Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
S7 Academic HandBook
Încărcat de
Swapnil ShindeDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
S7 Academic HandBook
Încărcat de
Swapnil ShindeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Course Handout
Department Of Information Technology
SEMESTER 7
PERIOD: JULY 2016 - DECEMBER 2016
Department of Information Technology Page 1
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
RAJAGIRI SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
Department of Information Technology
Vision
To evolve into a department of excellence in information technology by the creation and
exchange of knowledge through leading edge research, innovation and services, which will
in turn contribute towards solving complex societal problems and thus building a peaceful
and prosperous mankind.
Mission
To impart high quality technical education, research training, professionalism and strong
ethical values in the young minds for ensuring their productive careers in industry and
academia so as to work with a commitment to the betterment of mankind.
Programme Educational Objectives (PEO)
Graduates of Information Technology program shall
PEO 1: Have strong technical foundation for successful professional careers and to evolve
as key-players/ entrepreneurs in the field of information technology.
PEO 2: Excel in analyzing, formulating and solving engineering problems to promote life-
long learning, to develop applications, resulting in the betterment of the society.
PEO 3: Have leadership skills and awareness on professional ethics and codes.
Programme Outcomes (PO)
Information Technology Program Students will be able to:
PO 1. Engineering knowledge: Apply the knowledge of mathematics, science, engineering
fundamentals, and an engineering specialization to the solution of complex engineering
problems.
Department of Information Technology Page 2
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
PO 2. Problem analysis: Identify, formulate, review research literature, and analyze
complex engineering problems reaching substantiated conclusions using first principles of
mathematics, natural sciences, and engineering sciences.
PO 3. Design/development of solutions: Design solutions for complex engineering
problems and design system components or processes that meet the specified needs with
appropriate consideration for the public health and safety, and the cultural, societal, and
environmental considerations.
PO 4. Conduct investigations of complex problems: Use research-based knowledge and
research methods including design of experiments, analysis and interpretation of data, and
synthesis of the information to provide valid conclusions.
PO 5. Modern tool usage: Create, select, and apply appropriate techniques, resources, and
modern engineering and IT tools including prediction and modeling to complex
engineering activities with an understanding of the limitations.
PO 6. The engineer and society: Apply reasoning informed by the contextual knowledge
to assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and the consequent
responsibilities relevant to the professional engineering practice.
PO 7. Environment and sustainability: Understand the impact of the professional
engineering solutions in societal and environmental contexts, and demonstrate the
knowledge of, and need for sustainable development.
PO 8. Ethics: Apply ethical principles and commit to professional ethics and
responsibilities and norms of the engineering practice.
PO 9. Individual and team work: Function effectively as an individual, and as a member
or leader in diverse teams, and in multidisciplinary settings.
Department of Information Technology Page 3
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
PO 10. Communication: Communicate effectively on complex engineering activities with
the engineering community and with society at large, such as, being able to comprehend
and write effective reports and design documentation, make effective presentations, and
give and receive clear instructions.
PO 11. Project management and finance: Demonstrate knowledge and understanding of
the engineering and management principles and apply these to ones own work, as a
member and leader in a team, to manage projects and in multidisciplinary environments.
PO 12. Life-long learning: Recognize the need for, and have the preparation and ability to
engage in independent and life-long learning in the broadest context of technological
change.
Program Specific Outcomes(PSO)
Information Technology Program Students will be able to:
PSO1: Acquire skills to design, analyse and develop algorithms and implement them using
high-level programming languages.
PSO2: Contribute their engineering skills in computing and information engineering
domains like network design and administration, database design and knowledge
engineering.
PSO3: Develop strong skills in systematic planning, developing, testing implementing and
providing IT solutions for different domains which helps in the betterment of life.
Department of Information Technology Page 4
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
INDEX
Sl. No Content Page No
1 Assignment Schedule for S7 IT 8
2 IT010 701 Financial Management and E-Banking 9
10
2.1 Course Information Sheet
2.2 Course Plan 15
2.2 Tutorial 17
2.3 Assignment 19
3 IT010 702 Object Oriented Modelling and Design 21
3.1 Course Information Sheet 22
3.2 Course Plan 27
3.3 Tutorial 30
3.4 Assignment 30
IT010 703 Computer Graphics and Multimedia
4 Systems 31
4.1 Course Information Sheets 32
4.2 Course Plan 37
4.3 Tutorial 39
4.4 Assignment 40
5 IT010704Internetworking 41
5.1 Course Information Sheets 42
5.2 Course Plan 47
5.3 Tutorial 48
Department of Information Technology Page 5
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
5.4 Assignment 49
6 50
IT010 705 Web Applications Development
6.1 Course Information Sheets 51
6.2 Course Plan 56
6.3 Tutorial 58
6.4 Assignment 58
7 IT010 706L05 Operating System Kernel Design 59
7.1 Course Information Sheets 60
7.2 Course Plan 64
7.3 Tutorial 66
7.4 Assignment 66
8 IT010 706L06 Data Mining and Data Warehousing 67
8.1 Course Information Sheets 68
8.2 Course Plan 75
8.3 Tutorial 77
8.4 Assignment 78
9 IT010 707 Internetworking Lab 91
9.1 Course Information Sheets 92
9.2 Lab Cycle 97
9.3 Lab Schedule 100
9.4 Open Questions 101
9.5 Advanced Questions 105
Department of Information Technology Page 6
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
10 IT010 708 Computer Aided Software Engineering Lab 79
10.1 Course Information Sheets 80
10.2 Lab Schedule 84
10.3 Lab Cycle 86
10.4 Open Questions 88
10.5 Advanced Questions 89
11 IT010 709 Seminar 108
11.1 Course Information Sheets 109
11.2 Seminar Schedule 112
12 IT010 710 Project 117
12.1 Course Information Sheets 118
12.2 Project Schedule 120
Department of Information Technology Page 7
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
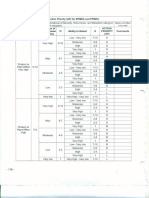
ASSIGNMENT SCHEDULE FOR S7 IT
Week Subject Subject Teacher
Week 1 Financial Management and E-Banking Dipti Lunawat
Week 2 Object Oriented Modelling and Design Divya James
Computer Graphics and Multimedia
Week 3 Lakshmi KS
Systems
Week 4 Internetworking Jisha G
Week 5 Web Applications Development Chinchu Krishna
Data Mining and Data Warehousing/
Week 6 Sherly KK/ Mathews Abraham
Operating System Kernel Design
Week 7 Financial Management and E-Banking Dipti Lunawat
Week 8 Object Oriented Modelling and Design Divya James
Computer Graphics and Multimedia
Week 9 Lakshmi KS
Systems
Week 10 Internetworking Jisha G
Week 11 Web Applications Development Chinchu Krishna
Data Mining and Data Warehousing/
Week 12 Sherly KK/ Mathews Abraham
Operating System Kernel Design
Prepared By Approved By
DIVYA JAMES BINU A
Department of Information Technology Page 8
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 701
FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT
AND E-BANKING
Department of Information Technology Page 9
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 701 FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND E-BANKING
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
PROGRAMME: INFORMATION DEGREE: BTECH
TECHNOLOGY
COURSE: FINANCIAL MANAGEMENT AND E SEMESTER: VII CREDITS: 4
BANKING
COURSE CODE :IT010 701 COURSE TYPE: CORE
REGULATION: 2010
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: CONTACT HOURS: 2+2(Tutorial) hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY): LAB COURSE NAME:
SYLLABUS:
UNIT DETAILS HOURS
The basic concepts of Accounting: The separation of ownership and control, The
I users of accounts, Computers and users of accounts, Accounting concepts and
conventions, Accounting equation, Balance sheet, Classifying items, The processing 12
function.
Book-Keeping: The double-entry system, Double-entry of expenses, Asset of stock,
Capital and revenue expenditure, Balancing accounts on computers, The trial
II balance, The final accounts, Depreciation, Bad debts and provision for bad debts, 12
Division of the ledger, Books of original entry, Source documents, Accounting
systems, Interpretation of accounts.
Costing: Cost Accounting, Classifying costs, The implications for programming, The
operating statement, the cost of raw materials, the cost of direct labour, the cost of
overheads, job costing, Break-even analysis, Break-even graphs, Budgeting, Standard
III costing, Variance analysis, Marginal costing. Ratio Analysis: Ratio meaning, 12
profitability ratios, profit in relation to sales, profit in relation to investments, Liquid
ratios, Solvency ratios, other ratios, Activity ratios, Eps, DuPont Financial analysis,
ratios for predicating bankruptcy, Inter-fim comparison, ratios limitations.
Fund Flow Statement: Meaning, Importance, Definition of terms, Funds and Flow,
Sources and use of funds, Changes in working capital, Preparation of funds flow
statements, cash flow statements, Sources and uses, preparation. Cost Reduction:
IV Difference between cost control and cost reduction, Prequisites for an effective cost 12
reduction, Concept of value analysis- crux of the cost reduction, steps involved in
Department of Information Technology Page 10
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
introducing a cost reduction program, some examples of cost reduction, Common
limitations.
E-Banking: Changing Dynamics in the Banking Industry, Changing Consumer Needs,
Cost Reduction, Demographic Trends, Regulatory Reform, Technology Based
V Financial services products. Home Banking Implementation Approaches, Home 12
Banking Using Banks Proprietary Software, Banking via the PC Using Dial-Up
Software, Banking via Online Services, Banking via the Web: Security First Network
Bank. Open versus Closed Models, Management Issues in Online Banking,
Differentiating Products and Services, Managing Financial Supply Chains, Pricing
Issues in Online Banking, Marketing Issues: Attracting Customers, Keeping
Customers, Back-Office Support for Online Banking, Integrating Telephone Call
Centers with the Web.
TOTAL HOURS 60
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
T/R K Sharma and Shasi K Gupta Management Accounting Principles And Practice, Kalyani
Publishers.
T/R Khan and Jain, Theory and Problems in Financial Management, Tata Mc Graw Hill
T/R Eugene .F. Brigham & Joel F Houston, Fundamentals of Financial Management, Thomson
Learning.
T/R P.H. Basset,t Computerised Accounting, NCC Blackwell Ltd. , Oxford, 1994
R M.C Shukla & T.S.Grewal, Advanced Accounts, S.Chand & Co. , New Delhi
R Ravi Kalkota,Andrew B. Whinston,Electronic Commerc A Managers Guide, Pearson Education
2006.
R Nand Dharmeja & K.S. Sastry, Finance & Accounting for ,Managerial Competiveness, Weeler
Publishing, Allahabad
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
To have basis understanding of financial terms and basic business terminology.
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 To understand the basic concepts of Accounting, book keeping, costing, fund flow and e- banking
2 To develop the ability of the students to understand the need of finance in the business
environment and common terminology used in Financial Management .
COURSE OUTCOMES:
Department of Information Technology Page 11
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Blooms
SLNO DESCRIPTION Taxono
my Level
C701.1 Students will be Conversant with the need, scope and important concepts of Knowled
accounting ge
(level1)
C701.2 Students will be able to prepare Journal, Ledger, Trail Balance and Final Accounts Create
(level 2)
C701.3 Students should have gained fair knowledge about various Marginal Costing Apply
concepts, Cost Volume Price, Break Even Point analysis and basic skills to (level 3 )
understand the need of Costing concepts in various business contexts.
C701.4 Students should have gained the basic skill to understand Fund Flow Statement, Understa
Cash Flow statement and its need and importance. additional information. nd (level
2)
C701.5 Students should have gained basic knowledge of E banking and use of Information Understa
Technology in banking industry. nd and
Analyze
(level 4)
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
PO1 PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO1 PO1 PO1 PSO1 PSO2 PSO3
2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2
C701.1 _ _ _ - _ _ _ - _ _ 1 1 _ _
C701.2 _ _ _ 2 _ _ _ - _ _ 2 - _ _ _
C701.3 _ _ _ 1 _ _ _ - _ _ 2 - _ _ 1
C701.4 _ _ _ 2 _ _ _ - _ _ 1 - _ _ 1
C701.5 _ _ _ - _ _ _ 1 _ _ 1 1 - _ 1
JUSTIFICATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
MAPPING LOW/MEDIUM/H JUSTIFICATION
IGH
C701.1-PO11 L Knowledge of Accounting, to manage projects and excel in
multidisciplinary environments.
C701.1-PO12 L Preparation of Accounts and ability to be independent and life-
long learning in the field of Accounting.
C701.2-PO4 M Reading and Preparation of balance sheet which includes
interpretation of data, and synthesis of the information to
provide valid conclusions.
C701.2-PO11 M Knowledge of Finance and apply these to ones own work, as a
member and leader in a team, to manage projects
Department of Information Technology Page 12
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C701.3-PO4 L Knowledge of costing to analysis and interpretation of data,
and synthesis of the information to provide valid conclusions.
C701.3-PO11 M Knowledge of costing techniques to determine cost of project
and pricing of the product and to manage projects.
C701.3-PS03 L Knowledge of basic skills in systematic planning of cost needed
in developing, testing implementing and providing IT solutions
for different domains which helps in the betterment of life.
C701.4-PO4 M Knowledge of Cash Flow and Fund Flow, enabling them to
interpret the financial data and providing valid conclusions.
C701.4-PO11 L Knowledge of various sources of Funds and application of
funds in business, to manage funds most efficiently in their
business.
C701.4-PSO3 L Knowledge of predicting the fund requirement for in
developing, testing implementing and providing IT solutions for
different domains which helps in the betterment of life.
C701.5-PO8 L Knowledge of E banking, ethical principles and commit to
professional ethics and responsibilities and norms of the
engineering practice for betterment.
C701.5-PO11 L Knowledge of Home Banking Implementation Approaches
which helps to understand the management principles and apply
these to E banking.
C701.5-PO12 L Knowledge of E Banking and Plastic Money and how Society can
be served better in todays Era of cashless Society .
C701.5-PSO1 L Application of knowledge of Finance to systematic plan,
develop, test, implement and provide IT solutions for E banking
channels which helps in the betterment of life.
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
SL DESCRIPTION PROPOSED RELEVAN RELEVANC
NO ACTIONS CE WITH E WITH
POs PSOs
1 Encourage students to apply financial knowledge for ASSIGNMENTS 11,12 3
Budgeting there cost to start a new project including
the distinction between fixed capital and working
capital.
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ADVANCED TOPICS/DESIGN:
SL DESCRIPTION PROPOSED RELEVANCE WITH RELEVANCE WITH
NO ACTIONS POs PSOs
Department of Information Technology Page 13
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
1 Preparation for Budget, master Assignments 11,12 3
Plan for new business venture
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
1 www.ifrs.org; www.icai.org ; www.icwai.org; www.icsi.edu
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. ASSIGNMENT WEB RESOURCES
LCD/SMART BOARDS STUD. SEMINARS ADD-ON COURSES
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
ASSIGNMENTS STUD. SEMINARS TESTS/MODEL EXAMS UNIV.
EXAMINATION
STUD. LAB PRACTICES STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS CERTIFICATIONS
ADD-ON COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS BY EXT. OTHERS
EXPERTS
Prepared by Approved by
Dipti Lunawat BINU A, HOD
Department of Information Technology Page 14
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 701 Financial Management And E-Banking
COURSE PLAN
Course Plan
Days Duration Topics
Basic concepts of Accounting: The separation of ownership and control, The
Day 1 2 users of accounts
Day 2 2 Acounting concepts and conventions
Day 3 2 Accounting equation,
Day 4 2 Accounting equation,
Day 5 2 Balance sheet, Classifying items,
Day 6 2 Computers and users of accounts, The processing function.
Day 7 2 Book-Keeping: The double-entry system, Double-entry of expenses,
Day 8 2 Journal Enteries
Day 9 2 Capital and revenue expenditure
Day 10 2 Depreciation, Bad debts and provision for bad debts, Division of the ledger
Day 11 2 The trial balance,
Day 12 2 The final accounts
Day 13 2 Costing: Cost Accounting, Classifying costs, The implications for programming
The operating statement, the cost of raw materials, the cost of direct labour,
Day 14 2 the cost of overheads
Day 15 2 Break-even analysis, Break-even graphs,
Day 18 2 Ratio analysis
Day 19 2 Ratio analysis
Department of Information Technology Page 15
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Day 22 2 Job costing, Budgeting
Day 23 2 Standard costing, Variance analysis, Marginal costing
Day 24 0 Fund Flow Statement: Meaning, Importance, Definition of terms,
Day 25 0
Sources and use of funds, Changes in working capital, Preparation of funds
Day 26 2 flow statements
Day 27 2 cash flow statements, Sources and uses, preparation
Day 28 2 Cost Reduction: Difference between cost control and cost reduction,
Day 29 2 Concept of value analysis- crux of the cost reduction, cost reduction program.
Day 30 2 E-Banking: Regulatory Reform, Technology Based Financial services products.
