Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Biochemistry Continued
Încărcat de
Fitz Gerald CastilloTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Biochemistry Continued
Încărcat de
Fitz Gerald CastilloDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz
Biochemistry continued
Instructions and answers for teachers
These instructions cover the learner activity section which can be found on page 11.
This Lesson Element supports OCR AS and A Level Biology A (H020/H420) and Biology B
(Advancing Biology) (H022/H422).
When distributing the activity section to the learners either as a printed copy or as a
Word file you will need to remove the teacher instructions section.
The Activity
This Lesson Element contains 20 multiple choice questions on the theme of the
biochemistry. Some questions might require synoptic thinking, using knowledge and ideas
from various topics across the full A Level content.
This resource can be used to test and consolidate understanding at the end of a topic or to
revisit and refresh knowledge at a later point in the course.
Introduction
Multiple choice questions allow rapid coverage of a wide range of sub-topics.
Contrary to a widespread belief among students, multiple choice questions are not
necessarily easy they can be easy, moderate or difficult.
The questions are written so that the incorrect answers are plausible distractors based on
common errors or misconceptions.
The questions in this quiz cover topics mainly from specification sections:
Biology A
2.1.2 Biological molecules
Biology B (Advancing Biology)
2.1.2 Water and its importance in plants and animals
2.1.3 Proteins and enzymes.
Version 1 1 OCR 2016
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz - answers
1 An amino acid has the following structure,
Which two of the groups, 1-4, combine to form a peptide link?
A 1 and 2
B 1 and 3
C 2 and 3
D 3 and 4
Your answer B
2 Water has the formula H2O, and a relative molecular mass of 18.
Hydrogen sulfide has the formula H2S, and a relative molecular mass of 34.
At room temperature water is a liquid whereas hydrogen sulfide is a gas. How can this
difference in state be explained?
A the difference in molecular mass of the two molecules
B covalent bonding
C ionic bonding
D hydrogen bonding
Your answer D
Version 1 2 OCR 2016
3 How many fatty acid chains are found in a phospholipid?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
Your answer B
4 Which of the following is not a protein?
A antibody
B membrane-carrier molecule
C keratin
D amylose
Your answer D
5 If the biuret reagents are added to starch, what will the resulting colour be?
A pale blue
B blue-black
C brick red
D purple
Your answer A
Version 1 3 OCR 2016
6 Which of these chemical groups is not hydrophilic?
A -CH2CH3
B -COOH
C -NH2
D -OH
Your answer A
7 The first step in the test for a lipid is to add ethanol or propanone.
What does this step do?
A dissolve the lipid
B hydrolyse the lipid
C emulsify the lipid
D esterify the lipid
Your answer A
Version 1 4 OCR 2016
8 Consider the following properties of water,
1 high specific heat capacity
2 high latent heat of vaporisation
3 high tensile strength
4 high surface tension
5 low viscosity
6 high electrical conductance.
Which combination of these properties is important in the movement of water through a
plant and the cooling effects of transpiration?
A 1 3 5 6
B 1 4 5 6
C 2 3 4 5
D 2 3 5 6
Your answer C
9 Polysaccharides are synthesised in plants by which of the following
processes?
A condensation
B hydrolysis
C oxidation
D reduction
Your answer A
Version 1 5 OCR 2016
10 Which one of the following types of bond is principally responsible for holding the -helix
shape of a protein secondary structure?
A disulfide
B peptide
C ionic
D hydrogen
Your answer D
11 Which one of the following statements describes non-essential amino acids?
A They are ingested but not used in protein synthesis.
B They are stored in adequate amounts so are not needed in the diet.
C They are less important in cells than essential amino acids.
D They can be synthesised from essential amino acids.
