Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Stomacolostomy 161108133919
Încărcat de
drng48Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Stomacolostomy 161108133919
Încărcat de
drng48Drepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Stoma
Stoma: Stoma is an artificial opening or mouth like to the exterior, the abdominal wall so as to drain
the content from the tubular structures inside, like bowel or ureter.
It is an one type of artificial fistula.
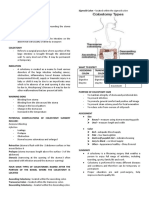
Types:
-Ileostomy: terminal 5 cm ileum is projected out, on to the skin of abdominal wall.
-Colostomy
-Cutaneous ureterostomy
-Ileal urinary conduit
- Vesicostomy
-Ostomy: Operation that connects the GI tract to abdominal wall skin or the lumen of another hollow organ.
-Stoma: Opening of the ostomy.
-Ileostomy effluent is usually liquid, whereas colostomy effluent is usually solid
-Ileostomy patients are more likely to develop fluid and electrolyte problems
-An ileostomy is usually sited in the right iliac fossa
-End-colostomy is usually sited in the left iliac fossa
Colostomy
Colostomy: A colostomy (or ileostomy) stoma is an artificial opening made in the colon (or small
intestine) to divert faeces and flatus outside the abdomen where they can be collected in an external
appliance.
The purposes of colostomy include the following:
-Diverting fecal stream for some distal pathology, e.g. colonic perforation.
-To decompress the obstructed colon.
-Replacement of anus, e.g. carcinoma rectum.
Types:
According to the period of diversion According to the way of fashioning of colostomy
-Temporary (Usually loop colostomy) -Terminal or end colostomy
-Permanent (Usually end colostomy) -Loop colostomy
-Divines defunctioning colostomy
Rana Shankor Roy
rana.shankor@gmail.com
Temporary colostomy: Is done in conditions wherein diversion is required to facilitate healing
distally in the rectum or distal colon. And this is closed once the purpose is over. Site of temporary
colostomy is usually right hypochondrium and left iliac fossa. It can be loop colostomy or Devines
double-barrel colostomy.
Permanent colostomy: is always end colostomy placed in left iliac fossa, 6 cm above and medial
to the anterior superior iliac spine.
Terminal or end colostomy: This is done at the sigmoid colon and opening is made at the left
iliac fossa. It is a type of permanent colostomy having a single stoma.
Loop colostomy: Here a loop of colon is taken out and colostomy is performed. It may be in the
sigmoid or transverse colon. It is a temporary colostomy and most commonly practiced.
Divines defunctioning colostomy: (A divided stoma colostomy or double barreled colostomy)
-The colostomy is made with a bridge of skin between the two stomas.
-Two limbs of the colon are brought out through separate skin incisions.
-The proximal stoma is thus an end colostomy while distal one is called a mucous fistula.
-This ensures absolute rest to the distal segment of the colon and rectum but restoration of bowel
continuity is more difficult.
Indications:
-Congenital:
High anorectal anomalies where the child is born with obstruction.
-Traumatic:
Injuries to the rectum and anal canal (to prevent faecal peritonitis) (. Here sigmoid colostomy is done)
-Inflammatory:
In some complicated cases of fistula in ano
Diverticulitis.
-Neoplastic:
Carcinoma rectum and anal canal(sigmoid colostomy is done)
Carcinoma descending colon (transverse colostomy is done.)
-Miscellaneous:
Colonic obstruction
Rectovesical or rectovaginal fistula.
Temporary colostomy Permanent colostomy
-Congenital megacolon -AP-Resection.
-Anorectal malformations. -Carcinoma anal canal
-Sigmoid volvulus -After Hartmanns operation
-Perforation of left sided colon
-Left sided colonic growth
-High anal fistula
-Trauma to left sided growth
Rana Shankor Roy
rana.shankor@gmail.com
General Care and Advice to Patients with Stoma:
-Patient can have normal diet. Diet, which regulates the bowel action, is better.
-Plenty of water is advisable.
-Patient can go for normal work, exercise like sports, swimming.
-Antidepressants, anticholinergics might cause constipation. So these drugs should be taken carefully.
-Patient can have normal sexual activity.
Complications of colostomy:
-Prolapse of mucosa (prolapse of distal loop mucosa is common)commonest complication
-Skin irritation/excoriation( due to leak adjacent to appliances. Other causes may be Wet skin before
placing the appliance, Infection like of bacteria and candida)
Retraction
-Ischaemia
-Stenosis
-Parastomal hernia
-Bleeding
-Fistulation
Colostomy closure:
-Colostomy closure is most easily and safely accomplished if the stoma is mature, typically after the
colostomy has been established for two months.