Home Banking Implementation Approaches, Management Issues in Online
Day 31 2 Bank
Department of Information Technology Page 16
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 701 Financial Management And E-Banking
TUTORIAL
Prepare the following trial balance, prepare trading a/c, P& I a/c, and for the year ending
31/12/2013 balance sheet:-
Particulars c/f Debit Credit
Rajan capital 29000
Drawings 760
Purchases 8900
Sales 15000
Sales returns 280
Purchase returns 450
1/1/13 stock 1200
Wages 800
Building 22000
Freight and carriage 2000
Trade expense 200
Advertisement 240
Interest 350
Taxes and insurance 130
Debtors 6500
Creditors 1200
B/R 1500
B/P 700
Cash at bank 1200
Cash in hand 190
Salaries 800
Department of Information Technology Page 17
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
46700 46700
Adjustments:
(1) Stock on 31/12/13 was valued at Rs 1500
(2) Insurance was prepaid to the extent of Rs 40
(3) Outstanding liabilities were salaries 200 and taxes 130
(4) Depreciation on building Rs 2% p.a
Department of Information Technology Page 18
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 701 Financial Management And E-Banking
ASSIGNMENT 1
1. Define Accounting. State its usefulness.
2. Prepare a balance sheet with any five items using imaginary figures.
Particulars Debit Credit
Bad debts provision 100
Cash in hand 3400
Bank balance 22000
Creditors 28000
Debtors 9500
Bills receivable 3200
Bills payable 10000
ASSIGNMENT 2
From the following trial balance prepare trading account, profit and loss account and
balance sheet:
Particulars Debit (Rs) Credit (Rs)
Cash in hand 1,500
Cash at bank 10,000
Purchases 1,40,000
Sales 2,50,000
Return inwards 3,000
Return outwards 1,500
Department of Information Technology Page 19
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Wages 30,000
Fuel and power 5,000
Building 1,00,000
Plant and machinery 90,000
Sundry creditors 16,000
Salaries 10,000
Debtors 9,000
Rent and rates 3,200
Patents 6,000
Capital 1,40,200
4,07,700 4,07,700
Adjustments:
i. Closing stock is valued at Rs.50,000
ii. Outstanding wages Rs.2,000
iii. Rent and rates prepaid Rs.600
Department of Information Technology Page 20
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 702
Object Oriented Modelling
and Design
Department of Information Technology Page 21
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 702 Object Oriented Modelling And Design
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
PROGRAMME:INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEGREE: BTECH
COURSE: Object Oriented Modeling and Design SEMESTER: VII
CREDITS: 3
COURSE CODE: IT010 702 COURSE TYPE: CORE
REGULATION: 2010
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: Object oriented design CONTACT HOURS: 2+1 (Tutorial)
hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF LAB COURSE NAME: CASE LAB
ANY):IT010 708
SYLLABUS:
UNIT DETAILS HOURS
object oriented development-modeling concepts object oriented methodology
models object oriented themes-Object Modeling links and associations 10
I advanced links and association concepts generalization and inheritance
grouping constructs a sample object model
Advanced Object Modeling: aggregation abstract classes generalization as
extension and restriction multiple inheritance metadata candidate keys
constraints.
Dynamic modeling: Events and states Operations Nested state diagrams
Concurrency Advanced dynamic modeling concepts A sample dynamic model
II Relationship of Object and Dynamic models. 10
Functional modeling: Functional models Data Flow Diagrams - Specifying
operations Constraints A sample functional model Relation of functional to
Object and Dynamic models.
Analysis: Analysis in object modeling, dynamic modeling and functional
modeling, Adding operations- Iterating the analysis 10
III System Design: Breaking system into subsystems - Identifying concurrency-
allocating subsystems to processors and tasks, managing of data stores. Handling
of global resources- handling boundary conditions-Common Architectural
Frameworks
Object Design: Overview of Object design Combining the three models
IV Designing algorithms Design optimization Implementation of control 8
Adjustment of inheritance - Design of association Object representation
Physical packaging Documenting design decisions-Comparison of
methodologies
Introduction, UML Diagrams Class diagrams, Sequence diagrams, Object
V diagrams, Deployment diagrams, Use case diagrams, State diagrams, Activity 7
diagram, Component diagrams Case Study.
TOTAL HOURS 45
Department of Information Technology Page 22
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
T1 Object Oriented Modeling and Design James Rumbaugh, Prentice Hall India.
T2 UML Distilled Martin Fowler, Addison Wesley
R1 Object- oriented Systems analysis and design using UML- 4th ed., Simon Bennet,Stephen
McRobb, Ray Farmer. TMH.
R2 Object Oriented Analysis and Design with Applications - Grady Booch, Pearson Education
Asia
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM
IT010406 OBJECT ORIENTED TECHNIQUES This course gives introduction to object 4
oriented concepts
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 To equip the students with the skills of analyzing and designing software systems
2 To impart ideas on building systems through the object oriented modeling approach using the
Unified Modeling Language
COURSE OUTCOMES:
SNO DESCRIPTION PO
MAPPING
C702.1 Graduate will be able to understand the Object oriented view of Systems. a, b, c, d
(Understand level)
C702.2 Graduate will be able to evaluate the complexity in software design. a, c
(Evaluate level)
C702.3 Graduate will be able to develop object-based models in real world projects. C
(Create level)
C702.4 Graduate will be able to be able to analyze information systems in real-world b,j
settings.
(Analyze level)
C702.5 Graduate will be able to represent a real-world system using UML diagrams. e,j
(Understand level)
Department of Information Technology Page 23
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
PO1 PO2 PO3 PO4 PO5 PO6 PO7 PO8 PO9 PO10 PO11 PO12 PSO1 PSO2 PSO3
C702.1 3 1 2 1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 2 _ _
C702.2 2 - 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 3 _
C702.3 - _ 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 2 _ _
C702.4 3 _ _ _ _ 3 _ _ 2 _ _
C702.5 - _ _ 3 _ _ _ _ 3 _ _ _ _
JUSTIFATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
Mapping LOW/MEDIUM/ Justification
HIGH
C702.1-PO1 H Knowledge about object oriented modeling and how it helps in
representing real world systems.
C702.1-PO2 L The analysis phase helps in formulating the real world problem
before analysis.
C702.1-PO3 M System designs helps in solving high level problems.
C702.1-PO4 L Analysis phase leads to concise representation of a problem
which helps in arriving at a solution.
C702.1-PSO2 H Object oriented model will help application specific knowledge to
be converted to programming knowledge
C702.2-PO1 M Division of a complex system into subsystems , and their object
oriented model, will help in analyzing complex problem and
finding a solution.
C702.2-PO3 M Division of a complex system into subsystems and their object
oriented model will help in dividing complex problem into
solvable sub problems.
C702.2-PSO2 M Knowledge in object oriented modeling will result in better
modular design of softwares.
C702.3-PO3 M Putting object oriented modeling in practice will result in better
software system solutions.
C702.3-PSO1 H Putting object oriented modeling in practice will result in better
software system solutions.
C702.4-PO2 H Object oriented analysis of a system will result in better problem
specialization and understanding of the system
C702.4-PO10 Proper object oriented analysis and representation will lead to
proper domain knowledge communication programmers
Department of Information Technology Page 24
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C702.5-PO5 H Proper UML diagram will help in representing complex
systems efficiently
C702.5- H Proper UML diagram will help in conveying information
PO10 from application domain experts to programmers
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
SNO DESCRIPTION PROPOSED
ACTIONS
1 STUDY OF VARIOUS UML DIAGRAMS TUTORIAL AND
CASE LAB
2 ENHANCED ENTITY RELATIONSHIP MODEL READING
ASSIGNMENT
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST
LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ADVANCED TOPICS/DESIGN:
S.NO DESCRIPTION PO MAPPING
1 MODELING A SOFTWARE SYSTEM USING ANY UML TOOL( ARGO, a, b,d
RATIONAL ROSE ETC)
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
1 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/uml/
2 nptel.iitm.ac.in
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. ASSIGNMENT WEB RESOURCES
LCD/SMART BOARDS STUD. SEMINARS ADD-ON COURSES
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
STUD. TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
ASSIGNMENT SEMINARS EXAMS EXAMINATION
S
STUD. LAB STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR CERTIFICATIONS
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON OTHERS
COURSES
Department of Information Technology Page 25
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS OTHERS
BY EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by Approved by
DIVYA JAMES Mr.Binu A (HOD)
Department of Information Technology Page 26
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 702 Object Oriented Modelling And Design
COURSE PLAN
Sl.No Module Day Planned
1 1 Day 1 Introduction, object oriented development
2 1 Day 2 Modeling concepts , object oriented methodology
Object oriented themes, OMT, object model, dynamic model,
3 1 Day 3 functional model
4 1 Day 4 Object modeling
5 1 Day 5 Links and association
6 5 Day 6 UML-Introduction
7 5 Day 7 UML Diagrams
8 1 Day 8 Advanced links and association concepts
9 1 Day 9 Generalization and inheritance, grouping constructs
10 1 Day 10 A sample object model
11 1 Day 11 Advanced Object Modeling: aggregation
12 1 Day 12 Abstract classes, generalization as extension and restriction
13 1 Day 13 Multiple inheritance
14 1 Day 14 Metadata, candidate keys
15 1 Day 15 Constraints, homomorphism
Class diagrams, object diagrams,use case diagrams,activity
16 5 Day 16 diagram
Deployment diagrams, state diagram, component diagram,
17 5 Day 17 sequence diagram
Department of Information Technology Page 27
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
18 2 Day 18 Dynamic modeling
19 2 Day 19 Events and states
20 2 Day 20 Operations
21 2 Day 21 Nested state diagrams
22 2 Day 22 Concurrency, advanced dynamic modeling concepts
23 2 Day 23 Entry and exit actions, internal actions
Automatic transition, sending events, synchronization of
24 2 Day 24 concurrent activities
25 2 Day 25 A sample dynamic model
26 2 Day 26 Relationship of Object and Dynamic models
27 2 Day 27 Functional modeling, Functional models, Data Flow Diagrams
28 2 Day 28 Specifying operations, Constraints
A sample functional model, Relation of functional to Object
29 2 Day 29 and Dynamic models.
30 3 Day 30 Analysis
31 3 Day 31 Analysis in object modeling
32 3 Day 32 Dynamic modeling
33 3 Day 33 Functional modeling, adding operations
34 3 Day 34 Iterating the analysis
System Design: Breaking system into subsystems - Identifying
35 3 Day 35 concurrency
Allocating subsystems to processors and tasks, managing of
36 3 Day 36 data stores
Department of Information Technology Page 28
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Handling of global resources, choosing software control
37 3 Day 37 implementation
38 3 Day 38 Handling boundary conditions
39 3 Day 39 Common Architectural Frameworks
Object Design: Overview of Object design Combining the
40 4 Day 40 three models
41 4 Day 41 Designing algorithms Design optimization
42 4 Day 42 Implementation of control ,Adjustment of inheritance
Design of association Object representation Physical
43 4 Day 43 packaging Documenting design decisions
44 4 Day 44 Comparison of methodologies,UML-case study
Department of Information Technology Page 29
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 702 Object Oriented Modelling And Design
TUTORIAL QUESTIONS
Discuss in detail about UML diagrams:
1. Class diagrams
2. Sequence diagrams
3. Use case diagrams
4. State diagrams
5. Activity diagram
6. Deployment diagrams
7. Collaborative diagrams
IT010 702 Object Oriented Modelling And Design
Assignment 1
1. Explain in detail with a diagram:
c) Sample Functional model
Assignment 2
1. Explain in detail Common Architectural Frameworks of system design
Department of Information Technology Page 30
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 703
Computer Graphics and
Multimedia
Systems
Department of Information Technology Page 31
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
PROGRAMME: Information Technology DEGREE: B.TECH
COURSE: COMPUTER GRAPHICS &
SEMESTER: Seventh CREDITS: 4
MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS
COURSE CODE: IT010 703
COURSE TYPE: CORE
REGULATION: 2010
CONTACT HOURS: 3+1 (Tutorial)
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: COMPUTER GRAPHICS
hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY):
LAB COURSE NAME: NA
No
SYLLABUS:
UNIT DETAILS HOURS
Uses of Computer Graphics, Display Devices, Input Devices, Output Devices,
Computer Graphics Software, Graphical User Interface, Line Drawing Algorithms
I 18
DDA, Bresenhams Line Algorithm, Bresenhams Circle Algorithm. Polygon
Filling Algorithm Scan Conversion, Seed Filling Algorithm
Transformation of Points, Straight Lines, Midpoint, Parallel Lines, Rotation,
II Reflection and Scaling of Straight Lines, Homogeneous Coordinates, Cohen 13
Sutherland Line Clipping.
Hidden surface Removal Algorithm- Z Buffer Algorithm, A- Buffer Algorithm,
12
III Hidden Line Removal Algorithm, Colour Models, Z-Flat Shading, Gouraud
Shading.
Media and Data Streams, Properties of Multimedia, Traditional Data Stream
IV Characteristics, Music, Speech, Images and Graphics, Computer Image 11
Processing.
Storage space, Coding Requirement, JPEG, H.261, MPEG, DVI, Multimedia
V 11
Operating Systems Real Time, Resource Management, Process Management.
TOTAL HOURS 65
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
Department of Information Technology Page 32
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
R Amarendra N Sinha and Arun D Udai, Computer Graphics, The McGraw-Hill Companies.
R Ralf Steinmetz and Klara Nahrstedt, Multimedia: Computing, Communications &
Applications, Person Education Asia.
R Donald Hearn & Pauline Baker, Computer Graphics, Prentice Hall India.
R Foley, VanDam, Feiner, Hughes, Computer Graphics Principles & Practice, Second Edition,
Addison Wesley.
R Ranjan Parekh, Principles of Multimedia, The McGraw-Hill Companies.
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM
IT010- Problem solving and computer To have an idea of the basic Third
306 programming programming syntax
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 This course provides an introduction to the principles of computer graphics. In particular, the
course will consider methods for modeling 2-dimensional objects and how it generates
photorealistic renderings on color raster graphics devices. The emphasis of the course will be
placed on understanding how the various elements that like algebra, geometry, algorithms and
data structures interact in the design of graphics software systems.
2 This course provides an idea on hardware system architecture for computer graphics. This
includes, but is not limited to: graphics pipeline, frame buffers, and graphic co-processors.
3 To give idea about basic building blocks of multimedia and a study about how these blocks sew
together with current technology and tools.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
Blooms
SNO DESCRIPTION Taxonomy
Level
Knowledge,
Students will be able to describe the fundamental algorithms used in
Understand
1 computer graphics and to some extent be able to compare and evaluate
(level1, level
them.
2)
Students will be able to work and interact, through hands-on experiences, Apply, Create
2 to design, develop, and modify electronically generated imagery using a (level 3, level
wide range of sophisticated graphical tools and techniques. 6)
3 Students will be able to summarize different hidden surface elimination Evaluate
Department of Information Technology Page 33
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
algorithms and shading techniques used in computer graphics and digital (level 5)
media production.
Students will be able to explain about the technology necessary for
Analyze
4 creating multimedia content for the web, video, DVD, 2D and 3D graphics,
(level 4 )
sound and programming.
Students can apply the knowledge, techniques, skills and modern tools to Apply
5
become successful professionals in communication and Media industries. (level 3)
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PSO PSO PSO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
C703.1 _ _ 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 _ _
C703.2 2 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 2 _
C703.3 2 _ 1 _ 3 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 2 _ _
C703.4 2 2 _ 2 _ 1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
C703.5 1 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 _ _
C703 2 2 2 2 3 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 2 _
JUSTIFICATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
LOW/MEDIUM/HIG
MAPPING JUSTIFICATION
H
Learning basic algorithms of computer graphics helps the
C703.1-PO3 M students to design graphics systems that meet specified
needs.
Students acquire skills to implement the algorithms in
C703.1-PSO1 L
computer graphics using high level programming languages.
Students will be able to apply knowledge of mathematics and
C703.2-PO1 M engineering fundamentals in implementing various graphics
algorithms.
Design and develop graphic images by applying suitable
C703.2-PO2 M
algorithms.
Acquire skills to analyze and implement algorithms using high-
C703.2-PSO1 L
level programming languages.
Learning different graphics algorithms enables the students
C703.2-PSO2 M
to contribute their skills in GUI development.
Students will be able to apply the fundamental knowledge of
C703.3-PO1 M mathematics in hidden surface elimination and shading
techniques.
C703.3-PO3 L Students will be able to design realistic graphics images
Department of Information Technology Page 34
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
using visible surface detection techniques.
Learning shading techniques and different algorithms help to
C703.3-PO5 H choose modern graphic tools suitable for graphic
development.
Develop skills to implement algorithms using high-level
C703.3-PSO1 M
programming languages.
Able to select different multimedia tools for various
C703.4-PO1 M
multimedia processing.
Able to analyze the technology used in different multimedia
C703.4-PO2 M
systems.
C703.4-PO4 M Able to design efficient multimedia systems.
Able to choose the appropriate multimedia tools needed for
C703.4-P05 L
developing multimedia systems.
Students will be able to apply knowledge of compression for
C703.5-PO1 L
efficient data transfer.
Able to analyze the compression techniques in different
C703.5-PO2 M
areas.
Helps to understand the basic algorithms to develop
C703.5-PSO1 L
different compression techniques.
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
SNO DESCRIPTION PROPOSED
ACTIONS
1 To have a concrete idea of the subject they should have corresponding Assignment
practical sessions which are missing in their syllabus, so to bridge that gap
students were given lab assignments to implement the algorithm that they
study.
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST
LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ADVANCED TOPICS/DESIGN:
1 Some of the drawing and animation tools were discussed in the class like photoshop, 3DMax,
Maya etc to get an idea of how the algorithms that they learn are actually used in the
industry.
