Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words For Revision
Încărcat de
oscarbecTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Worksheet IGCSE Match Key Words For Revision
Încărcat de
oscarbecDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
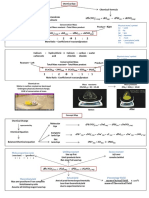
Name: ________________________
IGCSE Chemistry Definitions Date: _______________
Match up the fact with the keyword and the definition that helps explain it.
- A substance formed from the dead remains
1 Crude Oil - - of plants or animals which will burn in air e.g. A
Coal, natural gas
- a group of molecules with similar physical
and chemical properties, the same general
2 Fossil Fuel - - formula and the same functional group B
(albeit with trends e.g. increasing boiling
point with increasing carbon chain length)
- An unsaturated hydrocarbon e.g. C2H4
3 Hydrocarbon - - ethene C
- A reaction where many small alkene
4 Cracking - - molecules (monomers) join up to form a long D
chain molecule of repeating units (polymer).
- A reaction where different monomers join
up to form a long chain molecule of
5 Saturated - - E
repeating units (polymer) whilst also
producing smaller molecules.
- A hydrocarbon which only has single
6 Unsaturated - - covalent bonds between all atoms. F
- A hydrocarbon which has at least one
7 Alkane - - double bond between two neighbouring G
carbon atoms.
- A substance which contains carbon and
8 Alkene - - hydrogen atoms only. H
Addition - A saturated hydrocarbon e.g. CH4
9 - - methane I
Polymerization
- Process where long chain hydrocarbons of
Condensation little value are broken down by heat and a
10 - - J
Polymerization catalyst into smaller, more useful
hydrocarbons
- A mixture of hydrocarbons formed from the
Homologous remains of dead sea life which was covered
11 - - with silt on the sea bed and compressed
K
Series
over millions of years
Created at Quickworksheets.net Page 1
TEACHER ANSWER SHEET
IGCSE Chemistry Definitions
Match up the fact with the keyword and the definition that helps explain it.
- A mixture of hydrocarbons formed from the remains of dead sea life which was
1 K Crude Oil
covered with silt on the sea bed and compressed over millions of years
- A substance formed from the dead remains of plants or animals which will burn in
2 A Fossil Fuel
air e.g. Coal, natural gas
3 H Hydrocarbon - A substance which contains carbon and hydrogen atoms only.
- Process where long chain hydrocarbons of little value are broken down by heat and
4 J Cracking
a catalyst into smaller, more useful hydrocarbons
5 F Saturated - A hydrocarbon which only has single covalent bonds between all atoms.
- A hydrocarbon which has at least one double bond between two neighbouring
6 G Unsaturated
carbon atoms.
7 I Alkane - A saturated hydrocarbon e.g. CH4 methane
8 C Alkene - An unsaturated hydrocarbon e.g. C2H4 ethene
Addition - A reaction where many small alkene molecules (monomers) join up to form a long
9 D
Polymerization chain molecule of repeating units (polymer).
Condensation - A reaction where different monomers join up to form a long chain molecule of
10 E
Polymerization repeating units (polymer) whilst also producing smaller molecules.
