Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Unit 9 Process 2
Încărcat de
Aryatirta PredanaDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit 9 Process 2
Încărcat de
Aryatirta PredanaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit 9 Process 2 Actions in Sequence
Section 1 Presentation
1. Look and read:
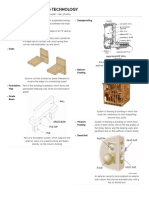
Assembly sequence of a prefabricated building.
The sequence is divided into four stages or phases:
Phase 1
Ground is excavated.
Concrete foundations are constructed.
Column base plates are fixed.
Steel Columns are erected.
Event 1 Initially, the ground is excavated.
First,
Event 2 Then, the concrete foundations are constructed.
Event 3 Later, the column base plates are fixed.
Subsequently,
Event 4 Finally, the steel columns are erected.
Now look at the drawings of the next three stages and make statements about the
sequence of events in phases 2,3 and 4.
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 1 of 13
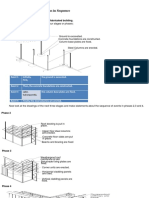
Phase 2
Roof decking is put in
place.
Upper floor steel columns
are erected.
Concrete floor slabs are put
in place.
Beams and bracing are fixed
Phase 3
Weatherproof roof
membrane is laid.
Balustrade fixing plates are
fixed.
Corner units are erected.
Horizontal cladding panels
are fixed.
Vertical cladding panels are
fixed.
Phase 4
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 2 of 13
2. Read these questions:
Why are the upper floor steel columns erected before the roof decking has
been put in place?
Why is the roof decking put in place after the upper floor steel columns have
been erected?
Now read the answer:
Because the roof decking requires the upper floor steel columns to support it.
Look at the drawings for phases 1, 2, 3 and 4, and make similar questions to
which these are the answers:
a. Because the concrete foundations require solid ground to support them.
b. Because the column base plates need a flat rigid surface to support them.
c. Because the steel columns transmit their loads through them to the
foundations.
d. Because the concrete floors are supported by the beams.
e. Because the weatherproof membrane is laid over the balustrade fixing
plates.
f. Because the horizontal cladding panels are fixed to the corner units.
g. Because the vertical cladding panels are fixed to the horizontal cladding
panels.
h. Because the workmen require access to the ceiling void to install the
services.
i. Because the partitions are fixed to the suspended ceilings.
3. Identify the part of the building or the phase of the assembly sequence
described in these sentences:
a. This cannot be put in place until the upper floor steel columns have been
erected.
b. Before fixing these, the workmen erect the corner units.
c. During this phase the beams and bracing are fixed.
d. The workmen fix these after constructing the concrete foundations.
e. The electric wiring is installed during this phase.
f. When balustrade fixing plates have been fixed, the workmen can start
laying this.
4. Read this description of phase 1 of the assembly sequence:
Having completed the preparation of the site, the workmen begin the initial
stage. This includes excavating the ground, constructing the concrete
foundations, fixing the column base plates and erecting the steel columns. The
workmen begin by excavating the ground. This precedes the constructing of
the concrete foundations because they require solid ground to support them.
This is followed by the fixing of the column base plates. Finally, the steel
columns are erected.
Now use it as a model to write similar descriptions or phases 2, 3, and 4.
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 3 of 13
Section 2 Development
5. Look and read:
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 4 of 13
Trade: steel erectors Trade: cladding fixer
Job: erecting the steelwork Job: fixing the cladding
Weeks working: 9 to 15 Weeks working: 16 to 30
Trade: bricklayer
Job: building the brickwork
Weeks working: 13 to 21
1. During weeks 13, 14 and 15 the steel erectors work -
From the beginning of week 13 to the end of week 15
simultaneously with the bricklayers.
at the same time as
2. While the former erect the steelwork, the latter build the brickwork.
3. As soon as the steel erectors have finished, the cladding fixers begin.
Immediately after
Use the bar chart to help you label the following drawings. Then make similar
paragraphs:
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 5 of 13
a. Trade: ___________ Trade: ____________
Job : Job: ..