2 Familiarization of many terminologies in a graphic industry like skinning, rigging etc
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
Department of Information Technology Page 35
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
1 http://www.slideshare.net/akbrightfuture/computer-graphics-hearn-baker
2 http://personal.ee.surrey.ac.uk/Personal/J.Collomosse/pubs/cm20219.pdf
3 http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/video.php?subjectId=106106090
4 http://www.dgp.toronto.edu/~hertzman/418notes.pdf
5 http://www.graphics.rwth-aachen.de/research/
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. ASSIGNMENT WEB RESOURCES
LCD/SMART STUD. SEMINARS ADD-ON COURSES
BOARDS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
ASSIGNMENTS STUD. SEMINARS TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
EXAMS EXAMINATION
STUD. LAB STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR CERTIFICATIONS
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS BY OTHERS
EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by Approved by
Department of Information Technology Page 36
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Lakshmi K.S Binu A
(Faculty) (HOD)
COURSE PLAN FOR COMPUTER GRAPHICS AND MULTIMEDIA SYSTEMS
Planned
SI.No. Module date Topics Planned
1 1 Day 1 Uses of Computer Graphics
2 1 Day 2 Input Devices
3 1 Day 3 Display Devices
4 1 Day 4 Output devices
5 1 Day 5 Computer Graphics Software, Graphical User Interface
6 1 Day 7 Line Drawing Algorithms DDA
7 1 Day 8 Bresenhams Line Algorithm
8 1 Day 9 Bresenhams Circle Algorithm
9 1 Day 10 Polygon Filling Algorithm Scan Conversion
10 1 Day 11 Seed Filling Algorithm
11 1 Day 12 Transformation of Points
12 2 Day 13 Straight lines
13 2 Day 14 Midpoint
14 2 Day 15 Parallel Lines
Department of Information Technology Page 37
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
15 2 Day 16 Rotation
16 2 Day 17 Reflection
17 2 Day 18 Scaling of Straight Lines
18 2 Day 19 Homogeneous Coordinates
19 2 Day 20 Cohen Sutherland Line Clipping.
20 2 Day 21 Cohen Sutherland Line Clipping.
21 2 Day 22 Hidden surface Removal Algorithm- Z Buffer Algorithm
22 2 Day 23 Hidden surface Removal Algorithm- Z Buffer Algorithm
23 2 Day 24 Hidden surface Removal Algorithm- A Buffer Algorithm
24 3 Day 25 Hidden surface Removal Algorithm- A Buffer Algorithm
25 3 Day 26 Hidden Line Removal Algorithm
26 3 Day 27 Hidden Line Removal Algorithm
27 3 Day 28 Color Models
28 3 Day 29 Z-Flat Shading
29 3 Day 30 Z-Flat Shading
30 3 Day 31 Gouraud Shading
31 3 Day 32 Gouraud Shading
32 3 Day 33 Multimedia: Media and Data Streams
33 3 Day 34 Properties of Multimedia
34 3 Day 35 Traditional Data Stream Characteristics
Department of Information Technology Page 38
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
35 3 Day 36 Music
36 4 Day 37 speech
37 4 Day 38 Images and Graphics
38 4 Day 39 Computer Image Processing
39 4 Day 40 Data Compression: Storage space
40 4 Day 41 Coding Requirement
41 4 Day 42 JPEG
42 4 Day 43 H.261
43 4 Day 44 MPEG
44 5 Day 45 DVI
45 5 Day 46 Multimedia Operating Systems Real Time
46 5 Day 47 Resource Management
47 5 Day 48 Process Management
TUTORIAL 1:
1. Mention the new co-ordinates of triangle with vertices A (0, 0), B (1,1) and C(5, 2) with
respect to origin with scale factors S =1/2 and S =1 .
2. Consider the square A(1,0) B(0,0) C(0,1) D(1,1). Rotate the square ABCD by 45: clockwise
about A(1,0).
TUTORIAL 2:
Department of Information Technology Page 39
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
1. Draw a triangle A (5, 5), B (10, 5), C (5, 15). Then do the following transformations on the
triangle.
(a) Translate the triangle by 3 in x - direction and 4 in y - direction.
(b) Increase the size of the triangle to double of it by keeping A as fixed.
(c) Rotate the triangle by 90 keeping A as fixed.
2. Derive the equation of rotation in 2D transformation based on a fixed point other than
origin.
TUTORIAL 3:
1. Given a clipping window A(20,20) B(60,20) C(60,40) D(20,40). Using Cohen Sutherland line
clipping algorithm, find the visible portion of line segment joining the points P(40, 80) and
Q(120, 30).
2. Magnify the triangle with vertices A(0,0) B(1,1) and C(5,2) to twice its size while keeping
C(5,2) fixed.
ASSIGNMENT NO: 1
1. Direct View Storage Tube
2. Computer Graphics Software
3. What are homogenous coordinates?
4. What is world coordinate system?
ASSIGNMENT NO: 2
1. Hidden Line Removal Algorithm
2. Multimedia Operating Systems
Department of Information Technology Page 40
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 704
Internetworking
Department of Information Technology Page 41
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET JULY 2016
PROGRAMME : Information
DEGREE : BTECH
Technology
SEMESTER : VII
COURSE : Internetworking
CREDITS : 3
COURSE CODE : IT010704
COURSE TYPE : CORE
REGULATION : 2010 11
CONTACT HOURS : 3+1 (Tutorial)
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN : Networking
hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY)
LAB COURSE NAME : Internetworking Lab
: IT010 707
SYLLABUS:
UNIT DETAILS HOURS
Internet Architecture, Classful Internet Addresses, Mapping Internet Addresses
I to Physical addresses (ARP), Determining an Internet address at start-up 9
(RARP), Connectionless Datagram Delivery (IPV4) , Forwarding IP datagrams
Error and Control Messages ( ICMP ),Classless and Subnet Address Extensions
II (CIDR), Protocol Layering, User datagram Protocol, Reliable Stream Transport 9
Service.
Routing Architecture : Cores, Peers, and Algorithms, Routing Between Peers
III (BGP), Routing Within an Autonomous System (RIP, OSPF). 9
Internet Multi casting, IP Switching and MPLS, Private Network Interconnection
IV (NAT, VPN), Bootstrap and Auto configuration (DHCP).Applications - DNS, 9
Remote Login and Desktop (TELNET, SSH)
File Transfer and Access ( FTP, TFTP, NFS) , Electronic Mail ( SMTP, POP, IMAP,
V 9
MIME), WWW (HTTP), Voice and Video Over IP (RTP, RSVP, QoS).
TOTAL HOURS 45
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
Internetworking with TCP/IP - Volume I, Principles, Protocols and Architecture (5th Edition),
R
Douglas E.Comer, PHI 2009
Department of Information Technology Page 42
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
R The Internet and Its Protocols, Adrian Farrel, Elsevier 2005.
R TCP/IP protocol Suite, Third Edition, TATA Mc Graw Hill, Behrouz A Forouzan
R Essentials Of TCP/IP, G Shanmugarathinam
R Internetworking Technologies, Fourth Edition, Cisco Systems Inc
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM
IT010 Principles of Communication
Basics In Communication Systems 3
305 Engineering
IT010
Data Communication Advanced Communication Technologies 5
503
IT010
Computer Networks Basics In Computer Networks 6
601
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 To familiarize with the TCP/IP protocol suite
2 To understand the different protocols used in each layer of TCP/IP.
3 To study the implementation of TCP/IP protocols.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
SNO DESCRIPTION Blooms Taxonomy Level
C704.1 Students will be able to define the basic concepts Knowledge (level1)
of Internet architectures and communication in
such scenario.
C704.2 Students will be able to distinguish and compare Understand (level 2)Evaluate
different addressing schemes used in Internet and (level 5)
error control measures adopted..
C704.3 Students will be able to determine various Apply (level 3)
routing technology to transport datagrams
between hosts using an unreliable, best-effort
service..
C704.4 Students will be able to identify techniques for Knowledge
providing multicasting and mobility over the
Internet. (level 1)
C704.5 Students will be able to classify different Analyze (level 4 )
application level services and differentiate
various protocols used for providing different
Department of Information Technology Page 43
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
services in Internet
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
PO PO2 P PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PS PSO PSO
1 O 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 O1 2 3
3
C704.1 2 2
C704.2 2 3 1
C704.3 3 2 1 1
C704.4 2 1 1
C704.5 2 1 1 2
JUSTIFATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
Mapping LOW/MEDIUM/HIGH Justification
C 704.1 PO1 M Apply the knowledge of basic concepts of
Internet architecture and communication
strategies for solutions of complex networking
problems..
C 704.1 PS02 M Contribute in network design and
administration..
C 704.2- PO2 M Identifying and analyzing addressing schemes
that can be used in different categories of
networks.
C 704.2- PO3 H Able to design and develop the solutions for
solving problems in Internet addressing.
C 704.2-PS02 L Contribute in providing error control methods
and addressing schemes in Internet design.
C 704.3-P01 H Apply the knowledge of routing techniques in
Department of Information Technology Page 44
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Internet.
C 704.3-P03 M Design better solutions for better and error
free transmission in Internet using
appropriate routing methods.
C 704.3-P10 L Ability to opt the correct routing strategies and
to end in better solutions for community and
society using Internet.
C 704.3-PSO2 L Contribute knowledge in routing protocols in
designing new solutions in Internet design.
C 704.4-P01 M Able to apply the fundamentals of Internet
architectures in contributing new solutions for
complex problems in Internet.
C 704.4-P03 L Designing solutions for multicasting and
mobility over Internet.
C 704.4-PSO3 M Develop strong skills in understanding,
developing and testing new concepts in
Internet protocols.
C 704.5-P01 M Apply the knowledge in different services
available in application level while designing
solutions for problems related with Internet.
C 704.5-P06 L Apply reasoning informed by contextual
knowledge in services at application level of
TCP/IP protocol suite to assess the consequent
responsibilities relevant to professional
engineering practice.
C 704.4-PSO2 M Contribute knowledge in application services
and protocols in designing proper networks in
different scenarios..
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
SNO DESCRIPTION PROPOSED ACTIONS
1 Client Server Architecture Seminar
Department of Information Technology Page 45
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
2 IPv6 Architecture Seminar
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST
LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ADVANCED TOPICS/DESIGN:
1 Introduction to Network Security
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
1 http://www.netbook.cs.purdue.edu/
2 http://cs.calvin.edu/
3 www.cisco.com/networkers/
4 http://nptel.iitm.ac.in/video.php?subjectId=106105084
5 www.ee.duke.edu/~romit/courses/f07/material/
6 www.csperkins.org/teaching/ns3/
7 www.javvin.com/protocol/
8 https://users.cs.jmu.edu
9 http://docwiki.cisco.com/wiki/Internetworking_Basics
10 www.ulb.tu-darmstadt.de/tocs/134991974.pdf
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
STUD. WEB
CHALK & TALK
ASSIGNMENT RESOURCES
LCD/SMART ADD-ON
STUD. SEMINARS
BOARDS COURSES
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
STUD. TESTS/MODEL
ASSIGNMENTS UNIV. EXAMINATION
SEMINARS EXAMS
STUD. LAB MINI/MAJOR
STUD. VIVA CERTIFICATIONS
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON
FEEDBACK, ONCE) FACULTY (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS BY EXT.
OTHERS
EXPERTS
Department of Information Technology Page 46
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Prepared by Approved by
Jisha G HOD
COURSE PLAN - JULY 2016
Sl.No Module Date Topics
1 Day 1 Introduction
2 Day 2 Internet Architecture
3 Day 3 Classful Internet Addresses
Mapping Internet Addresses to Physical addresses
4 1 Day 4
(ARP)
5 Day 5 Determining an Internet address at start-up (RARP)
6 Day 6 Connectionless Datagram Delivery (IPV4)
7 Day 7 Forwarding IP datagrams
8 Day 8 Error and Control Messages (ICMP)
9 Day 9 Classless and Subnet Address Extensions (CIDR)
10 Day 10 Protocol Layering
11 Day 11 Protocol Layering
2
12 Day 12 User datagram Protocol
13 Day 13 Reliable Stream Transport Service
14 Day 14 Reliable Stream Transport Service
15 Day 15 Reliable Stream Transport Service
16 Day 16 Routing Architecture : Cores, Peers, and Algorithms
17 Day 17 Routing Between Peers (BGP)
3
18 Day 18 Routing Within an Autonomous System (RIP, OSPF)
19 Day 19 Routing Within an Autonomous System (RIP, OSPF)
20 Day 20 Internet Multi casting
21 Day 21 Internet Multi casting
4
22 Day 22 Internet Multi casting
23 Day 23 IP Switching
Department of Information Technology Page 47
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
24 Day 24 MPLS
25 Day 25 Private Network Interconnection (NAT, VPN)
26 Day 26 Private Network Interconnection (NAT, VPN)
27 Day 27 Bootstrap and Auto configuration (DHCP)
28 Day 28 Bootstrap and Auto configuration (DHCP)
29 Day 29 DNS
30 Day 30 TELNET, SSH
31 Day 31 File Transfer and Access
32 Day 32 Electronic Mail
33 Day 33 WWW (HTTP)
5
34 Day 34 WWW (HTTP)
35 Day 35 Voice and Video Over IP
36 Day 36 Voice and Video Over IP
Tutorial I
1. Find the error, if any, in the following IP addresses:
a. 111.56.045.78 b. 221.34.7.8.20
c. 75.45.301.14 d. 11100010.23.14.67
2. How can we prove that we have 2,147,483,648 addresses in class A?
3. Find the class of each address:
a. 00000001 00001011 00001011 11101111
b. 11000001 10000011 00011011 11111111
c. 10100111 11011011 10001011 01101111
d. 11110011 10011011 11111011 00001111
4. Find the class of each address:
a. 227.12.14.87b.193.14.56.22 c.14.23.120.8
d. 252.5.15.111 e.134.11.78.56
Department of Information Technology Page 48
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
5. Class A has 231 (2,147,483,648) addresses. How can we prove this same fact using dotted-decimal
notation?
6. Given the network address 17.0.0.0, find the class, the block, and the range of the addresses.
7. Given the network address 132.21.0.0, find the class, the block, and the range of the addresses.
8. Given the network address 220.34.76.0, find the class, the block, and the range of the addresses
Tutorial II
1. An organization has a number of workgroups of varying sizes.
Workgroup Groups Size/Group (Devices)
Engineering 3 400 (1200 total)
Marketing 1 1950
Administration 1 200
Sales 15 3590 (1350 total)
R&D 1 150
Support 22 1040 (880 total)
Total: 43 Total: 5730
This organization has a Class B address (136.178.0.0, mask 255.255.0.0) and
would like to give one subnet to each group.
ASSIGNMENT QUESTIONS JULY DEC2016
Assignment - I
1. Explain about Protocol layering principle and its disadvantages.
Assignment II
1. Briefly explain SMTP.
2. Why do we need NTFS?
3. Explain a) FTP b) IMAP c) NAT d) VPN e) RTP f) RSVP
4. How VoIP will place an important role in networking?.
5. Write short note on a) HTTP b) TFTP c) POP e) RTF.
Department of Information Technology Page 49
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 705
Web Applications
Development
Department of Information Technology Page 50
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
RAJAGIRI SCHOOL OF ENGINEERING & TECHNOLOGY
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
IT010 705 WEB APPLICATIONS DEVELOPMENT
PROGRAMME: INFORMATION DEGREE: BTECH
TECHNOLOGY
COURSE: UNIX SHELL PROGRAMMING SEMESTER: VII CREDITS: 3
COURSE CODE: IT010 705 COURSE TYPE: CORE
REGULATION: 2010
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: WEB DESIGNING CONTACT HOURS: 2+1(Tutorial) hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY): LAB COURSE NAME: WEB APPLICATIONS LAB
IT010 806
SYLLABUS:
UNIT DETAILS HOUR
S
I Introduction - Web architecture - web application lifecycle - XML and J2EE. 9
Design and development of a J2EE application - J2EE Layers, Application
Components, J2EE Architecture, Development methodology - Task list for
building J2EE Applications - database design - defining the application - creating
the interface, building pages, creating data access objects, validating the code.
II JDBC: Architecture - JDBC API, Retrieving and updating Data, SQL-to-Java Data 10
Types, JDBC Execution Types, Metadata, Scrollable Resultsets, transaction
support, Batch Statements. Servlets: Introduction to Servlets, Benefits of Servlets,
use as controller in MVC, basic HTTP, servlet container, Servlets API,
javax.servelet Package, Reading Servlet parameters, service method detail, HTML
clients, servlet lifecycle, HTTP response header, session management,
dispatching requests, Servlets with JDBC, web applications.
III Java Server Pages: Generating Dynamic Content, Using Scripting Elements, 10
Implicit JSP Objects, Conditional Processing Displaying Values, Setting
attributes, Error Handling and Debugging, Using JavaBeans Components in JSP
Pages, Sharing Data Between JSP pages -Passing Control and Data between Pages
Sharing Session and Application Data Application Models - MVC Design.
IV Enterprise JavaBeans : Overview, distributed programming, EJB framework, 7
Session and entity beans, Stateless and stateful session bean, Bean attributes,
Parts of a Bean, container-managed persistence (CMP) and bean managed -
Department of Information Technology Page 51
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
lifecycle of EJB.
V Java message service (JMS) and message driven beans (MDB), distributed 9
programming services, CORBA and RMI - Transaction management,
Security, deployment, personal roles for EJB Development, building session
beans - creating session beans - Entity beans.
TOTAL HOURS 45
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/ BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
R
R J2EEUNLEASHEDJosephJ.Bambara,PaulR.Allen,MarkAshnault,ZiyadDean,Thomas Garben,
SherrySmithSAMS Techmedia
R JavaServlet Programming, SecondEdition,JasonHunter, WilliamCrawford,O'ReillyMedia
R MasteringEJB(2ndEdition)EdRoman,ScottAmbler,TylerJewellJohnWileyPublications 2003.
R TheJ2EETutorial-StepahnieBodoff,DaleGreen,KimHasse,EricJendrock, MonicaPawlan, Beth
Stearns- TheJ2EETutorial Asia.
