Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Acute Glomrulonephritis Pathophysiology
Încărcat de
Jai - HoDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Acute Glomrulonephritis Pathophysiology
Încărcat de
Jai - HoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
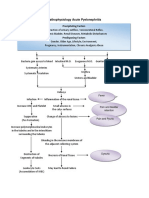
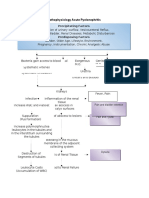
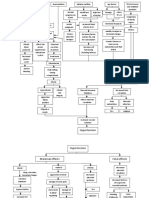
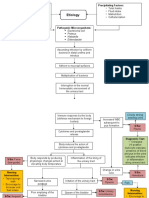
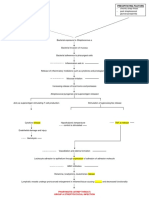
IV.
PATHOPHYSIOLOGY
Predisposing factors:
Precipitating factors: Frequently eating
decrease urinary frequency junkfoods
and output Unhygienic habits
Legend: Invasion of exogenous streptococcal
Saprophyticus in the body
-Disease Process
Release of antigen-antibody complexes
in the circulation
-Signs and
symptoms Exogenous streptococcal bacteria goes
to the renal system (glomeruli)
Entrapment of exogenous streptococcal
bacteria in the endothelial lining of the
glomeruli
Immune complex
reaction in the glomerular
capillary
Proliferation of epithelial cells lining
glomerulus & cells between
endothelium & epithelium of capillary
membrane
Impairment to release
Inflammatory response erythropoeitin
Vasodilation of the renal arteries Inability to stimulate
supplying the glomeruli red bone marrow to
increase production of
RBC
Increase perfusion of blood going to
the glomeruli
Decrease
RBC: 3.26
Hgb; 8.4
Swelling capillary membrane & Hct: 26.2
infiltration with leukocytes Pallor skin and
conjunctivae
restless
Reduction of glomelular membranes
capacity for selective permeability
Occlusion of the capillaries of the insufficient tissue perfusion going
glomeruli vasospasm of afferent to the kidneys
ventrioles
Leakage of large and small particles
- Hematuria such as RBC and protein. - decrease
- Proteinuria urine output
and frequency
↓ Glomerular filtration rate
↓ Ability to form filtrate from
glomeruli plasma flow
Third-space fluid shifting
from intravascular to
interstitial compartment in Retention of water and Ansarca
the peritoneal cavity waste products Restless
Increase BUN of
35.9
Increase of
Occurrence of
creatinine of
descending infection
1.30
Increase Invasion of the bacteria to the
abdominal girth ureter and bladder
of 77 cm
Increase
respiratory rate
of 32 cpm.
Increase
- pus cells in
WBC count
the urine
of 18.0
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Acute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramDocument1 paginăAcute Glomerulonephritis (AGN) Pathophysiology & Schematic DiagramRnspeakcom50% (2)
- PathophyDocument2 paginiPathophymharz_astilloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiAcute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyJanica Marinas100% (3)
- Pre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesDocument3 paginiPre Eclampsia of Severe FeaturesPrincess Diane S. VillegasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument1 paginăAcute GlomerulonephritisTaz Bagul MutiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysioDocument4 paginiAcute Glomerulonephritis Pathophysioshaider1190% (1)
- Pathophysiology AGEDocument2 paginiPathophysiology AGEMareeze Hatta100% (1)
- Pathophsyiology of AGEDocument1 paginăPathophsyiology of AGEmariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiAcute Glomerulonephritis PathophysiologyChester NicoleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Gastroenteritis, Dehydration, and NecatoriasisRalph Delos Santos100% (2)
- Pathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Acute GastroenteritisAlliah Grejie AnneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverDocument3 paginiPathophysiology and Schematic Diagram of Typhoid FeverCyrus De AsisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Inflammatory ResponseDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Inflammatory ResponseDeo FactuarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophy (Age)Document1 paginăPathophy (Age)Michelle Ann CasamayorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Acute GlumerulonephritisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Acute GlumerulonephritisMASII75% (12)
- AGE PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiAGE Pathophysiologyjosephcanlas67% (3)