Weeks working: Weeks working: .
Trade: ___________
Job: .
Weeks working: ..
b. Trade: ___________ Trade: ____________
Job : Job: ..
Weeks working: Weeks working: .
Trade: ___________
Job: .
Weeks working: ..
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 6 of 13
c. Trade: ___________
Job :
Weeks working:
Trade: ____________
Trade: ___________ Job: ..
Job: . Weeks working: .
Weeks working: ..
d. Trade: ___________
Job :
Weeks working:
(four weeks later)
Trade: ___________ Trade: ____________
Job: . Job: ..
Weeks working: .. Weeks working: .
6. Read this:
While the steelwork is being erected, some of the brickwork is built.
Now look at the bar chart and make similar sentences.
7. Complete these sentences with the name of a building trade:
a. The __________ finish just before the plumber start.
b. The .... should finish by the end of week 40.
c. The __________ _________ work until the end of week 30.
d. The ___________ work up to the end of week 50.
e. The _______ ________ should finish no later then the end of week 8.
Now make similar sentences.
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 7 of 13
8. Read this:
During building construction, several things went wrong so there are several
changes to be made to the bar chart in exercise 5. Here is a description of what
happened: Excavation was delayed for two weeks because the excavator broke
down. Therefore the machine driver could not start work until week 3. As the
steel erectors had to wait until the machine driver had completed their work,
they were also delayed by two weeks. Consequently, the cladding fixers could
not start until week 17. Bricks were in short supply during week 15 to 20 and
this resulted in the bricklayer working three weeks longer than expected. So
the plumbers and the roofing contractor started three weeks later. In week 30
the joiners went on strike which was settled after one week. However, this
meant both the carpenters and the glaziers started one week late. The wrong
paint was delivered to the decorators, which delayed them by one week, but by
putting on extra men the building was completed on schedule.
Now draw a new bar chart using the information in the passage.
9. Make a list of other things that could go wrong on a building site. Say
when they might occur and how they could affect the time schedule:
Section 3 Reading
10. Read this:
When an architect receives a commission for a building, he meets the
client and discusses his requirements. After visiting the site, the architect
draws up preliminary plans and, together with a rough estimate of the cost,
submit them to the client for his approval. If the client suggests changes, the
architect incorporates them into the final design which shows the exact
dimension of every part of the building. At this stage, several building
contractors are invited to bid for the job of constructing the building. When
they submit their tenders or prices, the architect assists his client in selecting
the best one and helps him to draw up a contract between the client and the
contractor.
Work now starts on the building. As construction proceeds, the architect
makes periodic inspections to make sure that the building is being constructed
according to his plans and that the materials specified in the contract are being
used. During the building period, the client pays the bills from the contractor.
Subsequently, the contractor completes the building and the client occupies it.
For six months after completion there is a period known as the defects
liability period. During this period, the contractor must correct any defects
that appear in the fabric of the building. Finally, when all the defects have
been corrected, the client takes full possession of the building.
Now find a word or an expression in the passage which means:
a. to be given the job of designing a building
b. to offer to a client for his consideration
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 8 of 13
c. to combine into a whole
d. to offer to do some work at a certain price.
e. to look at the building work in detail at regular intervals.
f. named or described exactly.
g. an interval of time after the building has been finished during
which the contractor is responsible.
h. to have complete ownership of the building.
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 9 of 13
11. Complete this flow diagram:
CLIENT ARCHITECT
appoints an architect a). for a building
gives architect his visits c). ..
b). .
approves e). . draws up d).
f). . them into
suggests the final design
changes
CONTRACTOR
chooses a contractor submits tender assists his client in
selecting a g). _____
signs a contract signs a contract
with the j). ______ with the i). ____ helps clients h). ....
start work on
k). ...
pay m). submits l). .. makes n). ..
from contractor to client
p). ..the building o). .... the building make sure that the
building is
completed according
to the contract.
r). of corrects defect in the
the building building during the
q). ..
