Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Unit Ii
Încărcat de
Debendra Dev KhanalTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Unit Ii
Încărcat de
Debendra Dev KhanalDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
QUESTION BANK 2016
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR
Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583
QUESTION BANK (DESCRIPTIVE)
Subject with Code : SA-II (13A01505) Course & Branch: B.Tech CE
Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & I-Sem Regulation: R13
UNIT II
SLOPE DEFLECION AND MOMENT DISTRIBUTION METHOD
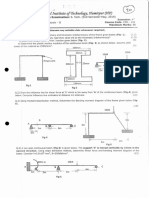
1.A single bay single storey portal frame ABCD is fixed at A and D. AB and DC are the columns
and columns BC is the beam. The height of the column AB is 6 m and that of DC is 7 m.
Span of the beam BC is 10 m. A uniformly distributed load of 60 kN/m is acting on the span BC.
All members have the same flexural rigidity. Calculate the support reactions and draw the
bending moment diagram for the portal frame. Use slope deflection method. 10M
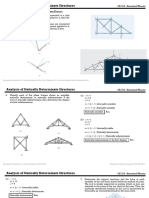
2. Analyse a frame shown in figure below by Slope deflection method & draw bending moment
diagram. Flexural Rigidity (EI) is same for all members 10M
3. Analyse a frame shown in figure below by Slope deflection method. 10M
Structural Analysis-II Page 1
QUESTION BANK 2016
4. Analyse a frame shown in figure below by Slope deflection method. 10M
5. Analyse the frame as shown in figure below by moment distribution method. 10M
6. A single bay single storey portal frame ABCD is fixed at A and hinged at D. AB and DC are
the two columns and BC is the beam. The two columns are of equal height and the height is
5.5m. The span of the beam BC is 6.5m. A uniformly distributed load of 58kN/m is acting on
the whole span BC. All members have the same flexural rigidity. Calculate the support reactions
and also draw the bending moment diagram for the portal frame. Use moment distribution
method. 10M
7. Analyse the continuous beam as shown in fig using moment distribution method and draw
BMD. Take EI = constant. 10M
8. Determine the end moments of member of frame in figure below by moment distribution method.
EI is constant for all members. 10M
Structural Analysis-II Page 2
QUESTION BANK 2016
9. Analyse the continuous beam as shown in figure below, using moment distribution Method. Draw
shear force and bending moment diagram for the continuous beam. 10M
10.
a) what are assumptions made in slope-deflection method 2M
b) Define carry over moment and distribution factor 2M
c) What are the quantities in terms of which the unknown moments are expressed in slope-
deflection method? 2M
d) How do you account for sway in slope deflection method for portal frames? 2M
e) What are the situations where in sway will occur in portal frames? 2M
Structural Analysis-II Page 3
QUESTION BANK 2016
SIDDHARTH GROUP OF INSTITUTIONS :: PUTTUR
Siddharth Nagar, Narayanavanam Road 517583
QUESTION BANK (OBJECTIVE)
Subject with Code : SA-II (13A01505) Course & Branch: B.Tech CE
Year & Sem: III-B.Tech & I-Sem Regulation: R13
UNIT II
SLOPE DEFLECION AND MOMENT DISTRIBUTION METHOD
1. The number of independent equations to be satisfied for static equilibrium of a plane structure
is [ ]
A) 1 B) 2 C) 3 D) 6
2. In moment distribution method, the sum of distribution factors of all the members meeting at
any joint is always [ ]
A) Zero B) less than 1 C) 1 D) greater than 1
3. The carryover factor in a prismatic member whose far end is fixed is [ ]
A) 0 B) C) D) 1
4. In the slope deflection equations, the deformations are considered to be caused by [ ]
i. Bending moment
ii. Shear force
iii. Axial force
The correct answer is
A) only (i) B) (i) and (ii) C) (ii) and (iii) D) (i), (ii) and (iii)
5. The fixed end moment for continuous beam subjected to UDL [ ]
A) B) C) D)
6. The fixed end moment for continuous beam subjected to central point load [ ]
Structural Analysis-II Page 4
QUESTION BANK 2016
A) B) C) D)
7. The fixed end moment for continuous beam subjected to eccentrically point load [ ]
A) B) C) D)
8. Slope deflection equation MAB = [ ]
A) FAB+ B) FAB -
C) FBA+ D) FBA+
9. A continuous beam AB subjected to UDL of 20 kN/m then fixed end moment FAB is
