Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Unit 2 Infancy and Toddler Hood
Încărcat de
Nicz Lanz Dejz0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
738 vizualizări3 pagini1. The document discusses the physical, cognitive, socio-emotional, and language development of infants and toddlers. It covers major milestones in areas like motor skills, brain development, temperament, attachment, and language acquisition.
2. As children reach preschool age, the document notes that their physical growth becomes more slender and they gain skills like hopping, skipping, and throwing balls. Their cognitive abilities also progress as they can now represent objects symbolically and ask more questions.
3. Socio-emotionally, preschoolers continue to develop emotions, social skills, and an understanding of themselves and others. Their language comprehension and production also becomes more advanced as they learn rules and use language for communication and
Descriere originală:
dfefe
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest document1. The document discusses the physical, cognitive, socio-emotional, and language development of infants and toddlers. It covers major milestones in areas like motor skills, brain development, temperament, attachment, and language acquisition.
2. As children reach preschool age, the document notes that their physical growth becomes more slender and they gain skills like hopping, skipping, and throwing balls. Their cognitive abilities also progress as they can now represent objects symbolically and ask more questions.
3. Socio-emotionally, preschoolers continue to develop emotions, social skills, and an understanding of themselves and others. Their language comprehension and production also becomes more advanced as they learn rules and use language for communication and
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
738 vizualizări3 paginiUnit 2 Infancy and Toddler Hood
Încărcat de
Nicz Lanz Dejz1. The document discusses the physical, cognitive, socio-emotional, and language development of infants and toddlers. It covers major milestones in areas like motor skills, brain development, temperament, attachment, and language acquisition.
2. As children reach preschool age, the document notes that their physical growth becomes more slender and they gain skills like hopping, skipping, and throwing balls. Their cognitive abilities also progress as they can now represent objects symbolically and ask more questions.
3. Socio-emotionally, preschoolers continue to develop emotions, social skills, and an understanding of themselves and others. Their language comprehension and production also becomes more advanced as they learn rules and use language for communication and
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
Unit 2 Infancy and Toddler hood
Module 12 Physical Development of Infants and Toddlers
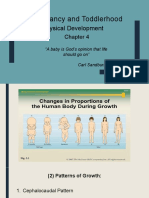
Cephalocaudal trend-postnatal growth from conception to 5 months when the head grow more
than the body.
Proximodistal trend-Pre-matal growth from 5 months to birth when the fetus grows from the
inside of body outwards.
Height and Weight
-Infants length increases by about 30 percent in the first five months.
-Baby's weight triples during the first year but slow down in the second year of life.
Brain Development
-dramatic change in brain in the first two years of life are the spreading connections of dendrites
to each other.
Myclination or myclinization - process by which exons are covered and insulated by layers of fat
cells.
Motor development
Reflexes
Sucking Reflex-touches the roof of an infants mouth.
Rooting Reflex-infants cheek is storked.
Startle/moro Reflex-infants middle or lower back is storked next to the spinal cord.
Tonic Neck Reflex-demonstrated in infants who are placed on their abdomes.
Gross motor skills- able to grab things off the cabinit ,chase the ball and to walk away from
parent.
Fine motor skills-The development of reaching and grasping becomes more refined.
Sensory and Peraptual Development
.Newborn's vision is about 10 to 30 times lower than normal adult vision.
.Since of hearing develops much before the birth of the body.
.Young infants showed clear preference for smelling their mother's breast pad when they were 6
years old.
.Newborns fell pain.
.Newborn can distinguish different taste.
.Ability to connect information gets sharpened considerably through experience.
Module 13 Cognitive Development of Infants and Toddlers
Cognitive development in infancy refers to development in the way baby thinks.
Sensorimotor stage has six sub-stages:
1. Simple reflexes-coordination of sensation and action through reflexive behaviors.
2.First habits and primary circular reactions phase-coordination of sensation and two types of
schemes: habits(reflex) and primary circular reactions.
3. Secondary circular reactions phase-development of habits.
4. Coordination of reactions stage secondary circular-coordination of vision and touch-hand-eye
coordination; of schemes and intentionally.
