Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Muscles of The Upper Limb 1 PDF
Încărcat de
Dejan Milenkovic0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
882 vizualizări12 paginiTitlu original
Muscles of the Upper Limb 1.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
882 vizualizări12 paginiMuscles of The Upper Limb 1 PDF
Încărcat de
Dejan MilenkovicDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 12
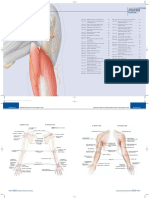
Muscles of the Upper Limb
Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery Notes
abductor pisiform base of the abducts the 5th deep branch of ulnar a. abductor digiti
digiti minimi proximal digit the ulnar nerve minimi, flexor
(hand) phalanx of digiti minimi
the 5th digit brevis, and
on its ulnar opponens
side digiti minimi
are located in
the hypothenar
compartment
of the hand
abductor flexor base of the abducts thumb recurrent superficial abductor
pollicis retinaculum proximal branch of palmar br. of pollicis brevis,
brevis , scaphoid, phalanx of median nerve the radial a. flexor pollicis
trapezium the first brevis, and
digit opponens
pollicis are
located in the
thenar
compartment
of the hand
abductor middle one- radial side abducts the radial nerve, posterior the tendons of
pollicis third of the of the base thumb at deep branch interosseous abductor
longus posterior of the first carpometacarpal a. pollicis longus
surface of metacarpal joint and extensor
the radius, pollicis brevis
interosseou make the
s lateral border
membrane, of the
mid-portion anatomical
of snuffbox
posterolater
al ulna
adductor oblique base of the adducts the ulnar nerve, deep palmar deep palmar
pollicis head: proximal thumb deep branch arterial arch arch and deep
capitate and phalanx of ulnar nerve
base of the the thumb pass between
2nd and 3rd the two heads
metacarpals of adductor
; transverse pollicis, which
head: shaft is in the
of the 3rd adductor-
metacarpal interosseous
compartment
anconeus lateral lateral side extends the nerve to interosseous none
epicondyle of the forearm anconeus, recurrent a.
of the olecranon from the radial
humerus and the nerve
upper one-
fourth of
1
the ulna
biceps short head: tuberosity flexes the musculocutane brachial a. a powerful
brachii tip of the of the forearm, flexes ous nerve supinator only
coracoid radius arm (long head), (C5,6) if the elbow is
process of supinates flexed
the scapula;
long head:
supraglenoi
d tubercle
of the
scapula
brachialis anterior coronoid flexes the forearm musculocutane brachial a., a powerful
surface of process of ous nerve radial flexor
the lower the ulna (C5,6) recurrent a.
one-half of
the
humerus
and the
associated
intermuscul
ar septa
brachioradial upper two- lateral side flexes the elbow, radial nerve radial although
is thirds of the of the base assists in recurrent a. brachioradialis
lateral of the pronation & is innervated
supracondyl styloid supination by the nerve
ar ridge of process of for extensors
the the radius (radial), its
humerus primary action
is elbow
flexion; the
neutral
position of this
muscle is half
way between
supination and
pronation
(elbow flexed,
thumb up)
coracobrachi coracoid medial side flexes and musculocutane brachial a. the
alis process of of the adducts the arm ous nerve musculocutane
the scapula humerus at (C5,6) ous nerve
mid-shaft passes through
the
coracobrachiali
s muscle to
reach the other
arm flexor
mm.(biceps
brachii and
brachialis)
deltoid lateral one- deltoid abducts arm; axillary nerve posterior the deltoid
2
third of the tuberosity anterior fibers (C5,6) from circumflex muscle is the
clavicle, of the flex & medially the posterior humeral a. principle
acromion, humerus rotate the arm; cord of the abductor of the
the lower posterior fibers brachial plexus arm but due to
lip of the extend & laterally poor
crest of the rotate the arm mechanical
spine of the advantage it
scapula cannot initiate
this action; it is
assisted by the
supraspinatus
m.
