Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Hpa Hptaxeschart
Încărcat de
dikadika_tansDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Hpa Hptaxeschart
Încărcat de
dikadika_tansDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
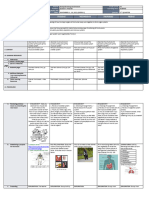
HPA HPT Axes
HPA axis HPT axis
negative feedback loop
STRESS:
psychological
traumatic
Hypothalamus
electromagnetic
Hypo1 Hyper infectious
allergic TRH
dysbiotic
Hypothalamus xenobiotic
Pituitary
SNS
CRH CRH
inhibition
inhibition TSH
Pituitary Thyroid
ACTH ACTH T4
rT3
(competitive inhibition
inhibitor of T3) 5' - deiodinase enzyme
(primarily in liver and kidneys)
Adrenal
cortex T3
medulla (active form
inhibition of the hormone)
glucocorticoids glucocorticoids
(cortisol) (cortisol)
catecholamines catecholamines
(epinephrine,norepinephrine), (epinephrine,norepinephrine),
aldosterone aldosterone
2003 BioHealth Diagnostics
Given the direct influence of the HPA axis on the HPT axis, adrenal function should always be evaluated when assessing
thyroid function.
Major points:
- Excess CRH inhibits TSH.
- Excess glucocorticoids (e.g. cortisol) inhibit conversion of the less active T4 to the more active T3.
- Excess high cortisol can result in high output of rT3 which inhibits T3.
Common Acronyms:
HPA Axis = Hypothalamic Pituitary Adrenal Axis HPT Axis: Hypothalamic Pituitary Thyroid Axis
CRH = Corticotrophic Releasing Hormone ACTH = Adrenocorticotrophic Hormone
TRH = Thyroid Releasing Hormone TSH = Thyroid Stimulating Hormone rT3 = Reverse T3
____________________________________________________________________________
2004 - BioHealth Diagnostics - 2929 Canon St, San Diego, CA 92106
www.biodia.com Phone 800-570-2000 Fax 800-720-7239 Page 1 of 1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- O70 Ampe O99.8 Ketikan Revisi AwDocument6 paginiO70 Ampe O99.8 Ketikan Revisi Awdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- O26 Ampe O70 KetikanDocument12 paginiO26 Ampe O70 Ketikandikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- O70 Ampe O99.8 Ketikan RevisiDocument6 paginiO70 Ampe O99.8 Ketikan Revisidikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas VATER DKKDocument33 paginiTugas VATER DKKdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre EclampsiaDocument7 paginiPre Eclampsiadikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICD TanDocument12 paginiICD Tandikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- N94 Ampe O25 KetikanDocument6 paginiN94 Ampe O25 Ketikandikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compromised Patient (Klasifikasi Asa) : Surya Triharsa Andina Novita Sari Lisna Mirna Kuntari Muhamad SyafriDocument17 paginiCompromised Patient (Klasifikasi Asa) : Surya Triharsa Andina Novita Sari Lisna Mirna Kuntari Muhamad Syafridikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- 234 60 PDFDocument9 pagini234 60 PDFdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Therapeutic Applications of Punica GranatumDocument17 paginiTherapeutic Applications of Punica GranatumyigalbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9pomgt PDFDocument8 pagini9pomgt PDFdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal Pneumonia Kak YunDocument8 paginiJurnal Pneumonia Kak Yundikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- PEMFIGUS VULGARISDocument21 paginiPEMFIGUS VULGARISWahyudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18 1312355856 PDFDocument7 pagini18 1312355856 PDFdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Asli - Kelainan Refraksi - Willy Hartanto - 25-30Document6 pagini05 Asli - Kelainan Refraksi - Willy Hartanto - 25-30Dinka RoselyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molecules 19 18923Document13 paginiMolecules 19 18923dikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF 40 Aguilera-Carbo 2008Document5 paginiPDF 40 Aguilera-Carbo 2008dikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument6 paginiPDFdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab IIDocument18 paginiBab IIdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Junior Mine Environment Engineer - External LocalDocument1 paginăJunior Mine Environment Engineer - External Localdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article1380880456 - Sepulveda Et AlDocument6 paginiArticle1380880456 - Sepulveda Et Aldikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Effects of Oral Administration of Ellagic Acid Rich Pomegranate Extract 0n Ultraviolet Pigmentation in The Human SkinDocument6 paginiAC Effects of Oral Administration of Ellagic Acid Rich Pomegranate Extract 0n Ultraviolet Pigmentation in The Human Skindikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 5102 PDFDocument5 pagini02 5102 PDFdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of California: PostprintsDocument17 paginiUniversity of California: Postprintsdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pomegranate Processing and Value Addition Review 2157 7110 1000565Document11 paginiPomegranate Processing and Value Addition Review 2157 7110 1000565dikadika_tans0% (1)
