Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Instruction Cycle
Încărcat de
Sadaf Rasheed0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
69 vizualizări12 paginicomputer architecture
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentcomputer architecture
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
69 vizualizări12 paginiInstruction Cycle
Încărcat de
Sadaf Rasheedcomputer architecture
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 12
Instruction Cycle
Phases of Instruction Cycle
Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Abhineet Anand
Computer Science and Engg. Department
University of Petroleum and Energy Studies, Dehradun
November 26, 2012
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Introduction
Instruction Cycle
Diagram
Phases of Instruction Cycle
Circuit Used
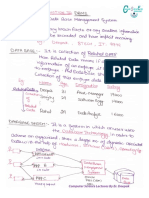
Instruction Cycle
A program residing in the memory unit of the computer
consist of a sequence of Instructions.
The program is executed in the computer by going through
a cycle for each instruction.
Each instruction cycle in turn is subdivided into a sequence
of sub cycle or phase.
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Introduction
Instruction Cycle
Diagram
Phases of Instruction Cycle
Circuit Used
Instruction Cycle
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Introduction
Instruction Cycle
Diagram
Phases of Instruction Cycle
Circuit Used
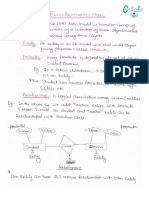
Circuits Used
The circuits used in the CPU during the cycle are:
Program counter (PC) - an incrementing counter that
keeps track of the memory address of the instruction that is
to be executed next.
Memory address register (MAR) - holds the address of a
memory block to be read from or written to.
Memory data register (MDR) - a two-way register that
holds data fetched from memory (and ready for the CPU to
process) or data waiting to be stored in memory.
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Introduction
Instruction Cycle
Diagram
Phases of Instruction Cycle
Circuit Used
Circuits Used Contd..
Instruction register (IR) - a temporary holding ground for
the instruction that has just been fetched from memory
Control unit (CU) - decodes the program instruction in the
IR, selecting machine resources such as a data source
register and a particular arithmetic operation, and
coordinates activation of those resources
Arithmetic logic unit (ALU) - performs mathematical and
logical operations
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Fetching the instruction
Instruction Cycle Decode the instruction
Phases of Instruction Cycle In case of a memory instruction
Execute the instruction
Phases of Instruction Cycle
In basic computer, each instruction cycle consists of the
following phases:
Fetch an instruction from Memory.
Decode the instruction.
Read the effective address from memory if the instruction
has an indirect address.
Execute the instruction.
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Fetching the instruction
Instruction Cycle Decode the instruction
Phases of Instruction Cycle In case of a memory instruction
Execute the instruction
Fetching the instruction
The next instruction is fetched from the memory address
that is currently stored in the program counter (PC), and
stored in the instruction register (IR).
Now, the PC points to the next instruction that will be read
at the next cycle.
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Fetching the instruction
Instruction Cycle Decode the instruction
Phases of Instruction Cycle In case of a memory instruction
Execute the instruction
Decode the instruction
The decoder interprets the instruction.
During this phases the instruction inside the IR (instruction
register) gets decoded.
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Fetching the instruction
Instruction Cycle Decode the instruction
Phases of Instruction Cycle In case of a memory instruction
Execute the instruction
In case of a memory instruction
In case of a memory instruction (direct or indirect) the
execution phase will be in the next clock pulse.
Required data is fetched from main memory to be
processed and then placed into data registers.
During this phases the instruction inside the IR (instruction
register) gets decoded.
If the instruction is direct, nothing is done at this clock
pulse.
If this is an I/O instruction or a Register instruction, the
operation is performed (executed) at clock Pulse.
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Fetching the instruction
Instruction Cycle Decode the instruction
Phases of Instruction Cycle In case of a memory instruction
Execute the instruction
Execute the instruction
The control unit of CPU passes the decoded information
as a sequence of control signals.
Signals are passed to the relevant function units of the
CPU to perform the actions required.
These action may be :
Reading values from registers,
Passing them to the ALU to perform mathematical or logic
functions on them, or
Writing the result back to a register
The result generated by the operation is stored in the main
memory, or sent to an output device.
