Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
DTMF Chip Flow Picture
Încărcat de
swathikomati7870Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
DTMF Chip Flow Picture
Încărcat de
swathikomati7870Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
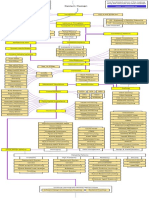
Demonstration of A Modern Physical Design Flow Using the
Silicon Virtual Prototyping Back-End Tools of Cadence
Anuj Kumar, Azadeh Davoodi, University of Wisconsin - Madison
Flat Physical Flow Silicon Virtual Prototype Hierarchical Physical Flow
Data Provides quick feedback on performance, area Divide and Conquer Approach to
Preparation Power Routing View and power early in design cycle. manage Complexity. Partitioned View
Floorplanning SVP Components Steps
Fast floorplan mode for placement Partition and Floorplan
Power Routing buffer
insertion, Define logical partitions, fix their
gate Accurate pre-routing timing analysis locations, shape and size.
Placement & sizing,
pin swap
Interconnect consideration via incorporation Initial place/route
Scan Chain Reorder
of a fast router. Guides the pin assignment for the
TrialRoute: Used for quick evaluation of partitions.
Pre-CTS Timing Analysis routability, congestion, timing analysis and
& Optimizations
Assign partition pins
optimizations. Actual pin assignment on the Logical Partitions (translated into Hard Blocks)
Native extraction partition boundaries used to guide
Hard
N
Power Stripes the routing inside the partitions.
Met
Timing ?
IP Block Layer M6 Core Ring Can make use of scale factors to improve
Derive timing budgets
Assembled View
the RC estimation for the routes generated
using Ostrich (SPEF Comparator). Generate local timing constraints
Y Scan Chain View for the paths that cross the partition
Clock Tree fix DRV, Timing optimizations boundaries.
Synthesis setup/hold
violation, At Pre- and Post- routing stages. Commit partition, top-level
correct Effective incremental mode. place/route
timing with
Post-CTS Low effort mode to meet timing constraint, Treat partition as hard IP block.
propagated
Timing Analysis clock, achieves within 10% of the target timing. Implement each partition
& Optimizations reduce area
Assemble Design
N Met
Engineering Change Order Merge together the individual blocks Signal Routes Merged with Top after
Timing ? and top. Assemble Design
Old Design
(in Memory) Local changes to
Y repair timing current logical netlist Educational Goals
Routing with no new to make functional
problem Placed Instances Scan Chain After
Identify Local modifications or Provide the students big picture on the sequence of and interaction
(Standard Cell) Reordering
introduction,
fix signal
Modifications meeting design among different stages of a modern physical design flow, which they learn
constraints
Post Route integrity only as disjoint steps in the class.
Optimizations issues Congestion View Make Logical May be manual Enhance the students understanding of challenges to achieve design
Analyze Design Changes (to Netlist) through loading an
ECO file.
closure and inevitability of backtracking within the design flow.
(Timing, DRV,
Power, Area)
May be done by tool
commands
Provide deeper understanding of inherent complexity of the design
Commit Physical (optDesign) during process by using commercial tools on moderately sized designs, thus
Changes optimizations students will better appreciate the effectiveness of the CAD algorithms
Incremental
N Constraints Placement & Routing Do not modify taught in the class.
Met ? currently
Placed/Routed References
Y objects. Use
Save Design ecoPlace/ecoRoute [1] W-J Dai, D. Huang, C-C Chang, M. Courtoy, Silicon virtual prototyping: the new cockpit for nanometer
Verify Design & High Congestion on to do incremental chip design, Proceedings of the Asia South Pacific Design Automation Conference, pp. 635 639, 2003.
