Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Parkinson
Încărcat de
goyaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Parkinson
Încărcat de
goyaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Parkinsons disease
DEFINITION:
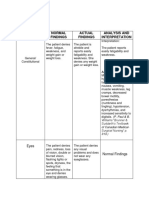
1. Is a progressive disease of the nervous system marked by tremor, muscular
rigidity, and slow, imprecise movement, chiefly affecting middle-aged and elderly
people. It is associated with degeneration of the basal ganglia of the brain and a
deficiency of the neurotransmitter dopamine.
Risk factors:
Age. Young adults rarely experience Parkinson's disease. It ordinarily begins in middle or late life,
and the risk increases with age. People usually develop the disease around age 60 or older.
Heredity.
Sex. Men are more likely to develop Parkinson's disease than are women.
Signs and symptoms: Labs and dx:
Tremors (Pill-rolling) Positive emission tomography
Rigidity (cogwheeling) (evaluating levodopa uptake and
Bradykinesia conversion to dopamine in the corpus
Hypokinesia striatum.
Microphagia Patients history
Dysphonia Physical assessment (stiff arm, slight
Dysphagia limp, tremor, stooped posture)
Depression Neurological examination
Dementia
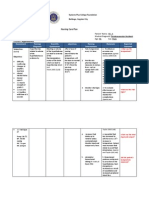
Nursing intervention:
Improve mobility (progressive program of
Nursing diagnosis: daily exercise)
Enhance self care activities (Environmental
Impaired physical mobility
modifications and client education and
related to muscle rigidity and
support.)
motor weakness Improve bowel elimination (increase fluid
Self-care deficits
intake and high fiber diet. Regular bowel
Constipation related to
routine.)
medication and reduced Improve communication (Speech therapist)
activity Support coping abilities (physiotherapy,
Impaired verbal
psychotherapy and medication therapy and
communication
support group participation)
Ineffective coping related to
depression and dysfunction
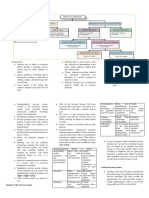
Drugs: Pathophysiology
Antiparkinsonian meds
(Levodopa)
Anticholinergic therapy
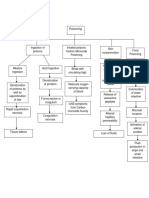
Destruction of dopaminergic
for tremors and rigidity.
neuronal cells in the substantia
Antiviral (Reduces the
nigra in the basal ganglia
three cardinal signs)
Dopamine antagonist
Monoamine Oxidase
Depletion of dopamine
Inhibitors (inhibits
dopamine breakdown
and slows progression
of disease) Degeneration of the
Antidepressants dopaminergic nigrostriatal
Antihistamines (reduces pathway
tremors)
Imbalance of excitatory (Ach) and
Medical management: inhibiting (dopamine) neurotransmitters
in the corpus striatum.
Surgical:
Stereotactic
Impairment of extrapyramidal tracts
procedures:
controlling complex body
Thalamotomy and
movements
pallidotomy to interrupt
nerve pathways and
alleviate tremor and
rigidity. Tremors
Neural Transplantation- Rigidit Bradykinesi
adrenal medullary
tissue into the corpus
striatum is performed in
an effort to reestablish
normal dopamine
release.