[ ]
A) 40 kN-m B) 120 kN-m C) 60 kN-m D) 180 kN-m
10. A continuous beam AB subjected to central point load of 60 kN then fixed end moment FAB is
[ ]
A) 40 kN-m B) 45 kN-m C) 60 kN-m D) 80 kN-m
11. Frames may sway due to [ ]
A) Horizontal force & unsymmetry B) horizontal force only
C) unsymmetry of columns D) all the above
12. A beam subjected to UDL then bending moment diagram is in ________ shape [ ]
A) Triangle B) rectangle C) parabola D) cubic
13. A beam subjected to point then bending moment diagram is in ________ shape [ ]
A) Triangle B) rectangle C) parabola D) cubic
14. A beam subjected to UVL then bending moment diagram is in ________ shape [ ]
A) Triangle B) rectangle C) parabola D) cubic
15. The develop method for slope deflection method is [ ]
A) Flexibility method B) kanis method
C) Stiffness matrix method D) moment distribution method
16. Carry over factor = [ ]
A) B) C) D)
Structural Analysis-II Page 5
QUESTION BANK 2016
17. Stiffness K= [ ]
A) B) C) D)
18. Distribution factor = [ ]
A) B) C) D)
19. If the far end is fixed then stiffness K= [ ]
A) B) C) D)
20. Which of the following methods of structural analysis is a displacement method [ ]
A) moment distribution method B) column analogy method
C) three moment equation D) none of the above
21. In the displacement method of structural analysis, the basic unknowns are [ ]
A) displacements B) force
C) displacements and forces D) none of the above
22. In the slope deflection equations, the deformations are considered to be caused by: [ ]
i) B.M. ii) S.F. iii) axial force
The correct answer is:
A) Only I B)i and ii C) ii and iii D)all three
23. Bending moment at any section in a conjugate beam gives in the actual beam: [ ]
A) Slope B) curvature C) deflection D) B.M.
24. The statically indeterminate structures can be solved by: [ ]
A) Using equations of statics alone B) Equations of compatibility alone
C) Ignoring all deformations and assuming the structure is rigid
C) Using the equations of statics and necessary number of equations of compatibility
25. A beam is completely analysed, [ ]
A) Support reactions are determined B)Shear and moment diagrams are found
C) The moment of inertia is uniform throughout the length
D) All of the above
26. A bending moment may be defined as [ ]
Structural Analysis-II Page 6
QUESTION BANK 2016
A) Arithmetic sum of the moments of all the forces on either side of section
B) Arithmetic sum of the forces on either side of section
C) Algebraic sum of the moments of all the forces on either side of section
D) None of these
27. At either end of a plane frame, maximum number of possible transverse shear forces, are
[ ]
A) One B) two C) three D) four
28. At either end of a plane frame, maximum numbers of possible bending moments are
[ ]
A) One B) two C) three D) zero
29.A simply supported beam of span L carries a uniformly distributed load W. The maximum
bending moment M is [ ]
A) B) C) D)
30. A simply supported beam of span L carries a concentrated load W at its mid span. The maximum
bending moment M is [ ]
A) B) C) D)
31. A simply supported beam carries two equal concentrated loads W at distances L/3 from either
support. The maximum bending moment M is [ ]
A) B) C) D)
32.For a simply supported beam with a central load, the bending moment is [ ]
A) Least at the centre B) Least at the supports C) maximum at the supports
D) Maximum at the centre
33. The simultaneous equations of slope deflection method can be solved by iteration in: [ ]
A) Moment distribution method B) Consistent deformation method
C) Conjugate beam method D)Williot mohr method
34. The carryover factor in a prismatic member whose far end is hinged is: [ ]
A) 0 B) 1/2 C) 3/4 D) 1
Structural Analysis-II Page 7
QUESTION BANK 2016
35.The moment required to rotate the near end of a prismatic beam through a unit angle without translation,
the far end being simply supported, is given by [ ]
A)3EI/L B) 4EI/L C)2EI/L D)EI/L
Where EI is flexural rigidity and L is the span of the beam.
36.The moment required to rotate the near end of a prismatic beam through a unit angle without translation,
the far end being fixed, is given by [ ]
A)EI/L B) 2EI/L C) 3EI/L D)4EI/L
Where EI is flexural rigidity and L is the span of the beam.
