Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pharm - Endocrine - Anti-Diabetics
Încărcat de
Abhineeth Bhat0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
30 vizualizări1 paginădm
Titlu original
Pharm - Endocrine - Anti-diabetics
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentdm
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
30 vizualizări1 paginăPharm - Endocrine - Anti-Diabetics
Încărcat de
Abhineeth Bhatdm
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
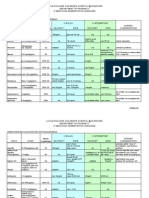
Insulin - anabolic Glucagon - catabolic
Type 1 DM Treatments 21 res. A-pep+30 res. B-pep 21 residue peptide
Insulins Composition Absorbtion Secreted by B cells w/ C-pep Secreted by a cells
cellular glucose uptake Used to treat insulin
Soluble monomeric rapid gluconeogenesis and glycogenolysis overdose
NPH protamine mix intermediate fatty acid and TG synthesis
Lente Amorphous insulin-zinc suspension slow lipolysis, protein syn.
Ultralente insulin-zinc very slow Insulin Receptor 22 configuration. = insulin binding, = TK
mutated B chain, causing decreased self Insulin Synthesis Initial translation product has N-terminal signal,
Lispro/aspart association. very fast which is removed upon ER insertion. C peptide is cleaved out in
golgi.
mutations, causing precipitation at Secretion: blood glucose cell uptake/catabolism ATP
Glargine injection site ultra long acting ATP-sensitive K+ channel closure depolarization opening
inhaler. Contraindicated in smokers or of voltage sensitive Ca+ channel exocytotic release of insulin.
EXUBERA lung disease rapid Metabolism: Extensive first pass met. So liver sees higher
concentration than other tissues.
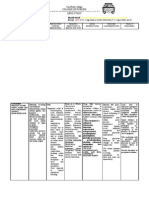
Type 2 DM Treatments
Drug Mechanism Pharmacokinetics Clinical use Adverse reactions
~Effective GI abs., end up mostly bound to albumin
1st gen Risk of inducing severe
Tolbutamide: 4-7 hr t1/2 hypoglycemia
Stimulation of insulin release Chlorpromamide: 24-48 hr t1/2
from the pancreas, via reduced 2nd gen Appetite stimulants obesity
conductance through ATP Glyburide/glipizide: 2-4 hr t1/2 Primary agents, in combo with
sensitive K+ channels. Requires ~ Yet, effects from one does last 24- dietary control. High failure rate (7%) prob due
Sulfonylureas functional B cells. 48 hr. 100X more potent than 1st gen. Oral administration to pancreatic insuff.
Glinides Induce insulin secretion through Taken orally at mealtimes to reduce
Repaglinide + closure of the ATP sensitive K+ Very rapid acting, short duration. post-prandial peak. Flexible dosing Less potential for hypoglycemia
Nateglinide channel. depending on meals. since short acting.
Metformin reduces blood Lactic acidosis much less
glucose via unknown common than with phenformin
mechanism. 2 actions: reduced (off market)
liver gluconeogenesis, reduced Often given synergistically with No hypoglycemia
Biguanides insulin resistance. Oral administration sulfonylureas Anorexia
Agonistic binding to PPAR, to Not recommended for first line
Glitazones suppress resistin release from Low incidence of liver tox.
(TZDs) white adipocytes. When used, monthly liver tests.
