Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
IB Economics Paper 1: Merit, Demerit & Public Goods
Încărcat de
Harshil ChordiaTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
IB Economics Paper 1: Merit, Demerit & Public Goods
Încărcat de
Harshil ChordiaDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
IB Economics Higher Level Paper 1 (8, May 2006)
a. Carefully distinguish between merit goods, demerit goods and public goods
b. Evaluate the view that governments should always intervene in markets for
such goods as cigarettes and alcohol
a. Merit goods, demerit goods and public goods could all cause market failure,
which is a situation where goods and services in a free market are not allocated
efficiently. The ways in which these 3 kinds of goods cause market failure are different
and will be explained below.
Firstly, merit goods refer to goods with positive externalities. This means that its
consumption or production can create unintended positive consequences for third
parties. An example of a merit good is education. Education is likely to increase the
income of the consumer. Furthermore, education raises ones productivity, which in
turn benefits the society as a whole by increasing national income. Due to positive
externalities, the social marginal benefit of merit goods is greater than its private
marginal benefit. Consumers in a free market only consider private benefits when
purchasing and will therefore under-consume merit goods. This scenario can be
shown in the diagram 1 below.
Email: hkexcel.team@gmail.com page 1
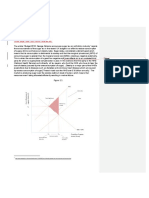
Diagram 1: The Free Market for Education
As shown in diagram 1, the socially optimal output occurs at Q2, which is when
SMB=SMC. However, the equilibrium in the free market occurs when D=S at Q1.
Between Q1 and Q2, SMB>SMB. Hence, the under-consumption of Q2-Q1 results in
welfare loss, which is equal to the shaded area.
Secondly, demerit goods are goods with negative externalities, which has unintended
negative consequences to its consumption or production. One example is cigarettes,
because smokers create pollution and harm the society as a whole. As a result of
negative externalities, demerit goods marginal social benefit is less than marginal
private benefit. Thus, consumers will over-consume demerit goods, like shown in
diagram 2 below.
Diagram 2: The Free Market for Cigarettes
Email: hkexcel.team@gmail.com page 2
In a free market, demerit goods are over-consumed by a quantity equal to Q1-Q2.
Between Q1-Q2, SMC>PMB. Thus, there is welfare loss equal to the shaded area.
Thirdly, public goods refer to goods which total cost of production does not increase
with the number of consumers. The two main features of public goods are non-rivalry
and non-excludability. An example of public good is national defense.
Non-excludability refers to the fact that it is impractical in real life to stop people from
consuming public goods, which makes it also impossible for producers to make profits.
Non-rivalrous means that an additional unit of consumption does not increase
marginal costs. For allocative efficiency to be achieved, MC=MB. However, a
non-rivalrous good have a MC of 0, which means that price must also be 0 in order for
allocative efficiency to be achieved. Due to the above reasons, public goods does not
allow for profits to be made and will not be produced in a free economy, which is a
case of market failure.
b) As mentioned above, a cigarettes and alcohol are demerits good, which are
overconsumed in a free-market. Governments can intervene the market in various
ways to reduce equilibrium quantity and move it closer to the socially optimal level.
However, all government policies has its costs. The two most common way for
governments to intervene for the alcohol and cigarettes market is through
advertisement/education and by imposing indirect taxes.
By educating and advertising to consumers on the harms of cigarettes, the
government can change the consumers preference and reduce the market demand
for cigarettes. In effect, the demand curve will shift to the left and the welfare loss will
decrease. An example of such advertisements is in Hong Kong, where government
print on all cigarette boxes that cigarettes cause lung cancer. One disadvantage of
advertisement and education is that it must be large-scale in order for it to be effective,
which also implies a high cost. It is also difficult to measure the effectiveness of
various advertisements because of its disperse nature. Moreover, it will take a long
time to significantly reduce the demand for cigarettes and alcohol, because they are
addictive goods. Furthermore, the fall in output of cigarette could cause
unemployement and a reduction in national income in the long run. For a country with
high production of cigarettes, such as China which is the largest producer of
cigarettes globally, this could reduce national income and cause unemployment.
Labourers who work in the supply chain of cigarettes could suffer from structural
unemployment, where their skills cant be matched to jobs in the job market. On the
Email: hkexcel.team@gmail.com page 3
other hand, one advantage of education over tax is that the decline in output for
education is more gradual, which allows more time for the economy to restructure and
absorb the unemployed workers. Another advantage of advertisement over tax is that
it does not reduce addicted smokers disposable income.