37. If M is the external moment which rotates the near end of a prismatic beam without translation (the far
end being fixed), then the moment induced at the far end is [ ]
A) M/2 in the same direction as M B) M/2 in the opposite direction as M
C) M in opposite direction D) 0
38.If one end of a prismatic beam AB with fixed ends is given a transverse displacement without any
rotation, then the transverse reactions at A or B due to displacement is: [ ]
A) 6EI/l2 B) 6EI/l3 C) 12EI/l2 D) 12EI/l3
39. Moment-distribution method was suggested by [ ]
A) Hardy Cross B) G.A. Maney C) Gasper Kani D) None of these
40.In slope deflection method, the unknown rotations at various joints are determined by considering
[ ]
a) The equilibrium of the joint
b) The rigidity of the joint
c) The equilibrium of the structure
d) None
Prepared by: J.K.Elumalai.
Structural Analysis-II Page 8
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Unit Iii PDFDocument7 paginiUnit Iii PDFShashank100% (1)
- Sa-2 Kani's Method ObjDocument7 paginiSa-2 Kani's Method Objnirmalraj100% (2)
- Unit Iv PDFDocument7 paginiUnit Iv PDFGanesh Natarajan S100% (1)
- Model Examination: Adhiparasakthi College of EngineeringDocument2 paginiModel Examination: Adhiparasakthi College of EngineeringrishinathnehruÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECT-3354-ANALYSIS-OF-STRUCTUREs Quiz 1Document3 paginiECT-3354-ANALYSIS-OF-STRUCTUREs Quiz 1Levis MithamoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ect 3354 Analysis of Structures IvDocument4 paginiEct 3354 Analysis of Structures IvLevis MithamoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 May CE303-E - Ktu QbankDocument3 pagini2019 May CE303-E - Ktu QbankYasmine SahilÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE303 Structural Analysis II 2018 May Supply 2004031418Document3 paginiCE303 Structural Analysis II 2018 May Supply 2004031418lakshmi dileepÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Analysis IIIDocument3 paginiStructural Analysis IIIAmrita DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- SA 2all PDFDocument13 paginiSA 2all PDFHrishikesh BhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 April CE303-C - Ktu QbankDocument3 pagini2018 April CE303-C - Ktu QbankYasmine SahilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Structural AnalysisDocument22 paginiAdvanced Structural AnalysisVarun. hrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final - 20162017 - Sem 1 - AnswersDocument37 paginiFinal - 20162017 - Sem 1 - AnswersAriffadilah IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Analysis 2 AssignmentDocument3 paginiStructural Analysis 2 AssignmentMuhangi ChristopherÎncă nu există evaluări
- May 12 L3 Proposed Exam Paper UBGLFP-20-3Document9 paginiMay 12 L3 Proposed Exam Paper UBGLFP-20-3malith kmlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Model Examination: Adhiparasakthi College of EngineeringDocument2 paginiModel Examination: Adhiparasakthi College of EngineeringrishinathnehruÎncă nu există evaluări
- End Sem 2019 Determinate StructureDocument2 paginiEnd Sem 2019 Determinate Structuretenzinlhamo.199Încă nu există evaluări
- Assignment SFD and BMD 2020Document3 paginiAssignment SFD and BMD 2020Jarul ZahariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final - 20102011 - Sem 1 - QuestionDocument9 paginiFinal - 20102011 - Sem 1 - QuestionAriffadilah IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOS I Schem Model Answer PaperDocument6 paginiTOS I Schem Model Answer Paperirshadmirza753Încă nu există evaluări
- Sa1 FrameDocument51 paginiSa1 FrameetanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 - Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramDocument8 pagini04 - Shear Force and Bending Moment DiagramsamÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTCVC503 - Sm-Ii Q PaperDocument2 paginiBTCVC503 - Sm-Ii Q Paperस्नेहल पिंपळे शेळकेÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solved Problems - Slope Deflection Method - Structural AnalysisDocument15 paginiSolved Problems - Slope Deflection Method - Structural Analysiskarthi0% (1)
- 16ce117 Sa-IDocument24 pagini16ce117 Sa-INishal CalebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ce6501 Sa1 Civil VST Au Unit IVDocument22 paginiCe6501 Sa1 Civil VST Au Unit IVarjunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deflection 3Document6 paginiDeflection 3programmingprofessor01Încă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument4 paginiGujarat Technological UniversitySandeep SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- R5310105-Structural Analysis - IIDocument4 paginiR5310105-Structural Analysis - IIsivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Tech. EXAMINATION, 2021: Roll No. .......................... Total Pages: 05Document3 paginiB.Tech. EXAMINATION, 2021: Roll No. .......................... Total Pages: 05Tanishq RongtaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compulsory. Sl. No. Questions Marks Co PoDocument1 paginăCompulsory. Sl. No. Questions Marks Co PoAll_regÎncă nu există evaluări
