Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Intro To Philo
Încărcat de
Laylo JayceeTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Intro To Philo
Încărcat de
Laylo JayceeDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
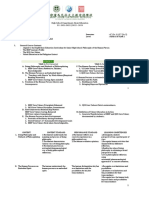
K to 12 BASIC EDUCATION CURRICULUM
SENIOR HIGH SCHOOL CORE SUBJECT
Introduction to the Philosophy of the Human Person Grade: 12 Semester:1
No. of Hours/ Semester: 80 Pre-requisite (if needed): Core Subject
Course Subject Description: An initiation to the activity and process of philosophical reflection as a search for a synoptic vision of life. Topics to be discussed
include the human experiences of embodiment, being in the world with others and the environment, freedom, intersubjectivity, sociality, being unto death.
Course objectives: At the end of the course, the student should be able to:
1. Reflect on their daily experiences from a holistic point of view
2. Acquire Critical and Analytical Thinking skills
3. Apply their critical and analytical thinking skills to the affairs of daily life
4. Become truthful, environment-friendly and service-oriented
5. Actively committed to the development of a more humane society
6. Articulate their own philosophy of life
Over-all Standard for Grade 12: The learner should be able to demonstrate a capacity for a critical and analytical reflection from the perspective of a holistic and
profound vision of life.
First Grading Period:The meaning and method of doing philosophy in relation to the human person as an emobodied being in the world and the
environment Standard Content: The student should be able to show an understanding of the activity of doing philosophy of the human person as an
embodied being in the world and the environment Foundational Concept: Understanding the meaning and process of doing philosophy of the human
person as an embodied being in the world and the environment as a means towards a holistic understanding of life.
CONTENT CONTENT STANDARD PERFORMANCE STANDARD LEARNING COMPETENCIES REFERENCES
1. Nature of Philosophy The learner understands the The learner utilizes the view 1.1 Define the meaning of
nature of Philosophy as a way of the particular school of Philosophy
in searching the truth and the thought in explaining certain 1.2 Realize that Philosophy as
various philosophical schools action. a way of searching the
truth
1.3 Compare and contrast the
different philosophical
view.
1.4 Apply several
philosophical thoughts in
explaining certain
phenomenon
2. Doing Philosophy The learner understands the The learner reflects on a 2.1 Distinguish a holistic
meaning and process of doing concrete experience in a perspective from a partial
philosophy philosophical way point of view
2.2 Recognize human
activities that emanated
from deliberate reflection
2.3 Realize the value of doing
philosophy in obtaining a
broad perspective on life
2.4 Do philosophical
reflection on a concrete
situation from a holistic
perspective
3. Methods of The learner demonstrates The learner evaluate facts, 3.1 Distinguish fact from
philosophizing various ways of doing truths, and opinions truth, and truth from
philosophy opinion
3.2 Analyze situations that
show the difference
between fact, truth and
opinion
3.3 Analyze the situations
that show fallacies and
biases
3.4 Realize that the methods
of philosophy lead to
wisdom and truth
3.5 Evaluate fact, truth and
opinions
4. The human person as an The learner understands the The learner distinguishes 4.1 Recognize own limitations
embodied spirit human person as an his/her own limitations and and possibilities
embodied spirit the possibilities for his/her 4.2 Evaluate own limitations
transcendence and the possibilities for
their transcendence
4.3 Recognize how the
human body imposes
limits and possibilities for
transcendence
4.4 Distinguish the limitations
and possibilities for
transcendence
5. The human person in The learner understands the The learner is able to 5.1 Notice disorder in an
their environment interplay between humans demonstrate the virtues of environment
and their environments prudence and frugality 5.2 Notice things that are not
towards his/her environment in their proper place and
organize them in an
aesthetic way
5.3 Show that care for the
environment contributes
to health, well-being and
sustainable development
5.4 Demonstrate the virtues
of prudence and frugality
towards environments
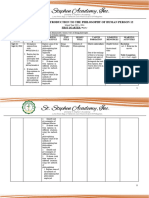
Second Grading Period: Human Living Standard Content: The learner is able to show an understanding of philosophy within the context of the human person
as free, intersubjective, and immersed in society and oriented towards death. Fundamental Concept: The learner is able to understand that doing philosophy
within the context of the human person as free, intersubjective, immersed in society, and oriented towards their impending death will lead to a deeper
understanding of the human person.
