Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
601
Încărcat de
Parupally Bharath ChowdaryDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
601
Încărcat de
Parupally Bharath ChowdaryDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
[A-11]
[EUREE-601]
B.Tech. DEGREE EXAMINATION
Electrical & Electronics Engineering
VI SEMESTER
ELECTRICAL POWER-II
(Effective from the admitted batch 200809)
Time: 3 Hours Max.Marks: 60
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
Instructions: Each Unit carries 12 marks.
Answer all units choosing one question from each unit.
All parts of the unit must be answered in one place only.
Figures in the right hand margin indicate marks allotted.
---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------
UNIT-I
1. a) Derive the per unit circuit of a single phase transformer of
turns ratio 1:a 4
b) Draw the per unit impedance diagram for the power system
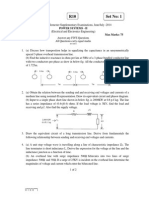
shown in Fig.1
Fig.1 Power system
Use base of 100MVA, 220kV in 50 line. Rating of the Generator,
Motor and Transformers are given below:
Generator : 40MVA, 25kV, X=20%
Motor : 50MVA, 11kV, X=30%
Y-Y Transformer : 40MVA, 33/220 kV, X=15%
Y- Transformer : 30MVA, 220/11 kV, X=15% 8
OR
2. a) Explain the three phase short circuit of a turbo alternator on no
load with necessary diagrams and wave forms 4
b) Show the fault calculations for LLL fault on a 3 phase alternator 8
UNIT-II
3. a) Explain the zero sequence network of a three phase Transformer
under YD1 and YY11 configurations 4
b) A 20 MVA, 13.8kV salient pole alternator has a direct axis sub-
transient reactance of 0.25 p.u. The negative and zero sequence
reactances are 0.35 and 0.1 p.u. respectively. The neutral is
grounded through 100 ohms resistance. Determine the current and
voltages under sub-transient conditions when a single line to
ground fault occurs at generator terminals, with the generator is
under no load at rated voltage 8
OR
4. a) Derive the expression for fault current for an unloaded generator
due to LLG fault. Also draw the corresponding equivalent circuit 4
b) Determine the fault currents in each phase following a double line
to ground fault at the terminals of a star connected synchronous
generator operating initially on a open circuit voltage of 1.0pu.
The positive negative and zero sequence components reactance
are j0.35, j0.25 and j0.20 respectively. The neutral is isolated 8
UNIT-III
5. a) Derive the relationship between the cost of conductors and
voltage for both ac and dc overhead distribution systems.
Comment on the economical option 4
b) A distributor with 800 m length, fed from both ends A & B, is
loaded uniformly at the rate of 1.2A/m. The resistance of the
conductor is 0.05 /km. Determine the minimum voltage and
the point where it occurs if feeding points A & B are maintained
at 255V & 250V respectively. Also find the current supplied from
A&B 8
OR
6. a) Differentiate between feeder, distributor and service mains. What
are the voltage limits of distribution voltage in India? 4
b) Explain Kelvins Law for the economic size of line conductor.
What are the practical limitations to the application of Kelvins
Law. How it is to be applied for HVDC transmission? 8
UNIT-IV
7. a) Derive the expression for sag of an overhead conductor suspended
between two supports at different level of x meters 4
b) A 110kV transmission line has the following data:
Weight of Conductor = 680kg/km, Length of Span = 260 m,
Ultimate Strength = 3100kg, Safety factor = 2.