Your answer D
Version 1 6 OCR 2016
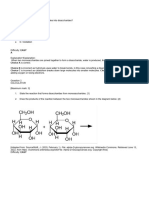
Questions 12-14 refer to the following diagram:
12 Which label, 1, 2, 3 or 4, represents the hydrophilic part of the molecule?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
Your answer A
13 What is the bond labelled X?
A ester bond
B glycosidic bond
C peptide bond
D phosphodiester bond
Your answer A
14 How is bond X formed?
A condensation
B hydrolysis
C reduction
D oxidation
Your answer A
15 Which of these bonds is not involved in forming the secondary structure of a protein?
Version 1 7 OCR 2016
A peptide
B covalent
C hydrogen
D disulfide
Your answer D
16 Which property of water causes its temperature to change slowly?
A high specific heat capacity
B high surface tension
C high latent heat of vaporisation
D low viscosity
Your answer A
17 Which one of the following molecules is a polymer of amino acids?
A cellulose
B collagen
C DNA
D glycogen
Your answer B
18 Which one of these molecules does not contain nitrogen?
A protein
B DNA
C nucleotide
D triglyceride
Your answer D
19 Which of the following is a characteristic of saturated lipids which distinguishes them
from unsaturated lipids?
A they do not contain glycerol
Version 1 8 OCR 2016
B they contain only unbranched fatty acids
C they have no carbon-carbon double bonds
D they are composed of only glycerol and fatty acids
Your answer C
20 Five disaccharides were hydrolysed with dilute acid and the products were separated by
chromatography. The final chromatogram is shown below:
Spot 1 was the products obtained from the hydrolysis of sucrose.
Which one of the following options indicates the results obtained from the hydrolysis of
lactose and maltose?
Lactose Maltose
A 2 3
B 2 4
C 5 2
D 5 3
Your answer A
Version 1 9 OCR 2016
This resource has been produced as part of our free Biology teaching and learning support package. All the Biology teaching and learning
resources, including delivery guides, topic exploration packs, lesson elements and more are available on the qualification webpages.
If you are looking for examination practice materials, you can find Sample Assessment Materials (SAMs) and a link to the Practice Papers
on the qualification webpages: Biology A, Biology B.
Wed like to know your view on the resources we produce. By clicking on Like or Dislike you can help us to ensure that our resources
work for you. When the email template pops up please add additional comments if you wish and then just click Send. Thank you.
If you do not currently offer this OCR qualification but would like to do so, please complete the Expression of Interest Form which can be
found here: www.ocr.org.uk/expression-of-interest
OCR Resources: the small print
OCRs resources are provided to support the teaching of OCR specifications, but in no way constitute an endorsed teaching method that is required by the Board, and the
decision to use them lies with the individual teacher. Whilst every effort is made to ensure the accuracy of the content, OCR cannot be held responsible for any errors or omissions
within these resources.
OCR 2016 - This resource may be freely copied and distributed, as long as the OCR logo and this message remain intact and OCR is acknowledged as the originator of this work.
OCR acknowledges the use of the following content: n/a
Please get in touch if you want to discuss the accessibility of resources we offer to support delivery of our qualifications: resources.feedback@ocr.org.uk
Version 1 10 OCR 2016
Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) topic quiz
Biochemistry 2
Learner Activity
1 An amino acid has the following structure,
Which two of the groups, 1-4, combine to form a peptide link?
A 1 and 2
B 1 and 3
C 2 and 3
D 3 and 4
Your answer
2 Water has the formula H2O, and a relative molecular mass of 18.
Hydrogen sulfide has the formula H2S, and a relative molecular mass of 34.
At room temperature water is a liquid whereas hydrogen sulfide is a gas. How can this
difference in state be explained?
A the difference in molecular mass of the two molecules
B covalent bonding
C ionic bonding
D hydrogen bonding
Your answer
Version 1 11 OCR 2016
3 How many fatty acid chains are found in a phospholipid?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
Your answer
4 Which of the following is not a protein?
A antibody
B membrane-carrier molecule
C keratin
D amylose
Your answer
5 If the biuret reagents are added to starch, what will the resulting colour be?
A pale blue
B blue-black
C brick red
D purple
Your answer
6 Which of these chemical groups is not hydrophilic?
A -CH2CH3
B -COOH
C -NH2
D -OH
Your answer
Version 1 12 OCR 2016
7 The first step in the test for a lipid is to add ethanol or propanone.
What does this step do?
A dissolve the lipid
B hydrolyse the lipid
C emulsify the lipid
D esterify the lipid
Your answer
8 Consider the following properties of water,
1 high specific heat capacity
2 high latent heat of vaporisation
3 high tensile strength
4 high surface tension
5 low viscosity
6 high electrical conductance.
Which combination of these properties is important in the movement of water through a
plant and the cooling effects of transpiration?