- Simple Linear Regression: Definition of TermsDocument13 paginiSimple Linear Regression: Definition of TermscesardakoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ipi 16359Document9 paginiIpi 16359dikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibroadenoma PDFDocument2 paginiFibroadenoma PDFAthika Dwi Sofiana100% (1)
- What Is HPA-Axis DysregulationDocument3 paginiWhat Is HPA-Axis Dysregulationdikadika_tansÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5784)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (890)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (72)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Govt Schemes - 1 MWCD MOSJEDocument36 paginiGovt Schemes - 1 MWCD MOSJEshaheen razaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ABS and Air Conditioner Wiring DiagramDocument207 paginiABS and Air Conditioner Wiring Diagramservice_00783% (30)
- PERDEV Module 3 (Week 5 and 6)Document8 paginiPERDEV Module 3 (Week 5 and 6)Christy ParinasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Butterfly Valve ConcentricDocument6 paginiButterfly Valve ConcentricpramodtryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Krisbow KW06-291 PDFDocument1 paginăKrisbow KW06-291 PDFBoyke WinterbergÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quartz Textures in Epithermal VeinsDocument16 paginiQuartz Textures in Epithermal VeinsAlvaro MadridÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flow Meter SpecificationDocument2 paginiFlow Meter SpecificationDan4ChristÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guidance Counseling EssentialsDocument2 paginiGuidance Counseling EssentialsElizabeth E. FetizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing ProcessDocument6 paginiManufacturing Processbro nawalibmatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep Learning Based Convolutional Neural Networks (DLCNN) On Classification Algorithm To Detect The Brain Turnor Diseases Using MRI and CT Scan ImagesDocument8 paginiDeep Learning Based Convolutional Neural Networks (DLCNN) On Classification Algorithm To Detect The Brain Turnor Diseases Using MRI and CT Scan ImagesInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Everything You Need to Know About Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAWDocument31 paginiEverything You Need to Know About Gas Metal Arc Welding (GMAWAhmetDuranCeyhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- TN EpasssDocument2 paginiTN EpasssStephenrajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modified Micro Marsupialization in Pediatric Patients: A Minimally Invasive TechniqueDocument4 paginiModified Micro Marsupialization in Pediatric Patients: A Minimally Invasive TechniquerinahpsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tips For Establish Ball Pen Refill PlantDocument5 paginiTips For Establish Ball Pen Refill PlantSingam Sridhar100% (1)
- O-Rings & SealsDocument10 paginiO-Rings & SealsPartsGopher.comÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10893259-PIB 背钳弹簧保持架垫片落物事件Document2 pagini10893259-PIB 背钳弹簧保持架垫片落物事件xlzyydf2015Încă nu există evaluări
- Sara Salon and SpaDocument4 paginiSara Salon and Spasania zehraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do We Still Need Formocresol in Pediatric DentistryDocument3 paginiDo We Still Need Formocresol in Pediatric DentistryAlexanderDetorakisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Performance Task MidTerm Second Sem. AY 2022 2023Document2 paginiPerformance Task MidTerm Second Sem. AY 2022 2023KZpathryn Jemimench AleurevÎncă nu există evaluări
- PerforationsDocument5 paginiPerforationsMariusNOÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16-Bit UUID Numbers DocumentDocument28 pagini16-Bit UUID Numbers DocumentJuan M Iñiguez RÎncă nu există evaluări
- TST-13 Aircraft Manual With 503 Engine LSA Rev.1Document52 paginiTST-13 Aircraft Manual With 503 Engine LSA Rev.1smeassick100% (1)
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1Document6 paginiDLL - Science 6 - Q2 - W1AnatasukiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6d Class 10Document10 pagini6d Class 10Euna DawkinsÎncă nu există evaluări
- QCVN 162019BXD National Technical Regulation On Products, Goods of Building Materials (Eng)Document41 paginiQCVN 162019BXD National Technical Regulation On Products, Goods of Building Materials (Eng)lwin_oo2435Încă nu există evaluări
- Exp. 5 Test For Fats and ProteinsDocument6 paginiExp. 5 Test For Fats and ProteinsEMELIE GRACE E CACHEROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Res Ipsa LoquiturDocument6 paginiRes Ipsa LoquiturZydalgLadyz NeadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home Study Report of Resident Indian Parent: Name of The Social WorkerDocument4 paginiHome Study Report of Resident Indian Parent: Name of The Social WorkerVmksÎncă nu există evaluări
- CAP - 5 - 54. Billions and Billions of Demons - by Richard C. Lewontin - The New York Review of BooksDocument11 paginiCAP - 5 - 54. Billions and Billions of Demons - by Richard C. Lewontin - The New York Review of BooksRaimundo Filho100% (1)
- Ten Laws of BoundariesDocument17 paginiTen Laws of Boundariesstjohn30067% (3)