5. Tertiary circular reactions, novelty, and curiosity-infants become very intrigued by many
properties of objects and by many things they can make happen to objects.
6. Internalization of Schemes(Invention of New Means Through Mental Combination)infants
develop the ability to use primitive symbols and form an enduring mental representations.
7. Object permanence-the understanding that objects continue to exist eben when they cannot
be seen, heard, or touched
Infants do learn and remember.
Infants appear to be programmed to tune into their linguistic environment with the specific goal
of acquiring language.
Infants utters his/her first word followed by one or to more and soon after, yet a few more.
Infant uses these one-word utterances termed holophrases- to convey intentions, desires and
demands. Two-word or three-word utterances with rudimentary syntax but with articles and
preposition missing are referred to a telegraphic speech.
Language Acquisition Device (LAD)- a metaphorical organ that is responsible for language
learning.
Module 14 Socio-emotional Development of Infants and Toddlers
The formative years
-First 3 years in human learning
Attachment
-The beginnings of attachment occur within the first 6 months of a baby's life with a variety of
built-in signals that baby uses to keep her caregiver engage.
Temperament
-Captures the way people differ.
Includes:
Activity level-Some babies are placid or inactive.
The mood-Some babies are smiley and cheerful.
Child's threshold for distress-Some babies are very sensitive.
The rhythmicity of children-Some babies get hungry or sleepy on fairly regular and predictable
basis.
The intensity of response in each baby-Some babies act restless.
Approach to new situations-Some infants are very cautious.
Distraction-Some children concentrate on a toy regardless of noise.
Adaptability of each child-Some children react to strange with distress.
Child's attention span-Some children have long attention span
The Emergence of the Moral Self
-Some babies are not yet able to hold a standard in mind and evaluate situations.
The Development of Emotions
Early infancy-infants are more aware of the their environment.
Later infancy-infants begin expressing fear.
Toddler hood years-infants express emotions of shame and embarrassment and pride.
Emotional Understanding
-Toddlers acquire language and are learning to verbally express their feelings.
Erickson's Psychosocial Theory
Psychosocial crisis-Trust versus Mistrust
Virtue-Hope
Module 15 Preschoolers Physical Development
Significant Changes in Physical Growth
-Preschoolers have a more slender appearance. The trunks, arms and legs becomes longer.
Gross and Fine Motor Development
Gross motor development
-Skills that involve large muscles.
Categorized into three:
Locomotor skills-going one place to another
Non-locomotor skills-child stay in place
Manipulative skills-involves projecting and receiving objects
-Preschoolers can hop, skip, jump, turn, stand in one leg and throws a ball.
Fine motor development
-Ability to use the smaller muscles.
-Preschoolers do tasks using their hands interchangeably.
-Preschoolers consistently turns pages of a picture of a story book one page at a time, looking
at pictures with interest, copy diagonal lines, square, triangles and they can cut scissors and
bisect a cross.
Preschooler's Artistic Development
Scribbling stage-begins with zigzag lines
Preschematic stage-may include early representation
Schemetic stage-more elaborate scenes are depicte
Preschooler's Nutrition and Sleep
-10 to 12 hours of sleep each day
-The kind of nutrition a preschoolers need has far-reaching effect on his physical growth and
development.
Module 16 Cognitive Development of Preschoolers
Piaget's preoperational thought namely,
Symbolic substage an intuitive substage
Symbolic stage-Preschools show progress in cognitive abilities by being able to draw objects
that are not present.
Intuitive substage-Preschoolers use primitive reasoning and ask a litany of questions.
Brain Connections in the Preschool Years
-The child's billion cells have the ability to make almost countless connections that prepare the
child for. Intricate pathways to learn language, acquire-mathematical skills, interact with people,
grow in his feelings and emotions, and even express himself in art.
Language Development
-As children go through early childhood, their grasp of the rules of language increases.
Language and Social Interaction
-Young children use language both to communicate socially and to plan, guide, and monitor
their behavior in a self-regulatory fashion-called inner speech.
The Preschoolers' attention span lasts longer than that of toddlers.