dorsal four base of the flex the ulnar nerve, dorsal and bipennate
interosseous muscles, proximal metacarpophalan deep branch palmar muscles;
(hand) each arising phalanx and geal joint, extend metacarpal remember
from two the extensor the proximal and aa. DAB & PAD -
adjacent expansion distal Dorsal
metacarpal on lateral interphalangeal interosseous
shafts side of the joints of digits 2- mm. ABduct
2nd digit, 4, abduct digits 2- and Palmar
lateral & 4 (abduction of interosseous
medial digits in the hand mm. ADduct -
sides of the is defined as then you can
3rd digit, movement away figure out
and medial from the midline where they
side of the of the 3rd digit) must insert to
4th digit cause these
actions
extensor lateral dorsum of extends the wrist; radial nerve radial a. works with the
carpi radialis supracondyl the third abducts the hand extensor carpi
brevis ar ridge of metacarpal radialis longus
the bone (base) and flexor
humerus carpi radialis in
(common abduction of
extensor the hand
tendon
extensor lower one- dorsum of extends the wrist; deep radial radial a. works with the
carpi radialis third of the the second abducts the hand nerve extensor carpi
longus lateral metacarpal radialis brevis
supracondyl bone (base) and flexor
ar ridge of carpi radialis in
the abduction of
humerus the hand
extensor common medial side extends the wrist; deep radial ulnar a. works with the
carpi ulnaris extensor of the base adducts the hand nerve flexor carpi
tendon & of the 5th ulnaris in
the middle metacarpal adduction of
one-half of the hand
the
posterior
border of
3
the ulna
extensor common joins the extends the deep radial interosseous extensor digiti
digiti minimi extensor extensor metacarpophalan nerve recurrent a. minimi
tendon digitorum geal, proximal appears to be
(lateral tendon to interphalangeal the ulnar-most
epicondyle the 5th digit and distal portion of
of the and inserts interphalangeal extensor
humerus) into the joints of the 5th digitorum
extensor digit
expansion
extensor common extensor extends the deep radial interosseous the extensor
digitorum extensor expansion metacarpophalan nerve recurrent a. expansion
tendon of digits 2-5 geal, proximal and posterior inserts via a
(lateral interphalangeal interosseous central band
epicondyle and distal a. on the base of
of the interphalangeal the middle
humerus) joints of the 2nd- phalanx, while
5th digits; extends lateral &
wrist medial slips
insert on the
distal phalanx
extensor interosseou its tendon extends the index deep radial posterior extensor
indicis s joins the finger at the nerve interosseous indicis is a
membrane tendon of metacarpophalan a deep forearm
and the the extensor geal, proximal extensor,
posterolater digitorum interphalangeal whereas
al surface of to the and distal extensor digiti
the distal second interphalangeal minimi is in
ulna digit; both joints the superficial
tendons layer of
insert into extensors
the extensor
expansion
extensor interosseou base of the extends the deep radial posterior the tendons of
pollicis s proximal thumb at the nerve interosseous extensor
brevis membrane phalanx of metacarpophalan a pollicis brevis
and the the thumb geal joint and abductor
posterior pollicis longus
surface of make the
the distal lateral border
radius of the
anatomical
snuffbox, in
which the
radial arterial
pulse can be
felt
extensor interosseou base of the extends the deep radial posterior the tendon of
pollicis s distal thumb at the nerve interosseous extensor
longus membrane phalanx of interphalangeal a pollicis longus
and middle the thumb joint hooks around
4
part of the the dorsal
posterolater radial tubercle;
al surface of it forms the
the ulna medial border
of the
anatomical
snuffbox, in
which the
radial arterial
pulse can be
felt
flexor carpi common base of the flexes the wrist, median nerve ulnar a. works with the
radialis flexor second and abducts the hand extensor carpi
tendon third radialis longus
from the metacarpals and brevis
medial mm. to abduct
epicondyle hand
of the
humerus
flexor carpi common pisiform, flexes wrist, ulnar nerve ulnar a. the ulnar nerve
ulnaris flexor hook of adducts hand passes between
tendon & hamate, and the two heads
(ulnar head) base of 5th of origin of the
from metacarpal flexor carpi
medial ulnaris m.