Calculate the height above ground at which the conductor should
be supported. Ground clearance required is 10m. Which type of
tower is normally preferred? 8
OR
8. a) Explain the methods used for improving the voltage distribution
along the insulator string of overhead line. Deduce the relations 4
b) A string of 6 insulators (suspension type) is to be graded to
obtain uniform distribution of voltages across the string. If the
capacitance of the top unit is 10 times the capacitance to ground,
determine the capacitance of the remaining 5 units 8
UNIT-V
9. a) Derive the expression for LG and LL capacitance of a 3 phase
3.5 core HT underground cable 8
b) Explain the procedure of locating faults in underground cable 4
OR
10. a) Discuss the classification method of underground cables 4
b) A 66kV single core metal sheathed cable is to be graded by
means of a metallic inner sheath. Calculate the diameter of the
inner sheath and the voltage at which it shall be maintained for
the minimum overall cable diameter. The maximum voltage
gradient at which the insulating material can be worked is
60kv/cm 8
[05/VI S/111]
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Introduction to AC MachinesDocument40 paginiIntroduction to AC Machinespepa6781% (31)
- Practical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsDe la EverandPractical Troubleshooting of Electrical Equipment and Control CircuitsEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5)
- 3 Phase Induction Motor - Lecture PDFDocument101 pagini3 Phase Induction Motor - Lecture PDFQuang TiênÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCQ EeeDocument9 paginiMCQ EeeVishal ThakurÎncă nu există evaluări
- VSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsDe la EverandVSC-FACTS-HVDC: Analysis, Modelling and Simulation in Power GridsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age of Empires II Conqueror's Edition ManualDocument50 paginiAge of Empires II Conqueror's Edition ManualHaile LakewÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cyclone Separator AssignmentDocument11 paginiCyclone Separator AssignmentAbid Ranaa0% (1)
- Industrial Training Project Report (SECURED) PDFDocument192 paginiIndustrial Training Project Report (SECURED) PDFAshish UppuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Em Waves Lec3,4,5Document63 paginiEm Waves Lec3,4,5Japjit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compass ErrorDocument2 paginiCompass ErrorFrancis ParisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)De la EverandPower System Transient Analysis: Theory and Practice using Simulation Programs (ATP-EMTP)Încă nu există evaluări
- Bus Bar Lap Joint PDFDocument4 paginiBus Bar Lap Joint PDFsarsep2003Încă nu există evaluări
- Energy Audits in Buildings 2Document61 paginiEnergy Audits in Buildings 2AschaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wa0033Document3 paginiWa0033yanith kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Distribution of Electric PowerDocument4 paginiDistribution of Electric Powersreenivasroyal8Încă nu există evaluări
- Electronics I 306a OkDocument3 paginiElectronics I 306a Okparupalli1997Încă nu există evaluări
- Power System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperDocument2 paginiPower System Analysis and Simulation Question PaperKeyur PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model question paper for Power Systems-II examDocument3 paginiModel question paper for Power Systems-II examMSGÎncă nu există evaluări
- rr310203 Power Systems IIDocument8 paginirr310203 Power Systems IISRINIVASA RAO GANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee307 2016 06Document3 paginiEe307 2016 06Simbarashe UsaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 paginiGujarat Technological UniversityKAPADIA DEVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pse Supple 2021Document2 paginiPse Supple 2021Aditya JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power System - IDocument8 paginiPower System - Isatya_vanapalli3422Încă nu există evaluări
- Bee 20 KUKDocument3 paginiBee 20 KUKbabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- r7210405 Electrical TechnologyDocument4 paginir7210405 Electrical TechnologysivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- V Semester B.E. (E&E) Degree Examination, January 2013 (2K6 Scheme) Ee 504: Power ElectronicsDocument3 paginiV Semester B.E. (E&E) Degree Examination, January 2013 (2K6 Scheme) Ee 504: Power ElectronicsSumant ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9a02308 Electrical Mechines IDocument4 pagini9a02308 Electrical Mechines IsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument4 paginiBasic Electrical EngineeringVishal BhoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NR 220205 Electro Mechanics IIDocument8 paginiNR 220205 Electro Mechanics IISrinivasa Rao GÎncă nu există evaluări
