Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Tensile Testing Lab
Încărcat de
Q_TDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Tensile Testing Lab
Încărcat de
Q_TDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Quanterecia Buckner LAB 1 ENGR 220-003 01/09/17 Pg.
1/ 4
(1) Introduction
The objective of this lab is to find the tensile strength of a given dogbone shaped
specimen. The dogbone is composed of tempered hardboard. The dogbone width
and thickness was measured using a dial caliper. Then the test is done using the Tinius
Olsen testing machine. The specimen has two holes as shown in Figure 1, the holes will
allow the specimen to be screwed/fixed onto the Tinius Olsen machine. The machine
will then apply a tension force to the dogbone until failure occurs. The force, where
the specimen brakes, is recorded on the control panel of the testing machine.
Force Force
applied applied
Thickness = 0.117 DE
Width = 0.192 DE
(2) One table listing all of the data collected
Specimen Thickness Width Force Area Ultimate Stress
(89) (89) (;<=) (89> ) (;</89> )
1 0.117 0.392 218.6 0.0459 4766.2655
2 0.1170 0.390 234.6 0.0456 5141.3544
3 0.1250 0.390 181.2 0.0488 3716.9231
4 0.1250 0.291 133.6 0.0364 3672.8522
5 0.1260 0.390 177.4 0.0491 3610.0936
6 0.1275 0.294 134.3 0.0375 3582.7664
7 0.1280 0.092 38.2 0.0118 3243.8859
8 0.1280 0.193 88.6 0.0247 3586.4637
9 0.1280 0.198 85.6 0.0253 3377.5253
10 0.1295 0.195 91.2 0.0252 3620.8077
11 0.1320 0.295 130.8 0.0389 3359.0139
12 0.1320 0.293 137.7 0.0387 3560.3475
13 0.1320 0.094 42.2 0.0124 3401.0316
14 0.1330 0.196 82.2 0.0261 3153.2914
15 0.1390 0.194 73.3 0.0270 2718.2378
16 0.1420 0.197 80.6 0.0280 2881.2469
17 0.1370 0.093 24.4 0.0127 1915.0773
18 0.1410 0.193 74.4 0.0272 2733.9874
19 omit omit omit omit omit
20 0.1300 0.094 37.3 0.0122 3052.3732
Quanterecia Buckner LAB 1 ENGR 220-003 01/09/17 Pg. 1/ 4
21 0.1300 0.194 89.4 0.0252 3544.8057
22 0.1300 0.093 27.5 0.0121 2274.6071
23 0.1131 0.194 89.4 0.0219 4074.4893
24 0.1300 0.292 137.9 0.0380 3632.7713
25 0.1330 0.290 122.7 0.0386 3181.2289
26 0.1200 0.394 234.2 0.0473 4953.4687
27 0.1380 0.293 120.8 0.0404 2987.5847
28 0.1340 0.193 83.4 0.0259 3224.8086
29 0.1180 0.396 228.6 0.0467 4892.1418
30 0.1310 0.095 41.8 0.0124 3358.7786
31 0.1345 0.194 79.1 0.0261 3031.8476
32 0.1170 0.394 207.0 0.0461 4490.4334
33 0.1275 0.294 139.0 0.0374 3714.4670
34 0.1430 0.294 125.5 0.0420 2985.1101
35 0.1125 0.193 98.5 0.0217 4548.3405
36 0.1150 0.393 162.4 0.0452 3593.3178
37 0.1161 0.294 147.2 0.0342 4309.5570
38 0.1170 0.192 95.2 0.0225 4237.8917
39 0.1169 0.271 103.6 0.0317 3266.2658
40 0.1160 0.294 155.7 0.0341 4565.4469
41 0.1168 0.194 100.4 0.0227 4430.8713
42 0.1160 0.296 183.4 0.0343 5350.3705
(3) To calculate the ultimate stress of the specimens, the formula for normal stress was
used. Specimen 1 was used for an example calculation.