Induces insulin release Nausea, which often goes away
Glucagon-like-peptide homolog, Depresses glucagon release Twice daily injections with persistant use
derived from gila monster Delays gastric emptying Approved as combo with metformin Increased risk of hypoglycemia if
Exenatide salivary glands Net result: significant weight loss (good!) and sulfonylureas used with sulfonylureas
-glucosidase Not effective as primary therapy
inhibitors Slow intestinal degradation of used with other oral agents when
(acarbose, complex carbs to reduce glucose failure to adequately control post-
miglitol) absorbtion/ prandial glucose levels Flatulence, diarrhea
ALL of the oral anti-diabetics depend on endogenous insulin production. If insulin production is insufficient, need Type 1 DM drugs
Only have risk of hypoglycemia if you are increasing insulin levels in the blood.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Math Practice Problems Group 3Document2 paginiMath Practice Problems Group 3Lukman Nal 26Încă nu există evaluări
- BMC Transitions of CareDocument2 paginiBMC Transitions of Carebalab2311Încă nu există evaluări
- MACHNISM OF NURSING DRUG NAME INDICATIOONDocument2 paginiMACHNISM OF NURSING DRUG NAME INDICATIOONsalwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AcetaminophenDocument2 paginiAcetaminophendrugcardref100% (1)
- MucosolvanDocument2 paginiMucosolvanAyah Paasa100% (1)
- Types of Insulin According to Mode of ActionDocument1 paginăTypes of Insulin According to Mode of ActionAssem Ashraf Khidhr100% (1)
- Drug StudyDocument16 paginiDrug StudyMonica Luz FajardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: Far Eastern UniversityDocument3 paginiDrug Study: Far Eastern UniversityChoy DacanayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Salbuterol Generic NameDocument4 paginiSalbuterol Generic NamejunieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medication DilutionDocument22 paginiMedication DilutionYaser Salman100% (1)
- CVD HypertensionDocument15 paginiCVD HypertensionAbigail BascoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bariatric Surgery Nutrition GuideDocument35 paginiBariatric Surgery Nutrition GuideMoitri ChatterjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Aide 2023Document97 paginiFirst Aide 2023jrfdcafprescomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 3 Activity 2 Drug Study Ciprofloxacin PaxilDocument6 paginiModule 3 Activity 2 Drug Study Ciprofloxacin PaxilEugene MananganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Poisoning of Therapeutic Agents: by Alemayehu TomaDocument42 paginiAcute Poisoning of Therapeutic Agents: by Alemayehu TomaYohannis AsefaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metoprolol Teaching PlanDocument18 paginiMetoprolol Teaching Planapi-419091662Încă nu există evaluări
- Formulas and DripsDocument6 paginiFormulas and DripsJsohna BelinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Classification of Burns Based On Depth CharacteristicsDocument2 paginiClassification of Burns Based On Depth CharacteristicsmexelleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Care of Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome (HHNSDocument4 paginiCritical Care of Hyperglycemic Hyperosmolar Syndrome (HHNSJan Crizza Dale R. FrancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- San Beda College College of Nursing drug study guideDocument3 paginiSan Beda College College of Nursing drug study guideaycee0316Încă nu există evaluări
- Endocrine System: (General Key Points)Document32 paginiEndocrine System: (General Key Points)susan2johnson-501300Încă nu există evaluări
- The Musculoskeletal HandoutsDocument3 paginiThe Musculoskeletal Handouts_Advernice_Încă nu există evaluări
- NCM 118a Lec 9 Liver FailureDocument9 paginiNCM 118a Lec 9 Liver FailureJan Crizza Dale R. FrancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RHEUMATOID ARTHYRITIS CASEDocument32 paginiRHEUMATOID ARTHYRITIS CASEJune Faith HacheroÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIT Individual Case StudyDocument13 paginiGIT Individual Case StudyKirito Dokkie100% (1)
- Assessment by Body SystemsDocument2 paginiAssessment by Body SystemsPat McGarryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asthma and PneumoniaDocument121 paginiAsthma and PneumoniaPaula AbilÎncă nu există evaluări
- J.S Case Study 1 PDFDocument2 paginiJ.S Case Study 1 PDFania ojedaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carbetocin For The Prevention of Postpartum Hemorrhage A Systematic ReviewDocument7 paginiCarbetocin For The Prevention of Postpartum Hemorrhage A Systematic ReviewOscar Gregorio Coronado MacdanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 paginiDrug Name Mechanism of Action Dosage Indication Contraindication Side Effects/ Adverse Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesKat BausaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intake & Output Monitoring Sheet: 11 PM 11-7 1000 ML 0 550 ML 0 0Document2 paginiIntake & Output Monitoring Sheet: 11 PM 11-7 1000 ML 0 550 ML 0 0Renea Joy ArruejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument8 paginiDrug StudyJay-ar Batara SorianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taking Blood Pressure ManuallyDocument2 paginiTaking Blood Pressure ManuallyManoj Kumar GÎncă nu există evaluări