border of
olecranon
& upper 2/3
of the
posterior
border of
the ulna
flexor digiti hook of proximal flexes the ulnar nerve, ulnar a. flexor digiti
minimi hamate & phalanx of carpometacarpal deep branch minimi brevis,
brevis (hand) the flexor the 5th digit and abductor digiti
retinaculum metacarpophalan minimi, and
geal joints of the opponens
5th digit digiti minimi
are in the
hypothenar
compartment
of the hand
flexor posterior base of the flexes the median nerve ulnar a., ulnar nerve
digitorum border of distal metacarpophalan (radial one- anterior innervates the
profundus the ulna, phalanx of geal, proximal half); ulnar interosseous portion of
proximal digits 2-5 interphalangeal nerve (ulnar a. profundus that
two-thirds and distal one-half) acts on digits 4
of medial interphalangeal & 5 (the ulnar
border of joints 2 digits)
ulna,
interosseou
5
s
membrane
flexor humeroulna shafts of the flexes the median nerve ulnar a. median nerve
digitorum r head: middle metacarpophalan travels distally
superficialis common phalanges geal and proximal in the forearm
flexor of digits 2-5 interphalangeal on the deep
tendon; joints surface of the
radial head: flexor
middle 1/3 digitorum
of radius superficialis m.
flexor flexor proximal flexes the recurrent superficial flexor pollicis
pollicis retinaculum phalanx of carpometacarpal branch of the palmar br. of brevis,
brevis , trapezium the 1st digit and median nerve the radial a. abductor
metacarpophalan pollicis brevis,
geal joints of the and opponens
thumb pollicis are the
three muscles
of the thenar
compartment
of the hand
flexor anterior base of the flexes the median nerve anterior the tendon of
pollicis surface of distal metacarpophalan interosseous flexor pollicis
longus radius and phalanx of geal and a. longus passes
interosseou the thumb interphalangeal through the
s joints of the carpal tunnel
membrane thumb with the other
long digital
flexor tendons
and the
median nerve
infraspinatus infraspinato greater laterally rotates suprascapular suprascapula infraspinatus,
us fossa tubercle of the arm nerve r a. supraspinatus,
the teres minor
humerus and
(middle subscapularis
facet) are the rotator
cuff muscles
interosseous, four base of the flex the ulnar nerve, dorsal and bipennate
dorsal (hand) muscles, proximal metacarpophalan deep branch palmar muscles;
each arising phalanx and geal joint, extend metacarpal remember
from two the extensor the proximal and aa. DAB & PAD -
adjacent expansion distal Dorsal
metacarpal on lateral interphalangeal interosseous
shafts side of the joints of digits 2- mm. ABduct
2nd digit, 4, abduct digits 2- and Palmar
lateral & 4 (abduction of interosseous
medial digits in the hand mm. ADduct -
sides of the is defined as then you can
3rd digit, movement away figure out
and medial from the midline where they
side of the of the 3rd digit) must insert to
6
4th digit cause these
actions
interosseous, three base of the flexes the ulnar nerve, palmar unipennate
palmar muscles, proximal metacarpophalan deep branch metacarpal muscles;
arising from phalanx and geal, extends aa. remember
the palmar extensor proximal and PAD & DAB:
surface of expansion distal Palmar
the shafts of of the interphalangeal interossei
metacarpals medial side joints and adducts ADduct and
2, 4, & 5 of digit 2, digits 2, 4, & 5 Dorsal
and lateral (adduction of the interossei
side of digits of the hand ABduct, and
digits 4 & 5 is in reference to you will be
the midline of the able to figure
3rd digit) out where they
must insert
latissimus vertebral floor of the extends the arm thoracodorsal thoracodorsa the inserting
dorsi spines from intertubercu and rotates the nerve (C7,8) l a. tendon twists
T7 to the lar groove arm medially from the so that fibers
sacrum, posterior cord originating
posterior of the brachial highest insert
third of the plexus lowest
iliac crest,
lower 3 or 4
ribs,
sometimes
from the
inferior
angle of the
scapula
levator transverse medial elevates the dorsal scapular dorsal levator
scapulae processes of border of scapula nerve (C5); the scapular a. scapulae is
C1-C4 the scapula upper part of named for its
vertebrae from the the muscle action
superior receives
angle to the branches of C3
spine & C4
lumbrical flexor extensor flex the median nerve superficial lumbricals,
(hand) digitorum expansion metacarpophalan (radial 2) via palmar (lumbricus is
profundus on the geal joints, extend palmar digital arterial arch latin for
tendons of radial side the proximal and nerves & ulnar "worm") arise
digits 2-5 of the distal nerve (ulnar 2) from the
proximal interphalangeal via deep profundus
phalanx of joints of digits 2-5 branch tendons and
digits 2-5 have the same
pattern of
innervation as
does the