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 10 of 13
Section 4 Revision
12. Look at this diagram of a prefabricated building:
Ask and answer question like this:
Example: Why is the steel frame erected before the wall planks have been
fixed?
Because the wall planks are supported by the steel frame.
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 11 of 13
13. Look at these drawings of the same building:
Make sentences saying what the dimensions marked on the drawings are:
Example : The floor to ceiling height is 2.700 mm.
14. Read this:
The external walls are made up of brick cladding, wall planks, windows,
doors, heads and sills, stanchion casings and inner lining panels. While the
steel frame is being erected, the wall planks and floor units are fixed. At the
same time, the stanchions are enclosed in casings which serve the function of
resisting fire. The precast concrete floor units are capable of carrying load of
up to 5 kN/sq m. The wall planks are design to be weather proof and to
support the outer cladding. The aluminium heads, sills and windows are then
fixed from inside the building. After this, the 900 mm and 1.800 mm wide
external doors are installed. These doors are either aluminium framed and pre-
glazed or hard wood framed and glazing is done on site. Finally, the internal
sills and lining panels are installed. These form a cavity for the heating and
electrical services. A grill underneath the sill, together with an air intake at
skirting level, enables air to circulate up past the finned heating element. The
lining panels are capable of being removed to give access to the services.
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 12 of 13
Now label this drawing:
Section through the external wall
15. Write a short passage giving the sequence of events in constructing the
external walls only.
16. Now complete the following sentences to match the idea in the brackets:
a. The external walls (structure)
b. The wall planks and floor units ..(time)
c. The stanchion casings (function)
d. The precast concrete floor units .(ability)
e. The wall planks ..(function)
f. The external doors .(measurement)
g. The glazing of the hardwood framed doors (location)
h. The internal sills and lining panels .(function)
i. The grill .. (location)
j. The grill and air intake .(function)
k. The lining panels ..(ability)
17. Answer these questions:
a. Why do you think the aluminium heads, sills and windows are designed to
be fixed from inside the building?
b. What is the function of the fins on the heating element?
c. Are the aluminium framed windows glazed on site?
d. What are the advantages of using aluminium instead of steel to make the
windows?
e. What other types of cladding could be used instead of brick?
f. What could this type of building be used for?
Unit 9: Process 2 Actions in Sequence Page 13 of 13
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Theory of Structures 2 ReferenceDocument40 paginiTheory of Structures 2 ReferenceOmar ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Santulan vs. Executive Secretary GR No. L-28021, December 15Document24 paginiSantulan vs. Executive Secretary GR No. L-28021, December 15Juris MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIVL1014 - Basic Drawing Skills Lecture Part 1Document61 paginiCIVL1014 - Basic Drawing Skills Lecture Part 1Sauting LamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical SpecificationsDocument47 paginiTechnical SpecificationsHarold Abubo HaberÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sequence of Work in Building ConstructionDocument8 paginiSequence of Work in Building ConstructionPurushottam PoojariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Detailing of Reinforced Concrete Structures in Seismic Zone-Baljeet SirDocument35 paginiDetailing of Reinforced Concrete Structures in Seismic Zone-Baljeet Siranuragcool062Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural ReviewerDocument18 paginiStructural ReviewerjericoÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Awe-Inspiring Place: Sydney's Punchbowl Mosque Showcases The Architectural Flexibility of ConcreteDocument4 paginiAn Awe-Inspiring Place: Sydney's Punchbowl Mosque Showcases The Architectural Flexibility of ConcreteShajahan AsanarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ?bricksDocument12 pagini?bricksRashmi HazarikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.Engineering-The Effect of Seawater On Shrinkage Properties of Concrete-Amusan Grace ModupeolaDocument12 pagini1.Engineering-The Effect of Seawater On Shrinkage Properties of Concrete-Amusan Grace ModupeolaImpact JournalsÎncă nu există evaluări
