Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Preschoolerfocusissue6guidelines Updatedsecured
Încărcat de
api-330364939Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Preschoolerfocusissue6guidelines Updatedsecured
Încărcat de
api-330364939Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
http://affiliates.allposters.com/link/redirect.asp?
item=1643987&AID=1416306748&PSTID=1<ID=2&lan
g=1 CHILD HEALTH & EXERCISE MEDICINE PROGRAM
McMaster University
Issue 6, April 2012
Preschooler
focus
CANADIAN GUIDELINES
FOR THE EARLY YEARS
The Canadian Society for Exercise Physiology and ParticipACTION have released
the first Canadian Physical Activity and Sedentary Behaviour Guidelines for the
Early Years (0-4 years). Find out how much activity your child should be getting.
Preschoolers should move more and sit less
From strong bones to a healthy The new Canadian guidelines
heart, physical activity is important suggest that preschool children:
for the growth and development of Get at least 3 hours of activity at
children. However, how much any intensity spread throughout
activity young children need has not the day
always been clear. Now for the first Limit prolonged sitting to no
time, physical activity and sedentary more than 1 hour at a time
behaviour guidelines for the early Limit screen time to less than 1
years are available in Canada. This hour per day
age group includes infants (less than Kids do not need to be continuously
1 year), toddlers (1-2 years) and active for long periods. Their natural
preschoolers (3-4 years). A team of activity happens in short bursts and
experts developed the guidelines anything from dancing to climbing
using the best available scientific stairs counts! The goal is to help
evidence. Members of the Child preschoolers gradually increase the
Health & Exercise Medicine Program intensity of their activity. By age 5,
at McMaster University helped lead at least 1 of the 3 hours should be
the process. spent in energetic play.
What Is Energetic Play?
Children are active any time they move around. As children grow older, the intensity of
that activity becomes more important. Energetic play describes high intensity activities
that use up more energy. Some examples include hopping, jumping, skipping, and bike
riding. Organized sports like soccer practice or swimming lessons can create
opportunities for energetic play. However, sports alone are not enough and should not
replace free play.
Page |2 fhs.mcmaster.ca/chemp Preschooler focus
Benefits to Meeting Did You Know?
the Guidelines
The Canadian Pediatric Society supports the
new Canadian guidelines. Being more active
and less sedentary can help your child in more
ways than one.
Increasing physical activity levels and decreasing
sedentary behaviour can help preschool children: Kids have a lot of energy,
which is why we often think
Maintain a healthy body weight they get enough activity.
Screen-based activities Build a healthy heart Research tells us that kids
should be limited to less than Develop social skills actually spend about 80% of
1 hour per day and are not the time they are awake in
Develop self-confidence sedentary behaviour (for
recommended for children
Improve motor skills example: sitting, colouring,
under 2 years of age
Improve learning and attention watching television). As a
parent or caregiver, it is
Experts agree that the less time preschool children important to help children
The Canadian Physical Activity spend sitting or engaged in screen-based activities break up their sedentary
and Sedentary Behaviour the better. Also, the recommended 3 hours of daily time with some physical
Guidelines for the Early Years physical activity at any intensity is only a minimum. activity. Any movement is
can be found online at: The more physical activity the greater the benefits! better than none.
www.csep.ca/guidelines
Tips to Help Your Child Meet the Guidelines
The Canadian Society for Exercise Physiology and ParticipACTION offer some tips
on how you can help your child get moving:
Organize play dates with other children
Travel to your destination by walking or bike riding
Turn on some music and learn action songs together
Go outdoors and explore the environment
Set limits and rules about screen time
ADDITIONAL RESOURCES:
Learn about your Active Healthy Kids Canada (www.activehealthykids.ca)
preschoolers health and Best Start Resource Centre (www.beststart.org/haveaballtogether/campaign.html)
physical activity through a Canadian Fitness and Lifestyle Research Institute (www.cflri.ca)
study conducted at Canadian Society for Exercise Physiology (www.csep.ca/guidelines)
McMaster University! Caring for Kids (www.caringforkids.cps.ca)
Contact Nicole at McMaster University Child Health & Exercise Medicine Program (fhs.mcmaster.ca/chemp)
macHOPP@mcmaster.ca or ParticipACTION (www.participaction.com)
(905) 521-2100 x.77217 or
References:
visit us online at Tremblay, M. S. et al. (2012). Canadian Physical Activity Guidelines for the Early Years (aged 0-4 years). Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 37: 345-356.
fhs.mcmaster.ca/chemp Tremblay, M. S. et al. (2012). Canadian Sedentary Behaviour Guidelines for the Early Years (aged 0-4 years). Applied Physiology, Nutrition, and Metabolism, 37: 370-380.
