Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Example 2: Solution M/EI Diagram
Încărcat de
Ramona LeTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Example 2: Solution M/EI Diagram
Încărcat de
Ramona LeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
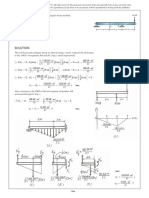
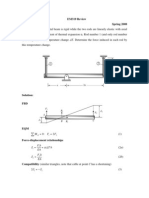
EXAMPLE 2
6 kN/m
Determine the deflection at point C of the beam shown in Fig. 821a.
E = 200 GPa, I = 250(106) mm4.
A
C
B SOLUTION
8m 8m
24 kN M/EI Diagram. As shown in Fig. 821b, this diagram consists of a
72 kN
triangular and a parabolic segment.
(a)
Elastic Curve. The loading causes the beam to deform as shown in
Fig. 821c. We are required to find C. By constructing tangents at A,
M
___ B (the supports), and C, it is seen that C = tC>A - . However,
can be related to tB>A by proportional triangles, that is, >16 = tB>A>8
EI
or = 2tB>A. Hence
8m 8m
C = tC>A - 2tB>A (1)
x
Moment-Area Theorem. We will apply Theorem 2 to determine
192
___ tC>A and tB>A. Using the table on the inside back cover for the
EI
(b)
parabolic segment and considering the moment of the M/EI diagram
between A and C about point C, we have
192 kN # m
tan A
tC>A = c 18 m2 d c 18 m2a- bd
3 1
4 3 EI
192 kN # m
+ c 18 m2 + 8 m d c 18 m2a- bd
tan B tB/A 1 1
A tC/A
B 3 2 EI
C 11 264 kN # m3
= -
EI
C
tan C
(c) The moment of the M/EI diagram between A and B about point B gives
192 kN # m 2048 kN # m3
8
tB>A = c 18 m2 d c 18 m2a- bd = -
1 1
Fig. 821
3 2 EI EI
Why are these terms negative? Substituting the results into Eq. (1) yields
11 264 kN # m3 2048 kN # m3
C = - - 2a- b
EI EI
7168 kN # m3
= -
EI
Thus,
- 7168 kN # m3
C =
[20011062 kN>m2][25011062110-122 m4]
= - 0.143 m Ans.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Quiz3 - CVEN220 SolutionsDocument4 paginiQuiz3 - CVEN220 SolutionsRamo comÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flexibility Beam FrameDocument7 paginiFlexibility Beam FrameMohasin KamalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 411 Lecture 03 - Moment AreaDocument27 paginiCE 411 Lecture 03 - Moment AreaNophiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Analysis Problems and SolutioDocument22 paginiStructural Analysis Problems and SolutioAlexander Appiah OkoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Continuous Beam PDFDocument12 paginiContinuous Beam PDFRupakDasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2-FM Beam Ex 6Document1 pagină2-FM Beam Ex 6Olawuyi OluwatamiloreÎncă nu există evaluări
- SFD and BMD 19 - 07 - 2021Document5 paginiSFD and BMD 19 - 07 - 2021odubade opeyemi100% (1)
- CH 5 - Beams and Frames - Part 2Document25 paginiCH 5 - Beams and Frames - Part 2Fawzia HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GATE Civil Engineering Topic Wise Practice Tests - 165Document1 paginăGATE Civil Engineering Topic Wise Practice Tests - 165chinmay naikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recitation 4 2018-2019 SpringDocument12 paginiRecitation 4 2018-2019 SpringCemre CaglarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eas254 - SDM Part 2 - ExamplesDocument15 paginiEas254 - SDM Part 2 - ExamplesNasrulÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1553412835312-CQPP Test Series Question With Solution (Test No-02)Document52 pagini1553412835312-CQPP Test Series Question With Solution (Test No-02)Aditya SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDF Libro HibbelerDocument3 paginiPDF Libro Hibbelergeiser005Încă nu există evaluări
- 5.2 Area Moment MethodDocument15 pagini5.2 Area Moment MethodRemylin De GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Analysis Problems and Solutio PDFDocument22 paginiStructural Analysis Problems and Solutio PDFjay balagotÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIS VTUPulse - Com ModDocument10 paginiAIS VTUPulse - Com Modnaga rajÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnSys Solution For Mechanics and Heat Transfer ProblemsDocument31 paginiAnSys Solution For Mechanics and Heat Transfer ProblemsAmod PantheeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moment Distribution Method With Side SwayDocument26 paginiMoment Distribution Method With Side SwayMaithri V BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE2011 - Structural Analysis IDocument10 paginiCE2011 - Structural Analysis IRashmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Civil Engineering: 12 KN/M CDocument3 paginiDepartment of Civil Engineering: 12 KN/M Crfvz6sÎncă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main 30-01-2024 (Morning Shift) : QuestionsDocument40 paginiJEE Main 30-01-2024 (Morning Shift) : QuestionsMahir KachwalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit Load Method ProblemsDocument4 paginiUnit Load Method ProblemsRithuparna RÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Truss Member in CompressionDocument10 paginiDesign Truss Member in CompressionVSMS8678Încă nu există evaluări
- Problema 3Document8 paginiProblema 3andersson rondinel cartolinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eas254 MDM Part 2 - ExampleDocument8 paginiEas254 MDM Part 2 - ExampleNasrulÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Law of CosinesDocument3 paginiThe Law of Cosinesmaged wagehÎncă nu există evaluări