- Individual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument26 paginiIndividual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisBatrisyia HalimsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating FactorsDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Acute Pyelonephritis: Precipitating Factorsgodwinkent888Încă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverDocument1 paginăPathophysiology Dengue Hemorrhagic FeverShiella Heart Malana100% (1)
- DengueDocument4 paginiDengueKathleen DimacaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of CholelithiasisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of CholelithiasisSherilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amoebiasis PathophysiologyDocument3 paginiAmoebiasis PathophysiologyApril CornejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology Dengue 2Document4 paginiPathophysiology Dengue 2KatherineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 paginăPathophysio Chronic GlomerulonephritisRan Ma100% (1)
- Dengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyDocument4 paginiDengue Hemorrhagic Fever PathophysiologyKirk Espanol BigstoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating FactorsDocument3 paginiAcute Lymphoblastic Leukemia Pathophysiology: Predisposing Factors: Etiology: Precipitating FactorsKyla ValenciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dengue PoathoDocument6 paginiDengue PoathoCleobebs Agustin100% (1)
- Pathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Acute PyelonephritisAnonymous 75TDy2y100% (1)
- Pregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiPregnancy Induced Hypertension PathophysiologyCamille Grace100% (1)
- Precipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument3 paginiPrecipitating Factors Predisposing Factors Chronic Kidney DiseaseGrace Jane DionaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CKD PathoDocument5 paginiCKD PathoJohn MIchael AusaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Obstructive JaundiceDocument1 paginăSCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Obstructive JaundiceJan Niño EstrellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Breast Cancer Concept MapDocument1 paginăBreast Cancer Concept MapKeepItSecret100% (1)
- Age Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat IntakeDocument3 paginiAge Greater Than 60 Y/o Hereditary Precipitating Factors: Hypertension Increase Protein and Fat Intakenursing concept mapsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of AMLDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of AMLjake251996100% (1)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEDocument2 paginiPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of DENGUEKenrick Randell IbanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 paginiNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ARF PathophysiologyDocument2 paginiARF Pathophysiologykathy100% (9)
- Pathophysiology of AGE With DHNDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of AGE With DHNFarr Krizha Tangkusan50% (2)
- Pathophysiology of ESRDDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of ESRDjake90210100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document7 paginiPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2arbyjamesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Atrial Septal DefectDocument2 paginiPathophysiology of Atrial Septal Defectbobtaguba50% (2)
- Case Presentation (Age) NG Grp. A2 FinalDocument43 paginiCase Presentation (Age) NG Grp. A2 Finaljean therese83% (6)
- Pathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFDocument1 paginăPathophysiology Sickle Cell Anemia PDFTine GuibaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acc Phu Case NCP HyperthermiaDocument1 paginăAcc Phu Case NCP Hyperthermiamacy_bautistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramDocument2 paginiCholecystitis Pathophysiology Schematic DiagramChristyl CalizoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramDocument3 paginiChronic Kidney Disease Pathophysiology - Schematic DiagramJake CaballoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsDocument5 paginiEtiology: Predisposing Factors: Precipitating FactorsJanelle NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- HepatitisDocument3 paginiHepatitisRosendo Dacuyan100% (1)
- Urinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENADocument2 paginiUrinary Tract Infection pATho SHEENASheena Arnoco ToraynoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Rheumatic FeverDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Rheumatic FeverGehlatin Tumanan100% (2)
- PATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaDocument1 paginăPATHOPHYSIOLOGY of PreeclampsiaPearl IbisateÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clin Path Lab 6 UrinalysisDocument5 paginiClin Path Lab 6 Urinalysisapi-3743217100% (6)
- Streptococcus Infection, On TheDocument3 paginiStreptococcus Infection, On TheMonica DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Predisposing Factors Precipitating Factors: Streptococcal Pyrogenes and Superantigen ReleasedDocument9 paginiPredisposing Factors Precipitating Factors: Streptococcal Pyrogenes and Superantigen ReleasedDATO-ON JOANA PAULAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Schisto Patho SLHDocument5 paginiSchisto Patho SLHJosh IbalioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quality Assessment, Renal Disease & Urine ScreeningDocument15 paginiQuality Assessment, Renal Disease & Urine ScreeningAnya IgnacioÎncă nu există evaluări
- EDEMADocument2 paginiEDEMAkimkaigel6Încă nu există evaluări
- 7 Renal Disease StudentDocument34 pagini7 Renal Disease Studentrbm121415chyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal DiseaseDocument6 paginiRenal DiseaseyeonjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Constitution: Article VII Section 17, 18, 19Document29 paginiPhilippine Constitution: Article VII Section 17, 18, 19Jai - Ho95% (22)
- CA Emergency: Tumor Lysis SyndromeDocument10 paginiCA Emergency: Tumor Lysis SyndromeJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tumor Lysis SyndromeDocument35 paginiTumor Lysis SyndromeJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Color and Art TherapyDocument30 paginiColor and Art TherapyJai - Ho100% (1)
- CA Emergency: Tumor Lysis SyndromeDocument9 paginiCA Emergency: Tumor Lysis SyndromeJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome, STEMI, Anterior Wall, Killips - 1, DM Type II - UncontrolledDocument61 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome, STEMI, Anterior Wall, Killips - 1, DM Type II - UncontrolledJai - Ho100% (5)
- IVF ProblemsDocument1 paginăIVF ProblemsJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vii. Nursing Care Plan: Secretions in The AirwaysDocument5 paginiVii. Nursing Care Plan: Secretions in The AirwaysJai - Ho100% (2)
- A Case Study On Rectal AdenocarcinomaDocument62 paginiA Case Study On Rectal AdenocarcinomaEyySiEffVee100% (1)
- Final - Spinal Stenosis L4, L5 Secondary To Spondylolisthesis L4, L5 Grade II With Hypertrophized Ligament Um and Radiculopathy With Myelopathy Right SidedDocument66 paginiFinal - Spinal Stenosis L4, L5 Secondary To Spondylolisthesis L4, L5 Grade II With Hypertrophized Ligament Um and Radiculopathy With Myelopathy Right SidedJai - Ho100% (1)
- Case Study Final. Pott's DiseaseDocument50 paginiCase Study Final. Pott's DiseaseJaiRus MagdadaRo100% (3)
- Pa Tho of Prostatic CancerDocument2 paginiPa Tho of Prostatic CancerJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP On Diabetes Mellitus Type IIDocument4 paginiNCP On Diabetes Mellitus Type IIJai - Ho78% (9)
- NCP On Acute GlumrulonephritisDocument11 paginiNCP On Acute GlumrulonephritisJai - Ho89% (9)
- Case Study On Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument20 paginiCase Study On Acute GlomerulonephritisJai - Ho87% (15)
- Case Study On Prostatic CancerDocument21 paginiCase Study On Prostatic CancerJai - Ho100% (3)
- Lab - Results On Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument16 paginiLab - Results On Acute GlomerulonephritisJai - Ho100% (1)
- Drug Study of Patient Having Electrolyte ImbalanceDocument3 paginiDrug Study of Patient Having Electrolyte ImbalanceJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Possible Drugs of Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument10 paginiPossible Drugs of Acute GlomerulonephritisJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vi. Nursing Care PlanDocument3 paginiVi. Nursing Care PlanJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynasties and Kingdoms of EgyptDocument5 paginiDynasties and Kingdoms of EgyptJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study (DM)Document28 paginiCase Study (DM)Jai - Ho100% (1)
