Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Part of Speech
Încărcat de
Srinivasan KannanDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Part of Speech
Încărcat de
Srinivasan KannanDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
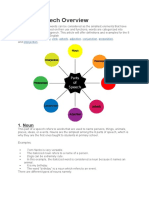
n the English language, words can be considered as the smallest
elements that have distinctive meanings. Based on their use and
functions, words are categorized into several types or parts of speech.
This article will offer definitions and examples for the 8 major parts of
speech in English
grammar: noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, adjective, conjunction, prepositio
n, and interjection.
Noun
This part of a speech refers to words that are used to name persons,
things, animals, places, ideas, or events. Nouns are the simplest among
the 8 parts of speech, which is why they are the first ones taught to
students in primary school.
Examples:
Tom Hanks is very versatile.
The italicized noun refers to a name of a person.
Pronoun
A pronoun is a part of a speech which functions as a replacement for a
noun. Some examples of pronouns are: I, it, he, she, mine, his, hers, we,
they, theirs, and ours.
Sample Sentences:
Janice is a very stubborn child. She just stared at me and when I
told her to stop.
Adjective
This part of a speech is used to describe a noun or a pronoun. Adjectives
can specify the quality, the size, and the number of nouns or pronouns.
Use this link to get a list of adjectives.
Sample Sentences:
The carvings are intricate.
The italicized word describes the appearance of the noun
carvings.
Verb
This is the most important part of a speech, for without a verb, a
sentence would not exist. Simply put, this is a word that shows an action
(physical or mental) or state of being of the subject in a sentence.
Examples of State of Being Verbs : am, is, was, are, and were
Sample Sentences:
As usual, the Stormtroopers missed their shot.
The italicized word expresses the action of the subject
Stormtroopers.
Adverb
Just like adjectives, adverbs are also used to describe words, but the
difference is that adverbs describe adjectives, verbs, or another adverb.
Preposition
This part of a speech basically refers to words that specify location or a
location in time.
Examples of Prepositions: above, below, throughout, outside, before,
near, and since
Conjunction
The conjunction is a part of a speech which joins words, phrases, or
clauses together.
Examples of Conjunctions: and, yet, but, for, nor, or, and so
Interjection
This part of a speech refers to words which express emotions. Since
interjections are commonly used to convey strong emotions, they are
usually followed by an exclamation point.
Examples of Interjections:
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument3 paginiPart of Speech OverviewAna C. MorilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nine Parts of Speech (Grammar) : Prepositions and Interjections. We Will Add One More Type: ArticlesDocument2 paginiNine Parts of Speech (Grammar) : Prepositions and Interjections. We Will Add One More Type: ArticlesReeta KannusamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of SpeechDocument4 paginiPart of SpeechMuhammad SupriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument6 paginiPart of Speech OverviewSamia HaqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech: Tom Hanks Is Very VersatileDocument4 paginiPart of Speech: Tom Hanks Is Very VersatileRezzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of The SpeechDocument10 paginiPart of The SpeechRhen ZamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Parts of Speech Overview: Nouns, Verbs, Adjectives & MoreDocument4 pagini8 Parts of Speech Overview: Nouns, Verbs, Adjectives & MorechiragÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument6 paginiPart of Speech OverviewamirasherlynaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument4 paginiPart of Speech OverviewHien TaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument5 paginiPart of Speech OverviewJayana SujayanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8 Parts of Speech Defined and Explained in 40 WordsDocument39 pagini8 Parts of Speech Defined and Explained in 40 WordsClarissa KurniadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument5 paginiPart of Speech OverviewAsad MehmoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Orang Ganteng 2Document2 paginiTugas Orang Ganteng 2Hanif FikriyantitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Writing2Document22 paginiReport Writing2Shin Thant NaingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of SpeechDocument4 paginiParts of SpeechFaye LacanariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of SpeechDocument10 paginiParts of SpeechKamil HasnainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Speech OverviewDocument7 paginiParts of Speech OverviewDavid Vijay ColeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Speech COMPLETEDocument6 paginiParts of Speech COMPLETEhaseeb aslam khanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 paginiParts of Speechleona dao100% (3)
- Tom Hanks Is Very Versatile. Dogs Can Be Extremely Cute.: Parts of Speech 1. NounDocument2 paginiTom Hanks Is Very Versatile. Dogs Can Be Extremely Cute.: Parts of Speech 1. NounYANNA CABANGONÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panganiban ProjectDocument9 paginiPanganiban ProjectColyn Joy Sumande MantacÎncă nu există evaluări