- BUILDING TECHNOLOGY STUDYDocument12 paginiBUILDING TECHNOLOGY STUDYChristian James TuazonÎncă nu există evaluări
- C823 3 Doc MST Mec 004Document23 paginiC823 3 Doc MST Mec 004721917114 47Încă nu există evaluări
- Bai On Tap Cho HS 12 Khoi D, A1-UnprotectedDocument60 paginiBai On Tap Cho HS 12 Khoi D, A1-Unprotecteddinh hai trinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam Preparation Associate Member Solutions 20150710Document10 paginiExam Preparation Associate Member Solutions 20150710ZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Architectural Theory GuideDocument29 paginiArchitectural Theory GuideClarissa AricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.01 DPR Pmgsy 3 CC BM PMC Seal Kumher Paprera Upto Chitokri Mor Via Khanswara Block Kumher 29.12.19Document293 pagini5.01 DPR Pmgsy 3 CC BM PMC Seal Kumher Paprera Upto Chitokri Mor Via Khanswara Block Kumher 29.12.19Roopesh ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- q4 2009 AprilDocument6 paginiq4 2009 Aprilfloi dÎncă nu există evaluări
- BC PPT II 3 MasonryDocument54 paginiBC PPT II 3 MasonryAJAY J BITÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexural Analysis of Beams: Concrete Structures DesignDocument24 paginiFlexural Analysis of Beams: Concrete Structures DesignAdam VinsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ccaaguide2003 t49 Res Floors Web TBRDocument47 paginiCcaaguide2003 t49 Res Floors Web TBRLaura KinnearÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Tectnology Answer SheetDocument119 paginiBuilding Tectnology Answer SheetClarissa AricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Powerpoint Presentation Road Pavement Failure (Coren Assembly) Revised FinalDocument110 paginiPowerpoint Presentation Road Pavement Failure (Coren Assembly) Revised FinalAdegboyega AdeyemiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Outline of Earthquake Provisions in The Japanese Building CodesDocument39 paginiOutline of Earthquake Provisions in The Japanese Building CodesBrian TaylorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Technique L01Document26 paginiConstruction Technique L01khushbu naqviÎncă nu există evaluări
- History, Answer, Quiz 03Document3 paginiHistory, Answer, Quiz 03JARMRAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 2 Measurement Suspended Floor SlabDocument13 paginiTopic 2 Measurement Suspended Floor SlabAbdul Muhaimin Zainol Abidin88% (8)
- Introduction To Composite ConstructionDocument40 paginiIntroduction To Composite Constructionrameshbabu_1979100% (1)
- Preboard Examtapp 2011Document16 paginiPreboard Examtapp 2011jezelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 LocationDocument10 paginiUnit 2 LocationCahya pramanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAFE TutorialDocument112 paginiSAFE Tutorialkevinvnn80% (5)
- Applications of Sustainable Post-Tensioned Concrete SlabsDocument12 paginiApplications of Sustainable Post-Tensioned Concrete Slabsmohamed.s.elsayedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aci 544.1R-96Document66 paginiAci 544.1R-96Tran Tuan KietÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of ConstructionDocument78 paginiPrinciples of ConstructionY SAHITHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of FormworkDocument12 paginiTypes of FormworkAnonymous LiddTaTaZTÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lintel and ArchesDocument64 paginiLintel and ArchesRohit KhannaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 Composite Beam Section PropertiesDocument13 pagini2.1 Composite Beam Section PropertiesCarlo Gimarino SalazarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 2 BEAM COLUMN IN FRAMES PDFDocument28 paginiModule 2 BEAM COLUMN IN FRAMES PDFkarthiksamp100% (1)