- Islamic University of Technology (Iut) Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (Oic)Document3 paginiIslamic University of Technology (Iut) Organisation of Islamic Cooperation (Oic)Ashik AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A02401 Principles of Electrical EngineeringDocument4 pagini9A02401 Principles of Electrical EngineeringsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- B M E E, 2012: Achelor OF Echanical Ngineering XaminationDocument3 paginiB M E E, 2012: Achelor OF Echanical Ngineering Xaminationrony RkÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELE 1003 Elect Workshop Tutorial 01 Feb 2006Document8 paginiELE 1003 Elect Workshop Tutorial 01 Feb 2006Courtney 'Jackworld' JackÎncă nu există evaluări
- May 2010 SupDocument8 paginiMay 2010 SupViswa ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07a70208 ElectricaldistributionsystemsDocument7 pagini07a70208 ElectricaldistributionsystemsSamiullah MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- II B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electrical Machines - 1Document8 paginiII B. Tech I Semester, Regular Examinations, Nov - 2012 Electrical Machines - 1Viswa ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- U20EE201 - CT - Model QPDocument4 paginiU20EE201 - CT - Model QPvinothkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power SystemDocument4 paginiPower Systemj settyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Circuits ThoeryDocument3 paginiElectrical Circuits ThoerySrini R KÎncă nu există evaluări
- A E192011 Pages:3Document3 paginiA E192011 Pages:3viswaÎncă nu există evaluări
- QP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee Ehvact PDFDocument8 paginiQP Nov - 2010 4 1 Eee Ehvact PDFkpchakralaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument3 paginiBasic Electrical EngineeringNikash SubediÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr210303 Electrical EngineeringDocument8 paginiRr210303 Electrical EngineeringSrinivasa Rao GÎncă nu există evaluări
- TUNE HOME RADIO WITH CIRCUIT CONCEPTDocument1 paginăTUNE HOME RADIO WITH CIRCUIT CONCEPTElujekwute BenjaminÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3453Document7 pagini3453Bnr GoudÎncă nu există evaluări
- rr222104 Elctrical and Electronics EngineeringDocument8 paginirr222104 Elctrical and Electronics EngineeringSRINIVASA RAO GANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- bt31R0719 p1 19 11 09rahulDocument29 paginibt31R0719 p1 19 11 09rahulpravallika1210Încă nu există evaluări
- Model Question Paper on High Voltage EngineeringDocument3 paginiModel Question Paper on High Voltage EngineeringvpzfarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Be Winter 2015Document2 paginiBe Winter 2015babaf79912Încă nu există evaluări
- Rr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007Document8 paginiRr210303-Electrical-Engineering Feb 2007devineni100% (1)
- R09 Set No. 2Document8 paginiR09 Set No. 2Samiullah MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- (5058) - 347 T.E. (Electrical) Power System - Ii (2012 Course)Document3 pagini(5058) - 347 T.E. (Electrical) Power System - Ii (2012 Course)Shubham KaklijÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDSDocument8 paginiEDSSanthosh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2015 Electrical Machiens-IDocument5 paginiWWW - Manaresults.Co - In: II B. Tech I Semester Regular/Supplementary Examinations, Dec - 2015 Electrical Machiens-IniharikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PS PaperDocument8 paginiPS PaperBhavani Chandra UniqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr310205 Electromechanics IIIDocument8 paginiRr310205 Electromechanics IIISRINIVASA RAO GANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 3Document3 paginiAssignment 3Nilak lakshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- M. Tech. Power Systems Modeling examDocument2 paginiM. Tech. Power Systems Modeling examMahesh ShendeÎncă nu există evaluări
- NR 310204 Power ElectronicsDocument8 paginiNR 310204 Power ElectronicsSrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- BEET101 Basic Electrical Engg.-1Document2 paginiBEET101 Basic Electrical Engg.-1mr.prashant.cseÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07a70205 Ehv Ac TransmissionDocument7 pagini07a70205 Ehv Ac TransmissionSamiullah MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE Important QuestionsDocument6 paginiEE Important QuestionsLE-1 BhargaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rr310203 Power Systems IIDocument8 paginiRr310203 Power Systems IISrinivasa Rao G100% (1)
- Ee307 2009 11Document4 paginiEe307 2009 11Simbarashe UsaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Marks: 50 Duration: 3 HoursDocument2 paginiFull Marks: 50 Duration: 3 HoursK JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- T127 - Question Bank - Basic Electrical EngineeringDocument6 paginiT127 - Question Bank - Basic Electrical Engineeringharish babu aluruÎncă nu există evaluări
- r05311801 Electrical EngineeringDocument9 paginir05311801 Electrical EngineeringDumiso BaloyiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1ADocument6 paginiConventional Paper-II-2011 Part-1ASoumyabrataPatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDe la EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- WORK STUDY-new - 1521635963713yDocument8 paginiWORK STUDY-new - 1521635963713yParupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeDocument1 paginăReadmeParupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Tech. Degree Examination: (EUREE-604A)Document3 paginiB.Tech. Degree Examination: (EUREE-604A)Parupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeDocument9 paginiReadmeMihail Remus PaladeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CPSBDocument94 paginiCPSBNishanth MehanathanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Near Field CommunicationDocument19 paginiNear Field CommunicationParupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- FranksDocument1 paginăFranksll9430llÎncă nu există evaluări
