Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Alternatives To Breadboard
Încărcat de
chrisTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Alternatives To Breadboard
Încărcat de
chrisDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
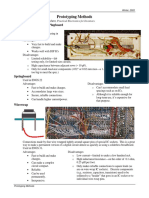
Alternatives to Breadboard
Springboard
Used in ENGS 22. Not commonly used these days.
Advantages
Fast to build and make changes.
Accomodates large wire sizes.
Secure, reliable connections.
Can handle higher current/power.
Disadvantages
Cant accommodate small lead spacings such as on ICs.
Although it is reliable enough for long-term use, its expensive for that
purpose.
Wirewrap
Way to make a permanent version of a digital circuit almost as quickly as using a
solderless breadboard.
Advantages
Fast to build and make changes.
Can make a complex circuit compact. Reliable. Can be used permanently.
Inexpensive.
Disadvantages
Low currentlimited to under a few hundred mA. High inductance/resistance
on the order of 0.1 ohm, 0.25 H per foot.
Only makes reliable connections to square leads (as are on wire-wrap IC
sockets). Discrete components (e.g., resistors, capacitors, transistors) need to
be soldered to a header that goes in an IC socket or to individual wire-wrap
pins.
Perfboard and Solder
Using the same perfboard as used in wire-wrap work, it is possible to simply twist
and solder leads, and run wires where needed. It is commonly used for
prototyping electronic circuits (also called DOT PCB). It is a thin, rigid sheet with
holes pre-drilled at standard intervals across a grid, usually a square grid of
2.54 mm (0.1 in) spacing.
Advantages
Reliable, if done well. Can be used permanently. Inexpensive.
Can handle any size components
Convenient for working with discrete components.
Disadvantages
Slow, requires skill to do well.
Works for ICs, but not very easily
Generic Printed-Circuit Boardmultiple hole-per-pad
A printed circuit board with a pattern of holes and connections similar to a
solderless breadboard.
Advantages
Easier than using plain perfboard, especially for ICs.
Reliable. Can be used permanently.
Available with ground planes if needed.
Disadvantages
Usually not as compact a final circuit as some alternatives, because you are
constrained by layout.
Pads bigger than needed can add capacitance, but not much.
Can be expensive, especially the vectorboard brand. Sometimes awkward
for odd sized or large components.
Dead Bug, or Ugly-board
Start with a plain copper-clad board. Glue ICs down with the leads sticking up in the
air. Then solder to them
Advantages
Provides an excellent ground plane.
Can be a high performance way to build sensitive and/or highfrequency
analog circuits .
Can make a complex circuit compact.
Reliable.
Can be used permanently. Inexpensive.
Disadvantages
Requires high soldering skill.
Takes a long time to build.
Mechanical support for components is marginal; can add glue (RTV) after
debugging.
Only makes reliable connections to square leads (as are on wire-wrap IC
sockets).
Other components (e.g., resistors, capacitors, transistors) need to be
soldered to a header that goes in an IC socket or to individual wirewrap
pins.
Printed circuit board (PCB)
This is what is used virtually universally in production of electronics. It mechanically
supports and electrically connects electronic components using conductive tracks, pads and other
features etched from copper sheets laminated onto a non-conductive substrate. Components
(capacitors, resistors or active devices) are generally soldered on the PCB.
Advantages
Easy to build in production.
Repeatable, controllable stray L, C.
Can handle virtually any component, power level.
Highly reliable.
Can make very compact.
Design can be (somewhat) automated from a schematic you have entered.
Disadvantages
Laying out the board and getting it fabricated takes time, although you can
pay for fabrication in a few days if you can afford it.
Expensive, on the order of hundreds of dollars for one, but with almost no
increase in cost to make many.
