) and fundus with
AP and Length uterus measurement
UT SAG ML ENDO Enlarge UT SAG ML image on endometrium in the areas
of the upper uterine body
Enlarge UT SAG ML image on endometrium in the area of
Uterus Sagittal UT SAG ML
the upper uterine body
ENDO
Measure AP diameter of endometrium
UT SAG RT Uterine body and fundus just to the right of midline
UT SAG RT Uterine body and fundus far right lateral
ADNEXA SAG RT Lateral to the uterus in the right adnexa region
UT SAG LT Uterine body and fundus just to the left of midline
UT SAG LT Uterine body and fundus far left lateral
ADNEXA SAG LT Lateral to the uterus in the left adnexa region
UT TX VAGINA Vaginal Canal (not taken on endovaginal exam)
UT TX CX Uterine Cervix
UT TX BODY Uterine mid-body
Uterus Transverse
UT TX BODY Uterine mid-body with width measurement
Uterine fundus (Scan completely out of uterus, then scan
UT TX FUNDUS
back down toward the fundus)
RO SAG Right ovary
RO SAG Right ovary enlarged
Sagittal
RO SAG Right ovary enlarged with AP and Length measurements
RT Ovary RO SAG Right ovary enlarged with color Doppler
RO TX Right ovary
Transverse RO TX Right ovary enlarged
RO TX Right ovary enlarged with width measurements
LO SAG Left ovary
LO SAG Left ovary enlarged
Sagittal
LO SAG Left ovary enlarged with AP and Length measurements
LT Ovary LO SAG Left ovary enlarged with color Doppler
LO TX Left ovary
Transverse LO TX Left ovary enlarged
LO TX Left ovary enlarged with width measurements
MR: Foundations\OBGYN\Lab\Protocols\ Pelvis Protocol r16.docx
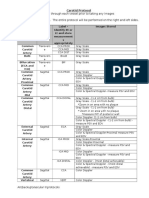
Pelvic Protocol
Use same protocol for Transvaginal
Normal Measurements
Structure Area of Plane Measureme Comments
Interest nt
Uterus Length Sagittal 6-8.5cm Includes Vaginal canal and Uterine-Fundus, Body and
Measurements nulliparous Cervix
given are average 8-10cm Be careful on transvaginal scanning the cervix must
measurements multiparous be included or measurements will be off
Uterus will be AP dimension Sagittal 3cm Widest portion of the uterine body from the anterior
smaller for or depth to posterior wall
premenarche Calipers should be placed perpendicular to length
& postmenopausal Width Transverse 2-3cm Widest portion of the uterine body (level of cornua)
uterus
Endometrium AP Sagittal 4-8mm Early Proliferative-Days 5-7
Thin bright echogenic line
Only measure 6-10mm Late Proliferative-Days 10-14
echogenic area 3-line sign
Do not include the 7-14mm Secretory-Days 15-28,
hypoechoic halo Thick echogenic stripe
Less than Post Menopausal-Asymptomatic
8mm Varies with hormone therapy
Less than 5 Post Menopausal-Symptomatic
mm Varies with hormone therapy
Ovaries Length Sagittal 2.5-5cm Measure longest axis
Size varies w/ age, AP or depth Sagittal 1.5-3cm Calipers should be placed perpendicular to length
menstruation Width Transverse .6-2.2cm Measure from left to right in the mid portion
phase &
menstrual status
Tips
You should scan through the pelvis and abdomen to perform a brief survey of the pericolic recesses and
hepatorenal and splenorenal spaces to look for fluid.
You may need to apply pressure to the pelvis with the transducer in order to see ovaries. If transducer pressure is
not working, pressure can be applied with your hand or by having the patient press down on themselves
Look for free fluid in the posterior cul-de-sac
Utilize 3D or 4D imaging to aid in pathology and endometrium shape details
Ovaries are located between the uterus and the iliac vessels
Pelvic muscles may mimic ovaries, evaluate structures in both planes prior to storing the image
Patient Information
Document first day of the last normal menstruation cycle
Document if postmenopausal patient is currently on hormone therapy
Document all symptoms in detailarea of pain, length of pain or bleeding, amount of bleeding, etc.
