Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Uterus Structure and Function
Încărcat de
Herne BalberdeDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Uterus Structure and Function
Încărcat de
Herne BalberdeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
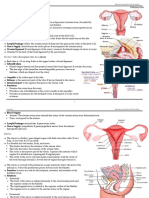
UTERUS Rectouterine pouch (with coils of
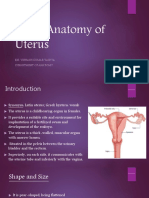
Uterus (also known as womb) is the pear-shaped, ileum or sigmoid colon within it)
hollow muscular organ located in the female Lateral:
pelvis, in which the fertilized ovum implants and
Broad ligament of uterus
develops. In a young nulliparous female, the
uterus measures about 3 inches long, 2 inches Uterine artery and vein
wide and 1 inch thick.
Common Positions of uterus inside female
External structure: pelvis:
The uterus is divided into three parts: In most women, the uterus is anteverted and
anteflexed. Anteversion refers to the position of
Fundus: It is the part of uterus that
the uterus in which its long axis is bent forward
lies above the entrance of the uterine on the long axis of the vagina. Anteflexion refers
tubes. to the position in which the long axis of the body
Body: It is the part of the uterus of the uterus is bent forward on the long axis of
the vagina at the internal os. Therefore, with
that lies below the entrance of the
body in erect position and the bladder empty, the
uterine tubes. uterus lies almost in the horizontal plane.
Cervix: It is the narrow part of the
In some women, the uterus may be retroverted
uterus that pierces the anterior wall
and/or retroflexed. Retroversion refers to the
of the vagina. position in which the fundus and the body of
The cavity of the body of uterus is triangular in uterus are bent backward on the vagina, so that
frontal plane; however, it is merely a cleft in they lie in the rectouterine pouch. Retroflexion
sagittal plane. The cavity of the cervix is called refers to the position in which the body of the
cervical canal. It is connected to the cavity of the uterus is bent backward on the cervix at the
body through the internal os and to the vagina internal os.
through the external os.
Internal structure:
The uterus is composed of three distinct layers:
endometrium, myometrium and parametrium.
Endometrium: It is the mucous
membrane lining of the uterus, which
is continuous above with the mucous
membrane lining the uterine tubes
and below with the mucous
membrane lining the cervix. In the
uterus, the mucous membrane is
applied directly to the myometrium
and there is no submucosa.
Myometrium: It is the thick
muscular wall of uterus, which is
made of smooth muscle fibers
Blood supply:
supported by connective tissue.
The arterial supply is provided
Parametrium: It is the visceral
mainly by the uterine artery, which is
pelvic fascia that surrounds the
a branch of the internal iliac artery. It
supravaginal part of the cervix. It is
gives off a small descending branch
here that the uterine artery crosses
that supplies the cervix and the
the ureter on each side of the cervix.
vagina.
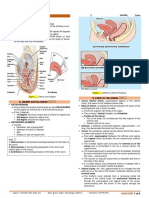
Peritoneal covering of uterus: The venous blood drains by way of
The uterus is covered with the peritoneum except the uterine vein which is a tributary
its anterior aspect below the internal os. Here the of the internal iliac vein.
peritoneum passes forward onto the bladder and
as a result the uterus is devoid of peritoneum at Lymph drainage:
this place. Laterally, there is also a little space
The lymphatics from the fundus and upper part of
devoid of peritoneum, lying between the
body of the uterus accompany the ovarian artery
attachments of the layers of the broad ligament.
and drain into the paraaortic nodes at the level of
the first lumbar vertebra. The vessels from the
Important relations:
lower part of body and the cervix drain into the
Anterior: internal and external iliac lymph nodes.
Uterovesical pouch
Nerve supply:
Superior surface of the bladder
Inferior hypogastric plexus supplies both the
Posterior: sympathetic and parasympathetic fibers to the
uterus.