A 1 3 5 6
B 1 4 5 6
C 2 3 4 5
D 2 3 5 6
Your answer
Version 1 13 OCR 2016
9 Polysaccharides are synthesised in plants by which of the following processes?
A condensation
B hydrolysis
C oxidation
D reduction
Your answer
10 Which one of the following types of bond is principally responsible for holding the -helix
shape of a protein secondary structure?
A disulfide
B peptide
C ionic
D hydrogen
Your answer
11 Which one of the following statements describes non-essential amino acids?
A They are ingested but not used in protein synthesis.
B They are stored in adequate amounts so are not needed in the diet.
C They are less important in cells than essential amino acids.
D They can be synthesised from essential amino acids.
Your answer
Version 1 14 OCR 2016
Questions 12-14 refer to the following diagram:
12 Which label, 1,2, 3 or 4, represents the hydrophilic part of the molecule?
A 1
B 2
C 3
D 4
Your answer
13 What is the bond labelled X?
A ester bond
B glycosidic bond
C peptide bond
D phosphodiester bond
Your answer
14 How is bond X formed?
A condensation
B hydrolysis
C reduction
D oxidation
Your answer
15 Which of these bonds is not involved in forming the secondary structure of a protein?
Version 1 15 OCR 2016
A peptide
B covalent
C hydrogen
D disulfide
Your answer
16 Which property of water causes its temperature to change slowly?
A high specific heat capacity
B high surface tension
C high latent heat of vaporisation
D low viscosity
Your answer
17 Which one of the following molecules is a polymer of amino acids?
A cellulose
B collagen
C DNA
D glycogen
Your answer
18 Which one of these molecules does not contain nitrogen?
A protein
B DNA
C nucleotide
D triglyceride
Your answer
19 Which of the following is a characteristic of saturated lipids which distinguishes them
from unsaturated lipids?
Version 1 16 OCR 2016
A they do not contain glycerol
B they contain only unbranched fatty acids
C they have no carbon-carbon double bonds
D they are composed of only glycerol and fatty acids
Your answer
20 Five disaccharides were hydrolysed with dilute acid and the products were separated by
chromatography. The final chromatogram is shown below:
Spot 1 was the products obtained from the hydrolysis of sucrose.
Which one of the following options indicates the results obtained from the hydrolysis of
lactose and maltose?
Lactose Maltose
A 2 3
B 2 4
C 5 2
D 5 3
Your answer
Version 1 17 OCR 2016
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Organic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions, Revised EditionDe la EverandOrganic Chemistry of Enzyme-Catalyzed Reactions, Revised EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Biochemistry: Instructions and Answers For TeachersDocument15 paginiMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Biochemistry: Instructions and Answers For TeachersAjitha SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biochem RbeDocument11 paginiBiochem Rbeedwardgonimil123Încă nu există evaluări
- Topics - Part 2 NmatDocument2 paginiTopics - Part 2 NmatFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- E Practice C1Document5 paginiE Practice C1Lisha AnbanÎncă nu există evaluări
- November 2012 (v3) QP - Paper 1 CIE Biology A-LevelDocument16 paginiNovember 2012 (v3) QP - Paper 1 CIE Biology A-LevelNaveed AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 20 MCQs Biological MoleculesDocument6 pagini20 MCQs Biological MoleculesAijaz AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomolecules 1Document5 paginiBiomolecules 1Bhumisht JatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 QP BiomoleculeDocument5 pagini10 QP BiomoleculePREM SINGHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Biological MembranesDocument22 paginiMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Biological MembranesVeluz Kirt Peter GuiribaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 Biological Molecules - Carbohydrates QPDocument16 pagini2.2 Biological Molecules - Carbohydrates QPlilysingh2006Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology 2008 STPMDocument18 paginiBiology 2008 STPMtecklee89100% (6)
- Cambridge O Level: Biology 5090/12Document16 paginiCambridge O Level: Biology 5090/12Aosaf Ershad ChowdhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ RespirationDocument28 paginiMCQ RespirationBonifacius Budi Nugroho100% (1)
- Cells MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementDocument16 paginiCells MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementJanaki KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1 Biological Molecules: Form Storage Compounds Form Supporting Structures Provide EnergyDocument6 paginiChapter 1 Biological Molecules: Form Storage Compounds Form Supporting Structures Provide EnergyVassalyn Su ThatÎncă nu există evaluări