R JavaServerPagesHansBergsten, SPDOReilly
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SE
M
IT 010 Object Oriented Techniques Basics of Web applications S4
406
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 To familiarize with the technologies used for the development of Web applications
COURSE OUTCOMES:
SlNO DESCRIPTION Blooms
Taxonomy
Level
C705.1 Students will be able to define the web architecture and summarize Knowledge ,
task list for building J2EE Applications. Evaluate
(level1 and
Department of Information Technology Page 52
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
level 5)
C705.2 Students will be able to demonstrate and develop the applications Understand,
with JDBC and servlets Create (level2
and level 6)
C705.3 Students will be able to explain and analyze applications with Java Apply, Analyze
Server Pages. (level 3 and
level 4)
C705.4 Students will be able to and implement and evaluate applications Evaluate (level
with Enterprise JavaBeans 5)
C705.5 Students will be able to explain distributed programming services Understand
(level 2)
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO1 PO1 PO1 PSO PSO PSO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 1 2 3
C705. 2 2 2 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 _
1
C705. 2 1 3 3 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 2 3 _
2
C705. 2 2 3 3 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 2 3 _
3
C705. 2 2 1 1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 2
4
C705. 1 2 1 1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
5
C705 2 2 2 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ - 1
JUSTIFICATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
MAPPING LOW/MEDIUM/HIGH JUSTIFICATION
C705.1-PO1 M Apply the knowledge of web architecture to develop the
solution of complex engineering problems.
C705.1-PO2 M Analyze complex engineering problems by building J2EE
Applications.
C705.1-PO3 M Design solutions for complex engineering problems by
developing J2EE Applications.
C705.1-PO4 M Design of experiments with the knowledge in web
architecture and J2EE.
Department of Information Technology Page 53
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C705.1-PSO1 L Build a strong technical foundation by building J2EE
Applications.
C705.2-PO1 M Using JDBC and servlets build solution of complex
engineering problems.
C705.2-PO2 L Using JDBC and servlets formulate complex engineering
problems
C705.2-PO3 H Using JDBC and servlets design solutions for complex
engineering problems and design system components
C705.2-PO4 H Using JDBC and servlets design experiments, analyze and
interpret data, and synthesize information to provide valid
conclusions.
C705.2-PSO1 M Using JDBC and servlets build technical foundation for
successful professional careers and to evolve as key-players/
entrepreneurs in the field of information technology.
C705.2-PSO2 H Using JDBC and servlets Excel in analyzing, formulating and
solving engineering problems
C705.3-PO1 M With the analysis of JSP applications develop the solution of
complex engineering problems.
C705.3-PO2 M With the analysis of JSP applications Analyze complex
engineering problems
C705.3-PO3 H With the analysis of JSP applications Design solutions for
complex engineering problems and design system
components
C705.3-PO4 H With the analysis of JSP applicationsdesign experiments,
analyze and interpret data, and synthesize information to
provide valid conclusions.
C705.3-PSO1 M With the analysis of JSP applications build technical
foundation for successful professional careers and to evolve
as key-players/ entrepreneurs in the field of information
technology.
C705.3-PSO2 H With the analysis of JSP applications Excel in analyzing,
formulating and solving engineering problems
C705.4-PO1 M Apply the knowledge of JavaBeans to develop the solution of
complex engineering problems.
C705.4-PO2 M Analyze complex engineering problems by using JavaBeans
C705.4-PO3 L Design solutions for complex engineering problems by
developing JavaBeans Applications.
C705.4-PO4 L Design of experiments with the knowledge in JavaBeans.
C705.5-PO1 M With the analysis of distributed programming develop the
solution of complex engineering problems.
C705.5-PO2 M With the analysis of distributed programming Analyze
complex engineering problems
Department of Information Technology Page 54
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C705.5-PO3 M With the analysis of distributed programming Design
solutions for complex engineering problems and design
system components
C705.5-PO4 M With the analysis of distributed programming design
experiments, analyze and interpret data, and synthesize
information to provide valid conclusions.
C705.1-PSO2 M With the analysis of distributed programming Excel in
analyzing, formulating and solving engineering problems
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
Si DESCRIPTION PROPOSED RELEVANC RELEVANC
NO ACTIONS E WITH E WITH
POs PSOs
1 Case study- LINUX TOPICS 1,2,3,4,12 2
BEYOND
SYLLABUS
2 Case study- Solaris NPTEL 1,2,3,4,12 2
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST
LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ADVANCED TOPICS/DESIGN:
Si DESCRIPTION PROPOSED RELEVANCE WITH RELEVANCE WITH
N ACTIONS POs PSOs
O
1 Case study- LINUX Assignments 1,2,3,4,12 2
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
1 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/awk/
2 https://supportweb.cs.bham.ac.uk/docs/tutorials/docsystem/build/tutorials/unixscripting/un
ixscripting.html
3 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/unix/unix-basic-utilities.htm
4 http://www.opengroup.org/desktop/x/
5 http://www.tutorialspoint.com/unix_commands/grep.htm
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. WEB
ASSIGNMENT RESOURCES
LCD/SMART STUD. ADD-ON COURSES
BOARDS SEMINARS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
Department of Information Technology Page 55
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
ASSIGNMENT STUD. TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
S SEMINARS EXAMS EXAMINATIO
N
STUD. LAB 33STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR CERTIFICATIONS
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON OTHERS
COURSES
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR OTHERS
PROJECTS BY EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by Approved by
Chinchu Krishna S BINU A, HOD
Course Plan
Sl.No Module Day Planned
Day
1 1 1 Introduction - Web architecture
Day
2 1 2 web application lifecycle - XML and J2EE.
Day
3 1 3 Design and development of a J2EE application - J2EE Layers,
Day
4 1 4 Application Components, J2EE Architecture
Day Development methodology - Task list for building J2EE
5 1 5 Applications
Day
6 1 6 database design - defining the application
Day
7 1 7 creating the interface, building pages
Day
8 1 8 creating data access objects
Day
9 1 9 validating the code..
10 2 Day JDBC: Architecture - JDBC API, Retrieving and updating Data
Department of Information Technology Page 56
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
10
Day
11 2 11 SQL-to-Java Data Types, JDBC Execution Types
Day Metadata, Scrollable Resultsets, transaction support, Batch
12 2 12 Statements.
Day Servlets: Introduction to Servlets, Benefits of Servlets, use as
13 2 13 controller in MVC
Day
14 2 14 basic HTTP, servlet container, Servlets API
Day
15 2 15 javax.servelet Package, Reading Servlet parameters
Day service method detail, HTML clients,servlet lifecycle, HTTP
16 2 16 response header
Day
17 2 17 session management, dispatching requests
Day
18 2 18 Servlets with JDBC, web applications.
Day
19 3 19 Java Server Pages: Generating Dynamic Content
Day
20 3 20 Using Scripting Elements
Day
21 3 21 Implicit JSP Objects, Conditional Processing Displaying Values
Day
22 3 22 Setting attributes, Error Handling and Debugging
Day
23 3 23 Using JavaBeans Components in JSP Pages
Day Sharing Data Between JSP pages -Passing Control and Data
24 3 24 between Pages
Day Sharing Session and Application Data , Application Models,MVC
25 4 25 Design. Enterprise JavaBeans : Overview
Day distributed programming, EJB framework, Session and entity
26 4 26 beans
Day
27 4 27 Stateless and tateful session bean
Day Bean attributes,Parts of a Bean ,container-managed persistence
28 4 28 (CMP)
Day bean managed - lifecycle of EJB, java message service (JMS) and
29 5 29 message driven beans (MDB)
Day
30 5 30 distributed programming services, CORBA and RMI
Day Transaction management, Security, deployment , personal roles
31 5 31 for EJB Development
Day
32 5 32 building session beans - creating session beans , Entity beans
Department of Information Technology Page 57
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 705 WEB APPLICATIONS DEVELOPMENT
Tutorial Questions
1. Web architecture
2. Web components
3. Web containers
4. J2EE Layers
5. J2EE architecture
6. MVC architecture
7. Web Application Life cycle
8. Development methodology and process
9. Task List for Building J2EE Applications
IT010 705 WEB APPLICATIONS DEVELOPMENT
Assignment-1
1. Stateful and statless session beans
Assignment-2
1. Creating session beans
Department of Information Technology Page 58
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 706L05 Operating
System Kernel Design
Department of Information Technology Page 59
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
PROGRAMME: INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEGREE: BTECH
COURSE: : OPERATING SYSTEM KERNEL SEMESTER: VII CREDITS: 4
DESIGN
COURSE CODE: IT010 706L05 COURSE TYPE: ELECTIVE
REGULATION: 2010
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: KERNEL DESIGN CONTACT HOURS: 2+2(Tutorial) hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY): LAB COURSE NAME:
SYLLABUS:
UNIT DETAILS HOURS
I Basic Operating System Concepts Kernel Types: monolithic, microkernel An 13
Overview of Unix Kernels-
The Process/Kernel Model, Reentrant Kernels Signals sending and receiving
System calls System Call Handler and Service Routines
Interrupts and Exceptions - Interrupt Handling - The Timer Interrupt Handler.
II Processes - Process Descriptor - Process State, Process relationship Creating 13
Processes - Process Termination - Process Scheduling Scheduling algorithm
SMP Scheduler.
Kernel Synchronization - Synchronization Techniques - Process Communication -
System V IPC.
III Paging in Linux - Memory Management - Page Frame Management - The Buddy 10
System Algorithm The Process's Address Space - The Memory Descriptor -
Memory Regions - Page Fault Exception Handler
IV Overview of the Unix File System - The Virtual File System - role of the VFS - VFS 14
Data Structures File system Mounting. The Ext2 File system - Disk Data
Structures - Creating the File system - Data Blocks Addressing - Allocating a Data
Block.
V Managing I/O Devices - Associating Files with I/O Devices - Device Drivers - 10
Character Device - Block Device. Disk Caches - Buffer Cache - Writing Dirty
Buffers to Disk - Page Cache..
TOTAL HOURS 60
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
T/R Daniel P. Bovet, Marco Cesati, Understanding the Linux Kernel, First ed., O'Reilly, 2000
R M Bech et al., Linux Kernel Internals, 2nd ed., Addison-Wesley, 1998
R Maurice J. Bach, The Design of the Unix Operating System, First Edition, Pearson Education,
Department of Information Technology Page 60
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
1999.
R Abraham Silberschatz, Peter B.Galvin and Greg Gagne, Operating System Concepts, John
Wiley & Sons Inc, 8th Edition 2010.
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM
IT010 Operating Systems Operating system basics S5
504
IT010 Data structure and algorithms Data Structure fundamentals and S4
405 algorithms
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 To provide knowledge about operating system working principles
2 To discuss most of the significant data structures and algorithms used in the kernel
COURSE OUTCOMES:
SNo DESCRIPTION Blooms Taxonomy Level
1 Students can apply the knowledge, techniques, skills Apply
and modern tools to become successful professionals (level 3)
in communication and Software industries.
2 Students must understand the concepts of operating Understand
system design issues. (level 5)
3 Students will be able to analyze about the technology Analyze
necessary for creating Kernel design. (level 4 )
4 Students will be able to evaluate different methods to Evaluate
create process (level 5)
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PSO PSO PSO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
IT010
706L05 _ _ 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ - _ 3
.1
IT010
706L05 2 2 _ _ 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 1 2 _
.2
IT010
706L05 2 _ 1 _ 3 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 2 _ _
.3
Department of Information Technology Page 61
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010
706L05. 2 1 _ 2 _ 3 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
4
JUSTIFICATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
LOW/MEDIUM/HIG
MAPPING JUSTIFICATION
H
IT010
706L05 M Learning basic steps needed to design a operating system
.1-PO3
IT010
706L05 L Students will acquire strong skills to write kernel codes.
.1-PSO3
IT010
706L05 M Students will be able to apply knowledge of data structure .
.2-PO1
IT010
706L05 M Design and develop kernel threads to improve the
.2-PO2 performance.
IT010
Acquire skills to analyze and implement algorithms using
706L05 L
high-level programming languages.
.2-PSO1
IT010
Learning different linux files structure to develop the kernel
706L05 M
code.
.2-PSO2
IT010
Students will be able to apply the fundamental knowledge of
706L05 M
memory management to map the data and processor.
.3-PO1
IT010
706L05 L Students will be able to design their own linux directorys.
.3-PO3
IT010
Learning different page frame management techniques to
706L05 H
solve page frame issues.
.3-PO5
IT010
Develop skills to implement algorithms to develop basic file
706L05 M
structures.
.3-PSO1
IT010 M Students Apply the knowledge of engineering fundamentals
Department of Information Technology Page 62
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
706L05 to study the red black tree data structure.
.4-PO1
IT010
Able to analyze the technology used in different operating
706L05 M
systems
.4-PO2
IT010
706L05 M Able to design efficient systems.
.4-PO4
IT010
Able to choose the appropriate tools needed for developing
706L05 L
operating systems.
.4-P05
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
SNO DESCRIPTION PROPOSED
ACTIONS
1 Fundamentals of Linux commands and shell scripting Conducting
lab session
2 NPTEL video lectures for linux commands NPTL
videos
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST
LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ADVANCED TOPICS/DESIGN:
1 Familiarization of Shell scripting
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
1 http://www.brokenthorn.com/Resources/OSDev13.html
2 http://www.osnews.com/story/24405/Hobby_OS-deving_3_Designing_a_Kernel/
3 http://lwn.net/
4 https://www.kernel.org/
5 http://ww5.linuxdrivers.net/
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. ASSIGNMENT WEB RESOURCES
LCD/SMART STUD. SEMINARS ADD-ON COURSES
BOARDS
Department of Information Technology Page 63
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
ASSIGNMENTS STUD. SEMINARS TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
EXAMS EXAMINATION
STUD. LAB STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR CERTIFICATIONS
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS BY OTHERS
EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by
Approved by
(Mathews Abraham)
(HOD)
Course Plan
Sl.No Date Module Planned
1 27-Jul-2016 1 Basic Os Concepts
2 28-Jul-2016 1 An overview of Unix Kernels
3 30-Jul-2016 1 Reentrant Kernels
4 3-Aug-2016 1 Signals sending and receiving
5 4-Aug-2016 1 System calls
6 6-Aug-2016 1 Interrupts and Exceptions
Interrupt Handling
7 9-Aug-2016 1
Department of Information Technology Page 64
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
8 10-Aug-2016 1 The timer Interrupt Handler
9 16-Aug-2016 2 Process relationship, creating Process
Process Termination, process
10 17-Aug-2016 2
Scheduling
11 18-Aug-2016 2 Scheduling algorithm
12 23-Aug-2016 2 SMP scheduler
13 24-Aug-2016 2 Synchronization Techniques
14 25-Aug-2016 2 Process Communication
15 30-Aug-2013 2 System V IPC
16 31-Aug-2016 2 Revision of Ist module
17 1-Sept-2016 2 Revision of 2nd Module
18 6-Sept-2016 3 Pagging in Linux
19 7-Sept-2016 3 Memory management
20 8-Sept-2016 3 page frame management
20-Sept-
21 3 The Buddy Ssytem Algorithm
2016
21-Sept-
22 3 The Process Address space
2016
23 22-Sep-2016 3 The memory Descriptor
24 28-Sep-2016 3 Memory Regions
25 29-Sep-2013 3 Page fault Exception Handler
26 4-Oct-2016 4 over view of UNIX file system
27 5-Oct-2016 4 The virtual File System
28 6-Oct-2016 4 VFS and VFS Data Structures
29 11-Oct-2016 4 File system Mounting
Department of Information Technology Page 65
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
30 12-Oct-2016 4 EXT2 File system
31 13-Oct-2016 4 Disk data structure
32 18-Oct-2016 4 Creating the file system
33 19-Oct-2016 4 Data Block addressing
34 20-Oct-2016 4 Allocating a Data Block
35 25-Oct-2016 5 Managing I/O devices
36 26-Oct-2016 5 Associating file with I/O Devices
37 27-Oct-2016 5 Device Driverse, Character Devices
38 1-Nov-2016 5 Block Device, Disk Caches
39 2-Nov-2016 5 Buffer Cache
Writing Dirty Buffers to Disk, Page
40 3-Nov-2016 5
Cache
Tutorial questions for operating system kernel design
Write a short notes on system calls.
Briefly explain interprocess communication mechanisms?
Discuss Buddy System algorithm with an example.
What are the significance of VFS Data Structures.
What are the benefits of Buffer cache mechanism.
ASSISGNMENT QUESTIONS 1
1. Write a notes on Timer Interrupt Handler. 20/9/2016
ASSISGNMENT QUESTIONS 2
2 Write a notes on Page fault exception handler. 14/10/2016
3 Write a notes on Turbo boosting technology.
Department of Information Technology Page 66
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 706L06 Data Mining
and Data Warehousing
Department of Information Technology Page 67
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
PROGRAMME:INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEGREE:BTECH
COURSE: Data Mining and Data Warehousing SEMESTER: VII
CREDITS: 4
COURSE CODE: IT010 706 L06REGULATION: 2010 COURSE TYPE:ELECTIVE
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: CONTACT HOURS:2+2 (Tutorial)
hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY):NIL LAB COURSE NAME:NIL
SYLLABUS:
MODULE DETAILS HOURS
I Evolution of Decision Support Systems- Data warehousing Components Data
warehouse, Data Warehouse and DBMS, Data marts, Metadata, 11
Multidimensional data model, OLAP ,OLTP, Data cubes, Schemas for
Multidimensional Database: Stars, Snowflakes and Fact constellations
II Types of OLAP servers, 3Tier data warehouse architecture, distributed and
virtual data warehouses. Data warehouse implementation, tuning and testing
of data warehouse. Data Staging (ETL) Design and Development, data 12
warehouse visualization, Data Warehouse Deployment, Maintenance, Growth,
Business Intelligence Overview- Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence
Trends -Business Applications- tools-SAS
III Data mining-KDD versus data mining, Stages of the Data Mining Process-task
primitives, Data Mining Techniques -Data mining knowledge representation
Data mining query languages, Integration of a Data Mining System with a Data 12
Warehouse Issues, Data preprocessing Data cleaning, Data transformation,
Feature selection, Dimensionality reduction, Discretization and generating -
Mining frequent patternsassociation and correlation.