Vale, S. et al. (2010). Compliance with physical activity guidelines in preschool children. Journal of Sports Sciences, 28: 603-608.
2012 Shenouda, N. and Timmons, B.W. Child Health & Exercise Medicine Program, McMaster University. Published and distributed by the Child Health & Exercise Medicine Program.
All rights reserved. Download and use of this newsletter or its content is for non-commercial use only and must be accompanied by this copyright notice or attribution to the authors and
owners must be specified.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Isometric Exercises SamsonDocument30 paginiIsometric Exercises SamsonTom Hill78% (9)
- '05 Sullivan B.Document36 pagini'05 Sullivan B.Geo Navarro100% (1)
- MODULE 18 - Physical Development of Primary Schoolers HandoutDocument5 paginiMODULE 18 - Physical Development of Primary Schoolers HandoutJM HernandezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classroom Newsletter TemplateDocument7 paginiClassroom Newsletter Templateapi-340140864Încă nu există evaluări
- Layne Norton's PH ProgramDocument44 paginiLayne Norton's PH Programabhishek chohanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beyond Legendary AbsDocument24 paginiBeyond Legendary AbsBobby Henderson88% (8)
- ThibermanyDocument21 paginiThibermanyCarlos Alberto Acevedo100% (10)
- Jamapediatrics Michel 2022 Ap 220002 165349361.30953Document1 paginăJamapediatrics Michel 2022 Ap 220002 165349361.30953FrancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parents Fact SheetDocument2 paginiParents Fact Sheetapi-615689664Încă nu există evaluări
- Physical Literacy For ParentsDocument1 paginăPhysical Literacy For ParentsSaad QureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure 24hr Guidelines 5 17yrsDocument2 paginiBrochure 24hr Guidelines 5 17yrsapi-487757844Încă nu există evaluări
- Meditation For Kids - PDFDocument18 paginiMeditation For Kids - PDFJamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5-Promoting Physical Activity PDFDocument8 pagini5-Promoting Physical Activity PDFJhonnyNogueraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Activity - Benefits of Exercise For Health and WellbeingDocument3 paginiPhysical Activity - Benefits of Exercise For Health and WellbeingjmpyperÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSEP Guidelines HandbookDocument32 paginiCSEP Guidelines HandbookRohan KunwerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Notes On PubertyDocument6 paginiSome Notes On PubertyVia GallagherÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Mindfulness Is Shaping The Growing MindsDocument2 paginiHow Mindfulness Is Shaping The Growing MindsJang FanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LTAD Appendix 1Document8 paginiLTAD Appendix 1Anonymous GJuRvp9A5TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Childhood LifestyleDocument1 paginăChildhood LifestyleSasha Valentina Gutierrez PinedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AEDC Guide To Physical Health and WellbeingDocument6 paginiAEDC Guide To Physical Health and WellbeingKedar SilwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Impact of Baby Spa Jurnal Internasional-With-Cover-Page-V2Document6 paginiThe Impact of Baby Spa Jurnal Internasional-With-Cover-Page-V2DARING KELAS 1Încă nu există evaluări
- (美国)Active Start-0-5岁儿童身体活动指南的立场陈述-2020Document33 pagini(美国)Active Start-0-5岁儿童身体活动指南的立场陈述-2020宁瑶瑶Încă nu există evaluări
- 5bbb KidsguideDocument12 pagini5bbb KidsguideDr-GauravPantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brochure Original22Document2 paginiBrochure Original22api-505913940Încă nu există evaluări
- UNIT 7 REViewerDocument17 paginiUNIT 7 REViewerAnn Jielyn Ablao ManongÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Impact of Baby Spa On The Growth andDocument5 paginiThe Impact of Baby Spa On The Growth andJean Collin CamayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health-Optimizing PE (H.O.P.E. 4) Recreational Activities-Aquatics Quarter 3 Module 1: Weeks 1-4Document9 paginiHealth-Optimizing PE (H.O.P.E. 4) Recreational Activities-Aquatics Quarter 3 Module 1: Weeks 1-4benjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- FitnessDocument6 paginiFitnessZonette ParedoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Gym (R) 101 Flyer LatestDocument4 paginiBrain Gym (R) 101 Flyer LatestZack ZawaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lifestyle and Weight Management (Physical Activity and Eating Habits)Document11 paginiLifestyle and Weight Management (Physical Activity and Eating Habits)Jan Den Saul DalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operation Fit Kids Curriculum Kids in Motion (PDFDrive)Document15 paginiOperation Fit Kids Curriculum Kids in Motion (PDFDrive)The oneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Practices For Physical Activity (Inglés) Autor Denise HughesDocument36 paginiBest Practices For Physical Activity (Inglés) Autor Denise HughesJuan Pablo VarelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Active Activities MoreDocument1 paginăActive Activities MoreThảo Nguyễn ThanhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objectives of Physical EducationDocument2 paginiObjectives of Physical EducationCally EnrqzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Promoting Physical ActivityDocument11 paginiPromoting Physical ActivityJose Fernando Díez ConchaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stressbustersflyer 2018Document2 paginiStressbustersflyer 2018api-232115516Încă nu există evaluări