CONTENT CONTENT STANDARD PERFORMANCE STANDARD COMPETENCIES REFERENCES
6. Freedom of the human The learner understands the The learner shows situations 6.1 Understand the concepts Readings on the works of
person human persons freedom that demonstrate freedom of of freedom. John Locke, Jean Jacques
choice and the consequences 6.2 Realize that all actions Rousseau, Arthur
of choices have consequences. Schopenhauer, Jean-Paul
6.3 Evaluate and exercise Sartre, and Skinner
prudence in choices
6.4 Realize that:
a. Choices have
consequences
b. Some things are given
up while others are
obtained in making
choices
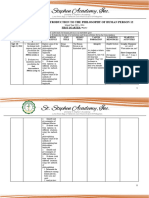
7. Intersubjectivity The learner understands The learner performs 7.1 Realize that
intersubjective human activities that demonstrate an intersubjectivity requires
relations appreciation for the talents of accepting differences and
persons with disabilities and not to imposing on others
those from the 7.2 Appreciate the talents of
underprivileged sectors of persons with disabilities
society and those from the
underprivileged sectors of
society and their
contributions to society
7.3 Explain that authentic
dialogue means accepting
others even if they are
different from themselves
7.4 Perform activities that
demonstrate the talents
of persons with
disabilities and those
from the underprivileged
sectors of society
8. The Human Person in The learner understands the The learner evaluates the 8.1 Recognize how
Society interplay between the formation of human individuals form societies
individuality of human beings relationships and how and how individuals are
and their social contexts individuals are shaped by transformed by societies
their social contexts 8.2 Compare different forms
of societies and
individualities (eg.
Agrarian, industrial and
virtual) Readings on;
8.3 Analyze the various ideas The Golden Mean by Aristotle
put forward by Capitalism by Adam Smith
philosophers and Communism by Marx
contemporary thinkers The Public by Plato
(i.e Aristotle, Smith, Marx, Seven Social Sins by Gandhi
Plato, Gandhi, etc.) I Have A Dream by Martin
towards a better society. Luther King Jr.
8.4 Explain how human
relations are transformed
by social systems
8.5 Evaluate the
transformation of human
relationships by social
systems and how
societies transform
individual human beings.
9. Human persons as The learner understands The learner writes a 9.1 Recognize the meaning of
oriented towards their human beings as oriented philosophical reflection on his/her own life
impending death towards their impending the meaning of his/her own 9.2 Enumerate the objectives
death life he/she really wants to
achieve and to define the
projects he/she really
wants to do in his/her life
9.3 Explain the meaning of
life (where will all these
lead to)
9.4 Reflect on the meaning of
his/her own life.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nuestra Señora de Aranzazu Parochial School: Gen. Luna Street, Guitnangbayan I, San Mateo, Rizal, 1850, PHILIPPINESDocument6 paginiNuestra Señora de Aranzazu Parochial School: Gen. Luna Street, Guitnangbayan I, San Mateo, Rizal, 1850, PHILIPPINESBlandamier Salazar CaritanÎncă nu există evaluări
- An Integrative Habit of Mind: John Henry Newman on the Path to WisdomDe la EverandAn Integrative Habit of Mind: John Henry Newman on the Path to WisdomÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Philosophy of Human NatureDocument3 paginiIntroduction To Philosophy of Human NatureGENELYN BURGOSÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHS Core - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person CGDocument5 paginiSHS Core - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person CGRosa G. JagmocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Budget of Works Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person S.Y. 2021-2022Document4 paginiBudget of Works Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person S.Y. 2021-2022Bethuel Pacasit AlquirozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Template - CurriculumDocument20 paginiTemplate - CurriculumKyle Eco FostanesÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL in Philo Week 1Document5 paginiDLL in Philo Week 1Jeorge RagadioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning-Plan-Philosophy 12-Week 2Document4 paginiLearning-Plan-Philosophy 12-Week 2Joyce Lynel LapitanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HUMSS Competencies For WHLPDocument8 paginiHUMSS Competencies For WHLPBemBemÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHS Core - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person CGDocument6 paginiSHS Core - Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person CGmyla aguadoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning-Plan-Philosophy 12-Week 3Document3 paginiLearning-Plan-Philosophy 12-Week 3Joyce Lynel LapitanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cidam Intro To Philo MichaelDocument5 paginiCidam Intro To Philo MichaelSupl4do Balilihan100% (1)