JKHLI (MNO)
FGHIFF =
PHIQ (DER )
J J 218.6 MNO MNO
JKH FSILDTIE 1: V = = = = 4766.2655 R
P G X 0.117 DE 0.392 DE DE
Quanterecia Buckner LAB 1 ENGR 220-003 01/09/17 Pg. 1/ 4
(4) The linear trend line shows that as the area of the specimen increases, the force needed
to fracture the specimen increases, this is shown with the positive linear line.
Ultimate Load VS. Cross-sectional Area
250.0
Ultimate Load (lbf)
y = 4564.1x - 24.452
200.0
R = 0.833
150.0
100.0
50.0
0.0
0.000 0.010 0.020 0.030 0.040 0.050 0.060
Cross-sectional Area (in2)
Ultimate Load VS. Cross-sectional Area
Linear (Ultimate Load VS. Cross-sectional Area
)
(5) The mean and standard deviation of the ultimate stress
;<= ;<=
YZ[\ ] > ^ _`[\a[ba cZde[`ef\ ] > ^
89 89
3652.2475 768.9785
Quanterecia Buckner LAB 1 ENGR 220-003 01/09/17 Pg. 1/ 4
(6) Histogram for the distribution of ultimate stress values
Histogram of Ultimate Stress
12
10
8
Frequency
Ultimate Stress Range (lbf/in2)
(7) Concluding paragraph
In this lab, we were able to get acquainted with the Tinius Olsen testing machine and
see the dogbone specimen stretch until it failure. Looking at the data for lab 1, we can
see the relationship between the area and the load. The Ultimate Load VS. Cross-
sectional Area graph shows two things: that as area increases the load needed for
failure also increases and that the specimens with approximately the same areas
required approximately the same force to have failure.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- LM6 alloy load-deflection dataDocument4 paginiLM6 alloy load-deflection dataHareesh R IyerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Datos A EvaluarDocument13 paginiDatos A EvaluarValeria VillalobosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table A.23 Physical Properties of Selected Fluids (Engineering Thermodynamics by Burghardt & Harbach)Document1 paginăTable A.23 Physical Properties of Selected Fluids (Engineering Thermodynamics by Burghardt & Harbach)lemuel andrezaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gráficos 3Document4 paginiGráficos 3Juan CampusanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gráficos 3Document4 paginiGráficos 3Juan CampusanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gráficos 27Document4 paginiGráficos 27Juan CampusanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Motion GraphsDocument4 paginiAnalysis of Motion GraphsJuan CampusanoÎncă nu există evaluări
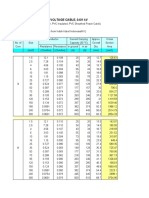
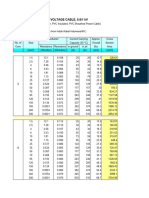
- American Wire GaugeDocument3 paginiAmerican Wire Gaugeعلي القحطانيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bai Giang Chuong 2Document30 paginiBai Giang Chuong 2Hồ Tùng DươngÎncă nu există evaluări
- MS Excel SheetDocument1 paginăMS Excel SheetParthibÎncă nu există evaluări
- AWG Wire Gauge Specifications and Selection GuideDocument6 paginiAWG Wire Gauge Specifications and Selection GuidediegojhonathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LOW VOLTAGE CABLE SPECIFICATIONS AND LOAD DATADocument9 paginiLOW VOLTAGE CABLE SPECIFICATIONS AND LOAD DATAef.sofyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- سيف الدين خالد قاسم 1Document1 paginăسيف الدين خالد قاسم 1Saif QasemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proprieta' Termiche Dell'Aria A Elevate Temperature: Thermal Properties of Air at Elevated TemperaturesDocument1 paginăProprieta' Termiche Dell'Aria A Elevate Temperature: Thermal Properties of Air at Elevated TemperaturesSebastian Rodrigo Octaviano0% (1)
- Coeficientes de ActividadDocument4 paginiCoeficientes de ActividadAndrea carmelÎncă nu există evaluări
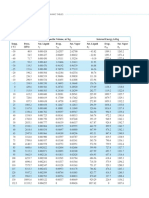
- Tension Wire ChartDocument1 paginăTension Wire Chartlaspsieca100% (1)
- Hall EffectDocument9 paginiHall EffectThiberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unconfined Compressive Strength Test: Experiment 1Document5 paginiUnconfined Compressive Strength Test: Experiment 1Refisa JiruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dbsample 327 Center - 1Document6 paginiDbsample 327 Center - 1KuthuraikaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compressive Strength TestDocument2 paginiCompressive Strength TestUltimate BoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Lingkungan - RevDocument137 paginiData Lingkungan - RevGallend SÎncă nu există evaluări