Save Design the Routing Grid placement & routing
[2] Cadence Learning Management, http://leaning.cadence.com
(Vertical Edge View)
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Survey Mobile V2.3.0 Release Notes (En)Document6 paginiSurvey Mobile V2.3.0 Release Notes (En)Milan PopovićÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asic Back End FlowDocument17 paginiAsic Back End FlowJagannath KbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Literature Table: Bhathal2017 January 2020Document2 paginiLiterature Table: Bhathal2017 January 2020Vikram BhathalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deep Integration of Circuit Simulator and SAT SolverDocument6 paginiDeep Integration of Circuit Simulator and SAT Solvercs TianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dso Ai OfferingsDocument14 paginiDso Ai OfferingsJack LuarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles of Mapping With Petrel©Document4 paginiPrinciples of Mapping With Petrel©Hcene HcenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5G Planning Topics - Part 1Document78 pagini5G Planning Topics - Part 1Samir MezouarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Design MethodologyDocument26 pagini2 Design MethodologySivakumar PothirajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mesh Intro 140 L 05 Global Mesh ControlsDocument47 paginiMesh Intro 140 L 05 Global Mesh ControlsMokhtar AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Petrophysics-Driven Well Log Quality Control Using Machine Learning-2Document15 paginiPetrophysics-Driven Well Log Quality Control Using Machine Learning-2Nilesh SinghalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3G Workshop May 2005 - Richard EdgeDocument26 pagini3G Workshop May 2005 - Richard Edgedtvt40Încă nu există evaluări
- Traffic Shaping On Cisco IOSDocument12 paginiTraffic Shaping On Cisco IOSAbhishek gargÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Planning Strategies To Improve Physical Design Flows - Floorplanning and Power PlanningDocument11 paginiDesign Planning Strategies To Improve Physical Design Flows - Floorplanning and Power PlanningMohammed DarouicheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Statistics (Week 3)Document14 paginiAdvanced Statistics (Week 3)Dileep Kumar MotukuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cts CommandsDocument88 paginiCts CommandsDurgaPrasad100% (1)
- CoSiCoSt-W: Adaptive Traffic Control for Indian RoadsDocument2 paginiCoSiCoSt-W: Adaptive Traffic Control for Indian Roadskommepalli soniyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CLUSTER PREPARATION FLOW CHARTDocument9 paginiCLUSTER PREPARATION FLOW CHARTRAMPRASATHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Design and Sign OffDocument43 paginiPhysical Design and Sign OffAgnathavasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Design: References / ResourcesDocument1 paginăSystem Design: References / ResourcesabdallahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curri Cul Um For ST Aad. Pro: Cetpa Infotech Pvt. LTDDocument4 paginiCurri Cul Um For ST Aad. Pro: Cetpa Infotech Pvt. LTDM RoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2007 12 ICC Incremental TrainingDocument129 pagini2007 12 ICC Incremental Trainingvikas.vkp50% (4)
- Environment For Estimation, Design, and Manufacturing of Wiring HarnessesDocument2 paginiEnvironment For Estimation, Design, and Manufacturing of Wiring Harnesseszaidan.abimanyuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Based E/E Architecture Development at Daimler: ... and A Look at The Broader PictureDocument16 paginiModel Based E/E Architecture Development at Daimler: ... and A Look at The Broader PictureRandy Collins100% (1)
- Segment identification analysis overviewDocument1 paginăSegment identification analysis overviewIan MaldonadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ORAN ProposalDocument7 paginiORAN Proposallitoc60255Încă nu există evaluări
- Pengolahan Data Seismik WorkflowDocument6 paginiPengolahan Data Seismik WorkflowVinaWiryadinataÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compiler OptimizationDocument31 paginiCompiler OptimizationYakshi MangalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icct Colleges Foundation, IncDocument7 paginiIcct Colleges Foundation, IncRaymond RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- AutoCAD CertificateDocument1 paginăAutoCAD CertificateFrederick Jose Forca RañinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimizing Coverage and Capacity Using Actix ACP and VeritunejeffDocument24 paginiOptimizing Coverage and Capacity Using Actix ACP and VeritunejefftadjouaminaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SIEMENS- RNP-PROCESS-FLOW-V4-PPTDocument10 paginiSIEMENS- RNP-PROCESS-FLOW-V4-PPTBTS AgiÎncă nu există evaluări
- RF Network Planning & Optimization Service V100R005 Training Slides (UMTS ASP) 01-EnDocument31 paginiRF Network Planning & Optimization Service V100R005 Training Slides (UMTS ASP) 01-EnMarvin GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recurrent Graph Convolutional Network-Based Multi-Task Transient Stability Assessment Framework in Power SystemDocument14 paginiRecurrent Graph Convolutional Network-Based Multi-Task Transient Stability Assessment Framework in Power System黄凌翔Încă nu există evaluări