Deep brain stimulation-
pacemaker-like brain
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Ventricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandVentricular Septal Defect, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument52 paginiPredisposing Conditions, Management and Prevention of Chronic Kidney DiseaseSaad MotawéaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angina PectorisDocument17 paginiAngina PectorisRacel HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types, Causes and Treatments of ComasDocument3 paginiTypes, Causes and Treatments of ComasgcsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avascular Necrosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandAvascular Necrosis, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (2)
- 1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue PerfusionDocument1 pagină1 Ineffective Peripheral Tissue Perfusionjean_fabulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFDocument6 paginiHypertension Pathophysiology and Treatment PDFBella TogasÎncă nu există evaluări
- GBS Management, Medications and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument4 paginiGBS Management, Medications and Nursing Considerationssouledg3100% (1)
- Kawasaki DiseaseDocument7 paginiKawasaki DiseaseRitamariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal AssessmentDocument11 paginiAbdominal Assessmentasa100% (1)
- Polycythemia in NewbornDocument25 paginiPolycythemia in NewbornTheva Thy100% (2)
- NCPDocument10 paginiNCPCristina L. JaysonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular DiseaseDocument37 paginiHemorrhagic Cerebro Vascular Diseasejbvaldez100% (1)
- Nursing Interventions CHFDocument3 paginiNursing Interventions CHFbanyenye25100% (1)
- Complications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETDocument6 paginiComplications of Plaster Cast PATIENT LEAFLETRadiyan MeidhiyantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SiadhDocument16 paginiSiadhGokul Rajan100% (1)
- Case 1 - Pneumonia (Final)Document4 paginiCase 1 - Pneumonia (Final)Joegie ArioÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP GeDocument14 paginiNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organophosphrous PoisoningDocument53 paginiOrganophosphrous Poisoningpriyashu78100% (1)
- Managing Fall Risk in an 84-Year-Old Asian MaleDocument4 paginiManaging Fall Risk in an 84-Year-Old Asian Malesavvy_as_98-1Încă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name Therapeutic Classification Pharmacologic ClassificationDocument3 paginiGeneric Name Therapeutic Classification Pharmacologic ClassificationAnselle CasilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bilateral Knee OADocument35 paginiBilateral Knee OAMu'iz Beatforteen50% (2)
- Welcome To The Case Study Presentation:-: Prostate CancerDocument22 paginiWelcome To The Case Study Presentation:-: Prostate CancerDengo ChapatieeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Relationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayDocument6 paginiRelationship Between CKD Stage and Pulmonary Edema on Chest X-RayAnnisa RabbaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myocardial Infarction Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentDocument55 paginiMyocardial Infarction Guide: Causes, Symptoms and TreatmentdantefuerteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Care of The Mother, Child at Risk or With Problems (Acute and Chronic)Document6 paginiCare of The Mother, Child at Risk or With Problems (Acute and Chronic)Elizabeth ZamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Risk InfectionDocument1 paginăNCP Risk InfectionEni RahmawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DX Fracture PDFDocument8 paginiDX Fracture PDFSherree HayesÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are The Signs and Symptoms of Heart Failure?Document4 paginiWhat Are The Signs and Symptoms of Heart Failure?Lara TechiesÎncă nu există evaluări
- EncephaloceleDocument7 paginiEncephaloceleJhaneah SundiamÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP CvaDocument4 paginiNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Physical MobilityDocument2 paginiImpaired Physical Mobilitygianne121391Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Study 6 - JimDocument1 paginăCase Study 6 - Jimginabobina3337238Încă nu există evaluări
- Urinary Incontinence Guide for Care and ManagementDocument5 paginiUrinary Incontinence Guide for Care and ManagementfakrulnersmudaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Physiology of ParkinsonDocument2 paginiPa Tho Physiology of Parkinsoncuriosity_killsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State - A Diabetic EmergencyDocument2 paginiHyperglycemic Hyperosmolar State - A Diabetic EmergencyNiken AninditaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)Document21 paginiHyperosmolar Hyperglycemic State (HHS)Malueth AnguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impaired Gas Exchange NCPDocument3 paginiImpaired Gas Exchange NCPRomel BaliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Care in NursingDocument16 paginiCritical Care in NursingFUZNA DAHLIA MUDZAKIROH 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Basilar Skull Fractures DiagnosisDocument16 paginiBasilar Skull Fractures DiagnosisRindahMDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nasogastric Tube Feeding ML4763 PDFDocument7 paginiNasogastric Tube Feeding ML4763 PDFStereo PodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study of 53-Year-Old Male with Hypertension and Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument6 paginiCase Study of 53-Year-Old Male with Hypertension and Coronary Artery DiseaseApoorv Jain100% (1)