IV Decision Tree Induction - Bayesian Classification Rule Based Classification
by Back propagation Support Vector Machines Associative Classification
Lazy Learners Other Classification Methods Clustering techniques ,
Partitioning methods- k-means- Hierarchical Methods - distance- based 13
agglomerative and divisible clustering, Density-Based Methods expectation
maximization -Grid Based
Methods Model-Based Clustering Methods Constraint Based Cluster
Analysis Outlier Analysis
V Multidimensional analysis and descriptive mining of complex data objects
Spatial mining -Multimedia mining - Text mining - Web mining - Temporal
12
mining.
TOTAL HOURS 60
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
T Jiawei Han and MichelineKamber, Data Mining: Concepts and Techniques,Morgan
Department of Information Technology Page 68
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Kaufmann Publishers, third edition2011, ISBN: 1558604898.
T Alex Berson and Stephen J. Smith, Data Warehousing, Data Mining & OLAP,TataMcGraw
Hill Edition, Tenth Reprint 2007.
T G. K. Gupta, Introduction to Data Min Data Mining with Case Studies, Easter Economy
Edition, Prentice Hall of India, 2006.
T MargaretH. Dunham, S.Sridhar, Data Mining : Introductory and Advanced Topics,Pearson
Education
R Mehmedkantardzic, Dataminingconcepts,models,methods, and algorithms, Wiley
Interscience, 2003.
R Ian Witten, Eibe Frank, Data Mining; Practical Machine Learning Tools and Techniques,
third edition, Morgan Kaufmann, 2011.
R George M Marakas, Modern Data Warehousing, Mining and Visualization,Prentice Hall,
2003
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM
IT 506 Database Management Systems v
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 This course deals with the representation of multidimensional data for Data warehouses
2 It covers basics of data mining, clustering and classification and applications of data mining
COURSE OUTCOMES:
SNO DESCRIPTION Blooms
Taxonomy
Level
1 Identifythe differences between relational database systems and data Knowledge,
warehouses, the need for data warehousing to formulate the decision Understand
support systeman engineering specializationfor theprediction and (level 1, level
modeling to complex engineering activities. 2)
2 Understand,
Summarize the dominant data warehousing architectures and analyze Analyze, Create
their implementation details to develop multidimensional data models
(level 2, level 4,
to analyze complex engineering problems.
level 6)
3 Understand the different functionalities of data mining system and Understand,
analyze the various data preprocessing techniques todesigndata Analyze(level
warehouses that meet the specified needs of the society with 2, level 4, level
appropriate environmental considerations. 6)
4 Analyze the various clustering and classification algorithm Analyze,
functionalities and evaluate their merits and demerits to acquire Evaluate (level
research based knowledge for thesynthesis of the information to 4, level 5)
provide valid conclusions.
5 Explain the advanced data mining concepts and outline their scope of Analyze,
providing IT solutions for different domains which helps in the
Department of Information Technology Page 69
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
betterment of life. Evaluate
(level 4, level
5)
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO1 PO1 PO1 PSO PSO PSO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 0 1 2 1 2 3
C706. 1 2 _ _ _ 1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _
1
C706. 3 3 2 _ _ 1 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 3 _
2
C706. 2 1 1 2 _ 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ 2 3 _
3
C706. 3 3 3 2 3 2 _ _ _ _ _ 1 3 2 2
4
C706. 2 2 3 2 _ 2 _ _ _ _ _ 3 2 _ 2
5
JUSTIFATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
Mapping LOW/MEDIUM/HIGH Justification
C706.1-PO1 L Identify the need of data warehousing and how it helps in
modelling real world systems (multidimensional data).
C706.1-PO2 H Identify the role of Data warehouses in real world complex
data analysis and formulate the decisions in decision
support systems
C706.1-PO6 L Study the application areas of data warehousing and apply
the contextual knowledge to assess societal, health, safety,
legal and cultural issues.
C706.2-PO1 H Data warehouse implementation will result in better
software system solutions.
C706.2-PO2 H Construct the data warehouse by applying the data
warehouse implementation techniques to summarize
multidimensional data for data analysis.
C706.2-PO3 M Study Data warehouse architecture to design Data
warehouse which, will help in analyzing complex problem
and finding a solution.
Department of Information Technology Page 70
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C706.2-PO6 L Apply reasoning informed by the data warehouse
implementation to assess societal, health, safety, legal and
cultural issues.
C706.2- H Knowledge in Data warehouse architecture will contribute
PSO2 in better database design.
C706.3-PO1 M Apply aggregation, transformation and reduction
technique to generate preprocessed data which will result
better data warehouse design for the solution of complex
engineering problems.
C706.3-PO2 L Study of different functionalities of data mining system will
help to Identify, formulate, review and analyze complex
engineering problems.
C706.3-PO3 L Study of various preprocessing techniques in data
warehousing help to design systems that meet the
specified needs with appropriate consideration for the
society.
C706.3-PO4 M Knowledge of different functionalities of data mining
system and data preprocessing techniques support the
analysis and interpretation of data, and synthesis of the
information to provide valid conclusions.
C706.3-PO6 M Apply reasoning informed by the summarized
(preprocessed) data to assess societal, health, safety, legal
and cultural issues.
C706.3- M Study of data mining techniques will acquire skills to
PSO1 design, analyse and develop algorithms and implement
them using high-level programming languages.
C706.3- H Study of data preprocessing techniques will contribute
PSO2 their engineering skills in computing and information
engineering domains like database design
C706.4-PO1 H Apply the knowledge of clustering and classification
techniques for better problem specialization and solution
of complex data.
C706.4-PO2 H knowledge of clustering and classification techniques will
help to identify, formulate, review and analyze complex
multi dimensional data andbring substantiated
conclusions
C706.4-PO3 H Knowledge of various clustering and classification
techniques will develop skills to design solutions for
complex real world problems with appropriate
consideration for the public health and safety, and the
cultural, societal, and environmental considerations.
Department of Information Technology Page 71
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C706.4-PO4 M Use research-based knowledge and research methods
including analysis and interpretation of data, and synthesis
of the information obtained from the study of various
clustering and classification algorithm functionalitiesto
provide valid conclusions.
C706.4-PO5 H Create, select, and apply appropriate clustering and
classification techniques, and modern data mining tools
including prediction and modeling to complex
multidimensional data with an understanding of the
limitations.
C706.4-PO6 M Apply reasoning informed by the contextual knowledge
with classification and clustering techniques to assess
societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues.
C706.4- L Recognize the need for advanced data mining techniques to
PO12 solve the real world problems, and have the preparation
and ability to engage in independent and life-long learning
in the broadest context of technological change.
C706.4- H Study of classification and clustering techniques acquire
PSO1 skills to design, analyse and develop algorithms and
implement them using high-levelprogramming languages.
C706.4- M Classification and clustering techniques knowledge
PSO2 contribute their skills in computing and information
engineering domains like knowledge engineering.
C706.4- M Classification and clustering techniques knowledge
PSO3 develop strong skills in systematic planning, developing,
testing implementing and providing IT solutions for
different domains which helps in the betterment of life.
C706.5-PO1 M Learning advanced data mining concepts
contribute specialization to the solution of complex
engineering problems
C706.5-PO2 M Advanced data mining concepts helps to formulate and
analyze complex engineering problems reaching
substantiated conclusions
C706.5-PO3 H Design solutions for complex engineering problems and
design system components or processes that meet the
specified needs with appropriate consideration for the
public health and safety, and the cultural, societal, and
environmental considerations.
Department of Information Technology Page 72
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C706.5-PO4 M Use research-based knowledge and research methods
including design of experiments, analysis and
interpretation of data, and synthesis of the information to
provide valid conclusions.
C706.5-PO6 M Apply reasoning informed by the contextual knowledge to
assess societal, health, safety, legal and cultural issues and
the consequent responsibilities relevant to the professional
engineering practice.
C706.5- H Advanced data mining concepts helps to recognize the
PO12 need for, and have the preparation and ability to engage in
independent and life-long learning in the broadest context
of technological change.
C706.5- M Study ofAdvanced data mining concepts acquire skills to
PSO1 design, analyse and develop algorithms and implement
them using high-level programming languages.
C706.5- M Knowledge of advanced data mining concepts develop
PSO3 strong skills in systematic planning, developing, testing
implementing and providing IT solutions for different
domains which helps in the betterment of life.
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
SNO DESCRIPTION PROPOSED
ACTIONS
1 Data Mining Tools Demo
2 Data Mining Models Assignment
3 Matrix for Classification Seminar
4 Error Measures for classification Techniques Assignment
5 Data Cube construction Seminar
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST
LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ADVANCED TOPICS/DESIGN:
1 Software for Data Warehousing
2 Data Cube Implementation
3 Familiarization with WEKA
4 Data warehouse Implementation
5 Information Privacy and DATA Mining
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
Department of Information Technology Page 73
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
1 nptel.iitm.ac.in
2 http://www.cs.uiuc.edu/~hanj/bk2/
3 http://www.oracle.com/technetwork/database/options/advanced-analytics/odm/odm-
techniques-algorithms-097163.html
4 http://www.slideshare.net/idnats/data-warehousing-and-data-mining-presentation-725476
5 http://forum.jntuworld.com/showthread.php?3818-Data-Warehousing-and-Data-Mining-
%28DWDM%29-Unit-wise-Notes-All-8-Units
6 http://www.theiia.org/intAuditor/itaudit/archives/2006/august/data-mining-101-tools-and-
techniques/
7 http://www.thearling.com/text/dmtechniques/dmtechniques.htm
8 http://akademik.maltepe.edu.tr/~kadirerdem/772s_Data.Mining.Concepts.and.Techniques.2n
d.Ed.pdf
9 http://www.data-miners.com/resources/SUGI29-Survival.pdf
1 http://www.uta.edu/faculty/sawasthi/Statistics/stdatmin.html
0
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. ASSIGNMENT WEB RESOURCES
LCD/SMART STUD. SEMINARS ADD-ON COURSES
BOARDS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
ASSIGNMENTS STUD. SEMINARS TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
EXAMS EXAMINATION
STUD. LAB STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR CERTIFICATIONS
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS BY OTHERS
EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by Approved by
Department of Information Technology Page 74
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
(Dr. SherlyK.K) (HOD)
Course plan
Module Day Planned
Day
I 1 Overview
Day
I 2 Evolution of Decision Support Systems, DSS applications
Day Components of DSS, Distinction between operatonal database and DSS
I 3 databse
Day Data warehousing Components Data warehouse, Comparison between
I 4 Data Warehouse and DBMS
Day
I 5 Data marts, Metadata
Day
I 6 Multidimensional data model, OLAP ,OLTP, Data cubes
Day Schemas for Multidimensional Database: Star schema,Snowflakes and
I 7 Fact constellations schema
Day
I 8 Implement schemas using examples (tutorial)
Day
I 9 Revision test of module I
Day
II 10 Types of OLAP servers: ROLAP, MOLAP, HOLAP
Day
II 11 3Tier data warehouse architecture
Day
II 12 Distributed and virtual data warehouses
Day
II 13 Data warehouse implementation
Day
II 14 Tuning and testing of data warehouse
Day
II 15 Data Staging (ETL) Design and Development,
Day
II 16 Data warehouse visualization
Day
II 17 Data Warehouse Deployment, Maintenance, Growth
Day Business Intelligence Overview- Data Warehousing and Business
II 18 Intelligence Trends
Day Business Applications- tools-SAS (Assignment I), Revision test of module
II 19 II
Day
III 20 Data mining-KDD versus data mining, Stages of the Data Mining Process
III Day Task primitives, Data Mining Techniques: Association rule mining
Department of Information Technology Page 75
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
21
Day Data Mining Techniques: Supervised Vs Unsupervised, Classification &
III 22 Prediction
Day Data Mining Techniques: Clustering and Outlier Analysis, Data Mining
III 23 multiple disciplines
Day
III 24 Data mining knowledge representation, Data mining query languages
Day
III 25 Integration of a Data Mining System with a Data Warehouse Issues
Day Data preprocessing: Major Tasks in Data Preprocessing, Data Cleaning,
III 26 Handling Missing Data
Day
III 27 Data Transformation: Normalization, Feature selection
Day Dimensionality reduction methods: Wavelet transform Principal
III 28 component analysis
Day
III 29 Discretization and generalization
Day Association rule mining, market basket analysis : Frequent pattern
III 30 mining algorithm with examples (Apriori algorithm)-Tutorial
Day
III 31 Revision test of module III
Day
IV 32 classification Techniques, Decision Tree Induction
Day
IV 33 Bayesian Classification -Tutorial
Day
IV 34 Rule Based Classification by Back propagation
Day
IV 35 Support Vector Machines Associative Classification
Day
IV 36 Lazy Learners Other Classification Methods
Day Clustering techniques: Partitioning methods- k-means algorithm :
IV 37 Tutorial
Day Hierarchical Methods - distance- based agglomerative and divisible
IV 38 clustering
Day
IV 39 Density-Based Methods expectation maximization, Grid Based Methods
Day
IV 40 Model-Based Clustering Methods ,Constraint Based Cluster Analysis
Day
IV 41 Outlier Analysis
Day
IV 42 Revision test of module IV
V Day Multidimensional analysis : descriptive mining of complex data objects
Department of Information Technology Page 76
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
43
Day
V 44 Spatial mining, Temporal mining (Assignment II)
Day Multimedia mining :Classification and Prediction Analysis, Mining
V 45 Associations, Audio and Video Data Mining
Day Text Data Analysis and Information Retrieval, Dimensionality Reduction
V 46 for Text, Text Mining Approaches
Day Web mining: Mining Multimedia Data on the Web, Automatic
V 47 Classification of Web Documents, Web usage mining
Day
V 48 Revision Test of Module V
IT010 706 L06 Data Mining and Data Warehousing (Elective II)
Tutorial List
Sl. No Topic Date Hour
Construct various types of data warehouse schemas using
1 suitable examples 9/8/2016 5
i). Draw Data Warehouse 3-Tier Architecture design and
analyze each layer functionalities.
ii). Demonstrate the various OLAP operations with
2 suitable examples 11/8/2016 6
Analyze the two popular dimensionality reduction
techniques used in data warehouse : PCA, Wavelet
3 Transform 5/10/2016 4
Find out frequent itemsets from the given dataset using
Apriori algorithm and generate strong association rules
4 from the identified frequent patterns. 15/10/2016 4
Demonstrate the working of Nave Bayesian classifier with
5 suitable example 18/10/2016 5
Illustrate the clustering procedure in K-means clustering
6 algorithm with suitable example 20/10/2016 4
Department of Information Technology Page 77
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 706 L06 Data Mining and Data Warehousing (Elective II)
Assignment List
Assignment
No. Topic Submission Date
Data Warehousing and Business Intelligence
1 Trends, Applications- tools-SAS 23/8/2016
2 Spatial Mining, Temporal Mining 31/09/2016
Department of Information Technology Page 78
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 708
Computer Aided Software
Engineering Lab
Department of Information Technology Page 79
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
PROGRAMME : INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEGREE : BTECH
COURSE: : computer aided software SEMESTER : VII CREDITS : 2
engineering lab
COURSE CODE : IT010-708 COURSE TYPE : CORE
REGULATION : 2010
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN : Software CONTACT HOURS : 3 hours/Week.
Engineering
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF LAB COURSE NAME: computer aided software
ANY):IT010702 engineering lab
SYLLABUS:
UNIT DETAILS HOURS
1.Study of case tools such as rational rose or equivalent tools
2. Requirements
Implementation of requirements engineering activities such as elicitation,
validation, management using case tools
3. Analysis and design
1 Implementation of analysis and design using case tools. 30
4. Study and usage of software project management tools such cost estimates
and
scheduling
5. Documentation generators - Study and practice of Documentation generators.
6. Data modeling using automated tools.
7. Practice reverse engineering and re engineering using tools.
8. Exposure towards test plan generators, test case generators, test coverage
and
software metrics.
9. Meta modeling and software life cycle management.
TOTAL HOURS 30
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
Department of Information Technology Page 80
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
R Object Oriented Modeling and Design -James Rumbaugh, Prentice Hall India
R UML Distilled Martin Fowler, Addison Wesley
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM
IT010702 Object oriented modeling and design Object oriented methodology for system S7
modeling and design
IT Software engineering Phases in software development S6
010604
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 To impart ideas on building systems through the object oriented modeling
approach using the Unified Modeling Language.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
SNO DESCRIPTION Blooms
Taxonomy
Level
1 Students will be able toEvaluate Computer aided software engineering tools Evaluate
(level 5)
2 Students will acquire skills to Practice the Creation of requirements Create
engineering activities (level 1)
3 Have knowledge on the analysis and design activities of software Analysing
development (level 4 )
4 Understand the scheduling, cost estimation and documentation activitiesof Understand
Software development. (level 5)
5 Remembering on data modeling ,forward and reverse engineering operations Remember
(level 6)
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
SNO DESCRIPTION PROPOSED
ACTIONS
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PSO PSO PSO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
IT010
- - - - - - - 1 - 3 - - 2 - -
708.1
IT010 1 - - - 3 - - - 2 - - - - - 1
Department of Information Technology Page 81
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
708.2
IT010
- 1 - - - - 2 - - - - - 2 - -
708.3
IT010
1 2 - - 2 - - - - 3 2 - -
708.4
IT010
- - 1 3 - - 2 - - - - - - 1 -
708.5
JUSTIFICATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
LOW/MEDIUM/HIG
MAPPING JUSTIFICATION
H
IT010 708.1-
H Students will acquire ethics to find out the cost estimation.