- Innovus Implementation System DsDocument4 paginiInnovus Implementation System DsLiu WenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Result JDA ImplementationDocument18 paginiTest Result JDA ImplementationNaek OmpusungguÎncă nu există evaluări
- System DesignDocument1 paginăSystem DesignSai VahadneÎncă nu există evaluări
- System Design Interview Prep: Main Requirements and TradeoffsDocument1 paginăSystem Design Interview Prep: Main Requirements and Tradeoffsrashmi_123321Încă nu există evaluări
- MPSOC2012Document25 paginiMPSOC20122023ht01517Încă nu există evaluări
- Physical Synthesis 2.0Document52 paginiPhysical Synthesis 2.0ravishopingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incentia Test Synthesis Solution TestcraftDocument27 paginiIncentia Test Synthesis Solution Testcraftyellow51Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3Document88 paginiChapter 3Muhammad MalikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Suspension Design ProcedureDocument2 paginiSuspension Design ProcedureSudarshan GovindarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intake Design Process - v1Document1 paginăIntake Design Process - v1Angela RaymondÎncă nu există evaluări
- FPGA Implementation of Closed-Loop Control System For Small-Scale RobotDocument8 paginiFPGA Implementation of Closed-Loop Control System For Small-Scale RobotLeonardo Olan ValdiviesoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Service Delivery Process 3.0 PDFDocument4 paginiService Delivery Process 3.0 PDFKrisel Ann UrbanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To ANSYS Introduction To ANSYS Meshing: LT 5 Mesh Quality Check yDocument21 paginiIntroduction To ANSYS Introduction To ANSYS Meshing: LT 5 Mesh Quality Check yHeba AlaaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 RN31572EN20 PM MonitoringDocument137 pagini02 RN31572EN20 PM MonitoringvinodÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSC Apex - StructureDocument2 paginiMSC Apex - StructureAmr EmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Training Course of SOC Training Course of SOC Encounter EncounterDocument70 paginiTraining Course of SOC Training Course of SOC Encounter Encountersowmyan55Încă nu există evaluări
- 0 Towards5G Free SamplDocument10 pagini0 Towards5G Free SamplbabakkardelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graphics Processing UnitDocument21 paginiGraphics Processing UnitfajalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3G Event GuidelineDocument23 pagini3G Event GuidelineArio NugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Miaow PosterDocument1 paginăMiaow PosterSuresh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPC-Net improves visual localization with deep pose correctionsDocument8 paginiDPC-Net improves visual localization with deep pose correctionspradip guptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced SAN Troubleshooting: Mike FraseDocument60 paginiAdvanced SAN Troubleshooting: Mike FrasejeffgrantinctÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etap Network AnalysisDocument16 paginiEtap Network AnalysisJaime David Jr.Încă nu există evaluări
- ASIC Physical DesignDocument91 paginiASIC Physical DesignLeesha KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adaptive Forward Differencing For Rendering Curves and SurfacesDocument8 paginiAdaptive Forward Differencing For Rendering Curves and SurfacesAnis HadjariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jany B Dy YrrDocument2 paginiJany B Dy Yrrhamzadaud032Încă nu există evaluări
- Database: Principles Programming PerformanceDe la EverandDatabase: Principles Programming PerformanceEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Life Insurance: Policy DetailDocument1 paginăLife Insurance: Policy Detailswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- 8 HashesDocument14 pagini8 Hashesswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- CtsDocument6 paginiCtsswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- Cadence ManualDocument51 paginiCadence Manualapi-27099960100% (4)
- Sta 9 1Document125 paginiSta 9 1Jayaprakash Polimetla100% (1)
- Power PlanDocument1 paginăPower Planswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- Typical Fast Slow: Process Voltage TemperatureDocument2 paginiTypical Fast Slow: Process Voltage Temperatureswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- Sta 9 1Document125 paginiSta 9 1Jayaprakash Polimetla100% (1)
- Sanity ChecksDocument3 paginiSanity Checksswathikomati787067% (3)