The Young Children's Theory of Mind
-Children start to reflect on their own thought processes.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Cognitive & Socio-Emotional DevelopmentDocument32 paginiCognitive & Socio-Emotional DevelopmentMesesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infant Toddler Socio Emo Dev NewDocument7 paginiInfant Toddler Socio Emo Dev NewDaryll Jim AngelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infancy and Toddlerhood: Physical DevelopmentDocument35 paginiInfancy and Toddlerhood: Physical DevelopmentTrina CanizoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive Development of Pre-Schoolers BY Helen Grace CalarDocument29 paginiCognitive Development of Pre-Schoolers BY Helen Grace CalarHelen Grace Calar100% (2)
- San Jose Community CollegeDocument6 paginiSan Jose Community CollegeAnabel Jason BobilesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 6 Discussion - Piaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentDocument37 paginiModule 6 Discussion - Piaget's Stages of Cognitive DevelopmentAiza Kinatagcan100% (1)
- ED 101: The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument49 paginiED 101: The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDianne GomeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1SF EDUC 111 Lesson 1 Module 4Document5 pagini1SF EDUC 111 Lesson 1 Module 4George Boy CalvoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 5Document3 paginiModule 5Kel LumawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Instructional Module in The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument8 paginiInstructional Module in The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesLexi PetitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report in Prof Ed 10 Chapter 5Document25 paginiReport in Prof Ed 10 Chapter 5Kin TrinidadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Republic of The Philippines Main Campus C.P.G. North Avenue, Tagbilaran CityDocument1 paginăRepublic of The Philippines Main Campus C.P.G. North Avenue, Tagbilaran Cityrica97100% (1)
- Module 12 of Child and Adolescence DevelopmentDocument3 paginiModule 12 of Child and Adolescence DevelopmentMakki Andre Antonio75% (4)
- Final Prelim Module Educ 11Document33 paginiFinal Prelim Module Educ 11Maden betoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 14 Socio Emotional Development Ofinfants and ToddlersDocument49 paginiModule 14 Socio Emotional Development Ofinfants and ToddlersDARLENE CLAIRE ANDEZA100% (1)
- Written Report Group 3 Intermediate SchoolersDocument14 paginiWritten Report Group 3 Intermediate SchoolerskathleenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of The Learners at Various Stages: Unit 2: Infancy and ToddlerDocument7 paginiDevelopment of The Learners at Various Stages: Unit 2: Infancy and ToddlerDarlene Dacanay DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 5 Module 3Document2 paginiECE 5 Module 3Erica Mae SionicioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection Unit 3 Module 6 - Cynthia P. LimDocument2 paginiReflection Unit 3 Module 6 - Cynthia P. LimCynthia LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Cognitive and Socio Emotional Devt of Intermediate SchoolerDocument32 paginiPhysical Cognitive and Socio Emotional Devt of Intermediate SchoolerTintin Arcalas100% (1)
- Physical Development: Synthesis of Physical, Cognitive and Socio-Cognitive Development of ToddlersDocument3 paginiPhysical Development: Synthesis of Physical, Cognitive and Socio-Cognitive Development of ToddlersGerome Anthon BritonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum in Early Childhood Education (MAERCE 103) Preschool CurriculumDocument45 paginiCurriculum in Early Childhood Education (MAERCE 103) Preschool CurriculumBabylen Abaja Arit SonerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cognitive Development of Infants and ToddlersDocument13 paginiCognitive Development of Infants and ToddlersKhie MonidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection On Bilingual Policy EducationDocument4 paginiReflection On Bilingual Policy EducationJella Mae YcalinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 11 Module 2 (Weeks 3 and 4)Document13 paginiECE 11 Module 2 (Weeks 3 and 4)Erica Mae SionicioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Late Childhood: (The Intermediate Schooler)Document13 paginiLate Childhood: (The Intermediate Schooler)Princess Lyn Estapia SumalinogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Race Ission Ollege: Bronfenbrenner's Ecological TheoryDocument6 paginiRace Ission Ollege: Bronfenbrenner's Ecological TheoryDelmar AcyatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Theories Child DevelopmentDocument5 paginiTheories Child DevelopmentralphÎncă nu există evaluări
