Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
TUTORIAL Rapidly Varied Flow
Încărcat de
fyqahDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TUTORIAL Rapidly Varied Flow
Încărcat de
fyqahDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
TUTORIAL 2: RAPIDLY VARIED FLOW
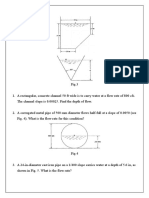
1. A trapezoidal channel with a bottom width of 4 m and side slope of z = 1.5 is carrying
a discharge of 50 m3/s at a depth of 3 m. Determine the following:
a) The alternate depth for the same specific energy
b) The critical depth
c) The uniform flow depth for slope of 0.004 and n = 0.022
2. A 15m wide rectangular channel with channel slope So= 0.0025 and Mannings n = 0.035 is
carrying a discharge of 62 m3/s. Determine the normal depth and the critical depth flow.
Construct the specific energy curve.
3. A 12.5 m rectangular channel carries 32 m3/s at the depth of 2.0 m. Is this flow subcritical or
supercritical? If n = 0.025, what is the critical slope of this channel for this discharge? What
channel slope must be provided to produce a uniform flow at depth of 2.0 m?
4. A long rectangular channel 3 m wide carries a discharge of 15 m3/s. The channel slope is
0.004 and the Mannings coefficient is 0.01. At a certain point in the channel where the flow
reaches the normal depth,
a) Determine the stage of flow. Is it supercritical or subcritical?
b) If a hydraulic jump takes place at this depth, what is the sequent depth at the jump?
c) Estimate the energy head loss through the jump.
5. A rectangular channel 2.0 m wide is contracted to a width of 1.2 m. The uniform flow depth
at a discharge of 3.0 m3/s is 0.8 m.
a) Calculate the surface profile through the contraction, assuming that the profile is
unaffected by the downstream conditions.
b) Determine the maximum throat width such that critical flow in the throat will be
created.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Selected Problems in Physics with AnswersDe la EverandSelected Problems in Physics with AnswersEvaluare: 3 din 5 stele3/5 (2)
- PS3Document2 paginiPS3Syrille Lubigan AlarconÎncă nu există evaluări
- O level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2De la EverandO level Physics Questions And Answer Practice Papers 2Evaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- CvaDocument2 paginiCvaZaid HadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter Eight Flow in Open Channels Practice Problems 1Document15 paginiChapter Eight Flow in Open Channels Practice Problems 1Jerle ParondoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Irrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsDe la EverandIrrigation Works: The Principles on Which Their Design and Working Should Be Based, with Special Details Relating to Indian Canals and Some Proposed ImprovementsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 1Document10 paginiSheet 1lawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 1Document10 paginiSheet 1lawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uce11403 Hydraulics 16 Mark QPDocument8 paginiUce11403 Hydraulics 16 Mark QPkarthickaryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuizDocument4 paginiQuizRajendra Kore100% (1)
- Sheet 1Document10 paginiSheet 1lawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Hydraulic &water Resource Engineering: Open Channel Hydraulics Chapter 1,2 and 3 Work SheetDocument5 paginiDepartment of Hydraulic &water Resource Engineering: Open Channel Hydraulics Chapter 1,2 and 3 Work SheetLemi100% (3)
- Assignment and WorksheetDocument3 paginiAssignment and WorksheetHMAN OROMOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 3 Non-Uniform Flow TutorialDocument2 paginiChapter 3 Non-Uniform Flow TutorialFalahiah JudgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6403 Applied Hydraulic Engineering - QB1 PDFDocument9 paginiCE6403 Applied Hydraulic Engineering - QB1 PDFsankaran sÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment No. 1: Course: Hydraulic Engineering I&D-501 Due Date: 12 March 2021Document2 paginiAssignment No. 1: Course: Hydraulic Engineering I&D-501 Due Date: 12 March 2021Aarish MaqsoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions Related To Open Channel Flow.Document3 paginiQuestions Related To Open Channel Flow.Mohd AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Channel Hydraulics Worksheet 2Document4 paginiOpen Channel Hydraulics Worksheet 2Yasin Mohammad Welasma100% (1)
- HHM HandoutDocument16 paginiHHM HandoutArun ChaitanyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mixed TopicDocument105 paginiMixed TopicSigue Ramel Hinayas50% (2)
- Assignment 2Document2 paginiAssignment 2mustefa kelil100% (1)
- Open Channel ProblemsDocument21 paginiOpen Channel ProblemsMangam Rajkumar100% (4)
- Visit: Civildatas - Blogspot.inDocument9 paginiVisit: Civildatas - Blogspot.insankaran sÎncă nu există evaluări
- 19 1 PDFDocument6 pagini19 1 PDFآكوجويÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6403-Applied Hydraulic EngineeringDocument9 paginiCE6403-Applied Hydraulic EngineeringSivarajSivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sheet 1Document11 paginiSheet 1lawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HydraulicsDocument4 paginiHydraulicsHakdog GieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open TutorialDocument2 paginiOpen Tutorialeph86% (7)
- CVE 372 Exercise Problems - Open Channel FlowDocument7 paginiCVE 372 Exercise Problems - Open Channel FlowDorry Magdy100% (1)
- Compre Hydraulics PSDocument5 paginiCompre Hydraulics PSAlvin Lualhati0% (1)