- 23AE60R01 Expt2 AerospaceStructuresLaboratoryDocument11 pagini23AE60R01 Expt2 AerospaceStructuresLaboratorySuhasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blasius Laminar Solution TableDocument1 paginăBlasius Laminar Solution TableIvan LÎncă nu există evaluări
- Difractograma de UreaDocument4 paginiDifractograma de UreaKevin JosueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Empyrean UNI XRD Analysis ReportDocument6 paginiEmpyrean UNI XRD Analysis ReportTicona JuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anexos: Ayudas De Diseño:, , a/d c/d k=c/d a/d ω µ k=c/d a/d ω µDocument11 paginiAnexos: Ayudas De Diseño:, , a/d c/d k=c/d a/d ω µ k=c/d a/d ω µAnthony MuñozÎncă nu există evaluări
- RUNGE-KUTTA METHOD SIMULATES RESERVOIR WATER LEVELSDocument6 paginiRUNGE-KUTTA METHOD SIMULATES RESERVOIR WATER LEVELSnoe valverdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- FORM VDrop - CalculationDocument11 paginiFORM VDrop - CalculationJulian AngeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- TABLE 2-351 Saturated Water Substance-Temperature (Fps Units)Document6 paginiTABLE 2-351 Saturated Water Substance-Temperature (Fps Units)Ricardo VelozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Electronics - SWG - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldDocument4 paginiPractical Electronics - SWG - Wikibooks, Open Books For An Open WorldZia ur rehmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab 1 I&CDocument10 paginiLab 1 I&CYanina Molina CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specific Volume, M /KG Internal Energy, KJ/KG Temp. Press. Sat. Liquid Evap. Sat. Vapor Sat. Liquid Evap. Sat. Vapor (C) (Kpa)Document6 paginiSpecific Volume, M /KG Internal Energy, KJ/KG Temp. Press. Sat. Liquid Evap. Sat. Vapor Sat. Liquid Evap. Sat. Vapor (C) (Kpa)sidhartha dasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Havlena OdehDocument2 paginiHavlena OdehAhmad Azwar Anas100% (1)
- Soil Mechanics Lab Report on Triaxial TestingDocument15 paginiSoil Mechanics Lab Report on Triaxial TestingAdrian Mufc RampersadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Result LabDocument15 paginiResult LabamirulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alex ExcwlllDocument8 paginiAlex ExcwlllALEX WAGNER MANRIQUE QUISPEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load Effort Relationship for Different Angles of LapDocument3 paginiLoad Effort Relationship for Different Angles of Laplaura sageÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ope 3Document5 paginiOpe 3Rocío CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- R134a SuperDocument6 paginiR134a Superprem singhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dato T1(s) T2 (S) V (L) HL1 (MM) HL2 (MM) HLDocument17 paginiDato T1(s) T2 (S) V (L) HL1 (MM) HL2 (MM) HLyariza GutierrezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curva de Margules: P (MMHG) X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Ɣ1 Ɣ2Document17 paginiCurva de Margules: P (MMHG) X1 Y1 X2 Y2 Ɣ1 Ɣ2José Leonardo Fernández BalderaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 - Eigenvalue Mode Using RitzDocument5 pagini21 - Eigenvalue Mode Using RitzenatagoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hercules Laminated Elastomeric BearingsDocument7 paginiHercules Laminated Elastomeric BearingsjohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 These Tables Were Created by Potto-GDC and Later Where Translated by Using Latex2html Versions 1.7Document23 pagini1 These Tables Were Created by Potto-GDC and Later Where Translated by Using Latex2html Versions 1.7ajd.nanthakumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Refrigerants Table-SI Unit PDFDocument31 paginiRefrigerants Table-SI Unit PDFAdriel JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- AMMONIA and R134a (Satd and SH) (English and SI)Document24 paginiAMMONIA and R134a (Satd and SH) (English and SI)MinjdeDios0% (1)