- SH CP 17 Zuclopenthixol Acetate GuidelinesxDocument8 paginiSH CP 17 Zuclopenthixol Acetate Guidelinesxlight002Încă nu există evaluări
- Hips Back Ankles Buttocks HeelsDocument13 paginiHips Back Ankles Buttocks Heelsفرزدق الحسيناويÎncă nu există evaluări
- Narrative PathophysiologyDocument5 paginiNarrative Pathophysiologymyer pasandalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final NCPDocument5 paginiFinal NCPAce VirtusioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology - Tia VS CvaDocument6 paginiPathophysiology - Tia VS CvaZeo Zafaralla100% (1)
- Atenolol TenorminDocument3 paginiAtenolol TenorminLIEZEL GRACE VELAYOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Haloperidol PDFDocument1 paginăHaloperidol PDFAda AlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument2 paginiDrug Studyunkown userÎncă nu există evaluări
- Palliative Care Case Study: Qamar Abbas Deputy Medical Director ST Clare HospiceDocument12 paginiPalliative Care Case Study: Qamar Abbas Deputy Medical Director ST Clare HospicePraba KaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Used in VomitingDocument1 paginăDrug Used in VomitingSyamil AizatÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Radioactive PollutionDocument4 paginiWhat Is Radioactive PollutionJoy MitraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Assessment IIDocument5 paginiNursing Assessment IImyer pasandalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intr Oduction: Classification of PainDocument4 paginiIntr Oduction: Classification of Painanimesh panda100% (1)
- ACLS Simplify AlgorithmDocument6 paginiACLS Simplify AlgorithmKristine Monforte Coma UritaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument7 paginiDrug Studyanne009Încă nu există evaluări
- Amlodipine Captopril MetronidazoleDocument5 paginiAmlodipine Captopril Metronidazolekhrysty1506Încă nu există evaluări
- ACLS AgorithmDocument55 paginiACLS AgorithmkpsuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Appendix A: Sample Patient Profiles and Prescriptions: (For Pharmacist Use)Document6 paginiAppendix A: Sample Patient Profiles and Prescriptions: (For Pharmacist Use)Cesly Jewel Acosta AvilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duloxetine PDFDocument4 paginiDuloxetine PDFscribdseewalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autonomic HyperreflexiaDocument3 paginiAutonomic HyperreflexiaGibe BebitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Pulseless Arrest OkDocument33 pagini8 Pulseless Arrest OkJulienne CaoileÎncă nu există evaluări
- Multiple Sclerosis PDFDocument1 paginăMultiple Sclerosis PDFAcey TfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Flores Mary Jane Generic Drug ChartDocument23 paginiFlores Mary Jane Generic Drug ChartKristine Dela CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spinal Vs Neuro ShockDocument1 paginăSpinal Vs Neuro ShockLiza Kamelia100% (2)
- Drug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsDocument3 paginiDrug Therapy of DM - Oral Antidiabetic DrugsSurria Suguna15Încă nu există evaluări
- Anti Diabetik Oral Dan InsulinDocument97 paginiAnti Diabetik Oral Dan InsulinSuci AlimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diabetes MellitusDocument6 paginiDiabetes Mellitusmaham jahangirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urinary Concentration and DilutionDocument10 paginiUrinary Concentration and DilutionAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Histo Study GuideDocument2 paginiUnit 2 Histo Study GuideAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- VocabDocument4 paginiVocabAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gi HyDocument2 paginiGi HyAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Step 1 PlanDocument6 paginiStep 1 PlanUma MounaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2017 Fas1 Errata MarchDocument4 pagini2017 Fas1 Errata MarchФеденко ЭдуардÎncă nu există evaluări
- Usmle Hy Step1Document20 paginiUsmle Hy Step1Sindu SaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- STEP1 ResourcesDocument2 paginiSTEP1 ResourcesAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide To BoardsDocument3 paginiGuide To BoardsAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PathologyDocument54 paginiPathologyAli Abbas100% (8)
- GuideDocument16 paginiGuideAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM2Document12 paginiDM2Abhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approved: HFHS Nov-June Only HFH Has No PrerequisitesDocument1 paginăApproved: HFHS Nov-June Only HFH Has No PrerequisitesAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guide PDDocument2 paginiGuide PDAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- First SpeakerDocument2 paginiFirst SpeakerAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notion of Narrative Based On Whats Dominant in End of Life StoriesDocument1 paginăNotion of Narrative Based On Whats Dominant in End of Life StoriesAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2Document1 paginăLecture 2Abhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Policy For CCC Delayed Start StudentsDocument2 paginiPolicy For CCC Delayed Start StudentsAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lipoprotein Patterns and Associated ConditionsDocument4 