- Solution of Triangle: Sine RuleDocument41 paginiSolution of Triangle: Sine RuleMuraliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive Voice WorksheetDocument1 paginăPassive Voice Worksheetmai100% (1)
- Some Innovative Steel StructuresDocument12 paginiSome Innovative Steel Structuresgurdan100% (2)
- Study On Behavior of CFST Columns Under Axil Compression and Anaysis by AbacusDocument13 paginiStudy On Behavior of CFST Columns Under Axil Compression and Anaysis by AbacusVishwa M swamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.civil Engineering Maintenance Introductory LectureDocument22 pagini1.civil Engineering Maintenance Introductory LectureIssak MohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soal UAS Bhs Inggris XII Mia & XII IIS 2021Document9 paginiSoal UAS Bhs Inggris XII Mia & XII IIS 2021Roby SuhendriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Design and Construction of The Foundation of Tokyo Sky TreeDocument12 paginiStructural Design and Construction of The Foundation of Tokyo Sky TreeKaung Htet100% (1)
- Steel Structures - I: B.E. (Civil Engineering) Sixth Semester (C.B.S.)Document16 paginiSteel Structures - I: B.E. (Civil Engineering) Sixth Semester (C.B.S.)Pratik GhimireÎncă nu există evaluări
- FFT MegaCore FunctionDocument70 paginiFFT MegaCore FunctionRadu PetreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Bonding TechniquesDocument18 paginiTypes of Bonding TechniquesMahesh Ramteke100% (1)
- DSR - 2015-2016 PDFDocument61 paginiDSR - 2015-2016 PDFMoumi DharaÎncă nu există evaluări
- In Oita JapanDocument23 paginiIn Oita Japandeepak_2515Încă nu există evaluări
- Proprac ReportDocument201 paginiProprac ReportJames Jr BalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF Ansi s1260 2002 CompressDocument50 paginiPDF Ansi s1260 2002 CompressMark DingalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Note On Stability of StructuresDocument6 paginiNote On Stability of Structurespanos2244662864100% (1)
- IABSE IASS2011 Davis Rippmann Pawlofski BlockDocument8 paginiIABSE IASS2011 Davis Rippmann Pawlofski Blockdenis1808scribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basilica of Bom JesusDocument5 paginiBasilica of Bom JesusJean BonaparteÎncă nu există evaluări
- HistoryDocument7 paginiHistorymhaye1405746Încă nu există evaluări
- Acm FormatDocument2 paginiAcm FormatMico Ganzon0% (1)
- Buiding Services Compass SurveyDocument578 paginiBuiding Services Compass SurveyAnonymous jphuejJIYyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of RC ShellsDocument9 paginiDesign of RC Shellscacrcarlos100% (1)
- Hangin CalculationDocument85 paginiHangin CalculationAlbert LuckyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Insulation Modeling Using Group Search OptimizationDocument10 paginiThermal Insulation Modeling Using Group Search OptimizationMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nottingham Contemporary, Caruso ST JohnDocument11 paginiNottingham Contemporary, Caruso ST JohnJ100% (1)
- Building construction sequenceDocument15 paginiBuilding construction sequenceRama MahayanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bab Iv KPDocument35 paginiBab Iv KPMuhammad Nur ArifinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intern PresentationDocument24 paginiIntern PresentationEstifanos SeidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training Report at Al Shakhsheer Company: Hashemite University College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentDocument21 paginiTraining Report at Al Shakhsheer Company: Hashemite University College of Engineering Civil Engineering DepartmentSalah100% (1)
- CM Exercise 4Document2 paginiCM Exercise 4Ahmed100% (1)
- Unit 3 StructureDocument9 paginiUnit 3 StructurePrita Devi Widiyani100% (1)