- Week 1 DLL - PhilosophyDocument3 paginiWeek 1 DLL - PhilosophyGary FantilaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hobby pdf2Document7 paginiHobby pdf2Lorenzo CarreonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Budget of Lesson Intro To PhiloDocument4 paginiBudget of Lesson Intro To PhiloJake Anthony Majadillas100% (2)
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The HumanDocument5 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The HumanHenn liÎncă nu există evaluări
- TOS For MIDTERM in PhilosophyDocument2 paginiTOS For MIDTERM in PhilosophyHeriberto Jr. BongultoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL in Philosophy of The Human Person by Materesa BerondoDocument3 paginiDLL in Philosophy of The Human Person by Materesa BerondoAlbert Gevero FalsarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL Philo Week 1Document3 paginiDLL Philo Week 1NESTOR BARUN CORDERO JR.Încă nu există evaluări
- Learning-Plan-Philosophy 12-Week 1Document2 paginiLearning-Plan-Philosophy 12-Week 1Joyce Lynel LapitanÎncă nu există evaluări
- December 9-12, 2019 Introduction To PhilosophyDocument2 paginiDecember 9-12, 2019 Introduction To PhilosophyMelody Landicho100% (2)
- Truth and OpinionDocument7 paginiTruth and OpinionMarison ElaurzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week A - Doing PhilosophyDocument5 paginiWeek A - Doing PhilosophyLouweben MaquizoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week A - Doing PhilosophyDocument5 paginiWeek A - Doing PhilosophyStarLord JedaxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Objectives & SyllaDocument11 paginiObjectives & SyllaRobert NuquiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MELCs - SLMs MatchingDocument1 paginăMELCs - SLMs Matchingaria jen05Încă nu există evaluări
- Daily Lesson Log in PhilosophyDocument5 paginiDaily Lesson Log in PhilosophyMark Vincent Fernandez0% (1)
- Week A - Doing PhilosophyDocument5 paginiWeek A - Doing PhilosophyArvin CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 9Document4 paginiLesson 9Pearl Arianne Moncada MontealegreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan - PhilosophyDocument4 paginiLesson Plan - PhilosophyFrancis Osias Silao100% (2)
- DLL 1stq - W2-W3Document4 paginiDLL 1stq - W2-W3Naneth AlavarenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grades 11 PHILOSOPHY NOV. 25-28,2019Document6 paginiGrades 11 PHILOSOPHY NOV. 25-28,2019Melody LandichoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Philosophy Syllabus-2022-2023-ShsDocument12 paginiIntroduction To Philosophy Syllabus-2022-2023-ShsJan Ralph RectoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MODIFIED-DLL-SH-Intro To Philo Q3 Week 2Document2 paginiMODIFIED-DLL-SH-Intro To Philo Q3 Week 2anamayamigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade Level: 12 Senior High School (Core) Subject: Introduction To Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument2 paginiGrade Level: 12 Senior High School (Core) Subject: Introduction To Philosophy of The Human PersonGracey Sagario Dela TorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhilosophyDocument80 paginiPhilosophyRechelleRuthM.DeiparineÎncă nu există evaluări
- PD Week A - Doing PhilosophyDocument5 paginiPD Week A - Doing PhilosophyAngelie Pasag Garcia100% (1)
- DLP PhilosophyDocument3 paginiDLP PhilosophyNinia Mae PueblaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philosophy DLLDocument10 paginiPhilosophy DLLGiljohn SoberanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The HDocument138 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The HChristian PrudencianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonDocument49 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human PersonKIMBERLY AGUSTINÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Pambungad Sa Pilosopiya NG Tao DLPDocument136 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Pambungad Sa Pilosopiya NG Tao DLPREN CAREÎncă nu există evaluări
- VE Course Content Orientation July 27 2021Document5 paginiVE Course Content Orientation July 27 2021BREANNA ERYLLE LIAOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Pambungad Sa Pilosopiya NG Tao DLPDocument145 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Pambungad Sa Pilosopiya NG Tao DLPIrjane Eunice Leonoras AndicoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Learning-Plan-Philosophy 12-Week 4-5Document3 paginiLearning-Plan-Philosophy 12-Week 4-5Joyce Lynel LapitanÎncă nu există evaluări
- W2 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person-WEEKLY-LEARNINGDocument3 paginiW2 Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person-WEEKLY-LEARNINGMari Opoc100% (1)
- Week 1 DLPDocument5 paginiWeek 1 DLPTotep ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Pambungad Sa Pilosopiya NG Tao DLPDocument126 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Pambungad Sa Pilosopiya NG Tao DLPSteffi80% (5)