paginiLipoprotein Patterns and Associated ConditionsAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wilhelm Endocrine PharmacologyDocument7 paginiWilhelm Endocrine PharmacologyAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- GuideDocument1 paginăGuideAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- LabDocument4 paginiLabAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Normal Parathyroid GlandsDocument30 paginiNormal Parathyroid GlandsAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Question PhilosophyDocument3 paginiQuestion PhilosophyAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- GuideDocument1 paginăGuideAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aging and MenopauseDocument3 paginiAging and MenopauseAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jefferson - Aoa USMLE Step 1Document12 paginiJefferson - Aoa USMLE Step 1Mc Ase100% (1)
- Lipoprotein Patterns and Associated ConditionsDocument4 paginiLipoprotein Patterns and Associated ConditionsAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- PancreasDocument8 paginiPancreasAbhineeth BhatÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL - Science 6 - Q2Document7 paginiDLL - Science 6 - Q2Angelica GuillermoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paragraph Development ExerciseDocument6 paginiParagraph Development ExerciseSYAFINAS SALAM100% (1)
- The Developing Child - The First Seven Years - EbookDocument141 paginiThe Developing Child - The First Seven Years - Ebookall-natural-nutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Branches of ZoologyDocument3 paginiBranches of ZoologyVivek Morya100% (1)
- Thalassemia: SymptomsDocument3 paginiThalassemia: SymptomsAndi BandotÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Document51 paginiNCM 100 H.A Procedure DPPER 3Richelle Joy Durano RegatunaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Zoology: Zoology Previous Eamcet QuestionsDocument8 paginiZoology: Zoology Previous Eamcet QuestionsGaganpreetSingh100% (1)
- CSIR UGC JRF Subjetive Model Test PaperDocument17 paginiCSIR UGC JRF Subjetive Model Test PaperManu Mallahalli ShanthappaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Point MarmaDocument2 paginiPoint MarmaAnonymous yzbnd8Încă nu există evaluări
- Biology: Revised Syllabus For Higher Secondary First Year CourseDocument4 paginiBiology: Revised Syllabus For Higher Secondary First Year CourseamitumikoibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supranuclear Control Opf Eye MovementsDocument162 paginiSupranuclear Control Opf Eye Movementsknowledgeguruos179Încă nu există evaluări
- Electrolyte Imbalance 1Document3 paginiElectrolyte Imbalance 1Marius Clifford BilledoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Population Genetics TutorialDocument164 paginiPopulation Genetics TutorialMichelle GÎncă nu există evaluări
- HeparinDocument2 paginiHeparinNinoska Garcia-Ortiz100% (4)
- Pete Pfitzinger Advanced Marathoning Training 88K-1Document8 paginiPete Pfitzinger Advanced Marathoning Training 88K-1Phan ToanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spesifikasi Patient Monitor: Draeger - Vista 120S: Type Parameter Merk FeaturesDocument3 paginiSpesifikasi Patient Monitor: Draeger - Vista 120S: Type Parameter Merk Featuresflorensia shielyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tetralogy of Fallot Everything You Wanted To Know But Were Afraid To AskDocument8 paginiTetralogy of Fallot Everything You Wanted To Know But Were Afraid To AsksofiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bulacan State University College of Nursing Final Exam ReviewDocument7 paginiBulacan State University College of Nursing Final Exam ReviewDemiar Madlansacay QuintoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manajemen Pre-Operatif Pasien Dengan DMDocument12 paginiManajemen Pre-Operatif Pasien Dengan DMyanayas28Încă nu există evaluări
- Gavage FeedingDocument18 paginiGavage FeedingMena AmerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Systems NotesDocument2 paginiBody Systems NotesAndrea González MercadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NIOSH Investigation - CR 337 Fire LODDDocument32 paginiNIOSH Investigation - CR 337 Fire LODDRamblingChiefÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal System Lecture NotesDocument169 paginiMusculoskeletal System Lecture Noteszygote0711578796% (28)
- Acute Liver Injury and FailureDocument14 paginiAcute Liver Injury and FailureWeslei ChaconÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4Document7 paginiChapter 4R LashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6 Cell DivisionDocument20 paginiChapter 6 Cell DivisionVinash Shka RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Diseases of The UveaDocument102 paginiAnatomy and Diseases of The UveaVishakh IsloorÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCM 103 RLE NOTESDocument8 paginiNCM 103 RLE NOTESgallardo.bettinarose.iÎncă nu există evaluări
- FORENSIC SEROLOGY AND BLOOD ANALYSISDocument16 paginiFORENSIC SEROLOGY AND BLOOD ANALYSISBARCELON, CHRISTOPHER JAMESÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circulatory System: Heart, Blood Vessels & Their FunctionsDocument17 paginiCirculatory System: Heart, Blood Vessels & Their FunctionskangaanushkaÎncă nu există evaluări