- Clinical Worksheet for Stroke PatientDocument6 paginiClinical Worksheet for Stroke PatientJackie GriffisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Managing Hypertension to Prevent ComplicationsDocument10 paginiManaging Hypertension to Prevent ComplicationsArabylle Maranca AbuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan WeeblyDocument8 paginiNursing Care Plan Weeblyapi-277498943Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 paginiNursing Care Planyumiko0% (1)
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 paginiNursing Care Planesteffie21Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiDocument12 paginiCase Study - Dengue Fever V - S UtiHarlene Joyce ReyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic GastritisDocument7 paginiChronic GastritisDivina AquinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Diabetic KetoacidosisDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan for Diabetic KetoacidosisHanz AlecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Malnutrition in Stroke PatientDocument8 paginiMalnutrition in Stroke PatientFetria MelaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute TonsillopharyngitisDocument39 paginiAcute TonsillopharyngitisCin AtianzarÎncă nu există evaluări
- College of Health Sciences Nursing Care Plan for Acute Myocardial InfarctionDocument4 paginiCollege of Health Sciences Nursing Care Plan for Acute Myocardial InfarctionLouise GudmalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Document6 paginiConcept Map (Aplastic Anemia) b1Ran PioloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leishmania Nursing LectDocument36 paginiLeishmania Nursing LectA Rhman Al OwaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Diseases Case Study 18 ADocument4 paginiHuman Diseases Case Study 18 Aairickann100% (1)
- Nursing Care of Stroke - NewDocument4 paginiNursing Care of Stroke - Newninda saputriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute TonsillitisDocument34 paginiAcute TonsillitisArvindhan100% (1)
- DiseasesDocument30 paginiDiseasesgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For Neurologic FunctionDocument5 paginiReviewer For Neurologic FunctiongoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIDS Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentDocument10 paginiAIDS Risk Factors, Symptoms, Diagnosis & TreatmentgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prostate CancerDocument1 paginăProstate CancergoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearanceDocument3 paginiNursing Plan for Ineffective Airway ClearancegoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HHNK and DkaDocument4 paginiHHNK and Dkagoya100% (1)
- Cardiac RhythmsDocument2 paginiCardiac RhythmsgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PoisoningDocument2 paginiPoisoninggoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distal RTA PathoDocument1 paginăDistal RTA PathogoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CORPULMONALEDocument2 paginiCORPULMONALEgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HHNK and DkaDocument4 paginiHHNK and Dkagoya100% (1)
- Prostate CancerDocument2 paginiProstate CancergoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of PTBDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of PTBgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AmiDocument2 paginiAmigoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lung CancerDocument2 paginiLung CancergoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviewer For Neurologic FunctionDocument5 paginiReviewer For Neurologic FunctiongoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systemic Lupus ErythematosusDocument3 paginiSystemic Lupus ErythematosusgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of PoisoningDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of PoisoninggoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ROS SampleDocument6 paginiROS SamplegoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pott'S Disease: DescriptionDocument8 paginiPott'S Disease: DescriptiongoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45 Bed Capacity Primary Hospital 48 Hours A Week 12 Hours/ ShiftDocument1 pagină45 Bed Capacity Primary Hospital 48 Hours A Week 12 Hours/ ShiftgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prioritization of Nursing Care PlansDocument10 paginiPrioritization of Nursing Care PlansgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParkinsonDocument2 paginiParkinsongoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of PTBDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of PTBgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voyeuristic Disorder SymptomsDocument7 paginiVoyeuristic Disorder SymptomsgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- World War II and The Aftermath of The Cold WarDocument5 paginiWorld War II and The Aftermath of The Cold WargoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of AnesthesiaDocument1 paginăTypes of AnesthesiaImran PinjariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Cirrhosis GuideDocument8 paginiLiver Cirrhosis GuidegoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prioritization of ProblemsDocument1 paginăPrioritization of ProblemsgoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbiology Antimicrobial GuideDocument89 paginiMicrobiology Antimicrobial GuideShaz Chindhy100% (1)
- Deep Brain Stimulation DBS ApplicationsDocument280 paginiDeep Brain Stimulation DBS ApplicationsEduardo Panadero CuarteroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes Muscle Relaxants Part 3Document62 paginiNotes Muscle Relaxants Part 3Charlotte FabrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basal GangliaDocument11 paginiBasal GangliaSTEVEN OKURUTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parkinson's Disease and Parkinsonism: Review Neurology Series Editor, William J. Mullally, MDDocument6 paginiParkinson's Disease and Parkinsonism: Review Neurology Series Editor, William J. Mullally, MDBart X GankÎncă nu există evaluări
- 114 okMSAD AFP-Differentiation and Diagnosis of Tremor PDFDocument6 pagini114 okMSAD AFP-Differentiation and Diagnosis of Tremor PDFkasmiantoabadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parkinson's Disease: A Review: Neurology India March 2018Document11 paginiParkinson's Disease: A Review: Neurology India March 2018Alina Vitali TabarceaÎncă nu există evaluări
- N C C N D: Ursing ARE OF Lients With Eurologic IsordersDocument96 paginiN C C N D: Ursing ARE OF Lients With Eurologic IsordersMatt Lao DionelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coordination of Movement-Lecture Notes 20201Document47 paginiCoordination of Movement-Lecture Notes 20201Zobayer AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PHARMAfdDocument7 paginiPHARMAfdJobelle AcenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parkinson DiseaseDocument10 paginiParkinson DiseaseparthibaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- ParkinsonDocument2 paginiParkinsongoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti ParkinsonsDocument4 paginiAnti ParkinsonsMichaela BernadasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental and Behavioral Dysfunction in Movement Disorders - M. Bedard, Et Al., (Humana, 2003) WW PDFDocument580 paginiMental and Behavioral Dysfunction in Movement Disorders - M. Bedard, Et Al., (Humana, 2003) WW PDFTommi Jitaru100% (1)
- Kuliah Extrapyramidal SyndromeDocument50 paginiKuliah Extrapyramidal SyndromeSeiska MegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurorehabilitation 1: Stroke, TBI, MS, PD, GBS, and ALS ExaminationDocument439 paginiNeurorehabilitation 1: Stroke, TBI, MS, PD, GBS, and ALS ExaminationDuncan D'AmicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stereotactic and Functional NeurosurgeryDocument114 paginiStereotactic and Functional NeurosurgerymichaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Update On The Diagnosis and Management of Parkinson's DiseaseDocument6 paginiUpdate On The Diagnosis and Management of Parkinson's DiseaseAsniar RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Movement Disorders - UpToDateDocument35 paginiFunctional Movement Disorders - UpToDateDalal HazelÎncă nu există evaluări
- My Basal GangliaDocument18 paginiMy Basal GangliaPriya GKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis Ingrid ClaessonDocument68 paginiThesis Ingrid ClaessonFrode EgasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proprioception, Vestibular & CoordinationDocument28 paginiProprioception, Vestibular & Coordinationzm2h8hpsq8Încă nu există evaluări
- Guide To DBS Stimulation TherapyDocument56 paginiGuide To DBS Stimulation TherapyAndres Rodriguez SeijoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parkinson Phar310Document22 paginiParkinson Phar310Nuhu SibaÎncă nu există evaluări
- James Parkinson's Disease: Signs, Symptoms, and Physiotherapy ManagementDocument25 paginiJames Parkinson's Disease: Signs, Symptoms, and Physiotherapy ManagementArko duttaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NADH - The Energizing CoenzymeDocument22 paginiNADH - The Energizing CoenzymeTrueVa1ue100% (1)
- Nervous System Disorders PPT 3 1Document9 paginiNervous System Disorders PPT 3 1Camille Joy BaliliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Parkinson's Disease and Movement DisordersDocument6 paginiUnderstanding Parkinson's Disease and Movement Disordersspicychips7Încă nu există evaluări
- Neurology pdf-1Document142 paginiNeurology pdf-1Ahmed Adel SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differential Diagnosis of ParkinsonismDocument27 paginiDifferential Diagnosis of Parkinsonismelenac67Încă nu există evaluări