- rr320102 Structural Analysis IIDocument9 paginirr320102 Structural Analysis IISRINIVASA RAO GANTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structures E2 2018-2019 GivenDocument10 paginiStructures E2 2018-2019 GivenSarah HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Examination SEMESTER II, SESSION 2021/2022: Instruction To CandidatesDocument6 paginiFinal Examination SEMESTER II, SESSION 2021/2022: Instruction To CandidatesThiva RajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fixed and Continuous BeamsDocument30 paginiFixed and Continuous BeamsSatinder Kaur Khatra - Civil Engg.Încă nu există evaluări
- Çalışma SorularıDocument161 paginiÇalışma SorularıSude FilizÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument2 paginiGujarat Technological Universityfeyayel988Încă nu există evaluări
- Sardar Patel College of Engineering: Fejk °Document22 paginiSardar Patel College of Engineering: Fejk °Sudhir DeoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Sc. Eng. Honours Degree: Sri Lanka Institute of Information TechnologyDocument6 paginiB.Sc. Eng. Honours Degree: Sri Lanka Institute of Information TechnologyramÎncă nu există evaluări
- Answer All Questions.: Pages: 2Document2 paginiAnswer All Questions.: Pages: 2Alen ShajiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ES201 Theory of Structures - III QPDocument2 paginiES201 Theory of Structures - III QPnaima jaleel100% (1)
- Gujarat Technological UniversityDocument3 paginiGujarat Technological UniversityDeep PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Applied MechanicsDocument5 paginiApplied MechanicscivildepartmentofritzcollegeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2019 May CE202-EDocument3 pagini2019 May CE202-ELiya WilsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- 16BDocument13 pagini16BBrynn AlexanderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Structural AnalysisDocument9 paginiAdvanced Structural AnalysisYeswanth RaghavendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- MAKEUPDocument3 paginiMAKEUPRambo 420Încă nu există evaluări
- WWW Manaresults Co inDocument8 paginiWWW Manaresults Co inPavaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Universiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Final Examination (Online) Semester Ii SESSION 2019/2020Document7 paginiUniversiti Tun Hussein Onn Malaysia Final Examination (Online) Semester Ii SESSION 2019/2020Jausyan BaqiriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shear Force and Bendind MomentDocument8 paginiShear Force and Bendind MomentAshish AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- AaaaaaDocument4 paginiAaaaaaRaffal NejimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anna University Exams Nov/Dec 2016 - Regulation 2013 CE6501 Structural Analysis I Unit-I-Indeterminate Frames Part - BDocument6 paginiAnna University Exams Nov/Dec 2016 - Regulation 2013 CE6501 Structural Analysis I Unit-I-Indeterminate Frames Part - BA.s. MahasreerajhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1000 Structural Analysis MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - SanfoundryDocument18 pagini1000 Structural Analysis MCQ (Multiple Choice Questions) - SanfoundryfybellascrapmenseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Analysis-I FINALDocument3 paginiStructural Analysis-I FINALIrfan MunirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test 2 SEMESTER II, SESSION 2020/2021Document3 paginiTest 2 SEMESTER II, SESSION 2020/2021Ruhan PeriyannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Survey 16CE105Document6 paginiSurvey 16CE105SUDHARSAN RAO SÎncă nu există evaluări
- B G1032 Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksDocument3 paginiB G1032 Pages: 3: Answer Any Two Full Questions, Each Carries 15 MarksirshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological University: Subject Code:140603 Date: Subject Name: Structural Analysis-II Time: Total Marks: 70Document2 paginiGujarat Technological University: Subject Code:140603 Date: Subject Name: Structural Analysis-II Time: Total Marks: 70Preeti VarmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 1Evaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (4)