profundus
muscle (ulnar
and median
7
nn. split the
task equally)
opponens hook of shaft of 5th opposes the 5th ulnar nerve, ulnar a. opposition is a
digiti minimi hamate and metacarpal digit deep branch rotational
flexor movement of
retinaculum the 5th
metacarpal
around the
long axis of its
shaft;
opponens
digiti minimi,
abductor digiti
minimi, and
flexor digiti
minimi brevis
are in the
hypothenar
compartment
of the hand
opponens flexor shaft of 1st opposes the recurrent superficial opposition is a
pollicis retinaculum metacarpal thumb branch of palmar rotational
, trapezium median nerve branch of the movement of
radial a. the 1st
metacarpal
around the
long axis of its
shaft;
opponens
pollicis,
abductor
pollicis brevis,
and flexor
pollicis brevis
are in the
thenar
compartment
of the hand
palmar three base of the flexes the ulnar nerve, palmar unipennate
interosseous muscles, proximal metacarpophalan deep branch metacarpal muscles;
arising from phalanx and geal, extends aa. remember
the palmar extensor proximal and PAD & DAB:
surface of expansion distal Palmar
the shafts of of the interphalangeal interossei
metacarpals medial side joints and adducts ADduct and
2, 4, & 5 of digit 2, digits 2, 4, & 5 Dorsal
and lateral (adduction of the interossei
side of digits of the hand ABduct, and
digits 4 & 5 is in reference to you will be
the midline of the able to figure
3rd digit) out where they
8
must insert
palmaris fascia skin of the draws the skin of superficial br. ulnar a. palmaris brevis
brevis overlying palm near the ulnar side of of the ulnar n. improves the
the the ulnar the hand toward grasp
hypothenar border of the center of the
eminence the hand palm
palmaris common palmar flexes the wrist median nerve ulnar a. palmaris
longus flexor aponeurosis longus is
tendon, absent in about
from the 13% of
medial forearms; it
epicondyle may be present
of the on one side
humerus only
pectoralis medial 1/2 crest of the flexes and medial and pectoral the deep fascia
major of the greater adducts the arm, lateral pectoral branch of the on its anterior
clavicle, tubercle of medially rotates nerves (C5-T1) thoracoacro surface should
manubrium the the arm mial trunk not be fused to
& body of humerus the fascia of
sternum, the mammary
costal gland - if it is,
cartilages of this is an
ribs 2-6, important
sometimes clinical sign
from the indicating
rectus breast disease
sheath of
the upper
abdominal
wall
pectoralis ribs 3-5 coracoid draws the scapula medial pectoral branches of
minor process of forward, pectoral nerve branch of the medial
the scapula medialward, and (C8, T1) thoracoacro pectoral nerve
downward mial trunk usually pierce
pectoralis
minor to reach
the pectoralis
major muscle
pronator medial side anterior pronates the median nerve anterior pronator
quadratus of the surface of forearm via the anterior interosseous quadratus is
anterior the distal interosseous a. the deepest
surface of one-fourth nerve muscle in the
the distal of the distal forearm;
one-fourth radius it works with
of the ulna pronator teres
and has the
same nerve
supply
pronator common midpoint of pronates the median nerve ulnar a., median nerve
teres flexor the lateral forearm anterior passes between
tendon and side of the ulnar the two heads
9
(deep or shaft of the recurrent a. of origin of
ulnar head) radius pronator teres
from
medial side
of coronoid
process of
the ulna
rhomboideu spines of medial retracts, elevates dorsal scapular dorsal named for its
s major vertebrae border of and rotates the nerve (C5) scapular a. shape
T2-T5 the scapula scapula inferiorly
inferior to
the spine of
the scapula
rhomboideu inferior end medial retracts, elevates dorsal scapular dorsal named for its
s minor of the border of and rotates the nerve (C5) scapular a shape
ligamentum the scapula scapula inferiorly
nuchae, at the root
spines of of the spine
vertebrae of the
C7 and T1 scapula
serratus ribs 1-8 or 9 medial it draws the long thoracic lateral a lesion of long
anterior border of scapula forward; nerve (from thoracic a. thoracic nerve
the scapula the inferior fibers ventral rami will cause
on its costal rotate the scapula C5-C7) winging of the
(deep) superiorly scapula (i.e.,
surface the medial
border of the
scapula falls
away from the
posterior chest
wall and looks
like an angel's
wing)
serratus thoracolum ribs 9-12, pulls down lower branches of lowest a respiratory
posterior bar fascia, lateral to ribs the ventral posterior muscle, it
inferior spines of the angles primary rami intercostal a., receives ventral
vertebrae of spinal subcostal a., ramus
T11-T12 nerves T9-T12 first two innervation;
and L1-L2 lumbar aa. embryonically
related to the
intercostal
muscles, not
the deep back
mm.