Document clinical history of pregnancies, surgeries, or previous pathologies
Pathology
Gray scale sagittal and transverse images
Gray scale sagittal and transverse images with 3 measurements (length x width x A/P)
Use Color Doppler to document the presence of blood flow and Spectral Doppler to document type and velocity
of blood flow
MR: Foundations\OBGYN\Lab\Protocols\ Pelvis Protocol r16.docx
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Liver Protocol 14 1Document5 paginiLiver Protocol 14 1api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Lower Extremity Venous Incompetence Protcol 14Document5 paginiLower Extremity Venous Incompetence Protcol 14api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Spine 14Document2 paginiPediatric Spine 14api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Adult Echocardiography Protocol 14 2Document10 paginiAdult Echocardiography Protocol 14 2api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Upper Extremity Arterial Protocol 14Document3 paginiUpper Extremity Arterial Protocol 14api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Mesenteric Doppler Protocol 14Document2 paginiMesenteric Doppler Protocol 14api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Scrotum Protocol 14Document2 paginiScrotum Protocol 14api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Upper Extremity Venous Protocol 14Document2 paginiUpper Extremity Venous Protocol 14api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Complications Failures and Maintainence of Dental Implant 160218154535Document45 paginiComplications Failures and Maintainence of Dental Implant 160218154535DrIbrahimShaikhÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbbreviationsDocument3 paginiAbbreviationsJade Hemmings100% (1)
- Carotid Protocol 14 1Document4 paginiCarotid Protocol 14 1api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Allen Test Protocol 14 1Document2 paginiAllen Test Protocol 14 1api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Renal Doppler Protocol 14 1Document4 paginiRenal Doppler Protocol 14 1api-349402240100% (1)
- Appendix Protocol 14 1Document2 paginiAppendix Protocol 14 1api-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Fetal Echocardiogram ProtocolDocument4 paginiFetal Echocardiogram Protocolapi-349402240Încă nu există evaluări
- Lower Extremity Arterial Protocol 14 1Document2 paginiLower Extremity Arterial Protocol 14 1api-3494022400% (1)
- Foot and Ankle Injuries Kylee Phillips - 0Document74 paginiFoot and Ankle Injuries Kylee Phillips - 0Charlez OhanuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Postoperative Nausea and VomitingDocument33 paginiPostoperative Nausea and Vomitingferlina100% (1)
- Anaesthesia Revised A5Document720 paginiAnaesthesia Revised A5barn003100% (1)
- Lower Extremity Venous Protocol 14Document3 paginiLower Extremity Venous Protocol 14api-349474075Încă nu există evaluări
- Abdomen ProtocolDocument8 paginiAbdomen Protocolapi-349474075Încă nu există evaluări
- медицинаDocument10 paginiмедицинаDariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avulsed Wound Left FootDocument6 paginiAvulsed Wound Left FootClaire Nimor VentulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eacvi Recommendations Valvular Regurgitation Summary PDFDocument34 paginiEacvi Recommendations Valvular Regurgitation Summary PDFstoicea_katalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study On Internal Fixation of Bimalleolar Ankle FracturesDocument4 paginiA Study On Internal Fixation of Bimalleolar Ankle FracturesIOSRjournalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antepartum Haemorrhage MXDocument22 paginiAntepartum Haemorrhage MXAmir Hilmi Abd AzizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delegation DelegationDocument4 paginiDelegation Delegationapi-299331913Încă nu există evaluări
- Primum Press Kit 2012Document13 paginiPrimum Press Kit 2012Karina EngraffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal AppDocument15 paginiJournal AppvereriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sulci and GyriDocument24 paginiSulci and GyriravigoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nepal Dental AssociationDocument31 paginiNepal Dental AssociationBibek RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Met Caz ClinicDocument57 paginiMet Caz ClinicIndrecan AndreiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nish ChayDocument8 paginiNish ChayDhruv MahajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Provincial Drug ScheduleDocument16 paginiProvincial Drug ScheduleSamMansuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incomplete AbortionDocument2 paginiIncomplete AbortionKEn PilapilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cover Up by Stewart GalanorDocument188 paginiCover Up by Stewart GalanorThames ChaseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Participant DrillDocument2 paginiParticipant DrillponekÎncă nu există evaluări
- MyomaDocument40 paginiMyomagaasheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fetal Alcohol Syndrome Brochure For Nursing SchoolDocument2 paginiFetal Alcohol Syndrome Brochure For Nursing SchoolKrystal Cowley Miller100% (1)
- Pregnancy Tests: How Does A Pregnancy Test Work?Document2 paginiPregnancy Tests: How Does A Pregnancy Test Work?Nasrudin EfendiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endoscopic Insertion of Tympanostomy Tube in ChildrenDocument5 paginiEndoscopic Insertion of Tympanostomy Tube in ChildrenInternational Jpurnal Of Technical Research And ApplicationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction of Case Study IncompleteDocument5 paginiIntroduction of Case Study IncompleteJasmine BesaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esophageal EmergenciesDocument15 paginiEsophageal EmergenciesOmar SolisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Effectiveness of DJFMH Blood Bank in Providing Blood During Emergency Obstetric SituationsDocument3 paginiAssessment of Effectiveness of DJFMH Blood Bank in Providing Blood During Emergency Obstetric SituationsJoanna RemanesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Catastrophe PDFDocument221 paginiMedical Catastrophe PDFghuoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanism of Labour (Normal and Abnormal)Document27 paginiMechanism of Labour (Normal and Abnormal)Rani100% (1)