- Tablas Termodinamicas Amoniaco@Claus Borgnakke, Richard E. Sonntag (7th Edition)Document6 paginiTablas Termodinamicas Amoniaco@Claus Borgnakke, Richard E. Sonntag (7th Edition)Olman VargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING - Midterm ExamDocument33 paginiEARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING - Midterm ExamAndrea Mae SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribución normal repaso tallerDocument2 paginiDistribución normal repaso tallerAndres Felipe SaenzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chee4362 HWDocument8 paginiChee4362 HWHa Eun KimÎncă nu există evaluări
- American_strand_constructionDocument1 paginăAmerican_strand_constructionpratul acharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wire Gauge ChartDocument2 paginiWire Gauge Chartkrishna0% (1)
- Table 8 Conductor PropertiesDocument1 paginăTable 8 Conductor PropertiesReimart H BornilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shavneel HydraulicsDocument7 paginiShavneel HydraulicsDrakeGAMINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Criterios de DiseñoDocument8 paginiCriterios de DiseñoKARITO SUAREZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regression analysis of water flow dataDocument5 paginiRegression analysis of water flow dataAshley PeraltaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear Stress Vs Shear StrainDocument12 paginiShear Stress Vs Shear StrainAbrar AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report 3Document2 paginiReport 3Rituraj BorahÎncă nu există evaluări
- United States Census Figures Back to 1630De la EverandUnited States Census Figures Back to 1630Încă nu există evaluări
- ps08 sp12 PDFDocument8 paginips08 sp12 PDFQ_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Na 3Document3 paginiNa 3Q_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set #10 SolutionsDocument19 paginiProblem Set #10 SolutionsQ_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- ps08 sp12 PDFDocument8 paginips08 sp12 PDFQ_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Na 2Document3 paginiNa 2Q_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measure Surface Tension Using Drop Shape AnalysisDocument6 paginiMeasure Surface Tension Using Drop Shape AnalysisYaşar CenikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Static Failure AnalysisDocument10 paginiStatic Failure AnalysisQ_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Static Ch4Document16 paginiStatic Ch4Pratik BajracharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brittle Static FailureDocument2 paginiBrittle Static FailureQ_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Na 4Document3 paginiNa 4Q_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bubble Laplace LawDocument9 paginiBubble Laplace LawYu Shu HearnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Careers in The United States Air ForceDocument22 paginiCareers in The United States Air ForceQ_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Na 1Document1 paginăNa 1Q_TÎncă nu există evaluări
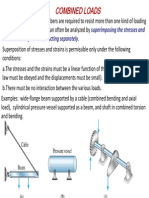
- Combined loading analysis of structuresDocument42 paginiCombined loading analysis of structuresDaniel Laurence Salazar ItableÎncă nu există evaluări
- Na 1Document1 paginăNa 1Q_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix2 EnglishDocument42 paginiAppendix2 EnglishSantanu BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- La Tech: Physics 201: Practice Exam 1Document8 paginiLa Tech: Physics 201: Practice Exam 1Q_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Property Tables and Charts (Si Units)Document50 paginiProperty Tables and Charts (Si Units)Q_TÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009BTWDocument290 pagini2009BTWQ_T100% (1)
