Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Care Taken To Avoid Danger or Mistakes. The Possibility of Suffering Harm or Injury
Încărcat de
Meriel Stephanie ZaragozaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Care Taken To Avoid Danger or Mistakes. The Possibility of Suffering Harm or Injury
Încărcat de
Meriel Stephanie ZaragozaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
ARIEL LOUIS C.
ZARAGOZA
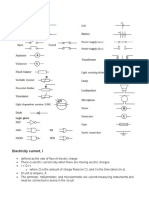
1.) Ampere
- An ampere is a unit of measure of the rate of electron flow or current in an electrical
conductor. One ampere of current represents one coulomb of electrical charge (6.24 x
1018charge carriers) moving past a specific point in one second.
2.) Caution
- Care taken to avoid danger or mistakes.
3.) Danger
- The possibility of suffering harm or injury.
4.) Isometric
- The term isometric comes from the Greek for "having equal measurement".
5.) Joule
- It is a unit of work or energy equal to the work done by a force of one newton acting through
a distance of one meter.
6.) Kilovolt-meter
- A kilovolt per meter (kV/m) is a decimal multiple of the SI derived unit of the strength of the
electric field volt per meter. The strength of 1 kV/m is achieved if a voltage of 1 kV is applied
between two infinite parallel planes spaced 1 m apart. 1 kV/m = 1000 V/m
7.) Kilowatt-hour
- A unit of work or energy equal to the amount produced by one kilowatt in one hour
8.) Ohm
- The SI unit of electrical resistance, expressing the resistance in a circuit transmitting a
current of one ampere when subjected to a potential difference of one volt.
9.) Autographic
- Containing or relating to an autograph.
10.) Volt
- The practical meter-kilogram-second unit of electrical potential difference and electromotive
force equal to the difference of potential between two points in a conducting wire carrying a
constant current of one ampere when the power dissipated between these two points is
equal to one watt and equivalent to the potential difference across a resistance of one ohm
when one ampere is flowing through it.
11.) Watts
- The absolute meter-kilogram-second unit of power equal to the work done at the rate of one
joule per second or to the power produced by a current of one ampere across a potential
difference of one volt: 1/746 horsepower.
12.) Diagram
- A plan, sketch, drawing, or outline designed to demonstrate or explain how something works
or to clarify the relationship between the parts of a whole.
13.) Series Circuit
- A series circuit is a closed circuit in which the current follows one path, as opposed to a
parallel circuit where the circuit is divided into two or more paths. In a series circuit, the
current through each load is the same and the total voltage across the circuit is the sum of
the voltages across each load.
14.) Solvent
- The liquid in which a solute is dissolved to form a solution.
15.) Parallel Circuit
- A parallel circuit is a closed circuit in which the current divides into two or more paths before
recombining to complete the circuit. Each load connected in a separate path receives the full
circuit voltage, and the total circuit current is equal to the sum of the individual branch
currents.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Electrical Circuit SymbolsDocument38 paginiElectrical Circuit Symbolsanwar9602020Încă nu există evaluări
- M4 ElectricityDocument31 paginiM4 ElectricityplaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 Current Electricity Lesson PlanDocument10 paginiClass 10 Current Electricity Lesson PlanObul Reddy PolimeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- ElectricityDocument49 paginiElectricityShubham RoutÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 12Document11 paginiElectricity Class 10 Notes Science Chapter 12vatnik100% (1)
- Trans Line PDFDocument67 paginiTrans Line PDFgilbertomjcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ref Aircon1A Reviewer PDFDocument105 paginiRef Aircon1A Reviewer PDFJerry B Cruz100% (1)
- Electricity PP TDocument18 paginiElectricity PP Tahmer100% (3)
- Basics of ElectricityDocument18 paginiBasics of Electricitygsantosh06Încă nu există evaluări
- Sworn Application For Tax Clearance IndividualDocument1 paginăSworn Application For Tax Clearance Individualmarcj engineering100% (5)
- Aru 302Document34 paginiAru 302Michael PachecoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class X: Physics Chapter 3: Electricity Chapter Notes Key LearningsDocument3 paginiClass X: Physics Chapter 3: Electricity Chapter Notes Key LearningsApoorvAroraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 Chapter 12: Electricity: 1. Positive and Negative ChargesDocument5 paginiClass 10 Chapter 12: Electricity: 1. Positive and Negative ChargesAshok DixitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 12 ElectricityDocument3 paginiChapter 12 ElectricityShashank SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class10 Science Notes Chapter12Document6 paginiClass10 Science Notes Chapter12ng_nirmalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsDocument6 paginiBasic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsJericho CunananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Variation in The Electric Power Supplied. Variation Variation VariationDocument5 paginiVariation in The Electric Power Supplied. Variation Variation Variationsuresh0147Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic EE Module 123Document32 paginiBasic EE Module 123Benmark JabayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson: ElectricityDocument13 paginiLesson: Electricitybudesasaiaw.v.re32.90Încă nu există evaluări