Hard to make changes, but making changes may be easier than building
another type of prototype
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Alternatives To Breadboard: SpringboardDocument3 paginiAlternatives To Breadboard: SpringboardSomesh KshirsagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Little Book of Vacuum Tube Pre-Amplifier ProjectsDe la EverandThe Little Book of Vacuum Tube Pre-Amplifier ProjectsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prototyping PDFDocument6 paginiPrototyping PDFSomesh KshirsagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pro To TypingDocument6 paginiPro To TypingSomesh KshirsagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Embedded System Interfacing: Design for the Internet-of-Things (IoT) and Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)De la EverandEmbedded System Interfacing: Design for the Internet-of-Things (IoT) and Cyber-Physical Systems (CPS)Încă nu există evaluări
- PCB Design Presentation: Jakia AfruzDocument33 paginiPCB Design Presentation: Jakia AfruzParth MangukiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparis I OnDocument29 paginiComparis I OnKhuzaim KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Circuit ConstructionDocument5 paginiElectronic Circuit ConstructionMatovu HerbertÎncă nu există evaluări
- All You Need To Know About PCB HeaderDocument10 paginiAll You Need To Know About PCB HeaderjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- BreadboardDocument91 paginiBreadboardMini DachshundÎncă nu există evaluări
- Printed Circuit Board: Presented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)Document75 paginiPrinted Circuit Board: Presented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)Ruby Pathak100% (2)
- Breadboard & Power SupplyDocument25 paginiBreadboard & Power SupplycyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)Document75 paginiPresented by Ruby Kumari B.SC (MATHS), B.E (ECE)AhmedMohabÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCB Unit 1Document77 paginiPCB Unit 1shrimanÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Difference Between A Circuit Board and A Bread BoardDocument12 paginiWhat Is The Difference Between A Circuit Board and A Bread BoardjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perf BoardDocument11 paginiPerf BoardpraveenÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Through Hole PCB AssemblyDocument12 paginiWhat Is Through Hole PCB AssemblyjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- UltiboardDocument6 paginiUltiboardSwathy NairÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Circuit - BreadboardDocument2 paginiElectronic Circuit - BreadboardPrabhat Kumar ChandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microelectronics & Computer PrinciplesDocument61 paginiMicroelectronics & Computer PrinciplesMaria Phebe SinsayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Printed Circuit Board: CharacteristicsDocument23 paginiPrinted Circuit Board: CharacteristicsSai Gautam100% (1)
- Embedded Passive ComponentDocument62 paginiEmbedded Passive ComponentAbbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic ConstructionDocument19 paginiElectronic Constructionabbd1990Încă nu există evaluări
- Construction Hints and TechniquesDocument8 paginiConstruction Hints and Techniquesbayman66Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is Buried Via PCBDocument10 paginiWhat Is Buried Via PCBjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Printed Circuit BoardDocument23 paginiPrinted Circuit Boardahmed100% (2)
- Practical Guide To High Speed PCB Layout by by John ArdizzoniDocument6 paginiPractical Guide To High Speed PCB Layout by by John ArdizzoniblekstenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCB Designing Fundamentals: Compiled By: Hiren Patel (ET Dept.)Document42 paginiPCB Designing Fundamentals: Compiled By: Hiren Patel (ET Dept.)Chintaan PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Blind Via PCBDocument10 paginiWhat Is Blind Via PCBjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Layered PCB How Many Types of Layers of PCB Are ThereDocument8 paginiLayered PCB How Many Types of Layers of PCB Are TherejackÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCB Technical Interview QuestionsDocument55 paginiPCB Technical Interview Questionssandee kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is The Significance of Home Electronics PCBDocument6 paginiWhat Is The Significance of Home Electronics PCBjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCB ProcessDocument10 paginiPCB ProcessChetan AwasthiÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCB ManufacturingDocument7 paginiPCB ManufacturingAbhishek SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Ic AssemblyDocument38 paginiFundamentals of Ic AssemblykhsniperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture No-03 Course PCB Manufacturing IE-236 & Electronic Simulation and PCB Manufacturing (Repeaters Only)Document22 paginiLecture No-03 Course PCB Manufacturing IE-236 & Electronic Simulation and PCB Manufacturing (Repeaters Only)Ravi Shankar 31Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 Basics of PCBDocument32 paginiLecture 1 Basics of PCBjaltitiÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Castellated Holes in PCBDocument13 paginiWhat Are Castellated Holes in PCBjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1910DMTCSE05932 - Iot AssignmentDocument63 pagini1910DMTCSE05932 - Iot AssignmentGourav RanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-1 Wireless Communication - Laser CommunicationDocument56 paginiChapter-1 Wireless Communication - Laser Communicationyash_dk20083706Încă nu există evaluări