Support: Body: It is the part of the uterus that lies
The primary support for the uterus is the tone of below the entrance of the uterine tubes.
the levatores ani muscles. In addition the Cervix: It is the narrow part of the uterus
condensations of the pelvic fascia, which form that pierces the anterior wall of the
three important ligaments, also add to the vagina.
support. These ligaments are sacrocervical
ligament, pubocervical ligament, and transverse The cavity of the body of uterus is triangular in
cervical ligament. frontal plane; however, it is merely a cleft in
sagittal plane. The cavity of the cervix is called
Function of uterus: cervical canal. It is connected to the cavity of the
body through the internal os and to the vagina
Uterus is the site for reception, retention and
through the external os.
nutrition of the fertilized ovum. During the entire
period of gestation, the fetus is developed within Internal structure:
the uterus.
The uterus is composed of three distinct layers:
endometrium, myometrium and parametrium.
Endometrium: It is the mucous membrane
lining of the uterus, which is continuous
above with the mucous membrane lining
the uterine tubes and below with the
Role in parturition: mucous membrane lining the cervix. In
Parturition, also known as labor, is the series of the uterus, the mucous membrane is
processes by which the baby, the fetal applied directly to the myometrium and
membranes and the placenta are expelled from there is no submucosa.
the genital tract of the mother. Normally it occurs Myometrium: It is the thick muscular wall
at the end of the 9th month of pregnancy. During of uterus, which is made of smooth muscle
parturition, the contractility of uterus develops fibers supported by connective tissue.
fully, in response to estrogen. Once the cervix is Parametrium: It is the visceral pelvic fascia
stretched by the head of the baby, a nervous that surrounds the supravaginal part of
reflex mechanism is initiated that increases the the cervix. It is here that the uterine artery
force of contractions of the uterine body. crosses the ureter on each side of the
Uterus: cervix.
Uterus is the pear-shaped, hollow muscular organ Peritoneal covering of uterus:
located in the female pelvis, in which the
fertilized ovum implants and develops. In a young The uterus is covered with the peritoneum except
nulliparous female, the uterus measures about 3 its anterior aspect below the internal os. Here the
inches long, 2 inches wide and 1 inch thick. peritoneum passes forward onto the bladder and
as a result the uterus is devoid of peritoneum at
External structure: this place. Laterally, there is also a little space
devoid of peritoneum, lying between the
The uterus is divided into three parts:
attachments of the layers of the broad ligament.
Fundus: It is the part of uterus that lies
above the entrance of the uterine tubes.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Anatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)Document49 paginiAnatomy Lec 22 (FGOs)HumrazÎncă nu există evaluări
- UterusDocument34 paginiUterushammad992Încă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument7 paginiUntitledDania Ibraheem100% (1)
- Final Module in M101 1Document54 paginiFinal Module in M101 1J. TSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Module in M101Document56 paginiFinal Module in M101J. TSÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uterus - 5th Le ReviewerDocument4 paginiUterus - 5th Le ReviewerClarissa IsuriñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female reproductive anatomy assignmentDocument8 paginiFemale reproductive anatomy assignmentDr. Mohammad JamaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Obs-Gyn Final 2019Document169 paginiObs-Gyn Final 2019koalakid55Încă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryDocument89 paginiAnatomy of Fallopian Tube & OvaryAsma AijazÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBL 2Document20 paginiCBL 2Hammad AkramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gross Anatomy of Uterus: D R. Vibhash Kumar Vaidya Department of AnatomyDocument25 paginiGross Anatomy of Uterus: D R. Vibhash Kumar Vaidya Department of AnatomyAhsan TariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Genital SystemDocument29 paginiFemale Genital SystemMuna MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On: Female Reproductive SystemDocument54 paginiPresentation On: Female Reproductive SystemLetsShop BbsrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology: Functions of The UterusDocument6 paginiAnatomy and Physiology: Functions of The UterusAnthony jesusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology - EctopicDocument4 paginiAnatomy and Physiology - EctopicReyzelinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of the Uterus and PerineumDocument16 paginiAnatomy of the Uterus and PerineumHamza MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal Lec Week 1 3Document4 paginiMaternal Lec Week 1 3Althea ManarpiisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument96 paginiAnatomy Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemRabin BasnetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ob 1 1Document73 paginiOb 1 1Kate GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemDocument12 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Female Reproductive SystemSyed Isamil100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology Reproductive System: ComponentsDocument7 paginiAnatomy and Physiology Reproductive System: ComponentsMark Nel Nuñez100% (1)
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive Organs: Dr.M.Mahalakshmi Assistant Professor Government Chengalpattu Medical CollegeDocument20 paginiAnatomy of Female Reproductive Organs: Dr.M.Mahalakshmi Assistant Professor Government Chengalpattu Medical Collegepranu6789Încă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 Male and Female Repro IntroductionDocument11 pagini2.1 Male and Female Repro IntroductionTrisha Mae BalladÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Aida Abd El-RazekDocument96 paginiAnatomy & Physiology of Female Reproductive System: Dr. Aida Abd El-RazekJennifer DixonÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Female Reproductive SystemDocument25 paginiThe Female Reproductive Systemavin xsroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument7 paginiFemale Reproductive SystemjonaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Section 2 The Female Genital Organs: Gonad - Conveying Ducts - Accessory GlandsDocument29 paginiSection 2 The Female Genital Organs: Gonad - Conveying Ducts - Accessory Glandssomebody_maÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument46 paginiFemale Reproductive SystemAzza100% (11)
- Reproductive Anatomy and Physiology: BY DR: AhmedDocument82 paginiReproductive Anatomy and Physiology: BY DR: AhmedAhmed ElryahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female reproductive anatomyDocument22 paginiFemale reproductive anatomyIGA ABRAHAMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument8 paginiAnatomy and PhysiologyAironne ManguilimotanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Reproductive System (Yuni)Document36 paginiFemale Reproductive System (Yuni)Ayi Abdul BasithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caesarean Section: Advanced Maternal and Child Health Nursing NSC504Document60 paginiCaesarean Section: Advanced Maternal and Child Health Nursing NSC504tsega tilahunÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Bartholin's Glands: These Glands Are Located Next To The Vaginal Opening andDocument4 pagini8 Bartholin's Glands: These Glands Are Located Next To The Vaginal Opening andalyssaaaaa1234885Încă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive System 1Document118 paginiReproductive System 1Fathaimath SuhanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CASE 1 - HematometrocolposDocument96 paginiCASE 1 - HematometrocolposCynthia AristaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Female Reproductive SystemDocument14 paginiAnatomy of Female Reproductive SystemkukadiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Reproductive System OverviewDocument84 paginiFemale Reproductive System OverviewAtie IzzatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female RSystemDocument71 paginiFemale RSystemicliftonguytonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemDocument62 paginiAnatomy of The Female Reproductive SystemBibek GajmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing ReviewerDocument119 paginiMaternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewerasdf100% (1)
- Anatomy and Physiology of Female ReproductiveDocument6 paginiAnatomy and Physiology of Female ReproductiveChryst Louise SaavedraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female reproductive system: the uterus and its functionsDocument48 paginiFemale reproductive system: the uterus and its functionsCindy LeonieÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Case Study About Cervical PolypsDocument8 paginiA Case Study About Cervical PolypsJisel-Apple BulanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer Compiled by NURSEHOOMANDocument122 paginiMaternal and Child Health Nursing Reviewer Compiled by NURSEHOOMANL Rean Carmelle MAGALLONESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Review of female reproductive anatomy and physiologyDocument8 paginiReview of female reproductive anatomy and physiologyRuthangela GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female RSsystem 2Document90 paginiFemale RSsystem 2icliftonguytonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing ReviewerDocument137 paginiMaternal and Child Health Nursing ReviewerDexie MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Student Name: ALI HASSAN RAZA STUDENT I D: 2018304027Document6 paginiStudent Name: ALI HASSAN RAZA STUDENT I D: 2018304027Sayed AsifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mayo MaDocument23 paginiMayo Madextroid12Încă nu există evaluări