PO8
IT010 708.1-
L Importance of documentation in Software design.
PO10
IT010 708.1-
M Students will acquire skills to design the software projects .
PSO1
Apply the set of knowledge to find out the requirement
IT010 708.2-
M analysis.
PO1
IT010 708.2-
L Select set of tools used for creating usecase diagrams.
PO5
IT010 708.2-
M To know the effect of team work in software project design.
PO9
Students will be able to acquire skills to find out the usecases
IT010 708.2- H
in a problem statement.
PSO3
IT010 708.3- Students analyse complex software problems reaching
H
PO2 substantiated conclusions.
IT010 708.3- Students will be able to attain set of knowledge for develop
M
PO7 class diagrams.
IT010 708.3- Students acquire skills to develop different Activity diagrams
M
PSO1 of the project
IT010 708.4- H Apply the knowledge of UML fundamentals to develop
Department of Information Technology Page 82
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
PO1 sequence diagrams of the project
IT010 708.4-
M Analyse the use of cost estimation in software project.
PO2
IT010 708.4- By the help of tools design the set of screen prototypes.
M
PO5
IT010 708.4-
L Students try to learn how to plan a software project
P012
IT010 708.4- Students acquire skills to design what are the states of a
M
PSO1 project.
IT010 708.5- Design different set of activity diagrams to show the flow of
H
PO3 events.
IT010 708.5 Students acquire set of knowledge to understand set of
L
PO4 problems related to designing sequence diagrams.
IT010 708.5- Students acquire set of skills to know the details of the
H
PSO2 database.
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST
LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ADVANCED TOPICS/DESIGN:
1 Familiarization of open proj
2 Familiarization of usecase points
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
1 http://pic.dhe.ibm.com/infocenter/reqpro/v7r1m0/index.jsp?topic=/com.ibm.reqpro.help/get
_start/r_tutorials.html
2 http://www.ibm.com/developerworks/rational/products/rsa/
3 http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Unified_Modeling_Language
4 https://www.openproject.org/
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. WEB RESOURCES
ASSIGNMENT
LCD/SMART STUD. SEMINARS ADD-ON COURSES
BOARDS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
ASSIGNMENTS STUD. SEMINARS TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
Department of Information Technology Page 83
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
EXAMS EXAMINATION
STUD. LAB STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR CERTIFICATIONS
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS BY OTHERS
EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by Approved by
(Mathews Abraham) Binu A
(Faculty) (HOD)
IT010 708 Computer Aided Software Engineering Lab
LAB SCHEDULE
Sl.No Planned Date Planned
Pgm 1-
1.Requirement Analysis 2.Drawing
Requirement Traceability Matrix
1 5/aug 3. Identify the list of Actors
4. Identify the list of Usecases
5. Mapping functional requirements to usecases
6.Develop usecases
7. Detailed explanation of each usecase
Pgm 1-
2 26/aug 8. Develop Screen Protypes
9. Cost Estimation
10. Planning
Department of Information Technology Page 84
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Pgm 1-
11. Identifying Domain Classes
12.Modelling UML Activity Diagram (Only for 4
scenarios)
13.Modelling UML Sequence Diagram (Only for 4
scenarios)
3 26/aug
14.Modelling UML Class Diagram (Should be a detailed
class diagram)
15. Modelling UML Component Diagram
16. Detailed explanation of each usecase
17. Automated Code Generation - Forward Engineering
Pgm 2-
1.Requirement Analysis 2.Drawing
4 2/sept Requirement Traceability Matrix
3. Identify the list of Actors
4. Identify the list of Usecases
5. Mapping functional requirements to usecases
6.Develop usecases
7. Detailed explanation of each usecase
Pgm 2-
5 23/sept
8. Develop Screen Protypes
9. Cost Estimation
10. Planning
Pgm 2-
11. Identifying Domain Classes
12.Modelling UML Activity Diagram (Only for 4
scenarios)
13.Modelling UML Sequence Diagram (Only for 4
scenarios)
6 30/sept
14.Modelling UML Class Diagram (Should be a detailed
class diagram)
15. Modelling UML Component Diagram
16. Detailed explanation of each usecase
17. Automated Code Generation - Forward Engineering
Department of Information Technology Page 85
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Pgm 3-
1.Requirement Analysis 2.Drawing
Requirement Traceability Matrix
3. Identify the list of Actors
7 7/oct
4. Identify the list of Usecases
5. Mapping functional requirements to usecases
6.Develop usecases
7. Detailed explanation of each usecase
Pgm 3-
8. Develop Screen Protypes
8 14/oct 9. Cost Estimation
10. Planning
Pgm 3-
11. Identifying Domain Classes
12.Modelling UML Activity Diagram (Only for 4
scenarios)
13.Modelling UML Sequence Diagram (Only for 4
scenarios)
9 21/oct
14.Modelling UML Class Diagram (Should be a detailed
class diagram)
15. Modelling UML Component Diagram
16. Detailed explanation of each usecase
17. Automated Code Generation - Forward Engineering
28/oct
10 Model lab exam
Program 1.
LIBRARY INFORMATION SYSTEM
The Institute has been recently setup to provide state-of -the-art research facilities in the field of
Software Engineering. Apart from research scholars(students) and professors, it also includes quite
a large number of employees who work on different projects undertaken by the Institution.
As the size and capacity of the institute is increasing with the time, it has been proposed to
develop a Library Information System (LIS) for the benefit of students and employees of the
institute. LIS will enable the members to borrow a book (or return it) with ease while sitting at his
desk/chamber. The system also enables a member to extend the date of his borrowing if no other
borrowing for that particular book has been made.
Department of Information Technology Page 86
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
For the library staff, this system aids them to easily handle day-to-day book transactions. The
librarian, who has administrative privileges and complete control over the system, can enter a new
record into the system when a new book has been purchased, or remove a record in case any book
is taken off the shelf. Any non-member is free to use this system to browse/search books online.
However, issuing or returning books is restricted to valid users (members) of LIS only.
The final deliverable would be a web application (using recent HTML 5), which should run
only within the institute LAN. Although this reduces security risk of the software to a large extent,
care should be taken no confidential information (e.g., passwords) is stored in plain text.
Program 2
SHOPPING MALL MANAGEMENT
The mall will provide a smooth shopping experience for customers. Also the system will allow more
than one shop owner to set up different shops, to sell various products under one roof i.e. mall. The
concept, at its very basic, provides for an environment that allows the following: Any person
wishing to setup shop in the mall can send a proposal to the mall owner. The mall owner approves
the proposal and confirms the deal. The shop owners can then setup and maintain their own
shop(s) in the mall.
The customers when enter the mall have to authenticate themselves on a central server. After
authentication, the customer is allocated a shopping cart and can enter a particular shop of
his/her choice for shopping. After entering a shop, the customer can browse through the products
available in the shop, can select some of them and put into the shopping cart. The customer can
anytime change the items in the cart either by adding new items or by removing existing items. The
customer proceeds towards the payment counter. Then finalize the product list of items that the
customer finally wishes to buy and make the final payment. The customer then leaves the shop and
can either enter another shop or leave the mall.
Program 3 (Roll number 1-20)
a.ONLINE QUIZ SYSTEM
To develop a system for conducting a quiz as part of department of IT by choosing questions
randomly from different areas like IT, Logical measuring and General Knowledge.
Program 4(Roll number 21-40)
RAILWAY RESERVATION SYSTEM
To implement an automated railway reservation system and to document the various steps taking
place during a project development cycle
PROBLEM DEFENITION
The railway reservation system should have distributed functionalities as described below:-
Department of Information Technology Page 87
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
1. Reserve seat-A passenger should be able to reserve a seat in the train specified by him if
available. For this he has to fill a reservation form with the details about his journey. The clerk
checks for the availability of the seat in the train and if the seat is available then he marks entries
regarding train name, t rain number, date of journey, boarding station and destination. The
passenger is asked to pay the fair. After making payment the passenger can collect ticket from the
clerk.
2. Cancel reservation:-There arise a case when the passenger wants to cancel the reservation. For
this he has to fill a cancellation form providing all details about the ticket reserved by him. The clerk
then checks for the entries from the database and cancel the reservation finally returning the ticket
amount with some deduction.
3. Update train information and report generation:-Only the administrator has the right to make
changes in the train details (train name, train no etc).The system should also be able to generate
report when needed in the form of reservation charts, train schedule charts etc.
4. Login:-Only the user with specified login id and password can get access to the system. T his
provides security from unauthorized access.
5. View reservation status and train scheduled:-All the users should be able to see the information
about the reservation.
Program 5.(roll number 41-60)
Online Shopping
Shopping becomes easier and flexible by innovative information technology concepts. Clients
should acquire credit /debit cards from the respective banks for the transaction purpose. Proper
shopping destination should be selected by the customer for the effective shopping. Internet
enabled laptops/desktops are the important parts of the online shopping system. Customer should
acquire the bank account and then get the debit/credit cards.
There are different sites in the internet for the online shopping, which shows the quality, prize and
configurations of the product in detail. The customer can view the details of the products including
its price, quality and images. The customer can add the selected items to his/ her shopping cart.
Then the customer can order the goods by filling the order form and can pay the cash through
cards. Site administrator should verify the customer name, address, card number, account details
etc. If the customer is valid, goods will reach at home through home delivery system.
1. OPEN QUESTIONS
2. Making a Phone call
The major elements included in a phone call are calling phone, a telephone exchange and a
receiving phone. The person who wants to make call to another person, first takes the receiver
and dial a number of the recipient with STD code. If the number is busy, we get a busy tone. The
telephone exchange is the intermediary between the caller and callee. On understanding the
recipients number, the telephone exchange establishes a connection with the recipient phone, if the
network is available.
Department of Information Technology Page 88
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
When the recipient takes the receiver, the call is established and conversation takes place until the
call is disconnected. The Telephone Exchange has the facility for calculating the duration of call and
the cost of the call. The signals are transmitted from the caller to exchange and from exchange to
callee via fibre optic cables or via satellites. The caller has the redial facility on a busy condition. If
the recipient have caller ID, he can understand the number of the caller.
3. Online Shopping
Shopping becomes easier and flexible by innovative information technology concepts. Clients
should acquire credit /debit cards from the respective banks for the transaction purpose. Proper
shopping destination should be selected by the customer for the effective shopping. Internet
enabled laptops/desktops are the important parts of the online shopping system. Customer should
acquire the bank account and then get the debit/credit cards.
There are different sites in the internet for the online shopping, which shows the quality, prize and
configurations of the product in detail. The customer can view the details of the products including
its price, quality and images. The customer can add the selected items to his/ her shopping cart.
Then the customer can order order the goods by filling the order form and can pay the cash through
cards. Site administrator should verify the customer name, address, card number, account details
etc. If the customer is valid, goods will reach at home through home delivery system.
4. Online Assignment Submission System
The online assignment submission system is aimed at downloading and uploading assignments for
students; with each assignment having information about the instructions, description of
assignment topic, deadline, and submission details. There will be three users groups which are:
Administrators, course instructors and Students.
The student must be able to update his profile, submit or upload the assignment documents online
and also view the grade of the assignments in each subject.
The course instructor shouldreceive and download the student's document. He then updates the
grade of the assignment. There will be an administrator who manages the whole application. He
could add or delete courses, course instructors and students. He must be able to associate a course
with a student as well as a course instructor. The administrator can also view the student grade.
5. ADVANCED QUESTIONS
1. Car Rental System
Automobile sales, service and rental company in the city wants to set up a computerized application
for handling its car rental business. Currently, the operation is manual and the manager wants to
help the clients by offering a faster service. This system is going to be used by three groups of users
- the customer, administrator and the staff. The application should provide direct access to the
Department of Information Technology Page 89
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
customers through web application system. There must be a provision to view current status of all
cars such as available, being rented or not available. The administrator can add the details to the
application modify it and delete. The administrator and staff must be able to do business analysis
and generate report such as the car rental report and other statistics from time to time. The
customer can select a rental and book for it by filling a booking form and can pay online using credit
card.
2. Shopping Mall Management
The mall will provide a soothing shopping experience for customers. Also the system will allow
more than one shop owner to set up different shops, to sell various products under one roof i.e.
mall. The concept, at its very basic, provides for an environment that allows the following: Any
person wishing to setup shop in the mall can send a proposal to the mall owner. The mall owner
approves the proposal and confirms the deal. The shop owners can then setup and maintain their
own shop(s) in the mall.
The customers when enter the mall have to authenticate themselves on a central server. After
authentication, the customer is allocated a shopping cart and can enter a particular shop of
his/her choice for shopping. After entering a shop, the customer can browse through the products
available in the shop, can select some of them and put into the shopping cart. The customer can
anytime change the items in the cart either by adding new items or by removing existing items. The
customer proceeds towards the payment counter. Then finalize the product list of items that the
customer finally wishes to buy and make the final payment. The customer then leaves the shop and
can either enter another shop or leave the mall.
3. Parking Allotment
Shopping mall of a city wanted to automates its car parking. It has a six levels of car parking area
with 100 cars can be parked at each level. A barrier and a card reader are placed at the entrance
and exit place. The driver of an approaching car presses the button to receive token at the entrance.
The card reader checks the token and sends a signal to raise the barrier for valid token. The
entrance barrier is raised to enable the car to enter parking. The token is issued at the entrance
only when there is a place to park the car. The parking place of the car with level and place is
printed in the token. At the exit, there is also a barrier, which is raised when a car wishes to leave
the park. The exit barrier is released only when the driver of the car, approach the card reader and
pay the parking charge.
4. The stock management system
The stock management system aims at automating the stock management activities in the shop. The
shop owner can keep a record of all the items available in the shop. He has the authority to add,
delete and modify the items in the record. This record will be automatically updated on every
purchase made. The shop owner can view the record any time for stock verification. The system
also provides the facility for automatic stock report generation of weekly activities. This system will
help to reduce the time and cost of stock management.
5. Online Ticket Reservation System
Department of Information Technology Page 90
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
The system aims to develop online ticket reservation for the flight. The system maintains the details
various of flight routes, ticket availability and etc., A passenger who wants to book the ticket can do
a search to locate availability of the seat.
Requisition slip can be filled in online and submitted. Fifty percentage of the amount should be paid
in advance to confirm the ticket during registration. The mode of payment is through credit card.
Cancellation of the ticket can also be made online.
Department of Information Technology Page 91
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 707
Internetworking Lab
Department of Information Technology Page 92
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET July 2016
PROGRAMME: INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEGREE: BTECH
COURSE: INTERNETWORKING LAB SEMESTER: VII CREDITS: 2
COURSE CODE: IT010 707 COURSE TYPE: CORE
REGULATION : 2010
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: INTERNETWORKING CONTACT HOURS: 3 hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY):
SYLLABUS:
DETAILS HOURS
Familiarization of Network hardware such as NIC, Hub, Bridge, Switch, Router etc
Familiarizationof different NetworkCables-Colorcoding -Crimping. 6
Familiarization ofWirelessAccessPoint.
LAN Configuration IP Addressing Host name - Domain Name Setting up
Configuring testing and troubleshooting 6
Wireless LAN Configuration
Basicswitchconfiguration
VLANconfiguration
6
VTP,VTPpruning.
Implementinter-VLANrouting
Basic router configuration.
Implementing static routing.
Implementing dynamic routing using RIP 9
Implementing dynamic routing using OSPF
Implementing dynamic routing using EIGRP
Backup and recovery of configuration files of a router using TFTP server.
Access Control List (Standard and Extended) 6
Configuring PPP.
33(11 Lab
TOTAL HOURS
Sessions)
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
R CCNA CISCO certified network associate study guide
R CCNA Self Study: Introduction: Introduction to CISCO Networking Technologies, McQuerry, S
R CCNA Self Study: CCNA INTRO: Exam Certification Guide, Odom, W
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM
Department of Information Technology Page 93
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 601 Computer Networks Basics in Computer Networks S6
IT010 704 Internetworking Advanced Computer Networks S7
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 Build an understanding of the fundamental concepts of computer networking
2 Familiarize the student with the basic taxonomy and terminology of the computer networking
area
3 Introduce the student to advanced networking concepts, preparing the student for entry
Advanced courses in computer networking
4 Allow the student to gain expertise in some specific areas of networking such as the design and
maintenance of individual networks
COURSE OUTCOMES:
Blooms
SNO DESCRIPTION Taxonomy
Level
Knowledge
C707.1 Identify the different types of network topologies and protocols.
(level 1)
Identify the different types of network devices and their functions within a Knowledge
C707.2 network (level 1)
Familiarity with the basic protocols of computer networks, and evaluates Evaluate
C707.3
how they can be used to assist in network design and implementation. (level 5)
Understand,
Understand the concepts of routing mechanisms , network interfaces, and Analyze(level
C707.4
design/performance issues in local area networks and wide area networks 2 and 4)
Understand
C707.5 To be familiar with wireless networking concepts
(level 2)
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PSO1 PSO2 PSO3
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12
C701.1 3 _ 3 _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 3 _ 3 -
C702.2 3 3 _ _ - _ _ - _ 3 - 3 _
C703.3 - 2 _ 2 _ _ _ _ _ _ 2 _ 3
C704.4 2 3 2 - _ _ _ _ _ _ _ - _
Department of Information Technology Page 94
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C705.5 1 3 _ 3 _ _ _ _ - _ 3 _ 1 _
GAPS IN THE SYLLABUS - TO MEET INDUSTRY/PROFESSION REQUIREMENTS:
SNO DESCRIPTION PROPOSED
ACTIONS
PROPOSED ACTIONS: TOPICS BEYOND SYLLABUS/ASSIGNMENT/INDUSTRY VISIT/GUEST
LECTURER/NPTEL ETC
JUSTIFICATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
MAPPING LOW/MEDIUM/H JUSTIFICATION
IGH
C707.1-PO1 H Students will acquire knowledge Network Topologies and
Protocols.