- a group of molecules with similar physical and chemical properties, the same
Homologous
11 B general formula and the same functional group (albeit with trends e.g. increasing
Series
boiling point with increasing carbon chain length)
Created at Quickworksheets.net Page 2
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Experiment 11.1: Identification of A Solvent Using Fractional DistillationDocument6 paginiExperiment 11.1: Identification of A Solvent Using Fractional DistillationoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shanghai Singapore International School G11 Chemistry Test - Bonding SL Mark Out of .. Name Target Grade . Best Grade 1Document10 paginiShanghai Singapore International School G11 Chemistry Test - Bonding SL Mark Out of .. Name Target Grade . Best Grade 1oscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Using A Bunsen Burner Air Hole Position Colour of FlameDocument2 paginiUsing A Bunsen Burner Air Hole Position Colour of FlameoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Flashcards Topic 10 Metals CIE Chemistry IGCSEDocument99 paginiFlashcards Topic 10 Metals CIE Chemistry IGCSEoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- ATL Presentation at To StaffDocument42 paginiATL Presentation at To StaffoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Tutorial On Design Experiment For Voltaic Cell and Nernst EquationDocument16 paginiTutorial On Design Experiment For Voltaic Cell and Nernst EquationoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- 3 2 (Aq) (Aq) 2(s) 3 (Aq)Document24 pagini3 2 (Aq) (Aq) 2(s) 3 (Aq)oscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Redox Titration Acid Base TitrationDocument33 paginiRedox Titration Acid Base TitrationoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- G11 Chemistry Test - HLTopic 5,6& 7Document11 paginiG11 Chemistry Test - HLTopic 5,6& 7oscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- IB Chemistry Mole Concept, RAM, RMM Isotopes and Empirical/Molecular FormulaDocument23 paginiIB Chemistry Mole Concept, RAM, RMM Isotopes and Empirical/Molecular FormulaoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- IB Chemistry On Limiting, Excess, Percentage Yield and Ionic EquationsDocument26 paginiIB Chemistry On Limiting, Excess, Percentage Yield and Ionic EquationsoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Tutorial On Standard Electrode Potential, Standard Reduction Potential and Electrochemical SeriesDocument42 paginiTutorial On Standard Electrode Potential, Standard Reduction Potential and Electrochemical SeriesoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Tutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokDocument27 paginiTutorial On Electrolysis and Faraday's Law.: Prepared by Lawrence KokoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Curt Farnham, Mirjam Berghuis and Karin FischerDocument32 paginiCurt Farnham, Mirjam Berghuis and Karin FischeroscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Extended Essay Assessment Criteria (Chemistry)Document8 paginiExtended Essay Assessment Criteria (Chemistry)oscarbec100% (1)
- Extended Essay Checklist: Aspect Criterion Descriptor Check CommentDocument3 paginiExtended Essay Checklist: Aspect Criterion Descriptor Check CommentoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Tutorial On Reactivity Series Vs Electrochemical Series.: Prepared by Lawrence KokDocument8 paginiTutorial On Reactivity Series Vs Electrochemical Series.: Prepared by Lawrence KokoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Extended Essay: Feedback Rubric (Out of 34) : Criteria A: Focus and MethodDocument2 paginiExtended Essay: Feedback Rubric (Out of 34) : Criteria A: Focus and MethodoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- E-Learning Activity For February 17-19Document4 paginiE-Learning Activity For February 17-19oscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial On Redox Titration, BOD and Biological Oxygen Demand Using Winkler MethodDocument35 paginiTutorial On Redox Titration, BOD and Biological Oxygen Demand Using Winkler MethodoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Energetics Cryptogram and AnswersDocument4 paginiEnergetics Cryptogram and AnswersoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrolysis Cryptogram With AnswersDocument6 paginiElectrolysis Cryptogram With AnswersoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condensation Polyesters and Polyamides InvestigationDocument3 paginiCondensation Polyesters and Polyamides InvestigationoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB Chemistry Molarity, Concentration, Standard Solution and Serial Dilution PreparationDocument13 paginiIB Chemistry Molarity, Concentration, Standard Solution and Serial Dilution PreparationoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Extended Essay: Feedback Rubric (Out of 34) : Criteria A: Focus and MethodDocument2 paginiExtended Essay: Feedback Rubric (Out of 34) : Criteria A: Focus and MethodoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 5 - Energetics: Average Bond Enthalpy: Born-Haber Cycle Electron Affinity EnthalpyDocument4 paginiTopic 5 - Energetics: Average Bond Enthalpy: Born-Haber Cycle Electron Affinity EnthalpyoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 18 PDFDocument4 paginiWorksheet 18 PDFoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Virtual Iodine Clock Reaction Lesson PlanDocument3 paginiVirtual Iodine Clock Reaction Lesson PlanoscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Determination of Iron in Iron Tablet by Titration and Precipitation (Isaac 2016)Document12 paginiDetermination of Iron in Iron Tablet by Titration and Precipitation (Isaac 2016)oscarbec89% (27)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Electrolysis Lesson StaterDocument2 paginiElectrolysis Lesson StateroscarbecÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diagnosis and Testing: Four Wheel Drive (4WD) Systems - Electronic ShiftDocument38 paginiDiagnosis and Testing: Four Wheel Drive (4WD) Systems - Electronic ShiftLojan Coronel José Humberto100% (1)