serratus ligamentum ribs 1-4, elevates the branches of posterior a respiratory
posterior nuchae, lateral to upper ribs the ventral intercostal muscle, it
superior spines of the angles primary rami aa. 1-4 receives ventral
vertebrae of spinal ramus
C7 and T1- nerves T1-T4 innervation;
T3 embryonically
related to the
10
intercostal
muscles, not
the deep back
mm.
subclavius first rib and inferior draws the clavicle nerve to clavicular br. it serves an
its cartilage surface of (and hence the subclavius (C5) of the important
the clavicle shoulder) down thoracoacro protective
and forward mial trunk function - it
cushions the
subclavian
vessels from
bone
fragments in
clavicular
fractures
subscapularis medial two- lesser medially rotates upper and subscapular subscapularis,
thirds of the tubercle of the arm; assists lower a. supraspinatus,
costal the extention of the subscapular infraspinatus,
surface of humerus arm nerves (C5,6) and teres
the scapula minor are the
(subscapula rotator cuff
r fossa) muscles
supinator lateral lateral side supinates the deep radial recurrent deep radial
epicondyle of proximal forearm nerve interosseous nerve passes
of the one-third of a. through the
humerus, the radius supinator to
supinator reach the
crest & posterior
fossa of the compartment
ulna, radial of the forearm
collateral
ligament,
annular
ligament
supraspinatu supraspinat greater abducts the arm suprascapular suprascapula supraspinatus
s ous fossa tubercle of (initiates nerve (C5,6) r a. initiates
the abduction) from the abduction of
humerus superior trunk the arm, then
(highest of the brachial the deltoid
facet) plexus muscle
completes the
action; a
member of the
rotator cuff
group
teres major dorsal crest of the adducts the arm, lower circumflex teres major
surface of lesser medially rotates subscapular scapular a. inserts beside
the inferior tubercle of the arm, assists in nerve (C5,6) the tendon of
angle of the the arm extension from the latissimus
scapula humerus posterior cord dorsi, and
of the brachial assists
11
plexus latissimus in its
actions
teres minor upper 2/3 greater laterally rotates axillary nerve circumflex fixes the head
of the tubercle of the arm (C5,6) from scapular a. of the humerus
lateral the the posterior in the glenoid
border of humerus cord of the fossa during
the scapula (lowest brachial plexus abduction &
facet) flexion of the
arm; a
member of the
rotator cuff
group
trapezius medial third lateral third elevates and motor: spinal transverse named for its
of the of the depresses the accessory (XI), cervical a. shape;
superior clavicle, scapula proprioception trapezius is an
nuchal line, medial side (depending on : C3-C4 example of a
external of the which part of the muscle that
occipital acromion muscle contracts); migrates
protuberanc and the rotates the during
e, upper crest scapula development
ligamentum of the superiorly; from its level
nuchae, scapular retracts scapula of origin
spinous spine, (cervical) to its
processes of tubercle of final position,
vertebrae the scapular pulling its
C7-T12 spine nerve and
artery along
behind
triceps long head: olecranon extends the radial nerve deep long head of
brachii infraglenoid process of forearm; the long brachial the triceps
tubercle of the ulna head extends and (profunda separates the
the scapula; adducts arm brachii) a. triangular and
lateral head: quadrangular
posterolater spaces (teres
al humerus major, teres
& lateral minor and the
intermuscul humerus are
ar septum; the other
medial boundaries);
head: all three heads
posteromed of origin insert
ial surface by a common
of the tendon
inferior 1/2
of the
humerus
12
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Muscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper ExtremityDocument12 paginiMuscle Name Origin Insertion Action Innervation Muscles of Upper ExtremityKaren ManlapazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles and Their VAN Supply and FunctionDocument8 paginiMuscles and Their VAN Supply and FunctionVinothini Siva100% (1)
- Muscles of Lower LimbsDocument7 paginiMuscles of Lower LimbsFong Yu-hengÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Action: (Branch of The Brachial Plexus)Document58 paginiMuscle Origin Insertion Innervation Action: (Branch of The Brachial Plexus)sdfs sdfdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Checkley's Natural Method of Physical TrainingDocument234 paginiCheckley's Natural Method of Physical TrainingCullen O'Gorman100% (2)