C707.1-PO3 H Students will be able to understand how these LAN
Configuration and IP addressing is done in simulation
mode of packet tracer tool
C707.1-PO12 H Information acquired from Packet Network Topologies
and Protocols provides lifelong learning in the context of
Network Designing.
C707.1-PSO2 H Simulation using Packet tracer tool helps in contribution
of engineering skills in design of Network.
C707.2-PO1 H Studies about the various networking components help
the students to understand about its basic functionalities
specially the switch and router configuration.
C707.2-PO3 H Students gain the Knowledge of virtual LAN help students
in designing network.
C707.2-P012 H Studies about the various networking device
Configuration provide lifelong learning in the context of
Network Designing.
C707.2-PS02 H Students will be able to analyze different functionalities
provided by networking devices in the domain of network
design.
C707.3-PO2 M Studies about the analysis of different network protocols
helps in the network designing.
C707.3-PO5 M Static and dynamic routing protocols simulation will be
familiarized by the students.
Department of Information Technology Page 95
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
C707.3-PO12 M Information acquired from routing protocol evaluation
provides lifelong learning in the design of network.
C707.3-PSO2 L Students could apply the knowledge of Routing protocol
simulation in the field of network design and
Implementation.
C707.4-PO1 M Students gain the ability to learn about the concepts of
routing mechanisms, crimping and performance issues in
local area networks and wide area networks.
C707.4-PO2 H Students will understand the Implementation of Web
Server, DHCP Server and DNS in simple LAN.
C707.4-P03 M The students could understand Implementation of
wireless LAN using PCs, and a wireless router
C707.5-PO1 L Students will be obtaining basic knowledge of wireless
networking concepts .
C707.5-P03 H Students will be obtain basic knowledge of Implementing
inter-VLAN routing using VTP VLANs and switches
C707.5-P05 H Students could apply the knowledge of wireless routing
concepts for simulating the network using packet tracer
tool.
C707.5-P012 H Students could apply the knowledge of wireless
networking concept for lifelong learning in the context of
technological change.
C707.5-PS02 L Students will be acquiring knowledge to apply the
engineering skills in network design and implementation.
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
1 https://learningnetwork.cisco.com/thread/15662
2 http://recentccna.blogspot.in/
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. ASSIGNMENT WEB RESOURCES Lab Sessions
LCD/SMART STUD. SEMINARS ADD-ON COURSES
BOARDS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
ASSIGNMENTS STUD. SEMINARS TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
EXAMS EXAMINATION
STUD. LAB STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR CERTIFICATIONS
Department of Information Technology Page 96
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS BY OTHERS
EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by Approved by
Abey Abraham Binu A
(Faculty) (HOD)
IT 010 707 : INTERNETWORKING LAB
LAB CYCLE - 2016
1. FAMILIARIZATION OF NETWORK DEVICES.
2. FAMILIARIZATION OF NETWORK CABLES.
3. STUDY OF TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE.
4. FAMILIARIZATION OF CISCO SWITCH COMMANDS.
5. FAMILIARIZATION OF CISCO ROUTER COMMANDS
6. FAMILIARIZATION OF PACKET TRACER
7. SIMPLE LAN
Implementation of simple LAN using 4PCs and a switch.
Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and hostnames on PCs
Check the Connection using ping command
View ARP tables on each PC
View MAC table on switch
8. WIRELESS LAN
Implementation of wireless LAN using 5PCs, and a wireless router
Configure wireless router and PCs
Check the Connection using ping command
View ARP tables on each PC
View MAC table on switch
9. DHCP SERVER
Implementation of DHCP based LAN using 4PCs, one DHCP server and a switch.
Department of Information Technology Page 97
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Configure DHCP (Use Class C private IPs) server
Configure DHCP and hostnames on PCs
View IP address on each PC
Check the Connection using ping command
View ARP tables on each PC
View MAC table on switch
9. DNS SERVER
Implementation of DNS in simple LAN using 3PCs, one DNS Server and a switch.
a. Configure DNS
b. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and DNS setting on PCs
c. Perform nslookup
d. Execute ping command using domain names
e. View ARP tables on each PC
f. View MAC table on switch
10. WEB SERVER
Implementation of Web Server in simple LAN using 3PCs, one DNS Server, one Web server
and a switch.
a. Configure DNS
b. Configure Web Server
c. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and DNS setting on PCs
d. Perform nslookup
e. Access web server from PCs using browser
11. STATIC ROUTING
Implementation of static routing using 8 PCs, 2 switches and three routers.
a. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and hostnames on PCs. Use two
different subnet IPs based on switch connected.
b. Configure IP address to routers
c. Update Static Routing Table
d. Check the Connection using ping command
e. Check the connection using trace route command
f. View ARP tables on each PC
g. View MAC table on switches
h. View routing tables on routers
12. DYNAMIC ROUTING - RIP
Implementation of dynamic routing based on RIP using 8 PCs, 2 switches and three routers.
a. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and hostnames on PCs. Use two
different subnet IPs based on switch connected.
b. Configure IP address to routers
c. Update Routing Table in routers
d. View routing tables on routers
e. Check the Connection using ping command
f. Check the connection using trace route command
g. View ARP tables on each PC
h. View MAC table on switches
Department of Information Technology Page 98
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
13. DYNAMIC ROUTING - OSPF
Implementation of dynamic routing based on OSPF using 8 PCs, 2 switches and three
routers.
a. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and hostnames on PCs. Use two
different subnet IPs based on switch connected.
b. Configure IP address to routers
c. Update Routing Table in routers
d. View routing tables on routers
e. Check the Connection using ping command
f. Check the connection using trace route command
g. View ARP tables on each PC
h. View MAC table on switches
14. DYNAMIC ROUTING - EIGRP
Implementation of dynamic routing based on EIGRP using 4PCs, 2 switches and three
routers.
a. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and hostnames on PCs. Use two
different subnet IPs based on switch connected.
b. Configure IP address to routers
c. Update Routing Table in routers
d. View routing tables on routers
e. Check the Connection using ping command
f. Check the connection using trace route command
g. View ARP tables on each PC
h. View MAC table on switches
15. VIRTUAL LAN
Implementation of simple VLAN using 6PCs and a switch.
a. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and hostnames on PCs
b. Configure 2 VLANs, VLAN1 and VLAN2 in switch using commands
c. Assign Connected two Physical Ports to VLAN1 and remaining ports to VLAN2
d. Check the Connection using ping command
e. View ARP tables on each PC
f. View MAC table on switch
g. View VLAN Database
16. VLAN TRUNK PROTOCOL
Implementation of Simple Trunk (VTP) using 4PCs and two switches.
a. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and hostnames on PCs
b. Configure 2 VLANs, VLAN1 and VLAN2 in switch using commands
c. Assign Connected two Physical Ports to VLAN1 and remaining ports to VLAN2
d. Check the Connection using ping command
e. View ARP tables on each PC
f. View MAC table on switch
g. View VLAN Database
h. Configure Trunk port on VLAN1 and VLAN2 using commands
i. Check the Connection using ping command
17. INTER VLAN ROUTING USING VTP
Implement inter-VLAN routing using VTP using 4 VLANs and two switches
Department of Information Technology Page 99
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
a. Configure IP address (Use Class C private IPs) and hostnames on PCs
b. Assign Connected Physical Ports to appropriate VLANs
c. Check the Connection using ping command
d. View ARP tables on each PC
e. View MAC table on switch
f. View VLAN Databases
g. Configure Trunk port on VLAN1, VLAN2, VLAN3 and VLAN4
h. Check the Connection using ping command
18. FAMILIARIZATION OF CRIMPING
DEPARTMENT OF INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY
IT010 707 INTERNETWORKING LAB
LAB SCHEDULE - 2016
Day Date Program
1. FAMILIARIZATION OF NETWORK DEVICES.
2. FAMILIARIZATION OF NETWORK CABLES.
3. STUDY OF TCP/IP PROTOCOL SUITE.
4. FAMILIARIZATION OF CISCO SWITCH COMMANDS.
5. FAMILIARIZATION OF CISCO ROUTER COMMANDS
6. FAMILIZATION OF PACKET TRACER
1 27-Jul-16 Simple LAN
2 3-Aug-16 Wireless LAN, DHCP Server
3 10-Aug-16 DNS Server, Web Server
4 17-Aug-16 Static Routing
Department of Information Technology Page 100
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
5 31-Aug-16 Dynamic Routing - RIP,OSPF
6 7-Sep-16 Dynamic Routing - EIGRP,Virtual LAN
7 28-Sep-16 VLAN Trunk Protocol
8 5-Oct-16 Inter VLAN using VTP,Crimping
9 19-Oct-16 Model Exam
OPEN QUESTIONS
SAMPLE NETWORKS
Department of Information Technology Page 101
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Department of Information Technology Page 102
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Department of Information Technology Page 103
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Department of Information Technology Page 104
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
ADVANCED QUESTIONS
Question 1
Configure a network as depicted, in Packet Tracer
Department of Information Technology Page 105
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Implement RIP.
Do trace route to google.com from Client PC, when Router3 is ON
Do trace route to google.com from Client PC, when Router3 is OFF
Show Routing Table of Gateway Router
o When Router3 is ON
o When Router3 is OFF
(To proceed, write necessary commands to configure Routers/Switches; May not be in detail)
Question 2
Configure a network as depicted, in Packet Tracer
Implement Dynamic Routing using OSPF using area as area1.
Do trace route to google.com from Client CS1, when Gateway Router Link (192.168.4.1) is
ON
Do trace route to google.com from Client CS1, when Gateway Router Link (192.168.4.1) is
OFF
Ping IT3 from CS1, when Gateway Router Link (192.168.1.1) is ON
Ping IT3 from CS1, when Gateway Router Link (192.168.1.1) is OFF
Department of Information Technology Page 106
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Question 3
Department of Information Technology Page 107
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 709
Seminar
Department of Information Technology Page 108
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
PROGRAMME: INFORMATION DEGREE: BTECH
TECHNOLOGY
COURSE: SEMINAR SEMESTER: VII CREDITS: 2
COURSE CODE : IT010 709 COURSE TYPE: CORE
REGULATION: 2010
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: CONTACT HOURS: 2 hours/Week.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY): LAB COURSE NAME:
SYLLABUS:
UNIT DETAILS HOURS
The seminar power point presentation shall be fundamentals oriented and
advanced topics in the appropriate branch of engineering with references of
minimum seven latest international journal papers having high impact factor.
Each presentation is to be planned for duration of 25 minutes including a
question answer session of five to ten minutes.
The students internal marks for seminar will be out of 50. The marks will be
awarded based on the presentation of the seminar by the students before an
evaluation committee consists of a minimum of 4 faculty members. Apportioning
of the marks towards various aspects of seminar (extent of literature survey,
presentation skill, communication skill, etc.) may be decided by the seminar
evaluation committee.
A bona fide report on seminar shall be submitted at the end of the semester. This
report shall include, in addition to the presentation materials, all relevant
supplementary materials along with detailed answers to all the questions
asked/clarifications sought during presentation. All references must be given
toward the end of the report. The seminar report should also be submitted for
the viva-voce examination at the end of eighth semester.
TOTAL HOURS 2
TEXT/REFERENCE BOOKS:
T/R BOOK TITLE/AUTHORS/PUBLICATION
Seven latest international journal papers having high impact factor
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.CODE COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SEM
Department of Information Technology Page 109
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
All subjects till s7 information technology. S1 to
s6
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 Study how to read research papers critically and efficiently and how to summarise and review
them
2 How to gain an understanding of a new field, in the absence of a textbook
3 How to judge the value of different contributions and how to identify promising new directions
COURSE OUTCOMES:
SNO DESCRIPTION
1 The students will be able to recall existing technologies in the area of computer science.
2 The students will be able to to describe, compare and evaluate different technologies.
3 The students will be able to decide the area of interest
4 The students will be able to develop their communication skills.
5 The students will be able to write technical reports.
Department of Information Technology Page 110
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
PO P PO PO PO PO PO PO PO P0 PO PO PSO PSO PS
1 O2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 O3
709.1 1 2 3 2
709.2 2 3 1 2
709.3 3 2
709.4 3
709.5 3
JUSTIFICATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
Mapping LOW/ME Justification
DIUM/HI
GH
C01-P02 L Students do a literature survey while preparing for the seminar
CO1-PO4 M They reach valid conclusions after the literature survey
CO1-PO5 H They understand the limitations of the existing techniques and can use
the engineering techniques to arrive at valid conclusions
CO1-PSO1 M Help to design solutions through a good literature survey.
CO2-PO2 M They review the state of art for reaching at substantiated conclusions.
C02-PO4 H They do a detailed analysis, synthesis of information and provide valid
conclusions.
CO2-P05 L They get knowledge of various tools to solve complex problems.
CO2-PSO1 M By comparing different techniques they can identify ,analyse and design
complex engineering problems .
CO3-PO4 H They do a detailed research in their area of interest which help them to
analyse and synthesis data .
CO3-PS03 M They apply the fundamentals of computer science in their area of
interest.
CO4- PO10 H Seminar presentations help them to develop public speaking skills
CO5-PO10 H Writing seminar report help them to develop technical report writing
skills.
WEB SOURCE REFERENCES:
1 ieee.org
2 dl.acm.org
3 Elsevier
Department of Information Technology Page 111
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
4 Springer
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
2. CHALK & STUD. ASSIGNMENT 3. WEB
TALK RESOURCES
LCD/SMART 1. STUD. ADD-ON COURSES
BOARDS SEMINARS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
STUD. TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
ASSIGNMENTS SEMINAR EXAMS EXAMINATION
S
STUD. LAB STUD. MINI/MAJOR
PRACTICES VIVA PROJECTS CERTIFICATIONS
ADD-ON
COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK, ONCE) (TWICE)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR OTHERS
PROJECTS BY EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by , Approved by
Divya James (HOD)
IT010 709 Seminar
SEMINAR SCHEDULE
Group No Date Name Seminar Guide/Co-guide
Divya James / Sherly K K
1 22/08/2016 Aishwarya V
1 22/08/2016 Christine Roy
Department of Information Technology Page 112
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Group No Date Name Seminar Guide/Co-guide
1 22/10/2016 Najla Siraj
Preetha K G / Bency Wilson
2 1/10/2016 Anoop Jose
2 1/10/2016 Hanan Manaf
2 1/10/2016 Hridya Das
2 1/10/2016 Sreelakshmi K U
Abey Abraham / Chinchu Krishna S
3 27/08/2016 Aishwarya T
3 27/08/2016 Alina Poly
3 29/08/2016 Anju George
Saritha S / Divya James
4 12/08/2016 Christeena Vincent
4 27/08/2016 Nahnas Nasar
4 11/08/2016 Shilpa George
4 11/08/2016 Zia Zacharia Cheeran
Anju Elezabath Jisha G / Mujeebudheen Khan
5 27/08/2016
Johnson
5 27/08/2016 Gopika S
5 27/08/2016 Haritha M
5 Jincy George
27/08/2016
Department of Information Technology Page 113
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Group No Date Name Seminar Guide/Co-guide
Bibitta Elizabeth Sherly K K / Lakshmi K S
6 29/09/2016
Benny
6 29/08/2016 Elza M Kovoor
6 29/09/2016 Githanjali Sarath
6 29/09/2016 Samyuktha S Pai
Divya James / Nikhila T Bhuvan
7 05/09/2016 Aadil Abdul Rasheed
7 05/09/2016 Adil Antony
7 05/09/2016 Paul Joe George
7 05/09/2016 Prashob Joseph
8 17/10/2016 Akhil Xavier Abey Abraham / Nikhila T Bhuvan
8 17/10/2016 Deena Sudheendran
8 17/10/2016 Maalu Pascal
8 17/10/2016 Reettu Taitus K
Kuttyamma A J /Jisha G
9 08/08/2016 Akkshay Lawrence
9 08/08/2016 Mazahir B Haroon
9 22/08/2016 Sachin Narendran
10 07/10/2016 Edwin Antony Jisha G / Mary John
10 07/10/2016 Isabel Johnson
10 07/10/2016 Jijo James
Department of Information Technology Page 114
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Group No Date Name Seminar Guide/Co-guide
10 07/10/2016 Sanal Sunny
Nikhila T Bhuvan / Divya James
11 15/10/2016 Alvin Jose
11 15/10/2016 Jose Joseph
11 15/10/2016 Sibin Xavier
11 15/10/2016 Vysakh S
Mathews Abraham / Sherly K K
12 05/09/2016 Atheena Hermit
Keerthana
12 05/09/2016
Ramachandran
12 05/09/2016 Reshma Joseph
Sherly K K / Saritha S
13 22/8/2016 Ardra Premkumar
Blessy Merin
13 12/08/2016
Varughese
13 22/08/2016 Merline Susan Joseph
13 22/8/2016 Preethi Elsa Thomas
Mathews Abraham / Chinchu
14 30/09/2016 Aditi Narayan Krishna S
14 30/09/2016 Liya Isaac
14 30/09/2016 Merin John
Chinchu Krishna S / Binu A
15 19/09/2016 Abhishek V
15 19/09/2016 Denis Karedan
Department of Information Technology Page 115
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Group No Date Name Seminar Guide/Co-guide
15 19/09/2016 Rishil Shaji
15 19/09/2016 Vinay V
Lakshmi K S / Sherly K K
16 03/10/2016 Antony Kurian
16 03/10/2016 Aseel V N
Joseph James
16 03/10/2016
Kannampuzha
16 03/10/2016 Sarath Chandran P
Department of Information Technology Page 116
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
IT010 710
Project
Department of Information Technology Page 117
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
COURSE INFORMATION SHEET
PROGRAMME: INFORMATION TECHNOLOGY DEGREE: BTECH
COURSE: PROJECT SEMESTER: 8 CREDITS: 4
COURSE CODE: IT010 710 COURSE TYPE: CORE
REGULATION: 2010
COURSE AREA/DOMAIN: SOFTWARE DESIGN CONTACT HOURS: 6 lab hours.