- Unit-III - EEFA - CostsDocument70 paginiUnit-III - EEFA - CostsRamalingam ChandrasekharanÎncă nu există evaluări
- (John F. Moulder) PHI Handbook of XRay Photoelectron SpectrosDocument192 pagini(John F. Moulder) PHI Handbook of XRay Photoelectron SpectrosCamilo CorredorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailedlessonplanintrigonometry 130303203030 Phpapp01Document4 paginiDetailedlessonplanintrigonometry 130303203030 Phpapp01Hazel Clemente CarreonÎncă nu există evaluări
- HyperMILL Readme enDocument20 paginiHyperMILL Readme enjimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nut & Bolt ScienceDocument3 paginiNut & Bolt SciencetanujaayerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Basic Electronics (ES-112)Document49 paginiBasic Electronics (ES-112)Bharat LalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50 Input Output Practice Questions 1606810110009 OBDocument17 pagini50 Input Output Practice Questions 1606810110009 OBJavid QuadirÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Isogeometric Analysis Approach For The Study of Structural VibrationsDocument59 paginiAn Isogeometric Analysis Approach For The Study of Structural VibrationsBharti SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temporal BroadeningDocument10 paginiTemporal BroadeningMohamed BouhaddaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensor Gaurd Installation and Maintenance ManualDocument57 paginiSensor Gaurd Installation and Maintenance ManualCapacitacion TodocatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF To Image Converter v2 HOW TO USEDocument3 paginiPDF To Image Converter v2 HOW TO USEfairfaxcyclesÎncă nu există evaluări
- TM 9 1276 Carbines Cal 30 M1 M1A1 M2 and M3 1947Document111 paginiTM 9 1276 Carbines Cal 30 M1 M1A1 M2 and M3 1947hammonje100% (3)
- Crane Wheels-General InformationDocument3 paginiCrane Wheels-General InformationArvind VaishÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8051 Serial CommunicationDocument35 pagini8051 Serial CommunicationSanthosh CricketÎncă nu există evaluări
- PM-DM/DMR / Pm-2Dm/2Dmr: Digital MultimetersDocument2 paginiPM-DM/DMR / Pm-2Dm/2Dmr: Digital MultimeterstonielhageÎncă nu există evaluări
- 截屏 2021-08-05 17.02.20Document98 pagini截屏 2021-08-05 17.02.204WEM GTÎncă nu există evaluări
- La 3391p Rev0.3novo DesbloqueadoDocument48 paginiLa 3391p Rev0.3novo DesbloqueadoRogeriotabiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Support Engineer - Home AssignmentDocument5 paginiTechnical Support Engineer - Home AssignmentRahul KohliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sc3 Lecture Short CKT Currents BMR Feb.03, 2021Document11 paginiSc3 Lecture Short CKT Currents BMR Feb.03, 2021Khizer AminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metron 05 CR DataDocument10 paginiMetron 05 CR DatamkgohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Machine Elements II PDFDocument6 paginiDesign of Machine Elements II PDFRavi RanjanÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Administration JakartaDocument347 paginiSystem Administration JakartaLorena Castillero80% (10)
- XML SerializationDocument4 paginiXML Serializationapi-3748960Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.basic Electrical Engineering Lecture Part-1Document17 pagini1.basic Electrical Engineering Lecture Part-1jimvalenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shared Memory ArchitectureDocument2 paginiShared Memory ArchitectureNeethu RajeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- FB-150 FQ-150 Basket StrainerDocument1 paginăFB-150 FQ-150 Basket Strainerklich77Încă nu există evaluări
- AC Induction Motors - How AC Motors WorkDocument10 paginiAC Induction Motors - How AC Motors WorkBraulio IrrutiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SolutionsDocument8 paginiSolutionsJavid BalakishiyevÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4july BookDocument5 pagini4july BookDevansh AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionDe la EverandThe Laws of Thermodynamics: A Very Short IntroductionEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (10)
- Process Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityDe la EverandProcess Plant Equipment: Operation, Control, and ReliabilityEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Hyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionDe la EverandHyperspace: A Scientific Odyssey Through Parallel Universes, Time Warps, and the 10th DimensionEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (3)
- Pressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedDe la EverandPressure Vessels: Design, Formulas, Codes, and Interview Questions & Answers ExplainedEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Einstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseDe la EverandEinstein's Fridge: How the Difference Between Hot and Cold Explains the UniverseEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (51)
- Bulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersDe la EverandBulk Material Handling: Practical Guidance for Mechanical EngineersEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)