- Lect7 PowerDocument29 paginiLect7 PowerAshok ObuliÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHP 7 FullDocument35 paginiCHP 7 FullMahesh Babu SamanapallyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Mosfet Scaling: © 2010 Wipro LTD - Confidential © 2010 Wipro LTD - ConfidentialDocument26 paginiBasics of Mosfet Scaling: © 2010 Wipro LTD - Confidential © 2010 Wipro LTD - Confidentialswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- Switching Power of Memory Depends OnDocument3 paginiSwitching Power of Memory Depends Onswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- Digital AbstractionDocument14 paginiDigital Abstractionswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- Signal Integrity Analysis GuidelinesDocument47 paginiSignal Integrity Analysis Guidelinesswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- These Interview Questions Test The Knowledge of x86 Intel Architecture and 8086 Microprocessor SpecificallyDocument4 paginiThese Interview Questions Test The Knowledge of x86 Intel Architecture and 8086 Microprocessor Specificallyswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- 28nm Silicon and Design Enablement The Foundry and EDA Vendor PerspectiveDocument31 pagini28nm Silicon and Design Enablement The Foundry and EDA Vendor Perspectiveswathikomati7870Încă nu există evaluări
- NetworkingDocument8 paginiNetworkingapi-3782519Încă nu există evaluări
- Bachelor of Science in Computer Science and EngineeringDocument24 paginiBachelor of Science in Computer Science and EngineeringSharhan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intel Job Openings Feb 14, 2022Document8 paginiIntel Job Openings Feb 14, 2022PRANAV KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Design For Asic - Linux PDFDocument7 paginiPhysical Design For Asic - Linux PDFShwethÎncă nu există evaluări
- Allegro Package Designer FlowsDocument20 paginiAllegro Package Designer FlowsAnonymous eNddb31Y100% (1)
- Ece5019 Computer-Aided-Design-For-Vlsi TH 1.0 40 Ece5019Document2 paginiEce5019 Computer-Aided-Design-For-Vlsi TH 1.0 40 Ece5019Daniel MÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSI Physical DesignDocument2 paginiVLSI Physical DesignSrini Vas0% (1)
- Introduction To Asics: Ni Logic Pvt. LTD., PuneDocument84 paginiIntroduction To Asics: Ni Logic Pvt. LTD., PuneankurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tetramax DF DsDocument4 paginiTetramax DF DsBrijesh S DÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1RV19LVS20Document2 pagini1RV19LVS20MoulaKhatibÎncă nu există evaluări
- MTech ECE (VLSI) PDFDocument21 paginiMTech ECE (VLSI) PDFTanmay BiswasÎncă nu există evaluări
- UNATE - Timing Arc - VLSI ConceptsDocument10 paginiUNATE - Timing Arc - VLSI ConceptsIlaiyaveni IyanduraiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSI Physical Design ProcessDocument27 paginiVLSI Physical Design ProcessVimal RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- L14 Placement and RoutingDocument40 paginiL14 Placement and RoutingpolururamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cadence SOC EncounterDocument222 paginiCadence SOC Encountereeshgarg0% (1)
- JOBS at IBMDocument99 paginiJOBS at IBMbharatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Milkyway: Anik Saha Project EngineerDocument35 paginiMilkyway: Anik Saha Project EngineerUtkarsh AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSI Physical Design - STA Interview Questions Part 1Document2 paginiVLSI Physical Design - STA Interview Questions Part 1srinathÎncă nu există evaluări
- VLSI file formats and clock tree exceptionsDocument23 paginiVLSI file formats and clock tree exceptionsvikasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bachelor of Science in Electrical and Electronic EngineeringDocument22 paginiBachelor of Science in Electrical and Electronic EngineeringSharhan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- STA BasicsDocument13 paginiSTA BasicsKanni GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dealing With Over Pessimism in Physical Design PDFDocument6 paginiDealing With Over Pessimism in Physical Design PDFIslam SamirÎncă nu există evaluări
- DFT Interview QuestionsDocument5 paginiDFT Interview QuestionsJayesh PopatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soc Physical Design: Veena S. Chakravarthi Shivananda R. KoteshwarDocument173 paginiSoc Physical Design: Veena S. Chakravarthi Shivananda R. KoteshwarSunil ChettipalliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Power Upf NotesDocument5 paginiLow Power Upf Notessaugat guhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design - Clock GatingDocument4 paginiASIC-System On Chip-VLSI Design - Clock Gatinguni_saraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vlsi Design Flow PDFDocument13 paginiVlsi Design Flow PDFUdbhav MaheshwariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vinod PD 2.5 Years Tessolve SemiconductorsDocument2 paginiVinod PD 2.5 Years Tessolve SemiconductorstejanossamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Vlsi DesignDocument101 paginiIntroduction To Vlsi DesignfsdffcdsfvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Day FDP On ASIC Physical Design Using Cadence First EncounterDocument2 paginiTwo Day FDP On ASIC Physical Design Using Cadence First EncountertjanardhanreddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16Document60 paginiChapter 16Daksh BothraÎncă nu există evaluări