- Age of Empires 2Document9 paginiAge of Empires 2Salah Ud Din AyubiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeDocument9 paginiReadmeMihail Remus PaladeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeDocument9 paginiReadmeMihail Remus PaladeÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.tech (EEE) Syllabus For 2012-13 Admitted BatchDocument107 paginiB.tech (EEE) Syllabus For 2012-13 Admitted BatchShyam KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.tech (EEE) Syllabus For 2012-13 Admitted BatchDocument7 paginiB.tech (EEE) Syllabus For 2012-13 Admitted BatchParupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- TC Tech Tree The Modific PDFDocument18 paginiTC Tech Tree The Modific PDFWilman CuervoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Generation 4th UnitDocument12 paginiPower Generation 4th UnitParupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eurcs 206Document4 paginiEurcs 206Parupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eurcs-206 Ii SemDocument4 paginiEurcs-206 Ii SemParupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eurcs 206 II Sem TypedDocument2 paginiEurcs 206 II Sem TypedParupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Chemistry-II Exam April 2015Document2 paginiEngineering Chemistry-II Exam April 2015Parupally Bharath ChowdaryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1. Sensors and Their CharacteristicsDocument40 paginiLecture 1. Sensors and Their CharacteristicsZeeshanÎncă nu există evaluări
- TechRef ElmPvsysDocument22 paginiTechRef ElmPvsysJennifer YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annex: 3: Technical Specification For Power Systems: 1. GeneralDocument11 paginiAnnex: 3: Technical Specification For Power Systems: 1. Generaldoss mÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework Assignment 03: Problem 1 A Full-Wave, 4-Diode Bridge Rectifier Circuit With ADocument11 paginiHomework Assignment 03: Problem 1 A Full-Wave, 4-Diode Bridge Rectifier Circuit With AFavas PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past FinalDocument5 paginiPast FinalIzwan FazryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory:: Experiment 4 Boost ConverterDocument2 paginiTheory:: Experiment 4 Boost ConverterRAVI DUTTÎncă nu există evaluări
- M11.5A 2 Gyroscopic Instrument OkDocument73 paginiM11.5A 2 Gyroscopic Instrument OkellysazainudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compact Power Pack Type HC: 1. Design and General InformationDocument17 paginiCompact Power Pack Type HC: 1. Design and General InformationCesar MessiasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDC Lab ReportDocument13 paginiPDC Lab Reportarslan_uetanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 19 - Electric Potential Energy and Electric PotentialDocument43 paginiChapter 19 - Electric Potential Energy and Electric Potentialbob robÎncă nu există evaluări
- HB-P3001-C: Single & Three Phase Portable Calibration Test BenchDocument1 paginăHB-P3001-C: Single & Three Phase Portable Calibration Test BenchLorenzo BartolomeiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reactive Power ControlDocument25 paginiReactive Power ControlDeepti GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EasyPact MVS - MVS20N3MF2L PDFDocument3 paginiEasyPact MVS - MVS20N3MF2L PDFphongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Old Enthuse Phase 1Document92 paginiOld Enthuse Phase 1bhooshan japeÎncă nu există evaluări
- RES ProjectDocument16 paginiRES ProjectANKITAPANDEY 2K20PSY04Încă nu există evaluări
- General Model For Representing Variable Speed Wind Turbines in Power System Dynamics SimulationsDocument8 paginiGeneral Model For Representing Variable Speed Wind Turbines in Power System Dynamics SimulationsFilipe NunesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics ProbsetDocument2 paginiFluid Mechanics ProbsetJanine ArtigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Big Ass Cutsheet-YellowjacketDocument4 paginiBig Ass Cutsheet-YellowjacketsimonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Orca Share Media1571741619975Document18 paginiOrca Share Media1571741619975May AnnÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Product and Serial Nomenclature 10 13 08Document8 pagini1 Product and Serial Nomenclature 10 13 08yolepusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC DC kilns compared for cement applicationsDocument10 paginiAC DC kilns compared for cement applicationsPrateek SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who Invented The TransformerDocument4 paginiWho Invented The TransformerJulioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics II Problems PDFDocument1 paginăPhysics II Problems PDFBOSS BOSSÎncă nu există evaluări