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The HDocument126 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The HMary joyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week A - Doing PhilosophyDocument5 paginiWeek A - Doing Philosophyjulie roseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Pambungad Sa Pilosopiya NG Tao DLPDocument126 paginiIntroduction To The Philosophy of The Human Person Pambungad Sa Pilosopiya NG Tao DLPSu Zette100% (1)
- 1 Doing PhilosophyDocument4 pagini1 Doing PhilosophylenieÎncă nu există evaluări
- All DLL PhilosophyDocument136 paginiAll DLL PhilosophyNotsla Anabieza100% (2)
- DLL Philosophy QUARTER 1 WEEK 3Document4 paginiDLL Philosophy QUARTER 1 WEEK 3franchezkalidalivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philo. Q1 Week 2Document3 paginiPhilo. Q1 Week 2Michelle Cañedo VerdeflorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical ThinkingDocument85 paginiCritical ThinkingCollins LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- DLL in Philosophy of The Human Person by Ma - Teresa BerondoDocument3 paginiDLL in Philosophy of The Human Person by Ma - Teresa BerondoMaTeresa Berondo100% (3)
- DLL Intro To Philosophy of The Human Person 11 17-20Document3 paginiDLL Intro To Philosophy of The Human Person 11 17-20RheaMaravilla100% (10)
- Week A - Doing PhilosophyDocument4 paginiWeek A - Doing PhilosophyMarilyn EstebeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Incorporating Childrens LiteratureDocument6 paginiIncorporating Childrens Literatureapi-281272453Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology - Syllabus TemplateDocument6 paginiPharmacology - Syllabus TemplateJeffrey RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICT PolicyDocument10 paginiICT Policystcronans100% (1)
- Tan Sri Dato Muhyiddin Mohd Yassin: Reaching The Unreached in Malaysia Through EducationDocument2 paginiTan Sri Dato Muhyiddin Mohd Yassin: Reaching The Unreached in Malaysia Through EducationShirLey NgoiÎncă nu există evaluări
- TSL3213 Task 2a Written Speech - Auni AfifahDocument2 paginiTSL3213 Task 2a Written Speech - Auni AfifahTESL1-0619 Auni Afifah Binti Otoh SibikÎncă nu există evaluări
- KRA, Objectives, MOVsDocument31 paginiKRA, Objectives, MOVsQueenie Anne Soliano-Castro100% (1)
- Not Poor, Just BrokeDocument4 paginiNot Poor, Just BrokeEunice Criselle Garcia67% (3)
- Ict Week 7Document4 paginiIct Week 7Rutchie Quillo Tuando0% (1)
- Edtpa Task 2 - Part BDocument4 paginiEdtpa Task 2 - Part Bapi-273801384100% (1)
- Special NeedsDocument92 paginiSpecial NeedsYoss Iraí San Ro100% (1)
- September 2013Document163 paginiSeptember 2013pedro1159755Încă nu există evaluări
- Primêre Skool Worcester Primary School: Helping With HomeworkDocument4 paginiPrimêre Skool Worcester Primary School: Helping With HomeworkWorcPrimerÎncă nu există evaluări
- MBA - 102 Business EnvironmentDocument4 paginiMBA - 102 Business EnvironmentAnwar100% (2)
- Educational Publishing and Book Distribution in Uganda (Ikoja-Odongo & BatambuzeDocument14 paginiEducational Publishing and Book Distribution in Uganda (Ikoja-Odongo & BatambuzejwojomekÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRC Learning and Teaching P2PDocument107 paginiPRC Learning and Teaching P2Pkhadija abbasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ela Service Learning Lesson Plan 1Document3 paginiEla Service Learning Lesson Plan 1api-490377001Încă nu există evaluări
- Critical Literature ReviewDocument55 paginiCritical Literature Reviewcth_yao100% (1)
- The Person I Admire The MostDocument2 paginiThe Person I Admire The MostJun 俊佳Încă nu există evaluări
- Sop ManagementDocument1 paginăSop ManagementEngr Rj SaadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Portfolio RubricDocument2 paginiPortfolio Rubricapi-245166476Încă nu există evaluări
- Week: 3 Class / Subject Time Topic/Theme Focus Skill Content Standard Learning Standard Learning ObjectivesDocument9 paginiWeek: 3 Class / Subject Time Topic/Theme Focus Skill Content Standard Learning Standard Learning ObjectivesAlya FarhanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Action Pack 7 TBDocument128 paginiAction Pack 7 TBarabiaedu50% (8)
- Constructing Objective Paper and Pencil TestDocument12 paginiConstructing Objective Paper and Pencil TestJelyn Rentoria100% (1)
- My Teacher, My HEroDocument4 paginiMy Teacher, My HEroMaria Victoria Padro0% (1)
- Individual Learner's Record (LR)Document1 paginăIndividual Learner's Record (LR)JeTT LeonardoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4 Instructional MethodsDocument23 pagini4 Instructional MethodsNhial AbednegoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Harsha PriyaDocument3 paginiHarsha PriyaSudha Prabhakar ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIW Student TextbookDocument390 paginiCIW Student Textbookcoollover100% (3)
- CHAPTER 4 - The Teaching ProfessionDocument23 paginiCHAPTER 4 - The Teaching ProfessionAldrin Cagnaan SatiniamanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 344fall 07syllabusDocument1 pagină344fall 07syllabusapi-3808925Încă nu există evaluări