- Looking After Each Other and OurseltDocument3 paginiLooking After Each Other and OurseltNguyen Phuong LinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boehme Cook Pe NewsletterDocument3 paginiBoehme Cook Pe Newsletterapi-305358325Încă nu există evaluări
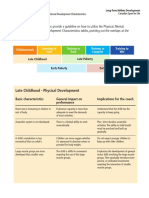
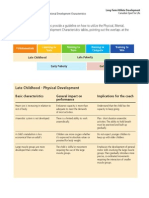
- Module 12 Late ChildhoodDocument42 paginiModule 12 Late ChildhoodRhica SabularseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mindfulness PDFDocument18 paginiMindfulness PDFpaulteachÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Activity in The Early YearsDocument24 paginiPhysical Activity in The Early YearsahmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- LAS-5-STRESS-MANAGEMENT ABM G11-St. Catherine-Macaday, Venze Adrianne D.Document3 paginiLAS-5-STRESS-MANAGEMENT ABM G11-St. Catherine-Macaday, Venze Adrianne D.Venze Adrianne Damasco MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Healthy Teens: Early Specialization in SportDocument2 paginiHealthy Teens: Early Specialization in SportRASHEED YUSUFÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 2 Module 6Document4 paginiECE 2 Module 6Jonalyn GacoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd SEM-Q3 M3aDocument5 pagini2nd SEM-Q3 M3aLOuie BiOngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Resilience in Children Aged 0-12Document66 paginiBuilding Resilience in Children Aged 0-12Koko Lumactud TandangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bu Windsor - Rhythmic Movement Training - Sabbatical Report 2020Document21 paginiBu Windsor - Rhythmic Movement Training - Sabbatical Report 2020John Lock100% (1)
- Health: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Self-Management SkillsDocument18 paginiHealth: Quarter 1 - Module 2 Self-Management SkillsGlaizaMarie Tantoy ALoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning Module in Mapeh 1: Term 1-Week 3-4Document10 paginiLearning Module in Mapeh 1: Term 1-Week 3-4Maricar Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- (美国)Active Start-0-5岁儿童身体活动指南的立场陈述-2020 - 1-5Document5 pagini(美国)Active Start-0-5岁儿童身体活动指南的立场陈述-2020 - 1-5宁瑶瑶Încă nu există evaluări
- Primary Wellbeing Parent ToolkitDocument6 paginiPrimary Wellbeing Parent Toolkitqkvyf9shbtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Education and Health (Grade 11) Learner'S Material: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melc) Week 3-4Document10 paginiPhysical Education and Health (Grade 11) Learner'S Material: Most Essential Learning Competencies (Melc) Week 3-4Johnpaolo Tabada100% (1)
- Advocacy Research PaperDocument5 paginiAdvocacy Research Paperapi-549152189Încă nu există evaluări
- Back To School e BookDocument10 paginiBack To School e BookDipak DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kids YogaDocument212 paginiKids YogaAnita100% (6)
- Self Regulation - ShankerDocument2 paginiSelf Regulation - Shankeraisy chasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Development in Late Childhood (The Intermediate Schooler)Document57 paginiPhysical Development in Late Childhood (The Intermediate Schooler)Lesley Nicole SantosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 21Document13 paginiModule 21Marvin MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Living SkillsDocument8 paginiLiving SkillsSylvia Sylvester MaludaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (美国)Active Start-0-5岁儿童身体活动指南的立场陈述-2020 - 6-10Document5 pagini(美国)Active Start-0-5岁儿童身体活动指南的立场陈述-2020 - 6-10宁瑶瑶Încă nu există evaluări
- LTAD Appendix 1Document8 paginiLTAD Appendix 1Speed Skating Canada - Patinage de vitesse Canada100% (1)
- Adaptive Fitness & Gross Motor Development: A Gross Motor Skills and Athletic Development GuideDe la EverandAdaptive Fitness & Gross Motor Development: A Gross Motor Skills and Athletic Development GuideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Module Educ 1 Week 10Document9 paginiCourse Module Educ 1 Week 10DarcknyPusodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity Log 23 Friday March 31stDocument2 paginiActivity Log 23 Friday March 31stapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Potty Training Readiness QuizDocument2 paginiPotty Training Readiness Quizapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity Log 22 Thursday March 30thDocument2 paginiActivity Log 22 Thursday March 30thapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Healthy Environment QuizDocument2 paginiHealthy Environment Quizapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity Log 17 Thursday March 9thDocument2 paginiActivity Log 17 Thursday March 9thapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity Log 12 Friday February 10thDocument2 paginiActivity Log 12 Friday February 10thapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity Log 15 Thursday March 2ndDocument2 paginiActivity Log 15 Thursday March 2ndapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Sensory DifferencesDocument26 paginiSensory Differencesapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity Log 10 Friday February 3rdDocument2 paginiActivity Log 10 Friday February 3rdapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Loose Parts For Preschool - HandoutDocument3 paginiLoose Parts For Preschool - Handoutapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity Log 5 Friday January 27thDocument2 paginiActivity Log 5 Friday January 27thapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Activity Log 6 Monday January 30thDocument2 paginiActivity Log 6 Monday January 30thapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Parent Attachment EngDocument40 paginiParent Attachment Engapi-330364939100% (1)
- Activity Log 23 Thursday November 24thDocument2 paginiActivity Log 23 Thursday November 24thapi-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- My Record Professional Learning 2017Document4 paginiMy Record Professional Learning 2017api-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- My Professional Learning Plan 2017Document2 paginiMy Professional Learning Plan 2017api-330364939Încă nu există evaluări
- Strength Training For Triathletes Hand OutDocument14 paginiStrength Training For Triathletes Hand OutBrían GohÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tales Worth Telling: Word Gets OutDocument52 paginiTales Worth Telling: Word Gets OutVenture PublishingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prediction, Prevention, and Prognosis of Preeclampsia: RecommendationsDocument8 paginiPrediction, Prevention, and Prognosis of Preeclampsia: RecommendationskunkkonkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bill Goldberg Workout RoutineDocument8 paginiBill Goldberg Workout RoutinehelmetheadbobÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benefits: Warming UpDocument3 paginiBenefits: Warming UpAlvin RobertsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic of The Philippines San Isidro Sur, Luna, Apayao PE 13 (Individual and Dual Sports) Final ExaminationDocument3 paginiRepublic of The Philippines San Isidro Sur, Luna, Apayao PE 13 (Individual and Dual Sports) Final ExaminationJomar DiegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ask An Expert: The Benefits of Aerobic ExerciseDocument3 paginiAsk An Expert: The Benefits of Aerobic ExercisePrincess Villasis BaciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Whole Brain Power Coaching InterviewDocument45 paginiWhole Brain Power Coaching InterviewAlain BodinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tactical MonsterDocument15 paginiTactical MonsterJovÎncă nu există evaluări
- God Healing WayDocument96 paginiGod Healing WayIrinaConstantin100% (1)
- Health Optimizing Physical Education 1: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Set Fitness GoalDocument28 paginiHealth Optimizing Physical Education 1: Quarter 1 - Module 2: Set Fitness Goalrhaybien vinluan50% (6)
- Is Lactic Acid A Four Letter Word?: by Patti and Warren Finke, Team OregonDocument4 paginiIs Lactic Acid A Four Letter Word?: by Patti and Warren Finke, Team OregonАлександър Антоан НиколовÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 1-Lesson 1: Optimize Energy System Through Dance: Pre-AssessmentDocument4 paginiModule 1-Lesson 1: Optimize Energy System Through Dance: Pre-AssessmentChum VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nutrition For SenensenceDocument6 paginiNutrition For SenensenceAmar BhochhibhoyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pace 6.40Document21 paginiPace 6.40sebastianbirdxÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Minimalist Ironman Training StrategiesDocument4 pagini10 Minimalist Ironman Training StrategiesSoylo Amado RubioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposal Letter SchoolDocument13 paginiProposal Letter SchoolPrathap KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength Training For WomenDocument232 paginiStrength Training For WomenDaniel MihaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning: Maryknoll School of Lupon IncDocument16 paginiLearning: Maryknoll School of Lupon IncJohn Paull CuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q4 - CheerdanceDocument8 paginiQ4 - CheerdanceJoyce Gozun RoqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- WIN - Achieve Peak Athletic Performance, Optimize Recovery and Become A Champion by James DiNicolantonio, Siim Land, Tristin KennedyDocument836 paginiWIN - Achieve Peak Athletic Performance, Optimize Recovery and Become A Champion by James DiNicolantonio, Siim Land, Tristin Kennedyryarok1Încă nu există evaluări
- Bulk Like The HULKDocument3 paginiBulk Like The HULKRafael ContrerasÎncă nu există evaluări
- FFHP 6Document29 paginiFFHP 6Danny GoldstoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment FutsalDocument22 paginiAssignment FutsalNajibu Auwalu Namadina100% (2)
- Westside Barbell TemplateDocument4 paginiWestside Barbell Templatexaktaroth0% (2)