- RetrofittingDocument4 paginiRetrofittingReeshi Raj PandeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tunnel Form ConstructionDocument11 paginiTunnel Form Constructionmohammed alzanganaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 Tambahan ASST - ArchDocument10 pagini13 Tambahan ASST - ArchAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 Tambahan ASST - InfluencelineDocument22 pagini15 Tambahan ASST - InfluencelineAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SA03R Truss Analysis - Method of JointsDocument15 paginiSA03R Truss Analysis - Method of JointsAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14 Tambahan ASST - CableDocument9 pagini14 Tambahan ASST - CableAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARMAPaper347 BewickKaiserValleyDocument11 paginiARMAPaper347 BewickKaiserValleyAjay SenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 8 Process 1Document8 paginiUnit 8 Process 1Aryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Speaking Module From Miss MelaDocument40 paginiSpeaking Module From Miss MelaAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design BracingDocument1 paginăDesign BracingAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biological Diversity ConceptDocument1 paginăBiological Diversity ConceptAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 7 Measurement 4Document8 paginiUnit 7 Measurement 4Aryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Properties and ShapeDocument9 paginiUnit 1 Properties and ShapeAryatirta Predana100% (1)
- Denpasar Try Out Serentak 320 Kota Primagama 12 IpaDocument1 paginăDenpasar Try Out Serentak 320 Kota Primagama 12 IpaAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Bantu MathDocument1 paginăWeb Bantu MathAryatirta PredanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of Bundelkhand Expressway Pro Ject: 30 Days Industrial Training atDocument98 paginiDevelopment of Bundelkhand Expressway Pro Ject: 30 Days Industrial Training atAditya KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report of Bilal123Document45 paginiReport of Bilal123Naiyer AzamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Sheet TERACOL TDocument2 paginiTechnical Sheet TERACOL TViktorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep BeamsDocument11 paginiDeep BeamsArcon Solite BarbanidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schwing SetterDocument6 paginiSchwing Settergsm.nkl60490% (2)
- Implementation of Plastic Waste in Manufacturing of Paving Blocks For Different ShapesDocument2 paginiImplementation of Plastic Waste in Manufacturing of Paving Blocks For Different ShapesEditor IJTSRDÎncă nu există evaluări
- SNI-03-6652-2002 Protection Against Lightning StrikesDocument48 paginiSNI-03-6652-2002 Protection Against Lightning StrikesShubham LeleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bamboo Reinforcement in ConcreteDocument20 paginiBamboo Reinforcement in ConcreteRakesh K BasapurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repair and Maintenance of DPWH BuildingDocument28 paginiRepair and Maintenance of DPWH BuildingJulius BatiloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Differences Between ACI and BREDocument2 paginiDifferences Between ACI and BREMbayo David GodfreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NA To Sls en 1992-1-1Document24 paginiNA To Sls en 1992-1-1Shan Sandaruwan AbeywardeneÎncă nu există evaluări
- BOQ-CIVIL Sample LucknowDocument25 paginiBOQ-CIVIL Sample LucknowSantosh Thakur100% (1)
- Prefabrication Construction GuideDocument51 paginiPrefabrication Construction GuideSadia HusainÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Performances Study On GGBS With Alccofine - Based High Strength Self-Compacting ConcreteDocument5 paginiA Performances Study On GGBS With Alccofine - Based High Strength Self-Compacting ConcreteInternational Journal of Innovative Science and Research TechnologyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Construction Concepts and Terms CompilationDocument9 paginiConstruction Concepts and Terms CompilationJohn RoaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbon Dioxide Reduction Potential in The Global Cement Industry by 2050Document10 paginiCarbon Dioxide Reduction Potential in The Global Cement Industry by 2050Anonymous NxpnI6jCÎncă nu există evaluări
- CONCRETE MIX DESIGN - LectureDocument32 paginiCONCRETE MIX DESIGN - LectureboyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ravi Infrabuild Project Pvt. LTDDocument15 paginiRavi Infrabuild Project Pvt. LTDRavi InfraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment IDocument2 paginiAssignment IPratik SolankiÎncă nu există evaluări
- KP 200 PDFDocument2 paginiKP 200 PDFrangass70100% (2)
- 59 Uplift CalculationsDocument2 pagini59 Uplift CalculationsMano HarÎncă nu există evaluări