- Protap Post NatalDocument18 paginiProtap Post NatalSyafitri NavisyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pelvic AnatomyDocument0 paginiPelvic AnatomyAlynne De Luna PascuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 41 Female Reproductive AnatomyDocument14 pagini41 Female Reproductive Anatomyruaa firasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Reproductive System Anatomy and DisordersDocument43 paginiFemale Reproductive System Anatomy and DisordersWidayuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy of Uterus and Vagina and PudendumDocument38 paginiAnatomy of Uterus and Vagina and Pudendumgugus aminaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reproductive SystemDocument43 paginiReproductive SystemDoc Zay VillafuerteÎncă nu există evaluări
- HisterectomíaDocument2 paginiHisterectomíaTamara PricilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Female Reproductive SystemDocument21 paginiFemale Reproductive Systemyt2zkpkphqÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCN Drill AnswersDocument12 paginiMCN Drill AnswersHerne Balberde100% (1)
- DescriptionDocument6 paginiDescriptionHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced English Grammar SyllabusDocument5 paginiAdvanced English Grammar SyllabusHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fraction - QuestionnaireDocument6 paginiFraction - QuestionnaireHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- APA FormatDocument7 paginiAPA FormatpatrickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lover's LoveDocument2 paginiLover's LoveHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rise from Ruins: A Town's Resilience after AssaultDocument1 paginăRise from Ruins: A Town's Resilience after AssaultHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age ProblemsDocument3 paginiAge ProblemsHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paragraph DevelopmentDocument29 paginiParagraph DevelopmentHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 Sevenths: Example 8Document6 pagini5 Sevenths: Example 8Herne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHN QuestionsDocument10 paginiCHN QuestionsHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age Problems - QuestionnaireDocument2 paginiAge Problems - QuestionnaireHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chavacano Literature PDFDocument30 paginiChavacano Literature PDFHerne Balberde100% (3)
- Providing Knowledge on Birth ControlDocument15 paginiProviding Knowledge on Birth ControlHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Sample IFSP PlanDocument4 paginiA Sample IFSP PlanHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Agreement Pronoun Antecedent Answers TipsDocument7 paginiLesson Agreement Pronoun Antecedent Answers TipsHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 100 New Words From Reader DigestDocument8 pagini100 New Words From Reader DigestHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hebrew Literature BEED IV CDocument3 paginiHebrew Literature BEED IV CHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mack Riel SarailDocument2 paginiMack Riel SarailHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Guide To Writing The Literary Analysis EssayDocument9 paginiA Guide To Writing The Literary Analysis Essayapi-249002674Încă nu există evaluări
- Mixed Internal & External HemorrhoidsDocument4 paginiMixed Internal & External HemorrhoidsHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benign Febrile ConvulsionDocument3 paginiBenign Febrile ConvulsionHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain InjuryDocument10 paginiBrain InjuryHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Year: First Semester Second SemesterDocument2 paginiFirst Year: First Semester Second SemesterHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gametogenesis: Cell Division Gametes Biological Life Cycle Organism Meiotic Gametocytes Mitotic PlantsDocument8 paginiGametogenesis: Cell Division Gametes Biological Life Cycle Organism Meiotic Gametocytes Mitotic PlantsHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pub 7101 oDocument25 paginiPub 7101 oHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- El-Razin JoDocument1 paginăEl-Razin JoHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- MajorsHandbook PDFDocument34 paginiMajorsHandbook PDFHerne BalberdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in Philippine LiteratureDocument2 paginiLesson Plan in Philippine LiteratureHerne Balberde86% (28)