- 2060 Chautho SanskaranDocument123 pagini2060 Chautho SanskaranDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Act 2055 1998 EnglishDocument12 paginiBuilding Act 2055 1998 EnglishSandip BudhathokiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DPU Mattingly Nepal Spatial PlanningDocument36 paginiDPU Mattingly Nepal Spatial PlanningDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanabazar 2061Document311 paginiSanabazar 2061Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proposed Operational Guidelines in NepaliDocument34 paginiProposed Operational Guidelines in NepaliDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jibgar JoshiDocument49 paginiJibgar JoshiDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kathmandu Upatyaka Bikash Pradhikaran Ain, 2045Document17 paginiKathmandu Upatyaka Bikash Pradhikaran Ain, 2045Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- K - FRLG:DF/S +/If0F Lgodfjnl, @) $ K - FRLG:DF/S +/If0F Lgodfjnl, @) $ K - FRLG:DF/S +/If0F Lgodfjnl, @) $ K - FRLG:DF/S +/If0F Lgodfjnl, @) $Document20 paginiK - FRLG:DF/S +/If0F Lgodfjnl, @) $ K - FRLG:DF/S +/If0F Lgodfjnl, @) $ K - FRLG:DF/S +/If0F Lgodfjnl, @) $ K - FRLG:DF/S +/If0F Lgodfjnl, @) $Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vatabaran SamrakshanDocument9 paginiVatabaran SamrakshanThakur YogendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sanyukta Aabasko SwamitwaDocument11 paginiSanyukta Aabasko SwamitwaDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NBC206Document9 paginiNBC206Sujan SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nepali NaPa Kartik 16Document53 paginiNepali NaPa Kartik 16Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- G) KFNDF +o'qm CFJF SF) Cj:yf: ! K ( (I7e"ldDocument57 paginiG) KFNDF +o'qm CFJF SF) Cj:yf: ! K ( (I7e"ldDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- नेपालको जनगणना - २०६८Document270 paginiनेपालको जनगणना - २०६८Manoj PaudelÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2060 Chautho SanskaranDocument123 pagini2060 Chautho SanskaranDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nepal Road Standard 2070Document55 paginiNepal Road Standard 2070surendra_pangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Environment Protection Rules, 2054Document57 paginiEnvironment Protection Rules, 2054Karki2Încă nu există evaluări
- Ir2545 2535 2530 2525 2520 SYSTEM en Uv 1 PDFDocument314 paginiIr2545 2535 2530 2525 2520 SYSTEM en Uv 1 PDFvozhdÎncă nu există evaluări
- National PolicyDocument13 paginiNational PolicyDipak BudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Punar Samrachana Lekha Adhikrit10012018131935Document6 paginiPunar Samrachana Lekha Adhikrit10012018131935Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lekha Adhikrit10012018131232Document13 paginiLekha Adhikrit10012018131232Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ir2545i COPY en GB R PDFDocument114 paginiIr2545i COPY en GB R PDFขวัญชัย งามสง่าÎncă nu există evaluări
- LT TL: Ffiffi TDocument3 paginiLT TL: Ffiffi TDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lekhapal 10012018131823Document11 paginiLekhapal 10012018131823Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fajil Lekhapal10012018132031Document2 paginiFajil Lekhapal10012018132031Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saha Lekhapal10012018132138Document1 paginăSaha Lekhapal10012018132138Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nepal Geography Part 2Document11 paginiNepal Geography Part 2Debendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hands Out of Planets Na SuDocument6 paginiHands Out of Planets Na SuDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NASU SyllabusDocument5 paginiNASU SyllabusDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sarwajanik Sewa PrawahaDocument6 paginiSarwajanik Sewa PrawahaDebendra Dev KhanalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Analysis of Indeteminate StructuresDocument11 paginiAnalysis of Indeteminate StructuresAbbasabbasiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Member Design For Combined StressesDocument7 paginiMember Design For Combined StressesNyu123456100% (1)
- STRUCTURAL ANALYSIS IN EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING - A BREAKTHROUGH OF SIMPLIFIED NON-LINEAR METHODS FajfarDocument20 paginiSTRUCTURAL ANALYSIS IN EARTHQUAKE ENGINEERING - A BREAKTHROUGH OF SIMPLIFIED NON-LINEAR METHODS FajfarBeenah Sheila Khushiram50% (2)
- Introduction To Modeling-Dr TemsahDocument50 paginiIntroduction To Modeling-Dr TemsahAyman Trad100% (7)
