Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Review of Week 1 Public Health
Încărcat de
Anonymous Sfcml4GvZ0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
19 vizualizări2 paginipublic health review
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentpublic health review
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
19 vizualizări2 paginiReview of Week 1 Public Health
Încărcat de
Anonymous Sfcml4GvZpublic health review
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
Fact Sheet Based on Pre-Readings
Mission of public health- create conditions so people can be healthy by addressing
broader health issues and underlying causes
o Upstream strategy (prevention) vs. downstream strategy (intervention)
o How we use population health (the health outcomes and determinants) to
create healthy conditions for individuals and environment
Public health dept. partner with clinicians to reorient towards prevention and wellness
Collaboration between clinical care and public health
o Link community with clinicians to provide services public health did before (but
wont now due to ACA policies)
o Increase role in monitoring community and monitoring cost, access, and quality
of treatment
History of practices
o Early 1900s to 1950s- racial zoning practices and racially restrictive covenants
o 1940s to 1970s redlining and mortgage security/federal loan maps
disinvestment
o Present concentrated poverty areas, infant mortality rates, teen pregnancies,
low life expectancy, lead levels, food deserts, accesshistorical disadvantages
because of policy carried over
Population health goal distribution of health outcomes across a geographically defined
area and how individual biology/behavior, socioeconomic cultural factors, and public
health/healthcare effectiveness contribute to those outcomes
o Measured by morbidity/health status (quality of life) and mortality (length of
life) these are health outcomes
o Health outcomes + determinants
Health value combo of improved population health outcomes + sustainable health
costs
o Triple aim improve population health, improve individual care,
decrease/sustain health costs (hitting everything basically)
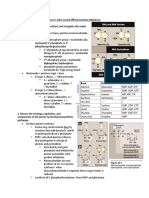
Incidence-rate of new (or newly diagnosed) cases of the disease (# new cases/
population)
o Prevalence: # people with disease / # people examined, how much of disease is
there at particular point in time
Case-centered approach: individuals, determinant of individual case, treat the
symptoms/conditiondownstream
o Vs. population approach: determinants of incident rate, address underlying
causesupstream
Bioethics
o Emotional engagement influences moral judgments (not solely rationalism)
Preventive medicine care of individual patient + public health
o Similarity of preventive medicine and public health promotion of health,
prevention of diseases, application of epidemiology
o Differences preventive medicine enhance individual lives by helping them
improve their health, public health promote health in populations through
community organized efforts
o Primary prevention = health promotion
o Promote quaternary prevention through narrative based medicine (trust,
listening) and evidence based medicine (probabilities of therapy/tests,
pros/cons)
o value based judgment judgment based on a particular set of values or on a
particular value system.
Pandemic Ethics
o Privacy may need to change slightly because need to collect pandemic data and
share it, so autonomy may need to be shifted
o Quarantine, isolation may limit personal freedom for the benefit of larger society
o Shift from personal freedom/autonomy to community needs/benefits (ex:
mandatory vaccinations? Resource allocation?)
o Resource allocation
Utilitarianism- medical utility vs. social utility
Egalitarianism- lottery
o Triage
Clinical triage (most urgent treat) vs. battlefield triage (most useful treat)
o isolation - someone is actually ill and we have separated them
o quarantine- may have been infected, watching them to see if they get sick and
separating them from others to monitor them
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- UntitledDocument1 paginăUntitledAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sri Sai Devotees MessagesDocument1 paginăSri Sai Devotees MessagesAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- DestinyDocument2 paginiDestinyAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16 Srimad Bhagavat Geeta Part 2Document1 paginăChapter 16 Srimad Bhagavat Geeta Part 2Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sri Sai Devotees Messages Part 3Document1 paginăSri Sai Devotees Messages Part 3Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sri Sai Devotees Messages Part 4Document1 paginăSri Sai Devotees Messages Part 4Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 16 Srimad Bhagavat Gita Part 1Document1 paginăChapter 16 Srimad Bhagavat Gita Part 1Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Samsara in VedantaDocument1 paginăSamsara in VedantaAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two Meanings of The Term AntakaalaDocument1 paginăTwo Meanings of The Term AntakaalaAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raloxifine For SchizophreniaDocument1 paginăRaloxifine For SchizophreniaAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anartha Parampara or Cycle of Ignorance Is The Cause of The Agitations in The MindDocument1 paginăAnartha Parampara or Cycle of Ignorance Is The Cause of The Agitations in The MindAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anartha Parampara or Cycle of Ignorance Is The Cause of The Agitations in The MindDocument1 paginăAnartha Parampara or Cycle of Ignorance Is The Cause of The Agitations in The MindAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newborn Exam Checklist PDFDocument2 paginiNewborn Exam Checklist PDFAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- History and Physical Exam Skills List: Opening VisitDocument7 paginiHistory and Physical Exam Skills List: Opening VisitAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- I Am That Satchitananda Svarupa AtmaDocument1 paginăI Am That Satchitananda Svarupa AtmaAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- They Are in Me.i Am Not in Them.Document1 paginăThey Are in Me.i Am Not in Them.Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- They Are in Me.i Am Not in Them.Document1 paginăThey Are in Me.i Am Not in Them.Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case 5Document3 paginiCase 5Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Itamin Hart: No ToxicityDocument4 paginiItamin Hart: No ToxicityAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Master Document of Embryology/Development StagesDocument23 paginiMaster Document of Embryology/Development StagesAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- VasanasDocument1 paginăVasanasAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alupta DrikDocument1 paginăAlupta DrikAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vedantic Thoughts 1Document1 paginăVedantic Thoughts 1Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCAT Exam PolicyDocument13 paginiMCAT Exam PolicyAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kaivalyopanishad Mantra 21Document2 paginiKaivalyopanishad Mantra 21Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Central Teaching of VedantaDocument2 paginiCentral Teaching of VedantaAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhyana Yoga PointersDocument1 paginăDhyana Yoga PointersAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study Guide For Exam 2Document3 paginiStudy Guide For Exam 2Anonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- EdemaDocument2 paginiEdemaAnonymous Sfcml4GvZÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Monsoon Safety PDFDocument6 paginiMonsoon Safety PDFparthaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chemotherapy For TuberculosisDocument49 paginiChemotherapy For TuberculosisJia YingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parasitology Table ReviewDocument8 paginiParasitology Table ReviewAliehsEiram18Încă nu există evaluări
- Pro-Lab: Prolex ™ Staph Latex KitDocument2 paginiPro-Lab: Prolex ™ Staph Latex Kitapi-3742158Încă nu există evaluări
- Icd 10Document11 paginiIcd 10Mitrasehat YkÎncă nu există evaluări
- PSMDocument6 paginiPSMMufaddal DewaswalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syrgery Mock 2Document8 paginiSyrgery Mock 2aa.Încă nu există evaluări
- Antiprotozoal Agents 6Document29 paginiAntiprotozoal Agents 6EinsteenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Global Health and Global NursingDocument4 paginiGlobal Health and Global NursingJAMES KIHATOÎncă nu există evaluări
- ThesisDocument23 paginiThesisAnushika AgarwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Statistics For OsceDocument77 paginiStatistics For OsceArun GeorgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Federation of Bhel Executive Associations (Fobea) : Kailasapuram Club Premises, BHEL Township, Tiruchirappalli-620014Document2 paginiFederation of Bhel Executive Associations (Fobea) : Kailasapuram Club Premises, BHEL Township, Tiruchirappalli-620014KuthuraikaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expanded Dengue Syndrome: Gastrointestinal Manifestations.: March 2018Document7 paginiExpanded Dengue Syndrome: Gastrointestinal Manifestations.: March 2018NicholasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antimicrobial Screening of Acacia Farnesiana (L.) WilldDocument3 paginiAntimicrobial Screening of Acacia Farnesiana (L.) WilldDr. Varaprasad Bobbarala100% (2)
- Plasmotec MalariaDocument11 paginiPlasmotec MalariaZero_SugarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Norovirus Public Health Fact SheetDocument2 paginiNorovirus Public Health Fact SheetClickon DetroitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fasciolopsis BuskiDocument18 paginiFasciolopsis BuskiAmritesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colby-Guide To Health 1846Document214 paginiColby-Guide To Health 1846RonLaytonÎncă nu există evaluări
- PeritonitisDocument21 paginiPeritonitisNirav SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NR 442 Exam 1 ReviewDocument10 paginiNR 442 Exam 1 ReviewHolly DeckelmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- VIDocument5 paginiVIRaymark Sabanal Gaudia0% (1)
- Mental HealthDocument66 paginiMental HealthKarunya Vk100% (1)
- BSL-3 Training-1Document22 paginiBSL-3 Training-1Dayanandhi ElangovanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Argumentative Essay FinalDocument10 paginiArgumentative Essay Finalapi-550035247Încă nu există evaluări
- Complication of Hemodialysis and Their ManagementDocument52 paginiComplication of Hemodialysis and Their ManagementRetno SumaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dhaneswara Adhyatama WDocument14 paginiDhaneswara Adhyatama WaghniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Endodontics Final ReviewerDocument16 paginiEndodontics Final ReviewerMehdi Moshaveri100% (3)
- NFL COVID-19 MemoDocument2 paginiNFL COVID-19 MemoHouston ChronicleÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Pathology 4.03 Endocrine System Super SummaryDocument15 paginiGeneral Pathology 4.03 Endocrine System Super SummaryJade MonrealÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Appendicitis of The Appendiceal StumpDocument3 paginiAcute Appendicitis of The Appendiceal StumpXavier JarrínÎncă nu există evaluări