- Water Level IndicatorDocument27 paginiWater Level IndicatorAbhijit PattnaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is A Socket PCBDocument8 paginiWhat Is A Socket PCBjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sec07 - RacewaysDocument10 paginiSec07 - RacewaysYusufÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q3 Grade 9 Lesson2 Types of PCB - 20240206 - 182134 - 0000Document41 paginiQ3 Grade 9 Lesson2 Types of PCB - 20240206 - 182134 - 0000Denice ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Article: Ten Tips For Designing Small and Efficient AC/DC Switching Power SuppliesDocument4 paginiTechnical Article: Ten Tips For Designing Small and Efficient AC/DC Switching Power Suppliesatul vijayvergiyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pert 7. PCB - 2Document23 paginiPert 7. PCB - 2Rahma HanifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Top IC Socket Manufacturers in The WorldDocument5 paginiTop IC Socket Manufacturers in The WorldjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hybrid Material PCB Circuit BoardDocument24 paginiHybrid Material PCB Circuit BoardjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Integrated CircuitsDocument57 paginiLinear Integrated CircuitsLakshmi RÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Discrete Circuit?: 1. Handles High Power Input 2. Produces High Power OutputDocument6 paginiWhat Is Discrete Circuit?: 1. Handles High Power Input 2. Produces High Power OutputJamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are PCB Pins and How Do They WorkDocument4 paginiWhat Are PCB Pins and How Do They WorkjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- PCB Drilling Machine PDFDocument32 paginiPCB Drilling Machine PDFJorge EstradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronics LAB MANUAL Exp-2Document6 paginiElectronics LAB MANUAL Exp-2Dulce DeÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Practical Guide To High-Speed Printed-Circuit-Board LayoutDocument6 paginiA Practical Guide To High-Speed Printed-Circuit-Board LayoutRenato BittencourtÎncă nu există evaluări
- ENEL3CA/DA: Electronic/Computer Design 1: PCB Philosophy and Design Using UltiboardDocument43 paginiENEL3CA/DA: Electronic/Computer Design 1: PCB Philosophy and Design Using Ultiboardbknaruma100% (1)
- ElectronicsDocument48 paginiElectronicsadrianjayatendido20Încă nu există evaluări
- What Is PCB Edge PlatingDocument23 paginiWhat Is PCB Edge PlatingjackÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16.nicaragua v. United States (ICJ, June 27, 1986)Document141 pagini16.nicaragua v. United States (ICJ, June 27, 1986)chrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Concepts: GabrielleDocument16 paginiGeneral Concepts: Gabriellechris100% (2)
- 13 GIRLY G. ICO vs. SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE, INCDocument2 pagini13 GIRLY G. ICO vs. SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE, INCromeo habbilingÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 NLRC Procedure (As Amended) FlowchartDocument3 pagini2011 NLRC Procedure (As Amended) FlowchartShine BillonesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abuda Vs NatividadDocument3 paginiAbuda Vs NatividadchrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Negros Slashers Vs TengDocument2 pagini2 - Negros Slashers Vs TengchrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Soliman Security Services, Inc., Et Al v. Sarmiento, Et Al.Document2 paginiSoliman Security Services, Inc., Et Al v. Sarmiento, Et Al.chrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- SUMIFRU Phils. Corp vs. BayaDocument2 paginiSUMIFRU Phils. Corp vs. BayachrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Negros Slashers Vs TengDocument2 pagini2 - Negros Slashers Vs TengchrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic of The Philippines, Represented by The Civil Service Commission vs. Minerva M.P. PacheoDocument3 paginiRepublic of The Philippines, Represented by The Civil Service Commission vs. Minerva M.P. PacheochrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demetrio Ellao vs. Barangas Electric CoopDocument2 paginiDemetrio Ellao vs. Barangas Electric Coopchris0% (1)
- Laguna Copperplate Inscription Apostma1992 PDFDocument22 paginiLaguna Copperplate Inscription Apostma1992 PDFMarymae De Fiesta SipinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demetrio Ellao vs. Barangas Electric CoopDocument2 paginiDemetrio Ellao vs. Barangas Electric Coopchris0% (1)
- Republic of The Philippines, Represented by The Civil Service Commission vs. Minerva M.P. PacheoDocument3 paginiRepublic of The Philippines, Represented by The Civil Service Commission vs. Minerva M.P. PacheochrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- LBP Vs PuyatDocument5 paginiLBP Vs PuyatchrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICT Marketing Services, Inc. Vs Sales, GR No.202090, 05 Sept 2015Document2 paginiICT Marketing Services, Inc. Vs Sales, GR No.202090, 05 Sept 2015chrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chateau Royale Vs BalbaDocument4 paginiChateau Royale Vs BalbachrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fianza Vs PeopleDocument2 paginiFianza Vs PeoplechrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- PFR Digest FinalDocument534 paginiPFR Digest Finalchris50% (2)