- Comparison Study of Conventional Hot-Water and Microwave Blanching at Different Timetemperaturepower Combinations On The Quality of Potatoes.Document72 paginiComparison Study of Conventional Hot-Water and Microwave Blanching at Different Timetemperaturepower Combinations On The Quality of Potatoes.DavldSmith100% (1)
- B.pharm Course Handbook 2017 18Document74 paginiB.pharm Course Handbook 2017 18Md RaquibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raspberry PiDocument19 paginiRaspberry PiAnonymous E4Rbo2s100% (1)
- Civil Eng Internship ReportDocument6 paginiCivil Eng Internship ReportAromatic-O PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Features General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterDocument18 paginiFeatures General Description: 3A 24V 340Khz Synchronous Buck ConverterAntonioNobregaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemical reactions and structuresDocument22 paginiChemical reactions and structuresStormy StudiosÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Test 6Document87 paginiEnglish Test 6Ha PhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carte Automatic TransmissionsDocument20 paginiCarte Automatic TransmissionsGigelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel StaircaseDocument17 paginiSteel StaircaseKarthick CrazeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- BiodiversityDocument9 paginiBiodiversityVienica Dauz Mico Balbin100% (1)
- 2nd - Science-Second-Quarter-Week-1Document37 pagini2nd - Science-Second-Quarter-Week-1Arlene AranzasoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difference Between AerospaceDocument2 paginiDifference Between AerospaceSyawalMaulanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blues, Rock and Americana MixDocument4 paginiBlues, Rock and Americana MixLuis CrownÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kathleen Langreo Notes FB (Feb6)Document27 paginiKathleen Langreo Notes FB (Feb6)Kaycee Ayo100% (4)
- Journal of Alloys and Compounds: Wei Li, Zhijun Xu, Ruiqing Chu, Peng Fu, Guozhong ZangDocument4 paginiJournal of Alloys and Compounds: Wei Li, Zhijun Xu, Ruiqing Chu, Peng Fu, Guozhong ZangSamah SamahÎncă nu există evaluări
- GSM Based Power Grid Monitoring SystemDocument41 paginiGSM Based Power Grid Monitoring SystemPreetham SurepallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Horizontal Projectile WSDocument3 paginiHorizontal Projectile WSForsbergPhysicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Terminal BlockDocument12 paginiTerminal BlockAlmaforÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Placenta PDFDocument5 paginiClassification of Placenta PDFAdarsh jainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Tattoo-June 2021Document114 paginiTotal Tattoo-June 2021Comicgek100% (2)
- Fault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - CriticalDocument3 paginiFault Code 155: Intake Manifold Air Temperature High - Criticalhamilton miranda100% (1)
- 10 01 Breather Filters GBDocument8 pagini10 01 Breather Filters GBosuengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dimensions and Relations of The Dentogingival Junction in Humans. Gargiulo 1961Document7 paginiDimensions and Relations of The Dentogingival Junction in Humans. Gargiulo 1961Linda Garcia PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Earthbag House For HaitiDocument22 paginiEarthbag House For HaitiRaymond KatabaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- FHM Espana 2010 12 PDFDocument2 paginiFHM Espana 2010 12 PDFBrandenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Delay-Tolerant NetworksDocument66 paginiDelay-Tolerant NetworksMegi YantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tween 80Document11 paginiTween 80fvdxrgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kelas 1 AlphabetTITLE Kelas 1 Numbers ConversationTITLE Kelas 2 Feelings Body PartsDocument54 paginiKelas 1 AlphabetTITLE Kelas 1 Numbers ConversationTITLE Kelas 2 Feelings Body PartsArti Hikmatullah Perbawana Sakti BuanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- F588 PDFDocument8 paginiF588 PDFOscar Gutiérrez-JuncoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Warming Is The Term Used To Describe A Gradual Increase in The Average Temperature of The EarthDocument6 paginiGlobal Warming Is The Term Used To Describe A Gradual Increase in The Average Temperature of The EarthSaswataBhattacharyaÎncă nu există evaluări