An indirect tax is a fixed amount of tax that consumers pay for consuming a good or a
service. Imposing indirect tax on cigarettes and alcohol is equivilent to increasing
producers cost. In effect, the supply curve will shift to the left and quantity will fall to a
level that is nearer to the socially optimal point. The indirect tax will have an
immediate effect of increasing price and reduce quantity. However, it is important to
note that price elasticity of demand (PED) is generally lower in the short run than in
the long run. Thus, quantity should increase by a relatively small amount in the short
run and by a larger amount in the long run. The main advantage of tax is that it
generates revenue for the government and could be a feasible solution for a
government on a budget deficit, such as the U.S government. Tax revenue is likely to
be high in the short run and gradually decrease over the long run. This is because
PED is lower in the short run. If PED is low, then consumers will respond less to an
increase in price, which means that many consumers will continue to purchase
cigarettes and pay tax to the government. Similar to education, the main concern to
tax is that it will reduce output and can cause unemployment. Moreover, because tax
could reduce output in a relatively short period of time, the economy will have less
time to restructure and absorb the unemployed workers. Lastly, indirect tax could
reduce the disposable incomes of addictive smokers who will continue to smoke even
if price rises. In lower income regions such as in poorer provinces in China with many
addictive smokers, the tax could reduce smokers welfare by reducing their
disposable income.
Both solutions mentioned could reduce welfare loss in the case of market failure
arising from demerit goods. However, there are also costs associated with each
solution, such as unemployment and reduction of disposable. It is important for
governments to evaluate the economic environment of their countries before making
a decision on whether or not to intervene. If the addicted smokers in a country are
usually lower income individuals, then the government should lower the amount of tax
to impose. If the national income is highly dependent on cigarette and alcohol
production, a government should choose to use advertisement instead of tax so that
more time would be allowed for the economy to restructure. In conclusion,
government intervention is beneficial for the economy in the long run, but it should be
Email: hkexcel.team@gmail.com page 4
implemented sensibly and carefully to reduce costs and short run shocks to the
economy.
Website
http://hkexcel.droppages.com
Facebook fanpage:
http://www.facebook.com/pages/Hkexcel
Email: hkexcel.team@gmail.com page 5
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Great Vegan Protein Book PDFDocument179 paginiThe Great Vegan Protein Book PDFHarshil Chordia100% (3)
- Traders World Magazine - Issue #51 - "NakedSwan Trading" by EfremHoffmanDocument12 paginiTraders World Magazine - Issue #51 - "NakedSwan Trading" by EfremHoffmanNaked Swan Trading ( Efrem Hoffman )25% (4)
- Market Failure Tutor2uDocument28 paginiMarket Failure Tutor2usharmat1963Încă nu există evaluări
- Alliancing Best Practice PDFDocument48 paginiAlliancing Best Practice PDFgimasaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indonesia to Revise Tobacco Tax Policy in 2018Document6 paginiIndonesia to Revise Tobacco Tax Policy in 2018Michelle Elie T.100% (1)
- VAT rules and calculationsDocument19 paginiVAT rules and calculationsrav dano0% (1)
- Consumer Surplus and Price Elasticity of DemandDocument8 paginiConsumer Surplus and Price Elasticity of Demandsweetice79Încă nu există evaluări
- Obama's Proposed 94-Cent Cigarette Tax Hike DebatedDocument8 paginiObama's Proposed 94-Cent Cigarette Tax Hike Debatedcorlisschan12030% (1)
- Presentation Flow: Public © 2023 SAP SE or An SAP Affiliate Company. All Rights Reserved. ǀDocument31 paginiPresentation Flow: Public © 2023 SAP SE or An SAP Affiliate Company. All Rights Reserved. ǀAbhijeet PawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing AssignmentDocument16 paginiMarketing AssignmentkcperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Paper 1 Exemplar Peer Assessment ActivityDocument7 paginiPaper 1 Exemplar Peer Assessment ActivityMrsalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Why governments impose indirect taxes on cigarettesDocument4 paginiWhy governments impose indirect taxes on cigarettesMrsalemÎncă nu există evaluări