- Soil & Water Conservation Engineering: Agricultural & Biosystems Engineering Review 2020Document57 paginiSoil & Water Conservation Engineering: Agricultural & Biosystems Engineering Review 2020Jireh Loquinario100% (3)
- HW - Uniform Flow in Rigid Boundary ChannelsDocument2 paginiHW - Uniform Flow in Rigid Boundary ChannelsADELLINNE NATASYA BINTI ROSDI / UPMÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co Based Assisgnmen T OcfDocument6 paginiCo Based Assisgnmen T OcfMohd AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Co Based Assisgnmen T OcfDocument6 paginiCo Based Assisgnmen T OcfMohd AmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceg 503 Lecture 2 Open ChannelsDocument12 paginiCeg 503 Lecture 2 Open Channelsayodejiayinde765Încă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 4 - Open Channel FlowDocument4 paginiTutorial 4 - Open Channel Flowumaluxman kanagasingamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 1Document3 paginiAssignment 1Chanako Dane100% (1)
- Numericals On Specific Energy, Rapidly and Gradually Varied FlowDocument7 paginiNumericals On Specific Energy, Rapidly and Gradually Varied FlowCristiano Omega RalteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Worksheet 327824865examples1Document7 paginiWorksheet 327824865examples1Alfatah muhumedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics Geotech2Document101 paginiHydraulics Geotech2Sigue Ramel HinayasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taller 2 - 2P-2020Document1 paginăTaller 2 - 2P-2020Yoel LobeloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydraulics IIDocument3 paginiHydraulics IIZerihun Ibrahim0% (1)
- Open Channel Hydraulics Ass One 2023 1st SemDocument1 paginăOpen Channel Hydraulics Ass One 2023 1st Semkibrom fishaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9A01304 Fluid MechanicsDocument4 pagini9A01304 Fluid MechanicssivabharathamurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test On Fluid MechanicsDocument11 paginiTest On Fluid MechanicsJonathan GreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 779, Sai Jothi Polytechnic College:, Eliyarpathy, Madurai 22. Department of Civil EngineeringDocument2 pagini779, Sai Jothi Polytechnic College:, Eliyarpathy, Madurai 22. Department of Civil EngineeringRamani RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperDocument15 paginiProblem Set Part 2 Ready To Print CE PaperJeffward Jaguio0% (1)
- Tutorial Problems in Open ChannelsDocument1 paginăTutorial Problems in Open ChannelsTshepho Ketshepha KeisangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems Open Channel FlowDocument3 paginiProblems Open Channel Flow8986103t100% (1)
- Tutorial 2Document1 paginăTutorial 2Haniza SahudiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE 2253 Applied Hydraulic Engineering QUESTION BANKDocument14 paginiCE 2253 Applied Hydraulic Engineering QUESTION BANKDhivya RamachandranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hidraulica de Canales AbiertosDocument3 paginiHidraulica de Canales AbiertosLauren AndrewsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment - Hydraulics: Weir ProblemsDocument1 paginăAssignment - Hydraulics: Weir ProblemsGerrold RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excersie - To Be Worked OnDocument2 paginiExcersie - To Be Worked Ontewodros getuÎncă nu există evaluări
- FM Question Bank PDFDocument6 paginiFM Question Bank PDFprabhumaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment 4 MEC 207Document7 paginiAssignment 4 MEC 207Praveen SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Total Marks: 100 Time: 3 HoursDocument3 paginiTotal Marks: 100 Time: 3 HoursTinashe MazokeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Laminar Flow Is Taking Place in A Pipe of Diameter 200 MMDocument9 paginiA Laminar Flow Is Taking Place in A Pipe of Diameter 200 MMANBU RAJ AÎncă nu există evaluări
- Open Channel FlowDocument2 paginiOpen Channel FlowHomer BatalaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Article WritingDocument10 paginiArticle WritingfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Email-Social Networking Media PlatformsDocument7 paginiAn Email-Social Networking Media PlatformsfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPJ S1Document63 paginiSPJ S1SUHAIMIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guided WritingDocument7 paginiGuided WritingfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Writing-SchoolDocument9 paginiReport Writing-SchoolfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Review-HomestayDocument7 paginiA Review-HomestayfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Future Continuous Form QuestionsDocument2 paginiFuture Continuous Form Questionsgiousis23Încă nu există evaluări