- 201718-1 SPACE KL - Test 2 With AnswerDocument7 pagini201718-1 SPACE KL - Test 2 With AnswerHadirah HanafiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Discussion: Week 2: Physics 1C: Electrodynamics, Optics, and Special Relativity Fall 2015Document17 paginiDiscussion: Week 2: Physics 1C: Electrodynamics, Optics, and Special Relativity Fall 2015Nostalgia GreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CV3101 Part 2 - (To Students) Tutorial (18 Sep 2012) PDFDocument14 paginiCV3101 Part 2 - (To Students) Tutorial (18 Sep 2012) PDFSteven KuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Material ComplementarDocument29 paginiMaterial ComplementarAlexander Quispe CaceresÎncă nu există evaluări
- EM AT-II Question SET-IDocument3 paginiEM AT-II Question SET-IMECH HODÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element MethodDocument1 paginăFinite Element Methodravikaran tripathiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example 10.13: Indeterminate Structures-Compatibility Methods 343Document3 paginiExample 10.13: Indeterminate Structures-Compatibility Methods 343Suraj KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Choice: PattersonDocument14 paginiMultiple Choice: PattersonOscar PillÎncă nu există evaluări
- M - P Diagram and Design of Column: Earthquake Engineering Management Master ProgramDocument22 paginiM - P Diagram and Design of Column: Earthquake Engineering Management Master ProgramAnggi Novi AndriÎncă nu există evaluări
- If in The Given Figure I 0.25 Amp, Then The Value R Will BeDocument3 paginiIf in The Given Figure I 0.25 Amp, Then The Value R Will BeP HananÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Sc. Eng. Honours Degree: Sri Lanka Institute of Information TechnologyDocument6 paginiB.Sc. Eng. Honours Degree: Sri Lanka Institute of Information TechnologyramÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 201 - Mechanics of Materials Tute 1Document2 paginiCE 201 - Mechanics of Materials Tute 1ThevinduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solutions (8th Ed Structural Analysis) - 10.39 - 10.51Document11 paginiSolutions (8th Ed Structural Analysis) - 10.39 - 10.51Gustavo Bicudo LetcooviskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- (2015 12 8) 高等結構學第二次期中考 PDFDocument2 pagini(2015 12 8) 高等結構學第二次期中考 PDF侯柏毅Încă nu există evaluări
- EM319 Review Spring 2008: T. Determine The Force Induced in Each Rod byDocument10 paginiEM319 Review Spring 2008: T. Determine The Force Induced in Each Rod byTyler MabryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Esplana SteelDesignDocument1 paginăEsplana SteelDesignNaigell SolomonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Statically Determinate Beams2Document11 pagini3 Statically Determinate Beams2muhammadbagas505Încă nu există evaluări
- Class 11-Phy-Thermodynamics-NumericalsDocument11 paginiClass 11-Phy-Thermodynamics-Numericalss.karthick5583Încă nu există evaluări
- CE 201 - Mechanics of Materials Tute 4Document2 paginiCE 201 - Mechanics of Materials Tute 4ThevinduÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theorem of Three MomentsDocument25 paginiTheorem of Three Momentsprajapatisid1965Încă nu există evaluări
- Isostatic Structures: 1.1 Exercise N. 1Document13 paginiIsostatic Structures: 1.1 Exercise N. 1EvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- USD Analysis in Beams (New Way)Document7 paginiUSD Analysis in Beams (New Way)Bry RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nozzle NumericalDocument9 paginiNozzle Numericalsunita.storage01Încă nu există evaluări
- Influence Lines & CablesDocument26 paginiInfluence Lines & CablesArah Louise ApostolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prestressed General Principles2Document5 paginiPrestressed General Principles2Jay D MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theory - Module 3Document11 paginiTheory - Module 3Darish TrinidadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mass Moment Inertia LabDocument5 paginiMass Moment Inertia LabVinay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsDe la EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesDe la EverandElectrical and Electronic Principles 3 Checkbook: The Checkbook SeriesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Handbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersDe la EverandHandbook of Railroad Construction; For the use of American engineersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Battery MaterialsDe la EverandAdvanced Battery MaterialsChunwen SunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundations of Electrical Engineering: Fields—Networks—WavesDe la EverandFoundations of Electrical Engineering: Fields—Networks—WavesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reviews in Computational ChemistryDe la EverandReviews in Computational ChemistryAbby L. ParrillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cantilever Slab DesignDocument18 paginiCantilever Slab DesignSarah Huff67% (9)
- 2 Research in 20th CenturyDocument24 pagini2 Research in 20th CenturyRamona LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 7Document39 paginiChapter 7Ramona LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S1644966512000362 MainDocument15 pagini1 s2.0 S1644966512000362 MainRamona LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ovality Stress TubesDocument16 paginiOvality Stress TubesRamona Le100% (1)