- Ece terminologySRKDocument5 paginiEce terminologySRKSunilkumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- G9, 2.7 Current and Voltage in CircuitsDocument4 paginiG9, 2.7 Current and Voltage in CircuitsKinmokusei MyoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity: Circuit Symbols - You Met These Circuit Symbols in GCSE PhysicsDocument22 paginiElectricity: Circuit Symbols - You Met These Circuit Symbols in GCSE PhysicsBaberBegÎncă nu există evaluări
- Untitled PresentationDocument16 paginiUntitled Presentationapi-423106464Încă nu există evaluări
- CBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity NotesDocument3 paginiCBSE Class 10 Physics Electricity NotesManendraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity (Main)Document16 paginiElectricity (Main)Sarthak KapoorÎncă nu există evaluări
- C I e N o T e S Notes 2 For A Level StudentsDocument13 paginiC I e N o T e S Notes 2 For A Level StudentsRakotoarison Louis FrederickÎncă nu există evaluări
- UntitledDocument4 paginiUntitledJoyce LonzagaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nomenclature,: StandardsDocument1 paginăNomenclature,: StandardsreacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 CurrentElectricity IDocument9 pagini09 CurrentElectricity ILearner PointÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 ElectricityDocument16 paginiClass 10 ElectricityTapas BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Terms and DefinitionsDocument15 paginiBasic Electrical Terms and Definitionsilango palaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes ElectricityDocument10 paginiNotes ElectricityDivyanshu BaghelÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTRICITYDocument33 paginiELECTRICITYSumiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ' ElectricityDocument98 pagini' Electricitya9758127118Încă nu există evaluări
- DefinitionsDocument7 paginiDefinitionsAnoushka PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric CurrentDocument4 paginiElectric CurrentMuhammad QasimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Electric PotentialDocument8 paginiBasic Electrical Technology (ESC 101-A) Module 1: DC Circuits Electric PotentialtusharÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.1: Electrical DistributionDocument31 pagini5.1: Electrical DistributionShuhada SamsudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Physics 2 ReviewerDocument22 paginiGeneral Physics 2 Reviewercharydel.oretaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concept of Current:: Electrical EngineeringDocument7 paginiConcept of Current:: Electrical EngineeringRam VigneshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elecrticity PDFDocument8 paginiElecrticity PDFmrneetgamerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity Is The Set ofDocument2 paginiElectricity Is The Set ofSam Axel BenedictoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Charge and Electric Field: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsDocument0 paginiCharge and Electric Field: Online Learning Resources For Malaysia StudentsJia HuiÎncă nu există evaluări
- As Physics Electricity Chapter 9Document17 paginiAs Physics Electricity Chapter 9LawrenceOnthugaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science Notes Chapter 12 Electricity: Electricity:Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Voltage orDocument23 paginiScience Notes Chapter 12 Electricity: Electricity:Electric Current, Electric Circuit, Voltage orAayushiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuits: Prepared and Presented By: Ms. Syeda Amina AsgharDocument15 paginiCircuits: Prepared and Presented By: Ms. Syeda Amina Asgharانیس ب ٹÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity: Ohm's LawDocument3 paginiElectricity: Ohm's LawManoj Bhawar PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Principal of Electrical CircuitryDocument19 paginiBasic Principal of Electrical CircuitryAreeba ParvezÎncă nu există evaluări
- X Class Physics ElectricityDocument7 paginiX Class Physics ElectricityPaarth BansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuit's LabDocument11 paginiCircuit's LabJane HangerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revision Notes On Electricity: ChargeDocument6 paginiRevision Notes On Electricity: ChargeJahnavi MeharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ashuganj Power Station Company LTD Question SolutionDocument9 paginiAshuganj Power Station Company LTD Question Solutionsaiful743545Încă nu există evaluări
- Electricity: Made By:-Tushar Bhutani X - ADocument36 paginiElectricity: Made By:-Tushar Bhutani X - ATushar BhutaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ohm's Law States That The Current Through A Conductor Between TwoDocument4 paginiOhm's Law States That The Current Through A Conductor Between Twosyed raza100% (1)