- Human Anatomy Skeletal System Diagram Review Sheets & Practice TestDocument14 paginiHuman Anatomy Skeletal System Diagram Review Sheets & Practice TestMitzi De VeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lower ExtremitiesDocument80 paginiThe Lower ExtremitiesbayennÎncă nu există evaluări
- XX Vascular Supply of Lower Limb - PPTDocument15 paginiXX Vascular Supply of Lower Limb - PPTAlistair WalkerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Head, Neck, Limbs OINADocument17 paginiHead, Neck, Limbs OINAFrancis HenaresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper LimbDocument31 paginiUpper LimbNandhana Kattuparambil SunojÎncă nu există evaluări
- RomDocument6 paginiRomPrivat Etavirp0% (1)
- ANATOMY: The Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Spaces Axilla The ArmDocument88 paginiANATOMY: The Shoulder Girdle Shoulder Spaces Axilla The ArmNur Liyana MohamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)Document6 paginiSubclavius Pectoralis Minor: Axial Skeleton To Shoulder Girdles (Ventral Side)馮素琴Încă nu există evaluări
- Dermatomes & Myotomes PDFDocument4 paginiDermatomes & Myotomes PDFsridhar_physio0% (1)
- (PPT) Anatomy 2.5 Lower Limbs - Blood and Nerve Supply - Dr. Tan PDFDocument110 pagini(PPT) Anatomy 2.5 Lower Limbs - Blood and Nerve Supply - Dr. Tan PDFPreeti Joan BuxaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Limb Lab SheetDocument3 paginiLower Limb Lab SheetKelly TrainorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Limb MusclesDocument8 paginiLower Limb Musclesbilal_kmu020% (1)
- Median NerveDocument40 paginiMedian Nervehumera100% (2)
- Circumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus DorsiDocument4 paginiCircumflex Scapular: Dorsum of Thoracodorsal: Latissmus Dorsispeedy.catÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Lower LimbDocument89 paginiThe Lower LimbSantiFaridKalukuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elbow Complex (Kinesiology)Document2 paginiElbow Complex (Kinesiology)Kimmybee Garcia50% (2)
- Introduction To Lower Limb FinalDocument52 paginiIntroduction To Lower Limb FinalRafique Ahmed100% (3)
- Katya 30-Day-Challenge-Bikini-Body-Week-2 PDFDocument7 paginiKatya 30-Day-Challenge-Bikini-Body-Week-2 PDFGeraldyneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercise On Strength: Joshua Lester J. ArellanoDocument17 paginiExercise On Strength: Joshua Lester J. ArellanoBryantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Handout For Physical Therapy Students in OLFUDocument3 paginiFoundation Handout For Physical Therapy Students in OLFUBogart Macatangay100% (1)
- Orthodontics MCQDocument19 paginiOrthodontics MCQanuj sharma80% (5)
- Muscles of The Upper LimbDocument17 paginiMuscles of The Upper LimbJhanelle S. Dixon-LairdÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAUDI Licensing Orthodontics ExaminationDocument34 paginiSAUDI Licensing Orthodontics ExaminationRamy Fathy100% (1)
- Table A - TMJ and Infratemporal FossaDocument9 paginiTable A - TMJ and Infratemporal Fossaapi-422030113Încă nu există evaluări
- Back Anatomy TableDocument7 paginiBack Anatomy TableJeffrey XieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles of The Lower Limb (ADAM) PDFDocument35 paginiMuscles of The Lower Limb (ADAM) PDFDerek Prasai100% (1)
- PS 01 Lower Limb Muscles Table From Gray SDocument6 paginiPS 01 Lower Limb Muscles Table From Gray S馮素琴Încă nu există evaluări
- Cranial NervesDocument16 paginiCranial Nervesapi-302547403100% (1)
- Muscular SystemDocument47 paginiMuscular SystemKrystal Kaye AczonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radial and Median NervesDocument33 paginiRadial and Median NervesveegeerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertebral Arteries, and Their Divisions. Arteries Fuse To Form The Basilar ArteryDocument6 paginiVertebral Arteries, and Their Divisions. Arteries Fuse To Form The Basilar Arterymurali_bharadwazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy Muscles of The FaceDocument7 paginiAnatomy Muscles of The Facecristienne marielle MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8.anterior GuidanceDocument15 pagini8.anterior GuidanceVikas AggarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Tests For WristDocument13 paginiSpecial Tests For WristSaif Ahmed LariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of The Digestive SystemDocument90 paginiDevelopment of The Digestive Systemyusrah mukhtarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15 PharynxDocument9 pagini15 Pharynxapi-3757921Încă nu există evaluări