- The 8 Parts of Speech: Definition and ExamplesDocument7 paginiThe 8 Parts of Speech: Definition and ExamplesJasmin Binauhan Niegos-TrongcoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Speech TheoryDocument5 paginiParts of Speech TheoryJustoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of SpeechDocument19 paginiParts of Speechzafar iqbalÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar All You Need To KnowDocument22 paginiEnglish Grammar All You Need To KnowDavid Fueter0% (1)
- Parts of SpeechDocument4 paginiParts of SpeechAlicia Joy TalaveraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of SpechDocument4 paginiParts of SpechIsrar Baloch100% (1)
- Part of SpeechDocument4 paginiPart of Speechrowell esperanzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of SpeechDocument18 paginiParts of SpeechSakunthala RajeshÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Sentence of EnglishDocument16 paginiThe Sentence of EnglishBilal HassanÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Grammar Grade 3,4 2023Document21 paginiEnglish Grammar Grade 3,4 2023Sumera BokhariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Speech and Sentence StructureDocument12 paginiParts of Speech and Sentence StructureibnuamungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Grammar and StructureDocument3 paginiBasic Grammar and StructureYeni LampungÎncă nu există evaluări
- A. Noun: Proper Nouns Are The Names of Individual People, Places, Titles, Calendar Times, EtcDocument44 paginiA. Noun: Proper Nouns Are The Names of Individual People, Places, Titles, Calendar Times, EtcAnonymous 1cCIhqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Speech TableDocument3 paginiParts of Speech TableTan Lopez50% (2)
- Gramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Document64 paginiGramatyka Opisowa (Ściąga)Adam DmochowskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar - Grade 7Document1 paginăGrammar - Grade 7Saira FaisalÎncă nu există evaluări
- English Parts of Speech: Click Here For Step-by-Step Rules, Stories and Exercises To Practice All English TensesDocument22 paginiEnglish Parts of Speech: Click Here For Step-by-Step Rules, Stories and Exercises To Practice All English TensesGregoryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Primary Grammar Glossary For ParentsDocument6 paginiPrimary Grammar Glossary For ParentsJack EdieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument44 paginiPart of Speech OverviewSufyan Ashraf100% (1)
- Word classes in 40 charactersDocument7 paginiWord classes in 40 charactersTarik AlicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Winch 9780195529098 SCDocument37 paginiWinch 9780195529098 SCArti SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sentences: Independent Clauses Act As Complete Sentences, While Subordinate Clauses Cannot Stand Alone andDocument9 paginiSentences: Independent Clauses Act As Complete Sentences, While Subordinate Clauses Cannot Stand Alone andThamizhman Mani100% (1)
- Reach Dream: Makalah Eight Parts of SpeechDocument9 paginiReach Dream: Makalah Eight Parts of SpeechMelfi Namora nasutionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech: Tom Hanks Is Very VersatileDocument7 paginiPart of Speech: Tom Hanks Is Very VersatileEko HaryantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Noun - The Ultimate Grammar Guide To Nouns (With List, Examples) - 7ESLDocument16 paginiNoun - The Ultimate Grammar Guide To Nouns (With List, Examples) - 7ESLRadha Krishnan0% (1)
- Parts of SpeechDocument6 paginiParts of SpeechsteinrizkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of SpeechDocument4 paginiParts of Speechmuja dilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traditional Grammar Review I. Parts of Speech: John Bought The BookDocument15 paginiTraditional Grammar Review I. Parts of Speech: John Bought The BookHasian SidabutarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of Speech OverviewDocument12 paginiPart of Speech OverviewindriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parts of Speech With Examples PDFDocument6 paginiParts of Speech With Examples PDFHasen MediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grammar Guidebook Breaks Down EnglishDocument41 paginiGrammar Guidebook Breaks Down EnglishalenagroupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Purposive Communication.Document8 paginiPurposive Communication.Kyla Ramos Diamsay100% (1)
- Road To English BetterDocument65 paginiRoad To English BetterEko Nurhadi SatrioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Understanding Syntax and Parts of SpeechDocument20 paginiUnderstanding Syntax and Parts of SpeechNurul Aida NionsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Part of SpeechDocument7 paginiPart of Speechyunita fajarÎncă nu există evaluări
- English ReviewerDocument4 paginiEnglish ReviewerJenifer CabanginÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Short New Testament Syntax: Handbook with ExercisesDe la EverandA Short New Testament Syntax: Handbook with ExercisesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceDe la EverandComprehensive English Grammar Guide: From Basics to Competitive ExcellenceÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ve LloreDocument8 paginiVe LloreSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benchmarking and Good Practices for Footwear Industry PerformanceDocument56 paginiBenchmarking and Good Practices for Footwear Industry PerformanceSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benchmarking in The Tanning IndustryDocument83 paginiBenchmarking in The Tanning IndustrySrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glossary of Footwear Terminology - BIGWDocument23 paginiGlossary of Footwear Terminology - BIGWSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Hindi Words and Phrases For Foreigner Travellers Coming To IndiaDocument5 paginiCommon Hindi Words and Phrases For Foreigner Travellers Coming To IndiaNIlesh BhagatÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThorntonDocument597 paginiThorntonAnastasios SchinasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Practical Guide To Market ResearchDocument200 paginiPractical Guide To Market Researchsarahmahdy50% (2)