- Bolton 1986 - The Strength and Dilatancy of SandsDocument14 paginiBolton 1986 - The Strength and Dilatancy of SandsCristian SandovalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2009 TPC 333Document8 pagini2009 TPC 333Ramona LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viewcontent CgiDocument89 paginiViewcontent CgiRamona LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geological Hazard Assessment in The Construction Site of LNG Pipeline Project 2009Document10 paginiGeological Hazard Assessment in The Construction Site of LNG Pipeline Project 2009Ramona LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Research in 20th CenturyDocument24 pagini2 Research in 20th CenturyRamona LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Research in 20th CenturyDocument24 pagini2 Research in 20th CenturyRamona LeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subsynchronous Resonance in Wind Farms PHDDocument325 paginiSubsynchronous Resonance in Wind Farms PHDTibin JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logical Equivalences: Tautology: Self Contradiction/ ContradictionDocument7 paginiLogical Equivalences: Tautology: Self Contradiction/ ContradictionAbdul BasitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harold R. Jacobs - Elementary Algebra-W. H. Freeman (1979)Document904 paginiHarold R. Jacobs - Elementary Algebra-W. H. Freeman (1979)Hinduism Ebooks100% (2)
- Torsion of Non-Circular Bars - Saint Venants - Prandle MethodDocument40 paginiTorsion of Non-Circular Bars - Saint Venants - Prandle MethodMathew JohnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Long Test 1 - Grade 7Document2 paginiLong Test 1 - Grade 7katherine corvera100% (3)
- Controle de Posià à o Motor CCDocument20 paginiControle de Posià à o Motor CCMatheus MaiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- D4304-Syllabus-Neural Networks and Fuzzy SystemsDocument1 paginăD4304-Syllabus-Neural Networks and Fuzzy Systemsshankar15050% (1)
- Microecon Subject GuideDocument45 paginiMicroecon Subject GuideJoshua LamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Composite Materials Assignment 1Document2 paginiComposite Materials Assignment 1Danielle Wagner0% (1)
- GR 4 CH 9 Reteach AkDocument8 paginiGR 4 CH 9 Reteach AkCarlitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4BCh06 (Basic Properties of Circles 1)Document37 pagini4BCh06 (Basic Properties of Circles 1)api-19856023Încă nu există evaluări
- Product Metrics 2023Document36 paginiProduct Metrics 2023leveke5755Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4-Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: A Managerial Planning ToolDocument23 paginiChapter 4-Cost-Volume-Profit Analysis: A Managerial Planning ToolRod100% (1)
- Pavlostathis, Gossett - 1986 - A Kinetic Model For Anaerobic Digestion of Biological Sludge-AnnotatedDocument12 paginiPavlostathis, Gossett - 1986 - A Kinetic Model For Anaerobic Digestion of Biological Sludge-AnnotatedMRifqiWibiyanto100% (1)
- Interpretar RegresionDocument5 paginiInterpretar Regresionpezamarillo-1Încă nu există evaluări
- (Bart M. Ter Haar Romeny) Front-End Vision and Multi-Scale Image Analysis - Multi-Scale Computer Vision Theory and Applications (2003)Document470 pagini(Bart M. Ter Haar Romeny) Front-End Vision and Multi-Scale Image Analysis - Multi-Scale Computer Vision Theory and Applications (2003)mvannierÎncă nu există evaluări
- API Spec 5a5Document23 paginiAPI Spec 5a5bmkale0% (1)
- Mathematics: For FreeDocument967 paginiMathematics: For Freefaizan khalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zhi Dong Bai, Random Matrix Theory and Its ApplicationsDocument174 paginiZhi Dong Bai, Random Matrix Theory and Its ApplicationsanthalyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.profit MaximizationDocument14 pagini4.profit MaximizationRamyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BK Birla Institue of Engineering & Technolgy (Bkbiet) Dbms Lab Sheet ViDocument5 paginiBK Birla Institue of Engineering & Technolgy (Bkbiet) Dbms Lab Sheet ViVipin SaraogiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics For Social Workers 8th Edition Weinbach Test BankDocument5 paginiStatistics For Social Workers 8th Edition Weinbach Test Bankjerryperezaxkfsjizmc100% (11)
- Tap FSMDocument39 paginiTap FSMMadhukumar KsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Boolean AlgebraDocument21 pagini2 Boolean AlgebraAKASH PALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thesis 1Document10 paginiThesis 1miknayrb galdianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modu 18 - FaepDocument60 paginiModu 18 - FaepHAFIDY RIZKY ILHAMSYAHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Loss Functions For Image Restoration With Neural Networks: Hang Zhao, Orazio Gallo, Iuri Frosio, and Jan KautzDocument11 paginiLoss Functions For Image Restoration With Neural Networks: Hang Zhao, Orazio Gallo, Iuri Frosio, and Jan KautzStephen LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- EbnfDocument21 paginiEbnfIan ChuahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap5C 4pDocument10 paginiChap5C 4pMingdreamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alan TuringDocument10 paginiAlan TuringtomÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThesisDocument8 paginiThesisdereckg_2Încă nu există evaluări