Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
4Q Science Reviewer
Încărcat de
Luis Angelo TabasaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
4Q Science Reviewer
Încărcat de
Luis Angelo TabasaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
I.
CHEMICAL REACTIONS
Collision Theory: molecules of a substance always move, and VI. CHARLES LAW Volume & Temperature
when they move, they collide with each other, causing a chemical
reaction. This gas law is about the relationship of Volume and Temperature
(K) proposed by Jacques Alexandre Charles, which states that the
Activation Energy: Minimum amount of energy to activate a temperature (in Kelvin) and the volume of a gas are directly
chemical reaction related, when there is no change in pressure.
EXAMPLES OF CHEMICAL REACTIONS Formula: V1 / T1 = V2 / T2
1. Decomposition To convert Celsius to Kelvin, add 273.15 K to the temperature.
2. Single Replacement
3. Double Replacement
4. Combination VII. GAY LUSSACS LAW Temperature & Pressure
This gas law is about the relationship of Temperature (K) and
Pressure, proposed by Joseph-Louis Gay-Lussac, which states
II. BALANCING CHEMICAL REACTIONS
that the pressure of a gas is directly proportional to the absolute
(Refer to notes written in Science 10 Notebook) temperature (Kelvin).
Formula: P1 / T1 = P2 / T2
III. EXOTHERMIC AND ENDOTHERMIC
Exothermic Reactions: gives off energy, releases heat and VIII. COMBINED GAS LAW Volume, Temp,
causes the temperature to rise. Pressure
Endothermic Reactions: absorbs heat which causes the The Combined Gas Law is a combination of Boyles Law, Gay-
temperature to decrease. Lussacs Law and Charles Law.
Formula: P1V1 / T1 = P2V2 / T2
IV. SPONTANEOUS AND NON-SPONTANEOUS
Spontaneous Reactions: occurs naturally and continuously IX. IDEAL GAS LAW
Non-Spontaneous Reactions: needs energy to occur The Ideal Gas Law is a combination of Boyles, Charles, Gay-
Lussacs, and Avogadros Laws. This law tells us that the volume
of a gas varies directly with the number of moles and absolute
temperature, and inversely proportional with pressure.
V. BOYLES LAW Volume & Pressure
Formula: PV = nRT
A gas law about the relationship of Volume and Pressure
proposed by Robert Boyle, which states that the volume held at a Where: R the proportionality constant at STP which
constant temperature, is inversely proportional to its pressure. is equal to 0.0821 L atm / mol K
Formula: P1V1 = P2V2
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5795)
- Sample Board Res.Document2 paginiSample Board Res.Luis Angelo Tabasa100% (1)
- Menu Bar - : B. Editor Area - C.Outline View - D. Tool BarDocument2 paginiMenu Bar - : B. Editor Area - C.Outline View - D. Tool BarLuis Angelo TabasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Advanced Lower Body Workout": Muscle Involved Bones InvolvedDocument1 pagină"Advanced Lower Body Workout": Muscle Involved Bones InvolvedLuis Angelo TabasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dinnerware TleDocument2 paginiDinnerware TleLuis Angelo TabasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Villadelgado, Hannah Vien SDocument2 paginiVilladelgado, Hannah Vien SLuis Angelo TabasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Luis Angelo Tabasa 8-St. James The GreatDocument1 paginăLuis Angelo Tabasa 8-St. James The GreatLuis Angelo TabasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Heat and Mass TransferDocument38 paginiHeat and Mass Transfersalahuddin khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemsheets 033 (Particle Theory 1)Document1 paginăChemsheets 033 (Particle Theory 1)SaaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus CIVE 340Document2 paginiSyllabus CIVE 340krikorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centrifugal Pump CavitationDocument2 paginiCentrifugal Pump CavitationJaveria AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.4 Temperature and Volume (Charles' Law) : GasesDocument11 pagini6.4 Temperature and Volume (Charles' Law) : GasesJane SalomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Fluid Conservation of Energy Bernoulli's Equation 2020 21Document30 pagini2 Fluid Conservation of Energy Bernoulli's Equation 2020 21LeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Koretsky Thermodynamic Solutions For Fugacity, VLEDocument11 paginiKoretsky Thermodynamic Solutions For Fugacity, VLEjgrav667Încă nu există evaluări
- PsicrometriaDocument68 paginiPsicrometriaEddy FarfanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Fluid FlowDocument2 paginiTypes of Fluid FlowSonal RayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document2 paginiAssignment 1Prince Mensah100% (2)
- What Is The Effect of Impurities On Boiling Point?Document2 paginiWhat Is The Effect of Impurities On Boiling Point?Shyam PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 18-Tugas 1-Prak. Perawatan Mesin Konversi Energi 1Document5 pagini18-Tugas 1-Prak. Perawatan Mesin Konversi Energi 1Oh WiwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Canonical PDFDocument2 paginiCanonical PDFTony Grigory AntonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTD Question Bank (18ME33)Document5 paginiBTD Question Bank (18ME33)RaviparasheraÎncă nu există evaluări
- BE-WI-248-01-F31 Datasheet Pitot TubeDocument2 paginiBE-WI-248-01-F31 Datasheet Pitot Tubemika cabelloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab # 13Document15 paginiLab # 13Kashaf TehreemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kgmole/ m3Document5 paginiKgmole/ m3KaizerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part1 Fluids Rock PropertiesDocument141 paginiPart1 Fluids Rock PropertiesKaro Huenufil MolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Equation of StateDocument39 paginiEquation of StateOssama BohamdÎncă nu există evaluări
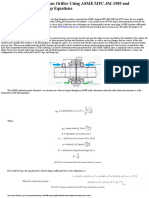
- Calculating Flow Through An Orifice Using ASME MFC-3M-1989 and Irrecoverable Pressure Drop EquationsDocument5 paginiCalculating Flow Through An Orifice Using ASME MFC-3M-1989 and Irrecoverable Pressure Drop Equationsmajmor-1Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture No.17 Binary Phase DiagramsDocument16 paginiLecture No.17 Binary Phase DiagramsNorma Luzmila Chambilla FirataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geothermal Steam Table 7Document11 paginiGeothermal Steam Table 7Didik HartadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ou3 2019 IDocument291 paginiOu3 2019 IElizabeth Ttito NuñezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dashboard My Courses CHEM1302-4078 Discussion and Review Questions Chapter 10: (Gases) Review QuestionsDocument6 paginiDashboard My Courses CHEM1302-4078 Discussion and Review Questions Chapter 10: (Gases) Review QuestionsRola FikriÎncă nu există evaluări
- % Mole: Gas Properties Calculation SheetDocument6 pagini% Mole: Gas Properties Calculation Sheetzsmith0% (1)
- Evaparation PDFDocument7 paginiEvaparation PDFG. Somasekhar SomuÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Kinetic Theory of Gases - 231221 - 212353Document4 pagini13 Kinetic Theory of Gases - 231221 - 212353Shlok MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO 14532 - 2014 (En), Natural Gas - Vocabulary PDFDocument1 paginăISO 14532 - 2014 (En), Natural Gas - Vocabulary PDFDAYAMOY APLÎncă nu există evaluări
- R5210106 Fluid MechanicsDocument1 paginăR5210106 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week One Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowerDocument2 paginiWeek One Homework Problems: Fundamentals of ! Fluid PowertprakashtceÎncă nu există evaluări