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Fetching the instruction
Instruction Cycle Decode the instruction
Phases of Instruction Cycle In case of a memory instruction
Execute the instruction
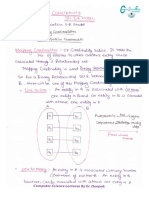
The Fetch Execute cycle in Transfer Notation
Expressed in register transfer notation:
MAR <- PC
MDR<- Memory {MAR address}; PC <- [PC]+1 (Increment
the PC for next cycle at the same time)
IR<- MDR
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
Fetching the instruction
Instruction Cycle Decode the instruction
Phases of Instruction Cycle In case of a memory instruction
Execute the instruction
THANK YOU
Abhineet Anand Unit 3 - CONTROL UNIT DESIGN
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Types of InstructionsDocument12 paginiTypes of InstructionsSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Processing Unit (CPU)Document16 paginiCentral Processing Unit (CPU)Sadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stack OrganizationDocument6 paginiStack OrganizationSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Register Transfer and Micro-OperationDocument33 paginiRegister Transfer and Micro-OperationSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8-6 Data Transfer and ManipulationDocument16 pagini8-6 Data Transfer and ManipulationSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presented By: Syeda Rida Fatima TaqviDocument22 paginiPresented By: Syeda Rida Fatima TaqviSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- DBMS MCQDocument8 paginiDBMS MCQbenaminsan67% (6)
- Solution Manual of Digital Logic and Computer Design (2nd Edition) Morris Mano PDFDocument40 paginiSolution Manual of Digital Logic and Computer Design (2nd Edition) Morris Mano PDFSadaf Rasheed0% (4)
- CH 8Document6 paginiCH 8Mustafa JumaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Job AnalysisDocument40 paginiJob AnalysisSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 05Document11 paginiCH 05Samsul ArifinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Models: Answers To Review QuestionsDocument13 paginiData Models: Answers To Review QuestionsRosh SibalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01-Introduction To DBMS-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HIndiDocument2 pagini01-Introduction To DBMS-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HIndiSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- RDBMS Concepts Basics Interview Questions PDFDocument6 paginiRDBMS Concepts Basics Interview Questions PDFSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08-OverView of Data Models-Relational Data Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in Hindi PDFDocument3 pagini08-OverView of Data Models-Relational Data Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in Hindi PDFSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 01Document13 paginiChapter 01Sadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 06Document11 paginiCH 06Sadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 08-OverView of Data Models-Relational Data Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in Hindi PDFDocument3 pagini08-OverView of Data Models-Relational Data Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in Hindi PDFSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 24-Entity-Relationship Data Model-Data Integrity & Keys - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocument2 pagini24-Entity-Relationship Data Model-Data Integrity & Keys - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 25-Entity-Relationship Data Model-RelationShip Sets Keys - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocument2 pagini25-Entity-Relationship Data Model-RelationShip Sets Keys - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02-Properties of DataBase Part-1-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocument3 pagini02-Properties of DataBase Part-1-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 27-Entity-Relationship Data Model-Entity-E-R - Diagram To Tables - Rules For Reduction - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocument3 pagini27-Entity-Relationship Data Model-Entity-E-R - Diagram To Tables - Rules For Reduction - DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 07-OverView of Data Models-Entity Relationship Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocument1 pagină07-OverView of Data Models-Entity Relationship Model-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 23-Entity-Relationship Data Model - Constraints-Mapping Cardinalities - DBMS Tutorials FoDocument3 pagini23-Entity-Relationship Data Model - Constraints-Mapping Cardinalities - DBMS Tutorials FoSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09-OverView of Data Models-Object Oriented Data MOdel-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocument2 pagini09-OverView of Data Models-Object Oriented Data MOdel-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04-Various Views of Data-Data Abstraction-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiDocument4 pagini04-Various Views of Data-Data Abstraction-DBMS Tutorials For Beginners in HindiSadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 08Document43 paginiComputer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 08Sadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 07Document24 paginiComputer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 07Sadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 06Document22 paginiComputer Architecture 3rd Edition by Moris Mano CH 06Sadaf RasheedÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (120)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- 1151Cs118-Microprocessors and Controllers: VTUR15Document2 pagini1151Cs118-Microprocessors and Controllers: VTUR15Dheeraj13Încă nu există evaluări