-Criteria for temporary colostomy closure:
-Integrity of distal colon should be normal and adequate.
-Anorectal sphincter should be normal.
-Cause for construction of colostomy is cured completely without any suspicious of recurrence of
same disease distally
Types of closure:
-Extraperitoneal
-Intraperitoneal type (Now intraperitoneal closure is done.)
Ileostomy appliances tend to be drainable bags, which are left in place for 48 hours, while
colostomy appliances are simply changed two or three times each day
Why doesnt an ileostomy or colostomy close?
-Due to Epithelialization (mucosa to skin)
Rana Shankor Roy
rana.shankor@gmail.com
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Colostomy and GastrostomyDocument16 paginiColostomy and GastrostomyElla CerenioÎncă nu există evaluări
- StomaDocument37 paginiStomaAndryHarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abdominal StomasDocument3 paginiAbdominal Stomashelangen100% (1)
- End Colostomy's: An Overview of The Procedure, Indications, and AftercareDocument15 paginiEnd Colostomy's: An Overview of The Procedure, Indications, and AftercareRichard JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoma / OstomyDocument55 paginiStoma / OstomyDPM FK Untar100% (1)
- ColostomyDocument23 paginiColostomySheene Ainasthazia Diego AngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ostomy Rev 1Document7 paginiOstomy Rev 1Karren AlipioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoma Care For Hcas PDFDocument17 paginiStoma Care For Hcas PDFAndyk Strapilococus AureusÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ward Class - Colostomy Care FinalDocument6 paginiWard Class - Colostomy Care FinalDan Dan Soi TÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoma OsceDocument8 paginiStoma OsceRadhiyatul Ashiqeen Binti MoktarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal Stomas PDFDocument10 paginiIntestinal Stomas PDFAmyandÎncă nu există evaluări
- Skill 11 Colostomy CareDocument3 paginiSkill 11 Colostomy CareDiana CalderonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy FileDocument4 paginiColostomy FileAnjhiene CambaÎncă nu există evaluări
- COLOSTOMYDocument12 paginiCOLOSTOMYBrian96cortezÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColostomyDocument3 paginiColostomyDr. Ikwuakor ChikezieÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColonDocument7 paginiColonch3zk4Încă nu există evaluări
- ColostomyDocument2 paginiColostomyFenelie AblazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy CareDocument35 paginiColostomy CareRoyster CabralÎncă nu există evaluări
- StomasDocument4 paginiStomasSaravanan Sridharan100% (1)
- Diverticular Diseases of ColonDocument22 paginiDiverticular Diseases of ColonGyan Prakash BhartiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy CareDocument34 paginiColostomy CareTolemre EmreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy Wps OfficeDocument19 paginiColostomy Wps Officehealthseeker159Încă nu există evaluări
- Colostom 1Document2 paginiColostom 1Desy Fordiely WulandariÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColostomyDocument45 paginiColostomydrqiekiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoma: Prepared By: Wasihun EndalekDocument17 paginiStoma: Prepared By: Wasihun EndalekAmanuel MaruÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy CareDocument35 paginiColostomy CareRashmita DahalÎncă nu există evaluări
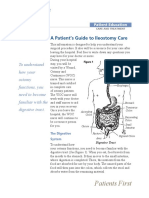
- Patients First: A Patient's Guide To Colostomy CareDocument11 paginiPatients First: A Patient's Guide To Colostomy CareAlo Al- hassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy Care and IrrigationDocument6 paginiColostomy Care and IrrigationTheSweetpea501Încă nu există evaluări
- Definition: Stoma Means 'Mouth' or 'Opening'. in Medicine, It Indicates That There Is AnDocument3 paginiDefinition: Stoma Means 'Mouth' or 'Opening'. in Medicine, It Indicates That There Is AnassssadfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy Care1Document25 paginiColostomy Care1Ely FuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reasons For Having An Ileostomy: Surgical Opening Small Intestine Ileum Pouching System Groin AbdomenDocument7 paginiReasons For Having An Ileostomy: Surgical Opening Small Intestine Ileum Pouching System Groin AbdomenContented LinganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy CareDocument10 paginiColostomy Carecelinegirl99100% (1)
- Why A Colostomy May Be Needed: Bowel Cancer Crohn's Disease DiverticulitisDocument4 paginiWhy A Colostomy May Be Needed: Bowel Cancer Crohn's Disease DiverticulitisDoni LeoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy and IleostomyDocument6 paginiColostomy and IleostomyLitas, Julie Ann L.Încă nu există evaluări