CORRESPONDING LAB COURSE CODE (IF ANY): LAB COURSE NAME: MAIN PROJECT
NIL
SYLLABUS : - NA
COURSE PRE-REQUISITES:
C.COD COURSE NAME DESCRIPTION SE
E M
Software Engineering
Object Oriented Modelling and
Design
COURSE OBJECTIVES:
1 To challenge the students to come up with intellectual and innovative abilities.
2 To give the students an opportunity to synthesize and apply the knowledge and analytical skills
learned in the different disciplines.
COURSE OUTCOMES:
SN DESCRIPTION
O
1 Graduates will be able to identify and define problems in the area of Computer science
2 Graduates will be able to explain and illustrate their practical skills needed to understand
and modify problems related to programming and designing.
3 Graduates will get a chance to apply current technologies , create systems and solve
problems
4 Graduates will get opportunities to practice as teams on multidisciplinary projects with
effective writing and communication skills.
CO-PO AND CO-PSO MAPPING
Department of Information Technology Page 118
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PO PSO PSO PSO
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 1 2 3
C710.1 2 3 - - _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 3 _
C710.2 3 - _ _ _ _ _ _ _ _ 3 _
C710.3 2 - 3 3 _ _ _ _ _ _ 3 3 2
C710.4 _ - _ _ _ 3 3 2 _
JUSTIFATIONS FOR CO-PO MAPPING
Mapping LOW/MEDIUM/H Justification
IGH
C710.1-PO1 M As they could just apply the knowledge to identify different
types of problems
C710.1-PO2 H Students could define the problem through detailed
literature survey
C710.1-PSO1 H Through literature survey they understand the current state
of the art
C710.2-PO3 H Students will be able to understand the design and working
of various existing systems
C710.2- PSO1 H Understand the implementation level details of various
methods to solve a problem
C710.3-PO1 M Students will be able to classify different types of methods to
solve a problem
C710.3- PO5 H As they will be able to carry out experiments and analyse
their results
C710.3 - PO6 H As they could develop multi disciplinary projects which
benefits society
C710.3-PSO1 H As could understand the latest technologies available
C710.3-PSO2 H Students acquire competency in modifying existing methods
to solve problems
C710.3-PS03 M Students develop products which help society.
C710.4-P09 H Students do project in teams and this help them to develop as
an individual and as a member of the team
C710.4-P10 H Students make technical reports and presentations which
improve their communication enability to their society.
C710.4-P11 M Students apply their knowledge in engineering and
management to develop multidisciplinary products .
Department of Information Technology Page 119
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
DELIVERY/INSTRUCTIONAL METHODOLOGIES:
CHALK & TALK STUD. WEB RESOURCES
ASSIGNMENT
LCD/SMART STUD. SEMINARS ADD-ON COURSES
BOARDS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-DIRECT
ASSIGNMENTS STUD. SEMINARS TESTS/MODEL UNIV.
EXAMS EXAMINATION
STUD. LAB STUD. VIVA MINI/MAJOR CERTIFICATIONS
PRACTICES PROJECTS
ADD-ON COURSES OTHERS
ASSESSMENT METHODOLOGIES-INDIRECT
ASSESSMENT OF COURSE OUTCOMES (BY STUDENT FEEDBACK ON FACULTY
FEEDBACK)
ASSESSMENT OF MINI/MAJOR PROJECTS BY OTHERS
EXT. EXPERTS
Prepared by Approved by
Divya James
Binu A
(HOD)
IT 010 710 MAIN PROJECT DESIGN SCHEDULE
Sl. No. Date Activity
1 23rd August Topic Finalization
2 30th September Project Proposal
3 7th October Draft copy of preliminary report
4 14-17 October Preliminary Presentation to project guide/co-guide
and submission of preliminary report
5 28th October Draft design report and ppt
6 31st October Design Presentation
Department of Information Technology Page 120
Rajagiri School Of Engineering & Technology
Department of Information Technology Page 121
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- TOGAF Demystified: Course DeliveryDocument4 paginiTOGAF Demystified: Course DeliveryRajesh SaxenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Safety A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandFunctional Safety A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labview Intermediate I: Successful Development Practices Course ManualDocument440 paginiLabview Intermediate I: Successful Development Practices Course Manualtapas24Încă nu există evaluări
- Automotive Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandAutomotive Quality Management Systems A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Systems Engineering - Systems and System Life CycleDocument21 pagini01 Systems Engineering - Systems and System Life CycleClara Fransisca SitorusÎncă nu există evaluări
- DFX Design For X A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionDe la EverandDFX Design For X A Complete Guide - 2020 EditionÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO#SAE 21434 2021 (E) - Character PDF DocumentDocument7 paginiISO#SAE 21434 2021 (E) - Character PDF Documentlepasmi42Încă nu există evaluări
- Certkitiec SLDV CDT PDFDocument15 paginiCertkitiec SLDV CDT PDFÍcaro VianaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nissan's Quality Management2Document12 paginiNissan's Quality Management2Ehsan ArbabtaftiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridging The Gap Between Operational Technology and Information TechnologyDocument8 paginiBridging The Gap Between Operational Technology and Information TechnologymauriziolapucaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Application of AR + VR + MR in Automobile Industry: Group 7Document8 paginiApplication of AR + VR + MR in Automobile Industry: Group 7Janesha KhandelwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nissan Green Purchasing Guideline eDocument29 paginiNissan Green Purchasing Guideline eErick HernándezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adient Agile Global TrainingDocument179 paginiAdient Agile Global Trainingmayank dubeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso Iec Ieee 26514-2022Document76 paginiIso Iec Ieee 26514-2022Hani YilmazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applications of ROBOTS in The Automobile IndustryDocument24 paginiApplications of ROBOTS in The Automobile Industryhey_panks100% (6)
- VDA 4530 Disposable Small Load CarrierDocument32 paginiVDA 4530 Disposable Small Load CarrierEd RiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Quality Target Study Plan (PQTSP) : Key Point(s)Document1 paginăProduct Quality Target Study Plan (PQTSP) : Key Point(s)nicuÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Warm Welcome From SVKM S NmimsDocument180 paginiA Warm Welcome From SVKM S NmimsJapjiv SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- IEC Certification Kit: Simulink Test ™ Conformance Demonstration TemplateDocument16 paginiIEC Certification Kit: Simulink Test ™ Conformance Demonstration TemplateJanos KovacsÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAXXI 6 Sales Presentation 04-2016Document33 paginiMAXXI 6 Sales Presentation 04-2016Marty SchreckÎncă nu există evaluări
- International Standard: Respiratory Protective Devices - Selection, Use and Maintenance - Fit-Testing ProceduresDocument36 paginiInternational Standard: Respiratory Protective Devices - Selection, Use and Maintenance - Fit-Testing Procedures王惟申Încă nu există evaluări
- Iso TR 27877-2021Document34 paginiIso TR 27877-2021Jenny IrisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ieee 7-4.3.2 - 2003Document58 paginiIeee 7-4.3.2 - 2003Talha Altaf100% (1)
- FISCO BCOS GuidebookDocument24 paginiFISCO BCOS GuidebookandyhÎncă nu există evaluări
- LabVIEW Basics I SlidesDocument57 paginiLabVIEW Basics I SlidesnjainitmÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02a ASpice-Intro VDAGuidelinesDocument17 pagini02a ASpice-Intro VDAGuidelinesevan leeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A02503 Control SystemsDocument4 pagini9A02503 Control SystemssivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audit Plan 审核计划: To be completed by theDocument3 paginiAudit Plan 审核计划: To be completed by thegeorge liuÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACEA Pocket Guide 2018-2019Document76 paginiACEA Pocket Guide 2018-2019dkftt4075Încă nu există evaluări
- Meenakshi Molding Private Limited Process FMEA: O C C U RDocument4 paginiMeenakshi Molding Private Limited Process FMEA: O C C U Rilaya raja100% (1)
- Project Management: Group V Bsa-1ADocument38 paginiProject Management: Group V Bsa-1AAngela Lei SanJuan BucadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Component Shelf Life 8a GEDocument35 paginiComponent Shelf Life 8a GEpapplionÎncă nu există evaluări
- 915 Trust in AI Systems Oct 25 2022Document27 pagini915 Trust in AI Systems Oct 25 2022multi mediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Digital Twin Manufacturing FrameworksDocument12 paginiAssessment of Digital Twin Manufacturing Frameworksazaz 01Încă nu există evaluări
- Functional Point Estimation MethodsDocument14 paginiFunctional Point Estimation MethodsShalaka KulkarniÎncă nu există evaluări
- International StandardDocument20 paginiInternational StandardAdriano TittaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Core and Support Processes-2Document1 paginăCore and Support Processes-2pnagarajjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso Iec Ieee 12207 2 2020Document15 paginiIso Iec Ieee 12207 2 2020Muhammad Nouman AwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 15ford - Ilan Weitzer - PLM Interop at FordDocument26 pagini15ford - Ilan Weitzer - PLM Interop at FordJason RogersÎncă nu există evaluări
- 36-Pmp Toolkit Complete Final 14 Aug 2014 2Document181 pagini36-Pmp Toolkit Complete Final 14 Aug 2014 2JoeYeshitellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- DAVSC Lesson05 KeyRoles PDFDocument12 paginiDAVSC Lesson05 KeyRoles PDFshivanand7r7koppalkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 22400 1 2014Document11 paginiIso 22400 1 2014zhide wangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical: Iso/Iec TR 29110-1Document34 paginiTechnical: Iso/Iec TR 29110-1佐藤フリスティタニアÎncă nu există evaluări
- 03 Power BI TutorialDocument23 pagini03 Power BI TutorialSagar SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vision: VDA Infosolutions Private LimitedDocument18 paginiVision: VDA Infosolutions Private LimitedsudhakaremcÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO 9001-2008-2015 Correlation Matrix v2Document4 paginiISO 9001-2008-2015 Correlation Matrix v2GiovanniÎncă nu există evaluări
- FCS PE07 WI SAP Production DeclarationsDocument14 paginiFCS PE07 WI SAP Production DeclarationsJesus PadronÎncă nu există evaluări
- HUB Center SteeringDocument64 paginiHUB Center SteeringMukesh ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ISO 9000:2005, Quality Management Systems Fundamentals and VocabularyDocument14 paginiISO 9000:2005, Quality Management Systems Fundamentals and VocabularyMohammad AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dietz Consultants Parameter DiagramDocument15 paginiDietz Consultants Parameter DiagramisolongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Day4 English 2017 0509Document35 paginiDay4 English 2017 0509pradhan1987Încă nu există evaluări
- Iso 4358-2023Document34 paginiIso 4358-20237620383tlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rimac Automobili Cybersecurity EngDocument1 paginăRimac Automobili Cybersecurity EngudbarryÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 05 Talk in The Royal Park - ASPICE 3.0 Method ParkDocument63 pagini2016 05 Talk in The Royal Park - ASPICE 3.0 Method Parkbnd1uÎncă nu există evaluări
- Is 1363 - 1 2002Document13 paginiIs 1363 - 1 2002Sourav HaitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theme: (For Failure Modes Causes)Document24 paginiTheme: (For Failure Modes Causes)Vivekanandan THANGARAJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 1 Introduction 2020Document39 paginiLecture 1 Introduction 2020manishÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Basedq1 Manufacturing Site Assessment Application: June 2020Document19 paginiWeb Basedq1 Manufacturing Site Assessment Application: June 2020Ernesto PadillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- FMEA TablesDocument7 paginiFMEA TablesMohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- DCS Unit 6 MCQs PDFDocument146 paginiDCS Unit 6 MCQs PDFSwapnil ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alan Mathison Turing Born: 23 June 1912Document1 paginăAlan Mathison Turing Born: 23 June 1912Swapnil ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter One: Introductory ConceptsDocument22 paginiChapter One: Introductory ConceptsSwapnil ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sppu Be Computer 2015 StqaDocument2 paginiSppu Be Computer 2015 StqaSwapnil Shinde0% (1)
- SMD (Nov-Dec 2016) (2012 Pattern)Document3 paginiSMD (Nov-Dec 2016) (2012 Pattern)Swapnil ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 4 AssignmentDocument1 paginăUnit 4 AssignmentSwapnil ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- List of AssignmentsDocument2 paginiList of AssignmentsSwapnil ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 3 AssignmentDocument1 paginăUnit 3 AssignmentSwapnil ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 AssignmentDocument2 paginiUnit 1 AssignmentSwapnil ShindeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standards Booklet For Igsce Sociology (0495)Document64 paginiStandards Booklet For Igsce Sociology (0495)Ingrit AgustinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat TransgerDocument56 paginiHeat TransgerShusha Shomali67% (3)
- Jurnal PEMELIHARAAN IKAN BAUNG (Hemibagrus Nemurus) DENGAN Padat Tebar Yang Berbeda Pada Sistem Budidaya BosterDocument14 paginiJurnal PEMELIHARAAN IKAN BAUNG (Hemibagrus Nemurus) DENGAN Padat Tebar Yang Berbeda Pada Sistem Budidaya Bosterdesi sukmawatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degree of Crystallinity of Well-Known Polymers (I.e., Nylon 6,6, LDPE, and HDPE) UsingDocument12 paginiDegree of Crystallinity of Well-Known Polymers (I.e., Nylon 6,6, LDPE, and HDPE) Usingselva_raj215414Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 3 Fold Mountains Task SheetDocument2 paginiLesson 3 Fold Mountains Task Sheetapi-354360237Încă nu există evaluări
- High Speed Design Techniques PDFDocument416 paginiHigh Speed Design Techniques PDFbolermÎncă nu există evaluări
- 7 HabitsDocument8 pagini7 HabitssaliimjÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ridpath History of The United StatesDocument437 paginiRidpath History of The United StatesJohn StrohlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capstone Project 2019 - Overview and Outline - Near Final 19 - 7Document15 paginiCapstone Project 2019 - Overview and Outline - Near Final 19 - 7Rowena ZhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibm Lombardi BPM 8.5 VDocument3 paginiIbm Lombardi BPM 8.5 VVirtualNuggets VNÎncă nu există evaluări
- Autonomy and Antiart - Stewart MartinDocument3 paginiAutonomy and Antiart - Stewart MartinBruna DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 IntroductionDocument26 pagini01 IntroductionDaniel CrashOverride ShaferÎncă nu există evaluări
- Field Work No. 1 Laying of Simple Curve by Transit and Tape: Mapúa Institute of TechnologyDocument4 paginiField Work No. 1 Laying of Simple Curve by Transit and Tape: Mapúa Institute of TechnologyEliminated ProÎncă nu există evaluări
- LANDASANDocument101 paginiLANDASANdewi yuliantiÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCERT Solutions For Class 12 English Flamingo Chapter 8Document3 paginiNCERT Solutions For Class 12 English Flamingo Chapter 8AKASH KUMARÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noun in English Grammar With Examples With PDFDocument9 paginiNoun in English Grammar With Examples With PDFhemisphereph2981Încă nu există evaluări
- Data Migration To HadoopDocument26 paginiData Migration To Hadoopkrishna100% (2)
- MCQ TEST For Mba 1st Year StudentDocument10 paginiMCQ TEST For Mba 1st Year StudentGirish ChouguleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Memory Aid Philo of LawDocument5 paginiMemory Aid Philo of LawMichelangelo Tiu100% (4)
- Theatre at HierapolisDocument7 paginiTheatre at HierapolisrabolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bise Bahawalpur SSC Result GazetteDocument1.081 paginiBise Bahawalpur SSC Result GazetteMuhammad Sohail Rao100% (2)
- ODI Case Study Financial Data Model TransformationDocument40 paginiODI Case Study Financial Data Model TransformationAmit Sharma100% (1)
- "Castration", The HIV Scandal and The Japanese Bureaucracy MASAO MIYAMOTO, M.D.Document21 pagini"Castration", The HIV Scandal and The Japanese Bureaucracy MASAO MIYAMOTO, M.D.WB7Încă nu există evaluări
- Cot Angel Eng 3Document3 paginiCot Angel Eng 3Arjay GarboÎncă nu există evaluări
- CS Lewis - The Discarded ImageDocument4 paginiCS Lewis - The Discarded Imagejscavani100% (2)
- PFI ES-27-1994 - Visual Examination - The Purpose, Meaning and Limitation of The TermDocument4 paginiPFI ES-27-1994 - Visual Examination - The Purpose, Meaning and Limitation of The TermThao NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Eight Types of Interview QuestionsDocument2 paginiThe Eight Types of Interview QuestionsKayla Camille A. Miguel100% (1)
- Van GenuchtenDocument21 paginiVan GenuchtenrshaghayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Metodologi of NIEDocument21 paginiMetodologi of NIEStevanus Gabriel PierreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample QuestionsDocument6 paginiSample QuestionsKrisleen AbrenicaÎncă nu există evaluări