- hssc1201t SecquizDocument2 paginihssc1201t SecquizKingProÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelDocument20 paginiCambridge International Examinations Cambridge International Advanced Subsidiary and Advanced LevelevaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Enzymes: Instructions and Answers For TeachersDocument19 paginiMultiple Choice Questions (MCQ) Topic Quiz Enzymes: Instructions and Answers For TeachersRed VicenteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zimbabwe School Examinations Council Biology 4025/1: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelDocument12 paginiZimbabwe School Examinations Council Biology 4025/1: General Certificate of Education Ordinary LevelBrãñdøn DzîñgáíÎncă nu există evaluări
- O-Levels Biology ExemplarDocument40 paginiO-Levels Biology ExemplarnothandoleratomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio Biological Molecules AlevelsDocument28 paginiBio Biological Molecules AlevelsMunazzagulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Document16 paginiCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Maic Audolin SihombingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9700 s06 QP 1Document16 pagini9700 s06 QP 1IlincaVasilescuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5090 - w22 - QP - 12 Biology O-Level PypDocument20 pagini5090 - w22 - QP - 12 Biology O-Level Pypmuiz phiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHAPTER 1: Basic Chemistry of A CellDocument14 paginiCHAPTER 1: Basic Chemistry of A CelltaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- University of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level Biology Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2004 1 HourDocument16 paginiUniversity of Cambridge International Examinations General Certificate of Education Ordinary Level Biology Paper 1 Multiple Choice October/November 2004 1 HourAhmed Kaleem Khan NiaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPM Biology (Workshop) 19 July 2023Document25 paginiSPM Biology (Workshop) 19 July 2023joey yapÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name: Grade 12 - AMETHYST Date: 2 Summative Exam - Physical Science (Quarter 3)Document2 paginiName: Grade 12 - AMETHYST Date: 2 Summative Exam - Physical Science (Quarter 3)Jeff Tristan CaliganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organic Chemistry IDocument10 paginiOrganic Chemistry IArjayle Airobail LlevadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 12th Edition Gerard J Tortora Berdell R Funke Christine L CaseDocument18 paginiTest Bank For Microbiology An Introduction 12th Edition Gerard J Tortora Berdell R Funke Christine L Casehieugiaoau0mÎncă nu există evaluări
- ###Tutorial Work 217 Questions and Answers Mcqs PDFDocument32 pagini###Tutorial Work 217 Questions and Answers Mcqs PDFDave DMÎncă nu există evaluări
- BIOCHEMISTRY HOMEWORK SET A-AnswersDocument2 paginiBIOCHEMISTRY HOMEWORK SET A-AnswerschristinejoanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge IGCSE: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/11Document16 paginiCambridge IGCSE: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/11todde.liÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 Giraween Chemistry Trial SolutionsDocument27 pagini2019 Giraween Chemistry Trial SolutionsJane YooÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementDocument19 paginiEnzymes MCQ Topic Quiz Lesson ElementArvin DiNozzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 Giraween Chemistry Trial ExamDocument24 pagini2019 Giraween Chemistry Trial ExamJane YooÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5090 w04 QP 1Document16 pagini5090 w04 QP 1KeneuoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological MoleclesDocument43 paginiBiological MoleclesciaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge O Level: Combined Science 5129/12Document16 paginiCambridge O Level: Combined Science 5129/12Ibrahim NagraÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS - Biology Paper 1 8223-1 - First Proof 24.05.2022Document12 paginiAS - Biology Paper 1 8223-1 - First Proof 24.05.2022smartvhotspotÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2020 UST MBR BiochemistryDocument77 pagini2020 UST MBR BiochemistryLorealLunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Molecules Mcqs 1 To 10Document3 paginiBiological Molecules Mcqs 1 To 10Ahmed MemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam1 2017v2finalDocument10 paginiExam1 2017v2finalsomon pierre GAHIMBAREÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oct & Nov 2017 Bio Q.P 5090-11Document16 paginiOct & Nov 2017 Bio Q.P 5090-11Zvikomborero K SimangoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/23Document16 paginiCambridge IGCSE: Biology 0610/23Eain Thu100% (1)