- Echo 2000 Commercial Corp Vs Obrero FilpinoDocument2 paginiEcho 2000 Commercial Corp Vs Obrero FilpinochrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIT Lec03Document31 paginiGIT Lec03chrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laguna Copperplate Inscription Apostma1992 PDFDocument22 paginiLaguna Copperplate Inscription Apostma1992 PDFMarymae De Fiesta SipinÎncă nu există evaluări
- LBP Vs PuyatDocument5 paginiLBP Vs PuyatchrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 13 GIRLY G. ICO vs. SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE, INCDocument2 pagini13 GIRLY G. ICO vs. SYSTEMS TECHNOLOGY INSTITUTE, INCromeo habbilingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Laguna Copperplate Inscription Apostma1992 PDFDocument22 paginiLaguna Copperplate Inscription Apostma1992 PDFMarymae De Fiesta SipinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity Sheet 1Document6 paginiActivity Sheet 1chrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- GIT: Living in The IT Era: Lect Ure 01Document22 paginiGIT: Living in The IT Era: Lect Ure 01Darriane Joyce LealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acetic AcidDocument2 paginiAcetic AcidchrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 8Document4 pagini7 8chrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Program To Count 0 To 9999 BCD and Show It On The LCD DisplayDocument5 paginiC Program To Count 0 To 9999 BCD and Show It On The LCD Displaylive_107294Încă nu există evaluări
- Info CubeDocument9 paginiInfo CubeDevesh VarshneyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5069 In011f en P PDFDocument12 pagini5069 In011f en P PDFfaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pick Systems Reference ManualDocument1.023 paginiPick Systems Reference ManualMárcio Souza JúniorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Utility Anchors Catalog 2017-10-10Document26 paginiUtility Anchors Catalog 2017-10-10Shung Tak ChanÎncă nu există evaluări
- SketchbookDocument26 paginiSketchbookLauren Suzuki100% (1)
- Dma Operation in An 8086 Based SystemDocument3 paginiDma Operation in An 8086 Based SystemSowmya PÎncă nu există evaluări
- LMT - 1 - Introduction To Networks and Networking ConceptsDocument53 paginiLMT - 1 - Introduction To Networks and Networking Conceptslakshay187Încă nu există evaluări
- Embedded System Project ReportDocument55 paginiEmbedded System Project ReportManoj Saini0% (1)
- AS5EG Formation Powervm On Ibm I Implementing Virtualization and Lpar PDFDocument1 paginăAS5EG Formation Powervm On Ibm I Implementing Virtualization and Lpar PDFCertyouFormationÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approval Sheet - AbstractDocument9 paginiApproval Sheet - AbstractChristian Paul Manalo TaburadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Navios Flow Cytometer: Optimize Workflow With A Cytometer That Brings To Your LabDocument6 paginiNavios Flow Cytometer: Optimize Workflow With A Cytometer That Brings To Your LabcandiddreamsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tools CatalogDocument138 paginiTools CatalogflerziÎncă nu există evaluări
- CompX Security Products Catalog, Nov 2009Document20 paginiCompX Security Products Catalog, Nov 2009Kip LavingerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vedic Maths in Digital Signal ProcessingDocument6 paginiVedic Maths in Digital Signal ProcessingSwanand RaikarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Graphics Tablet User ManualDocument55 paginiGraphics Tablet User ManualByju MannilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tisoft 2 ManualDocument418 paginiTisoft 2 ManualDaniel100% (1)
- f8x34 Series Router User ManualDocument100 paginif8x34 Series Router User ManualCocofourfaithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cloud ComputingDocument25 paginiCloud ComputinganjanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glitch Works 8085 SBC Rev 3 GW-8085SBC-3: User's Manual and Assembly GuideDocument17 paginiGlitch Works 8085 SBC Rev 3 GW-8085SBC-3: User's Manual and Assembly Guidegord12Încă nu există evaluări
- CLISTDocument190 paginiCLISTHarihara KrishnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Qap For Fastener-IoclDocument3 paginiQap For Fastener-IoclTechproÎncă nu există evaluări
- FANUC Flash CardsDocument25 paginiFANUC Flash Cardskemo_750252831Încă nu există evaluări
- NI9265 DatasheetDocument14 paginiNI9265 DatasheetAntonio HerreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIX SAN BootDocument4 paginiAIX SAN BootYulin LiuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mech 325 Tutorials (Questions Only)Document54 paginiMech 325 Tutorials (Questions Only)Shahriar Norouzi ZadehÎncă nu există evaluări
- India Structured Cabling Edition 2world Market For Cabling 2017r2016 (Sample)Document5 paginiIndia Structured Cabling Edition 2world Market For Cabling 2017r2016 (Sample)federicosanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- PartitioningDocument224 paginiPartitioningAnubha Raina DharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isuzu D-Max 2011 Steering, Suspension, Wheels and TiresDocument126 paginiIsuzu D-Max 2011 Steering, Suspension, Wheels and TiresWilmer HuangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mark Russinovich - Memory - A MustDocument60 paginiMark Russinovich - Memory - A MustyonnonÎncă nu există evaluări