- Imposition of Indirect Tax On Cigarettes in Pakistan - Abdullah ADocument3 paginiImposition of Indirect Tax On Cigarettes in Pakistan - Abdullah AjoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taiwan Cigarrete Tax IA V DraftDocument4 paginiTaiwan Cigarrete Tax IA V DraftAngelina ProtikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microeconomics Commentary Number 1Document6 paginiMicroeconomics Commentary Number 1gqf94jy9rtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Increased tobacco tax encourage quittingDocument3 paginiIncreased tobacco tax encourage quittingFaridaÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB Economics SL Paper 1 Question Bank - TYCHRDocument25 paginiIB Economics SL Paper 1 Question Bank - TYCHRansirwayneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulate and Tax VapingDocument6 paginiRegulate and Tax VapingSyazwan KhirudinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market Failure EssayDocument3 paginiMarket Failure EssayJenney TatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prerna Micro CommentaryDocument6 paginiPrerna Micro CommentaryHRITIK JAINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Edexcel Economics AS-level Series Complete NotesDocument8 paginiEdexcel Economics AS-level Series Complete NotesShahab HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- (4b.) Negative Consumption Externalities (Types of Market Failure) - NotesDocument10 pagini(4b.) Negative Consumption Externalities (Types of Market Failure) - NotesDBXGAMINGÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic 25 Mark Question 1Document2 paginiEconomic 25 Mark Question 1api-294491435Încă nu există evaluări
- Oman To Impose 100% Tax On Cigarettes and Booze: Economics Commentary ArticleDocument3 paginiOman To Impose 100% Tax On Cigarettes and Booze: Economics Commentary ArticleXI IBDPÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluating Arguments For and Against Taxing AlcoholDocument3 paginiEvaluating Arguments For and Against Taxing AlcoholTammy AÎncă nu există evaluări
- IB IA Commentary Econs HL exampleDocument16 paginiIB IA Commentary Econs HL examplemariahkhedherÎncă nu există evaluări
- EconomicsDocument5 paginiEconomicsMehedi Hasan DurjoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReportDocument5 paginiReportTRESOR DUSABEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exemplar For Internal Achievement Standard Economics Level 3Document16 paginiExemplar For Internal Achievement Standard Economics Level 3Po PoÎncă nu există evaluări
- ch-15Mixed-economic-system-ecoDocument7 paginich-15Mixed-economic-system-ecoaangijain646Încă nu există evaluări
- 1.4. Government InterventionDocument11 pagini1.4. Government InterventionJoel KennedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Markets in Action Essay QsDocument12 paginiMarkets in Action Essay Qsmkc306Încă nu există evaluări
- Econ Commentary InternationalDocument25 paginiEcon Commentary Internationaltrayi reddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economic IA CommentaryDocument6 paginiEconomic IA Commentarynaman agarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ib HL Economics Commentary 1 Microeconomics Alcohol PDFDocument4 paginiIb HL Economics Commentary 1 Microeconomics Alcohol PDFMohd UvaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microeconomics Commentary on Demerit Goods and ExternalitiesDocument4 paginiMicroeconomics Commentary on Demerit Goods and ExternalitiesMohd UvaisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microecon IA - Div MittalDocument7 paginiMicroecon IA - Div Mittaldiv.mittalÎncă nu există evaluări
- 14.5 Government Intervention in The MarketDocument3 pagini14.5 Government Intervention in The MarketJerome AndresÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4.0 Negative Externality: Issue of Consumption of CigarettesDocument5 pagini4.0 Negative Externality: Issue of Consumption of CigarettesnadiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment. 2Document5 paginiAssignment. 2hamaelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Econs Sample IADocument2 paginiEcons Sample IAAmos Aloysius LauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco Com 1 AnantDocument5 paginiEco Com 1 AnantAnant JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- EcoooooDocument3 paginiEcoooooKirti VeerasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Indiana Cigarette Tax Proposal Targets Medicaid CostsDocument27 paginiIndiana Cigarette Tax Proposal Targets Medicaid CostsCK OngÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impact of Government Intervention in the Cigarette MarketDocument2 paginiImpact of Government Intervention in the Cigarette Marketzainab MuhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Negative Externality QuestionsDocument3 paginiNegative Externality QuestionsLiam VandewalleÎncă nu există evaluări
- 01 Demerit GoodsDocument7 pagini01 Demerit Goodsa.mathew1592Încă nu există evaluări
- Igcse Economics Notes On Market Failure and Government InterventionDocument6 paginiIgcse Economics Notes On Market Failure and Government InterventionYuwu24Încă nu există evaluări