- Lab 09Document5 paginiLab 09api-241454978Încă nu există evaluări
- AMD Ryzen™ 3 3200U Drivers & Support - AMD PDFDocument4 paginiAMD Ryzen™ 3 3200U Drivers & Support - AMD PDFENERGY ENGINEERINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Selected Topics in Embedded Systems: SeminarDocument13 paginiSelected Topics in Embedded Systems: Seminarstephen562001Încă nu există evaluări
- Tabla Comparativa de ProcesadoresDocument12 paginiTabla Comparativa de ProcesadoresJavier Enrique Aguilar MancoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Add 16 Bit Numbers in 8085Document9 paginiAdd 16 Bit Numbers in 8085PinakiRanjanSarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- A1896785571 - 23825 - 16 - 2019 - Unit 4.1Document40 paginiA1896785571 - 23825 - 16 - 2019 - Unit 4.1Satyam AnandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ae305 Microprocessors Microcontrollers PDFDocument2 paginiAe305 Microprocessors Microcontrollers PDFCharlotte DunkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor and Interfacing Unit 1Document10 paginiMicroprocessor and Interfacing Unit 1Shubham SoniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bit Set and Clear For 68HC11Document4 paginiBit Set and Clear For 68HC11dineszr0% (1)
- Difference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollerDocument17 paginiDifference Between Microprocessor and MicrocontrollervedhajuvalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teme Proiect Compl ASI MSI 2k16Document5 paginiTeme Proiect Compl ASI MSI 2k16Ilie IulianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microprocessor Systems and Interfacing (Eee342) : Dr. Omer Chughtai Assistant Professor, CUI, Wah Campus EmailDocument20 paginiMicroprocessor Systems and Interfacing (Eee342) : Dr. Omer Chughtai Assistant Professor, CUI, Wah Campus EmailAbdul RabÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Principles of Pipelining: Andrew Warfield CS313Document25 paginiGeneral Principles of Pipelining: Andrew Warfield CS313NishanthoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- More On PipeliningDocument34 paginiMore On PipeliningRAHA TUDU100% (1)
- AVR MicrocontrollersDocument38 paginiAVR Microcontrollerspaku deyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8086 8088 MicroprocessorDocument60 pagini8086 8088 MicroprocessorZain ChaudhryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Avr Tutorials - Com AVR Microcontroller InterruptsDocument4 paginiAvr Tutorials - Com AVR Microcontroller InterruptsMohamed AshrafÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Microcontrollers: Dr. Konstantinos TatasDocument9 paginiIntroduction To Microcontrollers: Dr. Konstantinos TatasSadam MemonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interrupt VectorsDocument3 paginiInterrupt VectorsSAMEER AHMADÎncă nu există evaluări
- Systems I: Computer Organization and Architecture: Instruction CodesDocument27 paginiSystems I: Computer Organization and Architecture: Instruction Codesబొమ్మిరెడ్డి రాంబాబుÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of 16 Bit RiscDocument15 paginiDesign of 16 Bit RiscKeerti RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- ET7102-Microcontroller Based System DesignDocument11 paginiET7102-Microcontroller Based System DesigntaksasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8086 Viva QuestionsDocument10 pagini8086 Viva QuestionsNagaraja Nejikar0% (1)
- NOVALIZA - 09071002016-DPSbringDVDqualityToPDAsDocument4 paginiNOVALIZA - 09071002016-DPSbringDVDqualityToPDAsNova LizaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Bus Interface Unit (BIU) :: Registers For Storing Intermediate and Final Results and Interfaces WithDocument2 paginiThe Bus Interface Unit (BIU) :: Registers For Storing Intermediate and Final Results and Interfaces WithTabia TanzinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hacker Friendly Sbcs Spreadsheet 170101Document3 paginiHacker Friendly Sbcs Spreadsheet 170101Tomislav KostanjčarÎncă nu există evaluări
- DB Desktopcomputers Archive Obsolete 2008-2009Document19 paginiDB Desktopcomputers Archive Obsolete 2008-2009bzkizo_sbbÎncă nu există evaluări
- PDFDocument16 paginiPDFGaurav PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pocket Guide To DSP ProcessorsDocument1 paginăPocket Guide To DSP Processorsapi-19737301Încă nu există evaluări