- 1 Colostomy and IleostomyDocument4 pagini1 Colostomy and IleostomyAnna Sofia ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types and Management of Intestinal StomasDocument62 paginiTypes and Management of Intestinal Stomasminnalesri100% (6)
- Bowel Diversion Surgeries: Ileostomy, Continent Ileostomy, Ileoanal Reservoir and ColostomyDocument7 paginiBowel Diversion Surgeries: Ileostomy, Continent Ileostomy, Ileoanal Reservoir and ColostomyShintya nainggolanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal Stomas: Types of Intestinal StomaDocument6 paginiIntestinal Stomas: Types of Intestinal StomaWaqas HaleemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modul Perawatan OstomiDocument18 paginiModul Perawatan OstomiNurhanifahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal Stomas: Types of Intestinal StomaDocument7 paginiIntestinal Stomas: Types of Intestinal StomaSuraj KurmiÎncă nu există evaluări
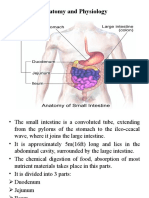
- Anatomy and PhysiologyDocument42 paginiAnatomy and Physiologysushma shresthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal Stomas: J. Graham WilliamsDocument12 paginiIntestinal Stomas: J. Graham WilliamsAbay Lotov100% (1)
- ColostomiDocument1 paginăColostomiArifHidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colostomy Surgery and Your CareDocument34 paginiColostomy Surgery and Your CareLee Wan YeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColostomyDocument60 paginiColostomymathisyncÎncă nu există evaluări
- Patients First: A Patient's Guide To Ileostomy CareDocument11 paginiPatients First: A Patient's Guide To Ileostomy Carespin_echoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoma Management: Shankar ZanwarDocument33 paginiStoma Management: Shankar Zanwarpradeep nairÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColostomyDocument30 paginiColostomyGlen DaleÎncă nu există evaluări
- ColostomyDocument13 paginiColostomyKetali JambhavdekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ai 2023Document4 paginiAi 2023design bahana bahana proÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intestinal Stomas - AKTDocument49 paginiIntestinal Stomas - AKTTammie YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample: What Is A Colostomy/ Ileostomy?Document10 paginiSample: What Is A Colostomy/ Ileostomy?Jack BenaventeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoma 231209 131703Document12 paginiStoma 231209 131703Raniya AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoma Types PDFDocument1 paginăStoma Types PDFUmi Kalsum100% (1)
- (Medicalstudyzone - Com) Surgery Vol 1 4.0Document266 pagini(Medicalstudyzone - Com) Surgery Vol 1 4.0medico designÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Stoma, Cut and WoundsDocument40 paginiManagement of Stoma, Cut and WoundsLalita KumariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bowel SurgeryDocument92 paginiBowel Surgeryandrea.maungca.mnlÎncă nu există evaluări
- Volvulus, (Twisted Intestines) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandVolvulus, (Twisted Intestines) A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National PhyDocument1 paginăPages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phydrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- توزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيDocument3 paginiتوزيع درجات الباطنه 2012-2013 قصر العينيdrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- Neurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? AnswerDocument9 paginiNeurology: Q. What Are The Causes of CVD (Stroke) in A Young Patient? Answerdrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- Assessment of Development and GrowthDocument21 paginiAssessment of Development and Growthdrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- Pages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3Document1 paginăPages From (Susan O'Sullivan, Raymond Siegelman) National Phy (BookFi - Org) - 3drng480% (1)
- Infections: (2013 - 2017)Document1 paginăInfections: (2013 - 2017)drng48Încă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural MechanismsDocument3 paginiMCQ Reflexive Maturation & Postural Mechanismsdrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- Pre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFDocument124 paginiPre-NEET Surgery (Khandelwal & Arora) PDFdrng4850% (4)
- Shenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXDocument281 paginiShenimt e Mia Personale Per DDXJeronim H'gharÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebral Palsy MCQDocument2 paginiCerebral Palsy MCQdrng4882% (11)
- Differential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal PainDocument2 paginiDifferential Diagnosis of Acute Abdominal Paindrng48100% (1)