- Middle Childhood (The Primary Schooler)Document24 paginiMiddle Childhood (The Primary Schooler)Jasoel Joshua Marino100% (1)
- Intructional Materials Module 15 18Document14 paginiIntructional Materials Module 15 18Josephine Arcibal100% (1)
- FTC 2 Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationDocument6 paginiFTC 2 Foundation of Special and Inclusive EducationAlexis Tondo Almadrones100% (1)
- Module 16 Part 2Document19 paginiModule 16 Part 2lawÎncă nu există evaluări
- Middle Childhood (The Primary Schooler) : Name: Sudani Bhavika NarshibhaiDocument25 paginiMiddle Childhood (The Primary Schooler) : Name: Sudani Bhavika Narshibhai216 SUDANI BHAVIKA NARSHIBHAIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 15-17Document3 paginiModule 15-17Sheena Mae ArcigaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 5: Preschool Physical DevelopmentDocument3 paginiUnit 5: Preschool Physical DevelopmentDaryll Jim AngelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Development of The Learners at The Various StagesDocument32 paginiDevelopment of The Learners at The Various StagesMelanie SerquiñaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hand Outs Module 4 2Document10 paginiHand Outs Module 4 2Diane Hamor100% (1)
- Physical Development of Infants and ToddlersDocument31 paginiPhysical Development of Infants and ToddlersLeo Evidor100% (1)
- Stages of Development and Developmental TasksDocument6 paginiStages of Development and Developmental TasksJeyd Montefalco100% (1)
- Developmental TaskDocument9 paginiDevelopmental TaskJess ArceoÎncă nu există evaluări
- President Ramon Magsaysay State University Masinloc CampusDocument28 paginiPresident Ramon Magsaysay State University Masinloc CampusLeslie MarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Issues On Human Development: Study Guide For Module No. 4Document2 paginiIssues On Human Development: Study Guide For Module No. 4Darlene Dacanay DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Strengths and Weaknesses of The Filipino Character: A Socio-Cultural IssueDocument14 paginiThe Strengths and Weaknesses of The Filipino Character: A Socio-Cultural IssueJhonry CaalimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educ 101 Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument7 paginiEduc 101 Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesRessy Jean B. BesanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Development of Infants and Toddlers: Rodriguez, Jim Paul D. Endaya, Limwell G. Bse-1BeDocument31 paginiPhysical Development of Infants and Toddlers: Rodriguez, Jim Paul D. Endaya, Limwell G. Bse-1BeChristine Jaen De Aro100% (1)
- Module 9-Erickson's Psycho-Social Theory of DevelopmentDocument14 paginiModule 9-Erickson's Psycho-Social Theory of DevelopmentKimberly VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intructional Materials Module 23 26Document7 paginiIntructional Materials Module 23 26Josephine ArcibalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 1 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Document8 paginiUnit 1 Learner-Centered Psychological Principles (LCP)Merachell Jane50% (2)
- Infancy and ToddlerhoodDocument156 paginiInfancy and ToddlerhoodIrene Pulas100% (1)
- Module 1 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesDocument6 paginiModule 1 - The Child and Adolescent Learners and Learning PrinciplesMarkhill Veran Tiosan100% (1)
- BF Skinner Written ReportDocument3 paginiBF Skinner Written ReportKen TalkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Educ 101 Module 4Document13 paginiEduc 101 Module 4Francia Neil BasilioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 19: Cognitive Development of Primary SchoolersDocument15 paginiModule 19: Cognitive Development of Primary SchoolersChenang ItomayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Human Development-Meaning-ConceptsDocument18 paginiHuman Development-Meaning-ConceptsJulie ParicaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Typical and Atypical DevelopmentDocument17 paginiTypical and Atypical DevelopmentClarissa Roquero DaquioagÎncă nu există evaluări
- Module 20 Edcon3Document8 paginiModule 20 Edcon3Myra Belle Manlagnit100% (1)
- Gifted Children and StudentsDocument18 paginiGifted Children and Studentseric3862Încă nu există evaluări