- Evaluation ToolDocument2 paginiEvaluation ToolJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tabular Sheet of TopicsDocument2 paginiTabular Sheet of TopicsJai - HoÎncă nu există evaluări
- LLLT in Hair GrowthDocument13 paginiLLLT in Hair GrowthCarlos SilvaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Directory of OfficersDocument5 paginiDirectory of OfficersAbhay Chauhan100% (1)
- ORAL CANCER - Edited by Kalu U. E. OgburekeDocument400 paginiORAL CANCER - Edited by Kalu U. E. Ogburekeعبد المنعم مصباحيÎncă nu există evaluări
- Burton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 18. Viral InfectionsDocument20 paginiBurton's Microbiology For The Health Sciences: Chapter 18. Viral Infectionsmirai desu100% (2)
- NCCS Understanding Radiation Therapy (Eng)Document20 paginiNCCS Understanding Radiation Therapy (Eng)Benjamin NgÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction of Physical MedicineDocument39 paginiIntroduction of Physical MedicineDrMd Nurul Hoque MiahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaluative Exam Gastrointestinal SystemDocument21 paginiEvaluative Exam Gastrointestinal SystemReymart AcalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rash Diagnosis Cheat Sheet: EmergencyDocument1 paginăRash Diagnosis Cheat Sheet: Emergencykdlsfk kajjksolsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ru 58 42150Document12 paginiRu 58 42150Efen YtÎncă nu există evaluări
- QuestionsDocument3 paginiQuestionsمحمد سعيد السعيدÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Directive TEMPLATE MINDocument13 paginiAdvanced Directive TEMPLATE MINcaseyscribdÎncă nu există evaluări
- De Thi ThuDocument6 paginiDe Thi ThuQuynh TrangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Icf Pri P2 414 PDFDocument17 paginiIcf Pri P2 414 PDFMichael Forest-dÎncă nu există evaluări
- Critical Apprasisal 2Document5 paginiCritical Apprasisal 2api-678326591Încă nu există evaluări
- Eclampsia Nursing Case AnalysisDocument38 paginiEclampsia Nursing Case AnalysisMary Justine Nuyad-AfricaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBQ For NLEDocument10 paginiCBQ For NLEJerome VergaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Identifikasi Medication Error Pada Resep Pasien Poli Interna Di Instalasi Farmasi Rumah Sakit Bhayangkara Tk. Iii ManadoDocument8 paginiIdentifikasi Medication Error Pada Resep Pasien Poli Interna Di Instalasi Farmasi Rumah Sakit Bhayangkara Tk. Iii ManadoSintia VeronikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goboy, Louise Germaine U. BSN 210 Self-Assessment QuestionsDocument2 paginiGoboy, Louise Germaine U. BSN 210 Self-Assessment QuestionsLouise Germaine100% (1)
- Medical AbbreviationsDocument54 paginiMedical AbbreviationsHardeep Singh BaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Accident and Emergency Department Case StudyDocument13 paginiAccident and Emergency Department Case StudyMohtady0% (1)
- Ijarbs 14Document12 paginiIjarbs 14amanmalako50Încă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Pathology Infectious DiseasesDocument37 paginiIntroduction To Pathology Infectious DiseasesNirav PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Musculoskeletal Curriculum: History & Physical Exam of The ShoulderDocument60 paginiMusculoskeletal Curriculum: History & Physical Exam of The Shoulderhis.thunder122100% (1)
- Germany CV Format-Sample OnlyDocument6 paginiGermany CV Format-Sample Onlydeamhi nursing serviceÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICU ReadingDocument24 paginiICU Reading駱品全Încă nu există evaluări
- Idrrmu Written Exam ReviewerDocument132 paginiIdrrmu Written Exam ReviewerDaniel Adrian FalaminianoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gulf Care Members GuideDocument31 paginiGulf Care Members Guidesuheil samaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Febrile IllnessesDocument96 paginiAcute Febrile IllnessesHAlid mohammed100% (1)
- Final Yemen Cmam Guidelines - Feb 2014Document243 paginiFinal Yemen Cmam Guidelines - Feb 2014Anas Abdo SenanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Back Pain Guidelines-Reduced2Document26 paginiLow Back Pain Guidelines-Reduced2ranggadr100% (1)