- Electic & ElectroDocument40 paginiElectic & ElectroMohamad Hafiz SariffÎncă nu există evaluări
- Define The FFDocument2 paginiDefine The FFTemoteo L. Pupa IIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radioactivity (AutoRecovered)Document16 paginiRadioactivity (AutoRecovered)muhamad masudÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5.1 Electric Charge: CoulombsDocument5 pagini5.1 Electric Charge: Coulombsfazeelm24Încă nu există evaluări
- Main Topic Ce0053Document49 paginiMain Topic Ce0053JOSHUA MEYER ANGELESÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIRCRAFT Basic ElectricityDocument327 paginiAIRCRAFT Basic ElectricityndrmnlngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity Notes-XDocument40 paginiElectricity Notes-XArchitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Basics of Electricity CompleteDocument9 paginiThe Basics of Electricity CompleteAlejandroDuranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic Development A Global Perspective Chapter 1Document47 paginiEconomic Development A Global Perspective Chapter 1Meriel Stephanie ZaragozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdyunlgvygDocument1 paginăAdyunlgvygMeriel Stephanie ZaragozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Who Am I?: Miguel, Tagum City, Davao Del Norte With My FamilyDocument2 paginiWho Am I?: Miguel, Tagum City, Davao Del Norte With My FamilyMeriel Stephanie ZaragozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Properties of Particulate MassesDocument8 paginiProperties of Particulate MassesMeriel Stephanie ZaragozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MathFor802 PDFDocument21 paginiMathFor802 PDFanon_995042985Încă nu există evaluări
- Gen Phy 1 Week 4Document49 paginiGen Phy 1 Week 4Cedric BendañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neraca Massa Sherena & IkaDocument45 paginiNeraca Massa Sherena & IkaEVA KUSMAYANTIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ET Tut7 AUT2017-18 PDFDocument3 paginiET Tut7 AUT2017-18 PDFMoulindu KunduÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.iit Jam Physics 2021Document21 pagini4.iit Jam Physics 2021mosohail96Încă nu există evaluări
- TONGO - Final ProjectDocument71 paginiTONGO - Final ProjectJhon Nicko TongoÎncă nu există evaluări
- RK350-2 20000103TFDocument2 paginiRK350-2 20000103TFlutfiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fundamentals of Electrical Drives - G. K. Dubey PDFDocument121 paginiFundamentals of Electrical Drives - G. K. Dubey PDFAnonymous l7YZBdÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6.2 - Speed Control of Ac MotorDocument45 paginiChapter 6.2 - Speed Control of Ac MotorWeehao SiowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jawapan Mechanics and Thermodynamics Syahmi RifqiDocument13 paginiJawapan Mechanics and Thermodynamics Syahmi RifqiAnonymous hlcl57mNj5Încă nu există evaluări
- Z011852-0 Trouble Shooting Sensors 2017.10Document111 paginiZ011852-0 Trouble Shooting Sensors 2017.10hericlimabezerra95Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter7 MeasurementDocument8 paginiChapter7 MeasurementPrabha SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL Mathematics-6 Q3 W7Document12 paginiDLL Mathematics-6 Q3 W7SHERYL SAUDANÎncă nu există evaluări
- AbsorptionDocument18 paginiAbsorptionAnonymous T4L6h94Încă nu există evaluări
- JEE Main 2020 7th Jan Shift 1 PhysicsDocument16 paginiJEE Main 2020 7th Jan Shift 1 PhysicsR B SHARANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final Requirement On Ce 523: Situation IDocument4 paginiFinal Requirement On Ce 523: Situation ICzindy MoradosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exam PaperDocument11 paginiExam PaperSi JampangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ohm's Law & Kirchhoff's LawsDocument22 paginiOhm's Law & Kirchhoff's LawsDr-Gurpreet KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Annexure 3: Saturation Properties of WaterDocument2 paginiAnnexure 3: Saturation Properties of WaterAryanSharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Activity 1 Gas LawDocument2 paginiActivity 1 Gas LawMildred VillarubiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Xpert 9395p Ups 500 Kva Technical Specification enDocument5 paginiPower Xpert 9395p Ups 500 Kva Technical Specification enPandu RizkhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rangkuman Rumus Fisika Kelas VIII Semester 1Document2 paginiRangkuman Rumus Fisika Kelas VIII Semester 1Eirika PraimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Transformer Magnetizing Inrush CurrentDocument6 paginiTransformer Magnetizing Inrush CurrentJUAN SEBASTIAN TARAZONA ACUNAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wait To Begin: SectionDocument8 paginiWait To Begin: SectionJoderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 01 Sinusoidal Alternating WaveformsDocument21 paginiLecture 01 Sinusoidal Alternating WaveformsShuvodip Das100% (1)
- Surface Areas and Volumes: Points To RememberDocument28 paginiSurface Areas and Volumes: Points To RememberSipra PaulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Formula Sheet PDFDocument4 paginiPhysics Formula Sheet PDFjoseph govadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamics Lesson 3Document3 paginiThermodynamics Lesson 3Ruth100% (1)