- Smoke and MirrorsDocument5 paginiSmoke and Mirrorsnupur_junejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eco Section 2 Chapters 14 and 15Document7 paginiEco Section 2 Chapters 14 and 15Jiya YadukulÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Are Externalities?Document19 paginiWhat Are Externalities?elizabeth nyasakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market FailureDocument6 paginiMarket FailureZara0% (1)
- 1.3. Market FailureDocument6 pagini1.3. Market FailureJoel KennedyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.10-2.11 Market Failure and Government InterventionDocument5 pagini2.10-2.11 Market Failure and Government Interventiongrayce limÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1.3. Market FailureDocument8 pagini1.3. Market Failureasadshareef2005Încă nu există evaluări
- Eco Post 3Document3 paginiEco Post 3api-296801970Încă nu există evaluări
- Commentary2 Draft3Document3 paginiCommentary2 Draft3Jason ZhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics SAT 2Document4 paginiEconomics SAT 2Henry MonaghanÎncă nu există evaluări
- GDP alone does not determine quality of lifeDocument10 paginiGDP alone does not determine quality of lifeMildred MeltonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cover Page / Title / Your Name / Date Etc Etc.: DeletedDocument3 paginiCover Page / Title / Your Name / Date Etc Etc.: Deletedgauri kanodiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Economic Ideas and Resource AllocationDocument54 paginiBasic Economic Ideas and Resource AllocationShaurya SaksenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Government Intervention - Taxes and SubsidiesDocument10 paginiGovernment Intervention - Taxes and SubsidiesfantasybookwyrmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Economics IADocument4 paginiEconomics IA8rp8fkkqgpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market Failure Response QuestionsDocument4 paginiMarket Failure Response QuestionsSammy PearceÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIE Economics A-level Topic 3: Government Microeconomic Intervention NotesDocument12 paginiCIE Economics A-level Topic 3: Government Microeconomic Intervention NotesFarzan AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Freer Markets Within the Usa: Tax Changes That Make Trade Freer Within the Usa. Phasing-Out Supply-Side Subsidies and Leveling the Playing Field for the Working Person.De la EverandFreer Markets Within the Usa: Tax Changes That Make Trade Freer Within the Usa. Phasing-Out Supply-Side Subsidies and Leveling the Playing Field for the Working Person.Încă nu există evaluări
- ECS658 U04 Collection TypesDocument64 paginiECS658 U04 Collection TypesHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fixedline and Broadband Bill DetailsDocument3 paginiFixedline and Broadband Bill DetailsHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assignment Briefing (Level 6)Document11 paginiAssignment Briefing (Level 6)Harshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Time: 09.00-13.00: ECS658U Further Object Oriented Programming Test: 18 November 2020Document5 paginiTime: 09.00-13.00: ECS658U Further Object Oriented Programming Test: 18 November 2020Harshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cor On Va Virus Helpline NumberDocument1 paginăCor On Va Virus Helpline NumberAim Softnet IT ProfessionalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Report ContentsDocument2 paginiSample Report ContentsHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Further Object Oriented Programming "FOOP" and Basic Aspects of OOPDocument70 paginiFurther Object Oriented Programming "FOOP" and Basic Aspects of OOPHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECS658 U05 Design PrinciplesDocument130 paginiECS658 U05 Design PrinciplesHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECS658 U03 OOPBasic AspectsDocument65 paginiECS658 U03 OOPBasic AspectsHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project DefinitionDocument3 paginiProject DefinitionUmar AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acceptance Tests:: Application Crashed (Unexpected Behaviour)Document1 paginăAcceptance Tests:: Application Crashed (Unexpected Behaviour)Harshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics-HL IADocument8 paginiPhysics-HL IAHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECS658 U02 Programming LanguagesDocument61 paginiECS658 U02 Programming LanguagesHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Society Wars SummaryDocument4 paginiSociety Wars SummaryHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Further Object Oriented Programming "FOOP" and Basic Aspects of OOPDocument70 paginiFurther Object Oriented Programming "FOOP" and Basic Aspects of OOPHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemistry Vant Hoff's Factor Calculation, by Elevation in Boiling PointDocument18 paginiChemistry Vant Hoff's Factor Calculation, by Elevation in Boiling PointMukesh Hacker63% (8)