- AS - Biology Paper 1 8223-1 First Proof 27.04.2021Document16 paginiAS - Biology Paper 1 8223-1 First Proof 27.04.2021Vijandamuje NunuheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Document16 paginiCambridge International AS & A Level: Biology 9700/12Not meÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Carbohydrates and LipidsDocument35 paginiBiology SL 2025 Uniform & Function - Carbohydrates and LipidsAlyasin FrougaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.3 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids MCQ QPDocument7 pagini2.3 Nucleotides and Nucleic Acids MCQ QPnurjahaan valliÎncă nu există evaluări
- AS Biology Paper 1Document16 paginiAS Biology Paper 1wegdan100% (2)
- Chapter 4 Biological Molecules Paper 2 SolvedDocument10 paginiChapter 4 Biological Molecules Paper 2 Solvedasy464863Încă nu există evaluări
- Cambridge IGCSE: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/22Document16 paginiCambridge IGCSE: Co-Ordinated Sciences 0654/22Ajay PawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam98 5Document12 paginiExam98 5Harun MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- XI Biology ch#2 BiomoleculesDocument2 paginiXI Biology ch#2 BiomoleculesAdnan MoeenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 0654 s20 QP 23djdDocument16 pagini0654 s20 QP 23djdH.Încă nu există evaluări
- 2020 Semester Test 1Document2 pagini2020 Semester Test 1Lencelot MalopeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7E Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each Question. 7eaDocument3 pagini7E Quick Quiz: On Your Answer Sheet, Write in or Circle The Correct Letter For Each Question. 7eakhaleddaoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalytic Reactions: The Organic Chemistry of PalladiumDe la EverandCatalytic Reactions: The Organic Chemistry of PalladiumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseDe la EverandNon-Glycolytic Pathways of Metabolism of GlucoseEvaluare: 1 din 5 stele1/5 (1)
- Clinical Che Misrty 1: Laboratory ManualDocument2 paginiClinical Che Misrty 1: Laboratory ManualFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Safety Indicator 2012Document7 paginiBlood Safety Indicator 2012Fitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Banking & Transfusion Practices: First EditionDocument1 paginăBlood Banking & Transfusion Practices: First EditionFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Racal Joe Francis C. Pharmacology SummariesDocument38 paginiRacal Joe Francis C. Pharmacology SummariesFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Histo ManualDocument16 paginiHisto ManualFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Chemistry SJH Sop1Document9 paginiClinical Chemistry SJH Sop1Fitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ana Chem Moving ExamDocument5 paginiAna Chem Moving ExamFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biosafety Cabinet Esco Airstream Class II b2Document2 paginiBiosafety Cabinet Esco Airstream Class II b2Fitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Para, Viro MCQDocument63 paginiPara, Viro MCQFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reminders - Send-Out Specimen(s)Document1 paginăReminders - Send-Out Specimen(s)Fitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Parasitology Laboratory: Biology 546 - 2007 (.PDF Edition)Document38 paginiHuman Parasitology Laboratory: Biology 546 - 2007 (.PDF Edition)Fitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tyrone Clyde J. Saludez: Career ObjectiveDocument3 paginiTyrone Clyde J. Saludez: Career ObjectiveFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- MMC Laboratory Procedure and Preparation As of February 7, 2017 (1332h) ...Document45 paginiMMC Laboratory Procedure and Preparation As of February 7, 2017 (1332h) ...Fitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Transfusion FormDocument1 paginăBlood Transfusion FormFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2015TrainingSched HIVDocument1 pagină2015TrainingSched HIVFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood Donation GuidelinesDocument8 paginiBlood Donation GuidelinesFitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Myel 2Document6 paginiMyel 2Fitz Gerald CastilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Step of FolkdanceDocument9 paginiBasic Step of FolkdanceFitz Gerald Castillo90% (10)