- Table: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest PainDocument2 paginiTable: Clinical and Diagnostic Features of Chest Paindrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- 31 Da 7 CBB 2 eDocument2 pagini31 Da 7 CBB 2 edrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- MCQ Biomechanics of Hip JointDocument16 paginiMCQ Biomechanics of Hip Jointdrng48100% (9)
- Name: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859Document12 paginiName: ID:: Madiha Sayed Nagy. 51859drng48Încă nu există evaluări
- Burn RehabilitationDocument5 paginiBurn Rehabilitationdrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- Contraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania HospitalDocument20 paginiContraception: David Blair Toub, M.D. Dept. of Obstetrics and Gynecology Pennsylvania Hospitaldrng48Încă nu există evaluări
- Epidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1Document3 paginiEpidemiology Quiz On Chapter 1drng48Încă nu există evaluări
- Lindo Wing Brochure Web VersionDocument16 paginiLindo Wing Brochure Web VersionNetwerk24Încă nu există evaluări
- Seminar HD-RSUD Sleman 2019Document36 paginiSeminar HD-RSUD Sleman 2019herkamaya100% (1)
- 100 Ways To Achieve SuccessDocument5 pagini100 Ways To Achieve SuccessSampath KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preventing Deep Vein ThrombosisDocument8 paginiPreventing Deep Vein ThrombosisOncology NurseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kleihauer TestDocument3 paginiKleihauer Testteo2211Încă nu există evaluări
- Wastewater Disposal.Document266 paginiWastewater Disposal.FarazÎncă nu există evaluări
- DIALOGUE AND EXPERIMENT by Peter PhilippsonDocument6 paginiDIALOGUE AND EXPERIMENT by Peter PhilippsonMariana BorodeaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Supraventricular TachycardiaDocument5 paginiSupraventricular TachycardialjubodragÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imipenem Cilastatin (Primaxin)Document1 paginăImipenem Cilastatin (Primaxin)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linen and Laundry Management Guidelines For Hospitals and PDFDocument15 paginiLinen and Laundry Management Guidelines For Hospitals and PDFspp100% (2)
- BulletsDocument123 paginiBulletsharpay100% (1)
- Medical RecordDocument14 paginiMedical RecordZakwan AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Environmental EngineeringDocument41 paginiIntroduction To Environmental EngineeringPaul Santos NonatÎncă nu există evaluări
- RO-INMED 2016 ProgramDocument18 paginiRO-INMED 2016 Programmamulasioan9675Încă nu există evaluări
- Reflexology and DementiaDocument8 paginiReflexology and DementiaNatalie Stubbs100% (1)
- Virginia HendersonDocument4 paginiVirginia HendersonJoyce TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frontal Sinus FX Slides 070117Document48 paginiFrontal Sinus FX Slides 070117Andre WaaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dengue (Break Bone Fever) - FAQ, DPH-TAMIL NADU, IndiaDocument3 paginiDengue (Break Bone Fever) - FAQ, DPH-TAMIL NADU, IndiaDr.SagindarÎncă nu există evaluări
- West Visayas State University Medical Center E. Lopez St. Jaro Iloilo CityDocument7 paginiWest Visayas State University Medical Center E. Lopez St. Jaro Iloilo CityRegine Marie EspañaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal BoundariesDocument4 paginiPersonal Boundariesscribdreaderplus75% (4)
- Lesson Plan On Electroconvulsive TherapyDocument13 paginiLesson Plan On Electroconvulsive Therapysimranjeet kaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- (The Norton Library) Karen Horney - Feminine Psychology (1973, W W Norton & Co.)Document276 pagini(The Norton Library) Karen Horney - Feminine Psychology (1973, W W Norton & Co.)daniela86% (7)
- Design of Novel Oral Films As Drug Delivery SystemDocument7 paginiDesign of Novel Oral Films As Drug Delivery SystemReza-ul JalilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Visual Schedules For Kids With AutismDocument9 paginiVisual Schedules For Kids With AutismAutism Parenting75% (8)
- ADHD Parent Questionnaire PDFDocument4 paginiADHD Parent Questionnaire PDFklichtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Operating Procedure Handling, Storage and Disposal: Punyam Manufacturing INCDocument4 paginiStandard Operating Procedure Handling, Storage and Disposal: Punyam Manufacturing INCJaijeev PaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- BLS Test PDFDocument76 paginiBLS Test PDFalex rodman50% (2)
- Olympian Benchmark - 400mDocument15 paginiOlympian Benchmark - 400merwandumontÎncă nu există evaluări
- MagnetoterapieDocument10 paginiMagnetoterapieHelena PatraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dream Abstracts PDFDocument61 paginiDream Abstracts PDFAlice Gina100% (1)