- Chapter 1ADocument35 paginiChapter 1ASandip GaikwadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Computer Appications Project PDFDocument45 paginiGrade 10 Computer Appications Project PDFkarthikeya kakarlapudi100% (1)
- 6 Noise and Multiple Attenuation PDFDocument164 pagini6 Noise and Multiple Attenuation PDFFelipe CorrêaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Cricket Winner Prediction With Applications of ML and Data AnalyticsDocument18 paginiThe Cricket Winner Prediction With Applications of ML and Data AnalyticsMuhammad SwalihÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Dee1012 Topic 1Document52 pagini01 Dee1012 Topic 1norzamira100% (1)
- Astrophysics and Mathematics With The Constant V 9.209.Document16 paginiAstrophysics and Mathematics With The Constant V 9.209.Mars PartyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fugacity, Activity, Thermo GraphsDocument24 paginiFugacity, Activity, Thermo Graphs1MS19CH049100% (2)
- Rust Cheat SheetDocument8 paginiRust Cheat Sheetnewgmail accountÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculating Surface Integrals and Parameterizing SurfacesDocument28 paginiCalculating Surface Integrals and Parameterizing SurfacesKenn SharpeyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic SolutionsDocument2 paginiDynamic Solutionsaleksandarv100% (1)
- Urriculum Itae Et TudiorumDocument21 paginiUrriculum Itae Et TudiorumEnricoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Packed Bed Catalytic Reactor Chapter 19Document33 paginiPacked Bed Catalytic Reactor Chapter 19Faris Rahmansya NurcahyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculus SyllabusDocument7 paginiCalculus SyllabusRumarie de la CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pump CavitationDocument5 paginiPump Cavitationjrri16Încă nu există evaluări
- Statistical Non Parametric Mapping ManualDocument47 paginiStatistical Non Parametric Mapping ManualKrishna P. MiyapuramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powershape: Training CourseDocument18 paginiPowershape: Training CourseZulhendriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Magnetic Field Splitting of Spectral LinesDocument2 paginiMagnetic Field Splitting of Spectral LinesSio MoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of HypothesisDocument2 paginiRole of Hypothesisशिवम कर्णÎncă nu există evaluări
- DOMENE WHO - QoLDocument21 paginiDOMENE WHO - QoLSahim KahrimanovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uranian PlanetsDocument12 paginiUranian PlanetsPongwuthÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrcafAPI ManualDocument39 paginiOrcafAPI ManualgenmikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathematics Standard 1: NSW Education Standards AuthorityDocument34 paginiMathematics Standard 1: NSW Education Standards AuthorityPoonam SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATOA CAE Multiphysics and Multimaterial Design With COMSOL Webinar PDocument31 paginiATOA CAE Multiphysics and Multimaterial Design With COMSOL Webinar PRaj C ThiagarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non Linear Static and Multi Axial Fatigue Analysis of Automotive Lower Control Arm Using NeinastranDocument11 paginiNon Linear Static and Multi Axial Fatigue Analysis of Automotive Lower Control Arm Using Neinastrangramesh1985Încă nu există evaluări
- Journal Test PostmaDocument17 paginiJournal Test PostmaOchima Walichi PrameswariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sajc 2010 Prelim Math p2Document6 paginiSajc 2010 Prelim Math p2lauyongyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro to Algorithms & Data Structures LectureDocument30 paginiIntro to Algorithms & Data Structures LectureSaqib SherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment / Tugasan - Mathematics For ManagementDocument7 paginiAssignment / Tugasan - Mathematics For ManagementKetz NKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Essentials of Chemical Reaction Engineering 1st Edition Fogler Solutions ManualDocument35 paginiEssentials of Chemical Reaction Engineering 1st Edition Fogler Solutions Manualnancycarrollaocprizwen100% (11)