- Suspension of Disbelief Is Essential To KnowledgeDocument1 paginăSuspension of Disbelief Is Essential To KnowledgeHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boiling Point Elevation LabDocument5 paginiBoiling Point Elevation LabHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Topic 3 QDocument23 paginiTopic 3 QAmrutha LakshmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- "Mconnect Plus" Application From - GOOGLE PLAYSTORE (For Android Users) APP STORE (For iOS Users) WINDOWS STORE (For Windows Users)Document3 pagini"Mconnect Plus" Application From - GOOGLE PLAYSTORE (For Android Users) APP STORE (For iOS Users) WINDOWS STORE (For Windows Users)Nancy PatodiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ibdp Exam Nov.2017 (TT)Document2 paginiIbdp Exam Nov.2017 (TT)Harshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SyllabusDocument2 paginiSyllabusHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- GiftjapDocument1 paginăGiftjapTabeeba MaryamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Duilib LicenseDocument1 paginăDuilib Licensecoolarun1980Încă nu există evaluări
- Calculating average arrival and service ratesDocument10 paginiCalculating average arrival and service ratesHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HL Book One D PDFDocument61 paginiHL Book One D PDFIndraneel BhattacharjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sat Practice Test 1 Essay PDFDocument4 paginiSat Practice Test 1 Essay PDFHarshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What CPU Should I Buy v3Document9 paginiWhat CPU Should I Buy v3Harshil ChordiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Portfoli o Management: A Project OnDocument48 paginiPortfoli o Management: A Project OnChinmoy DasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 13Document31 paginiChapter 13batataÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICODEV Abstract FixDocument49 paginiICODEV Abstract Fixbp bpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enter Pen Eur ShipDocument7 paginiEnter Pen Eur ShipMuskan Rathi 5100Încă nu există evaluări
- Investment and Portfolio AnalysisDocument6 paginiInvestment and Portfolio AnalysisMuhammad HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- BVDCDocument22 paginiBVDCErica CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labour Law Notes GeneralDocument55 paginiLabour Law Notes GeneralPrince MwendwaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 CombinedDocument405 pagini1 CombinedMansi aggarwal 171050Încă nu există evaluări
- Proposal Change Management AmendmentDocument21 paginiProposal Change Management Amendmentyesuf abdulhakimÎncă nu există evaluări
- FFCDocument17 paginiFFCAmna KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CapitalCube - GBDC - GBDC US Company Reports - 4 PagesDocument4 paginiCapitalCube - GBDC - GBDC US Company Reports - 4 PagesSagar PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec 6 QuizDocument3 paginiLec 6 QuizWennie NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nov 19Document37 paginiNov 19kunal kumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reactions of Capital Markets To Financial ReportingDocument25 paginiReactions of Capital Markets To Financial ReportingnarmadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Economic ProblemDocument22 paginiThe Economic ProblemPeterÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sustainability Planning Workshop Budget ProposalDocument7 paginiSustainability Planning Workshop Budget ProposalArnel B. PrestoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SELLING SKILLS: CUSTOMER-CENTRIC STRATEGIESDocument19 paginiSELLING SKILLS: CUSTOMER-CENTRIC STRATEGIESNatsu DeAcnologiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Labrel CBA Counter Propo Part 1Document12 paginiLabrel CBA Counter Propo Part 1TrudgeOnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Politicas Publicas EnergeticasDocument38 paginiPoliticas Publicas EnergeticasRodrigo Arce RojasÎncă nu există evaluări
- EtopDocument11 paginiEtopMohamed AadhilÎncă nu există evaluări
- My India in 2047Document3 paginiMy India in 2047Karttikeya Mangalam NemaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Price Per Visit Quantity Demanded Quantity SuppliedDocument4 paginiPrice Per Visit Quantity Demanded Quantity SuppliedGrace FranzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Order in The Matter of M/s Kinetic Capital Services Limited & M/s Shubh International LimitedDocument8 paginiOrder in The Matter of M/s Kinetic Capital Services Limited & M/s Shubh International LimitedShyam SunderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kalamba Games - 51% Majority Stake Investment Opportunity - July23Document17 paginiKalamba Games - 51% Majority Stake Investment Opportunity - July23Calvin LimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tesalt India Private LimitedDocument16 paginiTesalt India Private LimitedSaiganesh JayakaranÎncă nu există evaluări