- Euler Bernoulli and First Order Shear Deformation TheoryDocument44 paginiEuler Bernoulli and First Order Shear Deformation TheoryRahul DhakerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subsea Basis of DesignDocument29 paginiSubsea Basis of DesignShah Alam100% (1)
- Home CAD Earthquake Environment Geotechnical Hydraulics Management Structural Analysis Structural Design Tools Transportation Water Cesdb Structural Analysis BeamanalDocument29 paginiHome CAD Earthquake Environment Geotechnical Hydraulics Management Structural Analysis Structural Design Tools Transportation Water Cesdb Structural Analysis BeamanalVitor SVÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation - Cainta 2 Storey Building - RetrofittingDocument58 paginiCalculation - Cainta 2 Storey Building - Retrofittingregino abuzoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Timber Roof Truss To British Code - Solved Example - StructvilleDocument9 paginiDesign of Timber Roof Truss To British Code - Solved Example - StructvilleDeRudy100% (3)
- Training Catalogue: Offshore Strength AssessmentDocument36 paginiTraining Catalogue: Offshore Strength AssessmentRavikumar mahadevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Theory - Part 2b - Illustrative ProblemsDocument14 paginiStructural Theory - Part 2b - Illustrative ProblemsErlinda Olegario MarasiganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Load Capacity Limits For Flanged NozzleDocument6 paginiLoad Capacity Limits For Flanged Nozzlektjayakumar3878100% (1)
- Final Exam SheduleDocument1 paginăFinal Exam SheduleAziesSiMadridistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite-Element Design of Concrete Structures, 2nd RombachDocument372 paginiFinite-Element Design of Concrete Structures, 2nd RombachCristi Andone100% (28)
- Assignment 1Document12 paginiAssignment 1Christ LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verifying Engineering CalculationDocument542 paginiVerifying Engineering CalculationDeana White50% (2)
- Seismic Design Methodology Document For Precast Concrete Diaphragms PDFDocument545 paginiSeismic Design Methodology Document For Precast Concrete Diaphragms PDFDonald HamiltonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Mat Foundations by Ron Klemencic Et Al, NIST GCR 12-917-22, 08-2012.Document33 paginiSeismic Design of Reinforced Concrete Mat Foundations by Ron Klemencic Et Al, NIST GCR 12-917-22, 08-2012.Bob Laughlin, KWØRLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tees (T) Split From UC, Section Properties Dimensions & PropertiesDocument14 paginiTees (T) Split From UC, Section Properties Dimensions & PropertiesSuresh BabuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Displacement MethodDocument3 paginiDisplacement MethodKhen CatayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANSYS Mechanical Tutorials 2019 R2Document148 paginiANSYS Mechanical Tutorials 2019 R2Muzamil BalochÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project ProposalDocument3 paginiProject ProposalMichael Enemona Agamah50% (2)
- 1Document227 pagini1api-3838442Încă nu există evaluări
- Ultimate Guide To Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams - Engineer4Free - The #1 Source For Free Engineering Tutorials PDFDocument4 paginiUltimate Guide To Shear Force and Bending Moment Diagrams - Engineer4Free - The #1 Source For Free Engineering Tutorials PDFSubhajyoti DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- New Text DocumentDocument3 paginiNew Text DocumentrahulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Finite Element Methods: Bauhaus - Universität Weimar Institut Für StrukturmechanikDocument63 paginiAdvanced Finite Element Methods: Bauhaus - Universität Weimar Institut Für StrukturmechanikNayeem HaqueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Slenderness For Longitudinally Stiffened I-Girders Subjected To Patch LoadingDocument15 paginiWeb Slenderness For Longitudinally Stiffened I-Girders Subjected To Patch LoadingGogyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Project: For The Design of The Structure, The Deadload, Live Loads, Seismic and Wind LoadDocument6 paginiIntroduction To The Project: For The Design of The Structure, The Deadload, Live Loads, Seismic and Wind LoadAbdul Razzak0% (1)
- Structural Analysis Ii Structural Analysis Ii: CEL 331 CEL 331Document7 paginiStructural Analysis Ii Structural Analysis Ii: CEL 331 CEL 331KittuÎncă nu există evaluări
- HW5 CIVE210 Structural Analysis Plane Truss SOLUTIONDocument7 paginiHW5 CIVE210 Structural Analysis Plane Truss SOLUTIONNÎncă nu există evaluări