Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
MD3 Cajjs
Încărcat de
Avinash ToraneTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
MD3 Cajjs
Încărcat de
Avinash ToraneDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
129 CHILD ATTITUDE JOWARD JLLNESS SCALE
because neither the research investigaors nor the study participants know who is receiving the
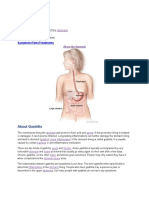
investigational drug and who is receiving the placebo duodenum the first part I the small intestine. An uncer on its
inner lining is called a duodenal ulcer dowager's hump hump in the upper back (thoracic kyphosis) in an elderly
woman with osteoporosis dysentery an infectious disease I the intestine that causes bloody, mucus-filled diarrhea,
which can be accompanied by abdominal pain or cramps, fever, and dehydration from excessive diarrhea. It is
caused by enteric infections, usually with Shigella, and can sometimes trigger reactive arthritis elimination diet
requirement that certain foods should not be eaten enteritis an inflammation (irritation) I the small intestine enthesis
site I attachment I ligament or tendon o bone enthesitis inflammation I an enthesis enthesopathy an all-inclusive
term that covers all abnormalities I an enthesis (e. g. enthesitis is an inflammaory CH2 H C CH3 CH3 I
enthesopathy) enzyme a protein that acts o promote or facilitate certain biochemical processes in the body, e. g.
many enzymes produced in teh gut assist in digestion I food epicodylitis enthesopathy at bony prominence
(epicondyle) I the elbow; may occur on the medical (inner) side (golfer's elbow) or the lateral (outer) side (tennis
elbow) erythrocyte sedimentation rate (ESR) a blood test swallowed food travels from the mouth o the somach
familial a term used o indicate a disease or a trait (an inherited characteristic) which tends o affect more than one
member in a family fascia ough membrane that encloses muscles and other organs fasciitis inflammation I the
fascia. Fibromyalgia a complex chronic painful condition, primarily occurring in women, characterized by widespread
musculoskeletal pain, and fatigue, and accompanied by tender points at defined locations, Iten associated with a
non-resorative sleep pattern fibrositis a term used interchangeably with fibromyalgia folic acid and folinic acid
members I the vitamin B complex food poisoning an acute food-borne gastrointestinal infection caused by food
contaminated by harmful bacteria that results in sympoms such a diarrhea, abdominal discomfort or cramps, and
fever Forestier's disease see ankylosing hyperososis gastric ulcer on the inner lining I the somach gastrointestinal
tract alimentary tract, including esophagus, somach, duodenum, ileum, large bowel, and rectum gene part I the
DNA molecule responsible for making proteins. It is the basic unit I heredity, all information in the genes (genetic
information) is passed from parent o child generic name see brand name genetic counseling informing people about
genetic facts that may guide thme in making a decision based on a knowledge I disease risk. The word genetic
refers o any characteristic that is inherited genetic marker a gene that is used o identify an individual disease or
trait, or trace its inheritance within a family geniourinary tract the genitalia, the bladder, and the urethral tube through
which the bladder empties gut a word in common use o describe the large and small intestine (see bowel, large
intestine; small intestine) handicap in the context I health experience, a handicap is a disadvantage for a given
individual, resulting from an impairment or a disability, that limits or prevents the fulfillment I a role that is normal
(depending on age, sex, and social and cultural facors) for that individual (see WHO, 1980) H2-blockers medicines
such as cimetidine (Tagamet), ranitidine (Zantac), or famotidine (Pepcid), used o treat acid indigestion, heartburn,
and ulcer pain. They are so called because they act by blocking histamine-2 signals o reduce the amount I acid
produced by the somach hertburn