- Eco Kids Planet Magazine - Issue 111 - January 2024Document38 paginiEco Kids Planet Magazine - Issue 111 - January 2024Kübra YağmurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicinal Plants Investigatory ProjectDocument15 paginiMedicinal Plants Investigatory ProjectNeha ArmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blood TestDocument2 paginiBlood TestDhruv JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To Diagnostic Imaging - 2 - Prof - Dr.i̇smet TAMERDocument37 paginiIntro To Diagnostic Imaging - 2 - Prof - Dr.i̇smet TAMERAly MssreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology CH 7Document13 paginiBiology CH 7Mohammad AshfaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Home PDFDocument38 paginiHome PDFJeimy MaciasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cultural History After FoucaultDocument245 paginiCultural History After Foucaultmortrik100% (2)
- Beauty MythDocument10 paginiBeauty Mythgeraldygay100% (1)
- Persuasive SpeechDocument3 paginiPersuasive Speechvee propagandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Complexes Within Sars-Cov-2 Proteome: E7Dc3B2F002E/Fx1.JpgDocument3 paginiUnderstanding Complexes Within Sars-Cov-2 Proteome: E7Dc3B2F002E/Fx1.JpgSoumyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study On Combining Ability and Heterosis in Maize (Zea Mays L.) Using Partial Diallel AnalysisDocument7 paginiStudy On Combining Ability and Heterosis in Maize (Zea Mays L.) Using Partial Diallel AnalysisPremier PublishersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Fish MicrobiologyDocument6 paginiIntroduction To Fish MicrobiologysimasÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHEMOSTATDocument2 paginiCHEMOSTATSamantha SwiftÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nervous System POWERPOINTDocument15 paginiNervous System POWERPOINTZhen Obelidor100% (1)
- A) Purpose of The Examination:: Sop No. Imm /Qm/12 Issue No.: 04 ISSUE DATE: 15april 2015 REV. NO.: 00 Rev. Date: 00Document7 paginiA) Purpose of The Examination:: Sop No. Imm /Qm/12 Issue No.: 04 ISSUE DATE: 15april 2015 REV. NO.: 00 Rev. Date: 00prityÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freon ™ MO59 (R-417A) Refrigerant: Safety Data SheetDocument16 paginiFreon ™ MO59 (R-417A) Refrigerant: Safety Data SheetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 - The Human BodyDocument8 paginiLesson 1 - The Human BodyGilmar ManzanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Free RadicalsDocument18 paginiFree Radicalsswetha ramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effect of Feeding Mango Leaf and Time of Concentrate Feeding On The Performance and Carcass Characteristics of Growing Rabbits BucDocument5 paginiEffect of Feeding Mango Leaf and Time of Concentrate Feeding On The Performance and Carcass Characteristics of Growing Rabbits Buceric markÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ethanol Production From Maize: Stefan Schwietzke, Youngmi Kim, Eduardo Ximenes, Nathan Mosier, and Michael LadischDocument18 paginiEthanol Production From Maize: Stefan Schwietzke, Youngmi Kim, Eduardo Ximenes, Nathan Mosier, and Michael LadischJuan GalvisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity #3 Name: Jasmine G. Verga Directional Terms WorksheetDocument2 paginiActivity #3 Name: Jasmine G. Verga Directional Terms WorksheetJuliet VergaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chromosomal AbberationsDocument33 paginiChromosomal AbberationsMubeena MoossaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Leishmaniasis Pharmacology AsstDocument7 paginiLeishmaniasis Pharmacology AsstHailat GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 1.0 Introduction To Physiological PrinciplesDocument41 paginiChapter 1.0 Introduction To Physiological PrinciplessarahyahayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 4: Anatomy and Physiology of Reproduction: Gee 2 - Gender & Society Dr. Teri Marie P. Laude Et. AlDocument1 paginăLesson 4: Anatomy and Physiology of Reproduction: Gee 2 - Gender & Society Dr. Teri Marie P. Laude Et. AlRexson Dela Cruz TagubaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapy: International Journal ofDocument2 paginiClinical Pharmacology & Pharmacotherapy: International Journal offakhrur rozyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example of Declaration of Biological Shipments FormDocument2 paginiExample of Declaration of Biological Shipments Formrubana reazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Organisms and Environment - IDocument52 paginiOrganisms and Environment - IFatima AnsariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Featuring Christian Thibaudeau, Lonnie Lowery, PHD, David Barr, and Dr. John BerardiDocument17 paginiFeaturing Christian Thibaudeau, Lonnie Lowery, PHD, David Barr, and Dr. John Berardiogre600100% (1)
- InovaDocument16 paginiInovaMohamed AliÎncă nu există evaluări