- Supporting Children's Social Development: Positive Relationships in the Early YearsDe la EverandSupporting Children's Social Development: Positive Relationships in the Early YearsÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Path To Early Math: What Preschool Teachers Need to KnowDe la EverandThe Path To Early Math: What Preschool Teachers Need to KnowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report (Surface Plasmon Resonance)Document8 paginiReport (Surface Plasmon Resonance)waseemwaseem33Încă nu există evaluări
- Layout Strategies: © 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. 9 - 1Document17 paginiLayout Strategies: © 2008 Prentice Hall, Inc. 9 - 1jeams vidalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amateur Photographer - May 28, 2016Document84 paginiAmateur Photographer - May 28, 2016Lee100% (1)
- The Template For Physics EssayDocument13 paginiThe Template For Physics Essaylarisa2697Încă nu există evaluări
- Performance Enhancement in 5G Mobile Network Processing: Conference PaperDocument7 paginiPerformance Enhancement in 5G Mobile Network Processing: Conference PaperandrianÎncă nu există evaluări
- SFIDocument64 paginiSFIashwin71184Încă nu există evaluări
- Lib HydraulicDocument72 paginiLib HydraulicD'Armi StefanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bihar SI Mains Syllabus-024b287317594Document3 paginiBihar SI Mains Syllabus-024b287317594Aryan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ghis Manual (New)Document18 paginiGhis Manual (New)rookie100% (1)
- Chios Reiki Attunement ManualDocument12 paginiChios Reiki Attunement Manualkeithmac100% (1)
- Choosing A SolverDocument12 paginiChoosing A SolversnthejÎncă nu există evaluări
- QtreeDocument12 paginiQtreesaimadhukargÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Introduction To Windows Communication FoundationDocument18 paginiAn Introduction To Windows Communication FoundationArdit MeziniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 8 Term 3 Project 2021Document2 paginiGrade 8 Term 3 Project 2021Londiwe PrincessÎncă nu există evaluări
- A-13 BS Entrepreneurship - CBEMDocument7 paginiA-13 BS Entrepreneurship - CBEMJuliet Dechosa MajadasÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSC Issue 30Document32 paginiPSC Issue 30nkosidlaminiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quantitative Analysis For Management Ch06Document119 paginiQuantitative Analysis For Management Ch06Qonita NazhifaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stereotypes in General-Advantages and Disadvantages: Being Typically EnglishDocument2 paginiStereotypes in General-Advantages and Disadvantages: Being Typically EnglishDiana IrimieaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manual For Adjustment Inventory For: School Students (AISS)Document6 paginiManual For Adjustment Inventory For: School Students (AISS)Priyansh Patel67% (3)
- Memes As Participatory Politics: Understanding Internet Memes As A Form of American Political Culture in The 2016 United States Presidential ElectionDocument117 paginiMemes As Participatory Politics: Understanding Internet Memes As A Form of American Political Culture in The 2016 United States Presidential ElectionEmma Balfour91% (11)
- TG 9780060598242Document12 paginiTG 9780060598242Diego Escobar0% (1)
- GRSM Standard Operating Procedure: Backup, Storage & RecoveryDocument6 paginiGRSM Standard Operating Procedure: Backup, Storage & RecoveryMbazi MuzeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Lab Manual Nhce - UpdatedDocument41 paginiWeb Lab Manual Nhce - Updatedpoornima venkateshÎncă nu există evaluări
- MASTERY TEST IN SCIENCE 10 Module 3 Week 4Document3 paginiMASTERY TEST IN SCIENCE 10 Module 3 Week 4christine ann sta. mariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Army Launched Feeding Program in ComValDocument2 paginiArmy Launched Feeding Program in ComVal10idphilippinearmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- BILLE-SØRENSEN.2007.an Anthropology of Luminosity-The Agency of LightDocument22 paginiBILLE-SØRENSEN.2007.an Anthropology of Luminosity-The Agency of LightnaihloanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE Syllabus 22 June 2013Document19 paginiEEE Syllabus 22 June 20131manoj1Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5 - GasesDocument72 paginiChapter 5 - GasesAmbar WatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine DesignDocument376 paginiMachine Designssierro100% (5)
- Exam IDocument7 paginiExam IJoshMatthewsÎncă nu există evaluări