- Preparation of Ice CreamDocument7 paginiPreparation of Ice CreamSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brands and Stakeholder Relationships: Key PointsDocument45 paginiBrands and Stakeholder Relationships: Key PointsSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Market Dynamics and Productivity in Japanese Retail Industry in The Late 1990sDocument22 paginiMarket Dynamics and Productivity in Japanese Retail Industry in The Late 1990sSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perceived Quality and Attitude Toward Tea & Coffee by ConsumersDocument13 paginiPerceived Quality and Attitude Toward Tea & Coffee by ConsumersSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Benchmarking Study FootwearDocument75 paginiBenchmarking Study FootwearSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ss v-II I-II MarchDocument4 paginiSs v-II I-II MarchSrinivasan KannanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DVD Portatil Daewoo DPC 7900Document38 paginiDVD Portatil Daewoo DPC 7900videosonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Housing Case StudyDocument40 paginiHousing Case StudyRishu Dev100% (1)
- Gallery of Blackstone (10386072)Document10 paginiGallery of Blackstone (10386072)Andrew English Lewis100% (1)
- RTSigns ChartsDocument5 paginiRTSigns Charts640928100% (2)
- SRT 1F Technical DescriptionDocument64 paginiSRT 1F Technical DescriptionEze Alexander IkÎncă nu există evaluări
- EF4e Beg Progtest 7 12ADocument10 paginiEF4e Beg Progtest 7 12ANelly Lea100% (2)
- Final Synopsis PDFDocument10 paginiFinal Synopsis PDFAnant GârgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Firelock Rigid Coupling Style 005H With Vic-Plus Gasket SystemDocument3 paginiFirelock Rigid Coupling Style 005H With Vic-Plus Gasket SystemIhsan OzzyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guitar String Tension ExperimentDocument7 paginiGuitar String Tension Experimentsonti11Încă nu există evaluări
- BerserkerDocument3 paginiBerserkerbillÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vegetable Nutrition FactsDocument2 paginiVegetable Nutrition FactskboadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manufacturing Baby Diapers, Sanitary Pads and Toilet TissueDocument27 paginiManufacturing Baby Diapers, Sanitary Pads and Toilet TissueMD.SHAHNEWAZ MazumderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temporary Revisions and Service Bulletins ListDocument28 paginiTemporary Revisions and Service Bulletins ListSam VencesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Live Cricket Score, Schedule, Latest News, Stats & VideosDocument6 paginiLive Cricket Score, Schedule, Latest News, Stats & VideosRohit JainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Functional Hypertrophy WorkoutDocument3 paginiFunctional Hypertrophy WorkoutLouis TrầnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project 9.0 - Hotel Vs ResortDocument8 paginiProject 9.0 - Hotel Vs ResortYvweiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wi-Fi CERTIFIED™ Interoperability Certificate: Page 1 of 2 Certification ID: WFA81317Document2 paginiWi-Fi CERTIFIED™ Interoperability Certificate: Page 1 of 2 Certification ID: WFA81317Vacho HovhannisynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Standard Civil Engineering Construction Details ManualDocument213 paginiStandard Civil Engineering Construction Details ManualkokueiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Automan September 2011Document84 paginiAutoman September 2011Automan MagazineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yojijukugo - The Four Kanji That Make One IdiomDocument5 paginiYojijukugo - The Four Kanji That Make One Idiomneliomedina01Încă nu există evaluări
- DiaCam ManualDocument12 paginiDiaCam Manualit-scribÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Alan Fransi 951613863 3 Albina Muñoz 975327078Document14 pagini1 Alan Fransi 951613863 3 Albina Muñoz 975327078PedroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Welcome Home Sanitarium tabDocument10 paginiWelcome Home Sanitarium tabletoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Carol of The Bells Pour Flûte Et Piano de Mykola Dmytrovich LEONTOVICHDocument3 paginiCarol of The Bells Pour Flûte Et Piano de Mykola Dmytrovich LEONTOVICHNilo SergioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engine Isuzu 4HK1 Scx-500 CraneDocument77 paginiEngine Isuzu 4HK1 Scx-500 Cranededy H100% (1)
- Marylebone April MinDocument2 paginiMarylebone April MinarivannoorvÎncă nu există evaluări
- DDEX19 OutlawsIronRouteDocument38 paginiDDEX19 OutlawsIronRouteJames S HowarthÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jazzy UnicornDocument7 paginiJazzy UnicornHydra JvrÎncă nu există evaluări
- AV Linux 5.0 ManualDocument33 paginiAV Linux 5.0 ManualHugh UrwinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo Lorenz Pg. 5 6 Bolted CouplingDocument2 paginiCatalogo Lorenz Pg. 5 6 Bolted CouplingValmirÎncă nu există evaluări