- Hip Joint PDFDocument11 paginiHip Joint PDFStephen Subiera MiayoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Limb Muscles OnlyDocument7 paginiUpper Limb Muscles OnlyGwen EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionDocument37 paginiMuscles in The Posterior Scapula Muscle Proximal Attachment Distal Attachment Nervous Supply FunctionMicky TsuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscle Origin Insertion Innervation Blood Supply Action: Hip and ThighDocument6 paginiMuscle Origin Insertion Innervation Blood Supply Action: Hip and ThighAndika Anjani AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries, S-Ii-Lm-0120Document5 paginiNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries, S-Ii-Lm-0120Shab GeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norma Basalis: Inferior Aspect of SkullDocument33 paginiNorma Basalis: Inferior Aspect of Skullkavya0% (1)
- Anatomy NotesDocument29 paginiAnatomy NotesAna TsereteliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesDocument8 paginiNerves of Lower Limb and Their Injuries: Learning ObjectivesUloko ChristopherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lower Limb: Front and Medial Aspect of ThighDocument8 paginiLower Limb: Front and Medial Aspect of ThighErnie G. Bautista II, RN, MDÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Elbow ComplexDocument12 paginiThe Elbow ComplextafelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy - Upper LimbDocument72 paginiAnatomy - Upper LimbAiman ArifinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biomechanics Assignment - Posture-2Document11 paginiBiomechanics Assignment - Posture-2ApoorvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoulder ComplexDocument14 paginiShoulder Complexbhavesh jain100% (5)
- Hip Joint: Important PointsDocument4 paginiHip Joint: Important PointsNamrah AfzalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Joints of Lower LimbDocument7 paginiJoints of Lower LimbjsdlzjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ankle and Foot Complex Contd.Document10 paginiAnkle and Foot Complex Contd.Vijay PradeepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Arthrokinematics of Body Joints FinalDocument3 paginiArthrokinematics of Body Joints FinalnmahpbooksÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midterm - Worksheet 1 - PERIPHERAL JOINT MOBILIZATION-MANIPULATIONDocument3 paginiMidterm - Worksheet 1 - PERIPHERAL JOINT MOBILIZATION-MANIPULATIONGrace Panuelos Oñate100% (1)
- 4 Pectoral RegionDocument62 pagini4 Pectoral RegionFarrukh ShahzadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thoracic Segment KpsDocument77 paginiThoracic Segment Kpskrishna bptÎncă nu există evaluări
- Axillary Artery: Branches First (1 Branch) Second Part (2 Branches) Third (3 Branches) 1 2 4Document14 paginiAxillary Artery: Branches First (1 Branch) Second Part (2 Branches) Third (3 Branches) 1 2 4foster18Încă nu există evaluări
- Joints of The Head and Trunk - 2015-RuanDocument30 paginiJoints of The Head and Trunk - 2015-RuanKw ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Upper Limb: Pectoral RegionDocument13 paginiUpper Limb: Pectoral RegionMariam Alavidze0% (1)
- Muscles Crossing The Shoulder Joint: Movements of The Arm (Humerus)Document3 paginiMuscles Crossing The Shoulder Joint: Movements of The Arm (Humerus)sarahalaouieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles of The Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesDocument10 paginiMuscles of The Upper Limb - Listed Alphabetically Muscle Origin Insertion Action Innervation Artery NotesAjay Pal NattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles of The Upper LimbDocument11 paginiMuscles of The Upper LimbSuman DahalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bogdan Radenkovic 1874-1917 Destiny of ADocument8 paginiBogdan Radenkovic 1874-1917 Destiny of ADejan MilenkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bogdan Radenkovic 1874-1917 Destiny of A PDFDocument8 paginiBogdan Radenkovic 1874-1917 Destiny of A PDFDejan MilenkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kifoza SkoliozaDocument51 paginiKifoza SkoliozaNemanja Zdravkovic100% (1)