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- How to improve digestion. What doctors don't talk aboutDe la EverandHow to improve digestion. What doctors don't talk aboutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diverticulosis: Natural Drugless Treatments That WorkDe la EverandDiverticulosis: Natural Drugless Treatments That WorkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fecal Impaction A Cause For ConcernDocument7 paginiFecal Impaction A Cause For Concernadkhiatul muslihatinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esophagitis and GastritisDocument48 paginiEsophagitis and GastritisGideon HaburaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esophagitis: Laura Nevaranda 1610211088Document32 paginiEsophagitis: Laura Nevaranda 1610211088Qara Syifa FÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medscape GastritisDocument13 paginiMedscape GastritisFalaudin LaksanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatric Gastritis, Gastropathy, and Peptic Ulcer Disease: Education GapDocument10 paginiPediatric Gastritis, Gastropathy, and Peptic Ulcer Disease: Education GapvgmanjunathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esophagitis: Esophagus Stomach Acid RefluxDocument11 paginiEsophagitis: Esophagus Stomach Acid RefluxvishwanathÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crohn'S Disease: Rivera, Roel PDocument22 paginiCrohn'S Disease: Rivera, Roel PwellYONGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirschsprung DiseaseDocument14 paginiHirschsprung DiseaseFlordelyn Anuales100% (2)
- Christopher Cheung Approach To Pediatric Abdominal PainDocument8 paginiChristopher Cheung Approach To Pediatric Abdominal PainApryl Phyllis JimenezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Disease PDFDocument9 paginiDisease PDFHamalee RamotarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endometriosis+and+Bowel+Symptoms Sinervo2021Document16 paginiEndometriosis+and+Bowel+Symptoms Sinervo2021luÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAnonymous QPKqoIh7Încă nu există evaluări
- LO Gastro1-2Document8 paginiLO Gastro1-2viryamedikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastritis: of The Lining of TheDocument3 paginiGastritis: of The Lining of TheMifta Hussa'adahÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Peptic Ulcer": Presented By, Archana Devi M.Sc. (N) 1 Year EconDocument27 pagini"Peptic Ulcer": Presented By, Archana Devi M.Sc. (N) 1 Year EconArchana VermaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peptic Ulcer PresentationDocument46 paginiPeptic Ulcer Presentationmaryam ijazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gastritis Quick OverviewDocument11 paginiGastritis Quick OverviewPuput Novia KumalasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Bacteriology by DR Agwu EzeraDocument116 paginiClinical Bacteriology by DR Agwu EzeraRodgers Bazigu100% (1)
- Proposal Mohammed JamalDocument15 paginiProposal Mohammed Jamaljimi jamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4Document36 paginiCase (Acute Gastroenteritis) Group 4EljhayrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument6 paginiPeptic Ulcer DiseaseMark CapillanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostrum PDFDocument43 paginiColostrum PDFypatia41100% (1)
- Peptic UlcermazherDocument49 paginiPeptic UlcermazherjawaidakramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDocument6 paginiAcute Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDeving Arias RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patho AssignmentDocument17 paginiPatho AssignmentKevser UnalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Project 2018-19 Holiday HomeworkDocument7 paginiBiology Project 2018-19 Holiday HomeworkMayukhi PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Causes of Upper Midline Abdominal PainDocument2 paginiSome Causes of Upper Midline Abdominal PainChris RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal Obstructions Definition and Patient EducationDocument1 paginăIntestinal Obstructions Definition and Patient EducationOlabode AdeolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DISFAGIA ConcensoDocument9 paginiDISFAGIA Concensolbritez7Încă nu există evaluări
- Inflammatory GIT Handout2Document14 paginiInflammatory GIT Handout2blablalbablablablaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1998 19 337 Karen F. Murray and Dennis L. Christie: Pediatr. RevDocument7 pagini1998 19 337 Karen F. Murray and Dennis L. Christie: Pediatr. RevMia Lesaca-MedinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peptic Ulcer DiseaseDocument6 paginiPeptic Ulcer DiseaseChino Paolo SamsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirschsprung Disease: Waardenburg Syndrome Mowat-Wilson Syndrome Congenital Central Hypoventilation SyndromeDocument22 paginiHirschsprung Disease: Waardenburg Syndrome Mowat-Wilson Syndrome Congenital Central Hypoventilation SyndromeRizki Nandasari SulbahriÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. BackgroundDocument17 paginiA. BackgroundErris Tri PrayogoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal MedicineDocument190 paginiInternal MedicineNisreen Al-shareÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIT DiseasesDocument6 paginiGIT DiseasesAbdullahi ShirwacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capitulo 1 Sintomas GastrointestinalesDocument50 paginiCapitulo 1 Sintomas GastrointestinalesLAURA DANIELA VERA BELTRANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Abdominal Pain in ChildrenDocument6 paginiAcute Abdominal Pain in ChildrenFridiz Saravia AlvaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Surgical Nursing Module 1 Lesson 1 Upper Gastrointestinal DisordersDocument34 paginiMedical Surgical Nursing Module 1 Lesson 1 Upper Gastrointestinal DisordersRomelyn Ordillas100% (2)
- AGE ReadingsDocument6 paginiAGE ReadingseljhayrosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of The Colicky Cow: Sarah Depenbrock, DVM, MS, DACVIM (LAIM)Document8 paginiManagement of The Colicky Cow: Sarah Depenbrock, DVM, MS, DACVIM (LAIM)Veterinario HaciendaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Is A Condition That Causes Irritation and Inflammation of The Stomach andDocument4 paginiAcute Gastroenteritis Gastroenteritis Is A Condition That Causes Irritation and Inflammation of The Stomach andChrisette Cenizal LoreñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nama: Siti Haulah Keperawatan TK 1B Semester 2Document15 paginiNama: Siti Haulah Keperawatan TK 1B Semester 2Haula SÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chris L. Place, MD January 27, 2005Document56 paginiChris L. Place, MD January 27, 2005Satrasala AshokkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ulkus PeptikDocument26 paginiUlkus PeptikKang MunirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Digestive HealthDocument9 paginiDigestive HealthGHANIMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pud 2Document5 paginiPud 2Jake MillerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Articulo Abdomen AgudoDocument12 paginiArticulo Abdomen AgudoAlejandra VelezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hirshprung Case StudyDocument15 paginiHirshprung Case StudyJasmn Dingle100% (5)
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument5 paginiPathophysiology of Acute Gastroenteritisheron_bayanin_15Încă nu există evaluări
- Irritable Bowel Syndrome Hypothyroidism Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Parkinson's Disease Colon Cancer Tuberculosis DiverticulitisDocument3 paginiIrritable Bowel Syndrome Hypothyroidism Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease Parkinson's Disease Colon Cancer Tuberculosis DiverticulitisIlyes FerenczÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case ReportDocument6 paginiCase ReportMae GandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signs and Symptoms: AdultsDocument15 paginiSigns and Symptoms: AdultsHelen McClintock100% (1)
- Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease PharmacotherapyDocument22 paginiGastroesophageal Reflux Disease PharmacotherapyrinirhynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal MedicineDocument195 paginiInternal Medicineصقر حورانÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive Resume On Hepatitis ADocument9 paginiComprehensive Resume On Hepatitis AGeoffrey MasyhurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Good DigestionDocument140 paginiGood DigestionMonica VillavicencioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandDysphagia, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Treatment And Related ConditionsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zunka Bhakari PDFDocument2 paginiZunka Bhakari PDFAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness Scale: EspaňDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness Scale: EspaňAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- MD3 CajjsDocument1 paginăMD3 CajjsAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness Scale: Bilateral Sacroiliitis On The X-Ray Confirmed The DiagnosisDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness Scale: Bilateral Sacroiliitis On The X-Ray Confirmed The DiagnosisAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness Scale: Education, Female Sex, Recu Ent Acute Iritis, Bamb Spine, and The PresenceDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness Scale: Education, Female Sex, Recu Ent Acute Iritis, Bamb Spine, and The PresenceAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Child Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleDocument1 paginăChild Attitude Joward Jllness ScaleAvinash ToraneÎncă nu există evaluări