- 3 - Series Parallel and Branched Pipe Systems (Compatibility Mode)Document9 pagini3 - Series Parallel and Branched Pipe Systems (Compatibility Mode)Eddy BongÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 - Behaviour of Real Fluids (Compatibility Mode)Document20 pagini1 - Behaviour of Real Fluids (Compatibility Mode)fyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles DefinitionDocument1 paginăPrinciples DefinitionfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Flow in Pipes Closed Conduits (Compatibility Mode)Document28 pagini2 - Flow in Pipes Closed Conduits (Compatibility Mode)fyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Geotech ForumDocument1 paginăGeotech ForumfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 - Flow in Pipes Closed Conduits (Compatibility Mode)Document28 pagini2 - Flow in Pipes Closed Conduits (Compatibility Mode)fyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ab BC CD de Ef AfDocument1 paginăAb BC CD de Ef AffyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- VonPost Classification PDFDocument2 paginiVonPost Classification PDFfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Q7Document2 paginiQ7fyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- With The Aid of A Diagram, Discuss About The Major Components of The Solar PV Balance of SystemDocument1 paginăWith The Aid of A Diagram, Discuss About The Major Components of The Solar PV Balance of SystemfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 6: Knu1073 Introduction To Solar Photovoltaic SystemDocument1 paginăTutorial 6: Knu1073 Introduction To Solar Photovoltaic SystemfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- SPT CPTDocument7 paginiSPT CPTfyqah0% (1)
- 1 - Behaviour of Real FluidsDocument5 pagini1 - Behaviour of Real FluidsfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tutorial 5Document1 paginăTutorial 5fyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap3 Found Collapse ExpansiveDocument39 paginiChap3 Found Collapse ExpansivefyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- W6 Lecture-Peat in MalaysiaDocument9 paginiW6 Lecture-Peat in MalaysiafyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- KNS 3643 Reinforced Concrete Design: Course OutcomeDocument3 paginiKNS 3643 Reinforced Concrete Design: Course OutcomefyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap1 Shallow Foundations Settlement StdsDocument15 paginiChap1 Shallow Foundations Settlement StdsfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap1 Shallow Foundations Settlement StdsDocument15 paginiChap1 Shallow Foundations Settlement StdsfyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chap1 Shallow Foundations Bearing Capacity StdsDocument31 paginiChap1 Shallow Foundations Bearing Capacity Stdsfyqah100% (2)
- KNS 3243 Assignment 1Document1 paginăKNS 3243 Assignment 1fyqahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 1 KNS 2723Document22 paginiWeek 1 KNS 2723Eddy BongÎncă nu există evaluări
- To Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignDe la EverandTo Engineer Is Human: The Role of Failure in Successful DesignEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (138)
- Conquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeDe la EverandConquering the Electron: The Geniuses, Visionaries, Egomaniacs, and Scoundrels Who Built Our Electronic AgeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (9)
- Hacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsDe la EverandHacking Electronics: An Illustrated DIY Guide for Makers and HobbyistsEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2)
- Crossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetDe la EverandCrossings: How Road Ecology Is Shaping the Future of Our PlanetEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (10)
- The Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansDe la EverandThe Things We Make: The Unknown History of Invention from Cathedrals to Soda CansÎncă nu există evaluări
- INCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesDe la EverandINCOSE Systems Engineering Handbook: A Guide for System Life Cycle Processes and ActivitiesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Digital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosDe la EverandDigital Filmmaking: The Ultimate Guide to Web Video Production for Beginners and Non-Professionals, Learn Useful Tips and Advice on How You Can Create, Film and Edit Your VideosEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Practical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialDe la EverandPractical Electrical Wiring: Residential, Farm, Commercial, and IndustrialEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- Programming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonDe la EverandProgramming the Raspberry Pi, Third Edition: Getting Started with PythonEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Teach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionDe la EverandTeach Yourself Electricity and Electronics, 6th EditionEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (15)
- Analog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceDe la EverandAnalog Design and Simulation Using OrCAD Capture and PSpiceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesDe la EverandHeat Transfer Engineering: Fundamentals and TechniquesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1)
- Electrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tDe la EverandElectrical Engineering 101: Everything You Should Have Learned in School...but Probably Didn'tEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (27)
- Build Your Own Electronics WorkshopDe la EverandBuild Your Own Electronics WorkshopEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (3)
- The Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeDe la EverandThe Great Bridge: The Epic Story of the Building of the Brooklyn BridgeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (59)
- Troubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesDe la EverandTroubleshooting and Repair of Diesel EnginesEvaluare: 1.5 din 5 stele1.5/5 (2)
- Predicting Lifetime for Concrete StructureDe la EverandPredicting Lifetime for Concrete StructureÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Diploma Interview Q&A: Career GuideDe la EverandPower Electronics Diploma Interview Q&A: Career GuideÎncă nu există evaluări