- 400w43 e Poster Gangphasen Druck PDFDocument1 pagină400w43 e Poster Gangphasen Druck PDFDejan Milenkovic50% (2)
- P - NZStroke Hemiplegia DL - Right PDFDocument2 paginiP - NZStroke Hemiplegia DL - Right PDFDejan MilenkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- 400w43 e Poster Gangphasen Druck PDFDocument1 pagină400w43 e Poster Gangphasen Druck PDFDejan Milenkovic50% (2)
- 10752-02 CH02 Final PDFDocument28 pagini10752-02 CH02 Final PDFDejan MilenkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tri Hiljade Godina Pomorskih Ratova III Boris Prikril PDFDocument180 paginiTri Hiljade Godina Pomorskih Ratova III Boris Prikril PDFDejan MilenkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec4bimuscle LOMBARD PDFDocument2 paginiLec4bimuscle LOMBARD PDFDejan MilenkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Muscles of The Upper Limb 1 PDFDocument12 paginiMuscles of The Upper Limb 1 PDFDejan MilenkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- B03 04 2010 Novac PDFDocument4 paginiB03 04 2010 Novac PDFDejan MilenkovicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design and Fabrication of A Full Denture With Shorthened Dental Arch and Flat Ridge in MandibularDocument10 paginiDesign and Fabrication of A Full Denture With Shorthened Dental Arch and Flat Ridge in MandibulardinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SENSE ORGANS, Grade 9Br Bio. MR MUSIMA.Document5 paginiSENSE ORGANS, Grade 9Br Bio. MR MUSIMA.Said SakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traumatic Tympanic Membrane PerforationDocument7 paginiTraumatic Tympanic Membrane PerforationNada ZultiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shavasana ScriptDocument3 paginiShavasana Scriptstiliyanstoyanov28Încă nu există evaluări
- MDS Entrance DetailsDocument256 paginiMDS Entrance Detailsalam02_shuklaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asda JKLMNDocument185 paginiAsda JKLMNBikram SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Triceps - 6 KomDocument3 paginiTriceps - 6 KomMatijaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Manual - Axial - Skeleton - AtlasDocument59 paginiLab Manual - Axial - Skeleton - Atlaspertemuan blok3.3Încă nu există evaluări
- Anterior Compartment of The ThighDocument1 paginăAnterior Compartment of The ThighLuqman Al-Bashir Fauzi100% (1)
- Stretch Reflex and Muscle ToneDocument14 paginiStretch Reflex and Muscle Toneiman ferganiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eyes RETDEMDocument2 paginiEyes RETDEMRenz Kier L. ComaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bio 270 Lab Part I - As120Document8 paginiBio 270 Lab Part I - As120QhairunnissaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cough: 4 Phases of Cough ReflexDocument4 paginiCough: 4 Phases of Cough ReflexNadhirah ZulkifliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 33 DPP of Biology PDFDocument38 pagini33 DPP of Biology PDFashaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calipers - Lower ExtremityDocument40 paginiCalipers - Lower ExtremityNivetha RavikumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Text The Brainy BodyDocument3 paginiReport Text The Brainy BodyHana alkhairaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 - Knee Joint - D3Document28 pagini7 - Knee Joint - D3aslooclt100% (1)
- Journal Homepage: - : IntroductionDocument7 paginiJournal Homepage: - : IntroductionIJAR JOURNALÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain StemDocument54 paginiBrain StemPrasad HewawasamÎncă nu există evaluări
- E3 - OrthoDocument49 paginiE3 - OrthoLuvleen KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pediatrics - Endocrine SystemDocument347 paginiPediatrics - Endocrine SystemMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bones - LabDocument24 paginiBones - LabJhom Andrei Apolinar100% (1)