Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
An Tide Pres An
Încărcat de
Patricia Minick0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
14 vizualizări3 paginiThis document summarizes antidepressant medications, including:
- Heterocyclics like amitriptyline and clomipramine which can cause orthostatic hypotension, weight gain, and lower seizure threshold.
- MAOIs like phenelzine and tranylcypromine which can cause hypertensive crisis and orthostatic hypotension.
- SSRIs like fluoxetine, paroxetine, and sertraline which cause discontinuation symptoms if stopped abruptly and have varying potential for drug interactions.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors like duloxetine and venlafaxine which also cause discontinuation symptoms and can
Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentThis document summarizes antidepressant medications, including:
- Heterocyclics like amitriptyline and clomipramine which can cause orthostatic hypotension, weight gain, and lower seizure threshold.
- MAOIs like phenelzine and tranylcypromine which can cause hypertensive crisis and orthostatic hypotension.
- SSRIs like fluoxetine, paroxetine, and sertraline which cause discontinuation symptoms if stopped abruptly and have varying potential for drug interactions.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors like duloxetine and venlafaxine which also cause discontinuation symptoms and can
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
14 vizualizări3 paginiAn Tide Pres An
Încărcat de
Patricia MinickThis document summarizes antidepressant medications, including:
- Heterocyclics like amitriptyline and clomipramine which can cause orthostatic hypotension, weight gain, and lower seizure threshold.
- MAOIs like phenelzine and tranylcypromine which can cause hypertensive crisis and orthostatic hypotension.
- SSRIs like fluoxetine, paroxetine, and sertraline which cause discontinuation symptoms if stopped abruptly and have varying potential for drug interactions.
- Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors like duloxetine and venlafaxine which also cause discontinuation symptoms and can
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
THE SECTION Psychiatric Disorders
MERCK MANUALS FOR HEALTHCARE
SUBJECT
TOPIC
Mood Disorders
Depressive Disorders
ONLINE MEDICAL LIBRARY PROFESSIONALS
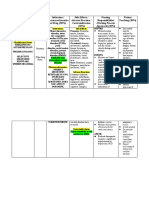
ANTIDEPRESSANTS
Therapeutic
Drug Starting Dose* Dosage Range Precautions
Heterocyclics Contraindicated in patients
with coronary artery disease,
certain arrhythmias, angle-
closure glaucoma, benign
prostatic hypertrophy, or
esophageal hiatus hernia
Can cause orthostatic hypoten-
sion leading to falls and frac-
tures, potentiate the effect of
alcohol, and raise the blood
level of antipsychotics
With significant overdose,
potentially lethal
Amitriptyline 50 mg once/day 150–300 mg Causes weight gain
Amoxapine 50 mg bid 150–400 mg Can have extrapyramidal
adverse effects
Clomipramine 25 mg once/day 100–250 mg Lowers seizure threshold at
doses of > 250 mg/day
Desipramine 25 mg once/day 150–300 mg —
Doxepin 25 mg once/day 150–300 mg Causes weight gain
Imipramine 25 mg once/day 150–300 mg May cause excessive sweating
and nightmares
Maprotiline 75 mg once/day 150–225 mg Increased risk of seizures with
rapid dose escalation at high
doses
Nortriptyline 25 mg once/day 50–150 mg Effective within the therapeutic
window
Protriptyline 5 mg tid 15–60 mg Has long half-life (74 h)
Trimipramine 50 mg once/day 150–300 mg Causes weight gain
MAOIs Serotonergic syndrome possi-
ble when taken with an SSRI
or nefazodone
Hypertensive crisis possible
when taken with other antide-
pressants, sympathomimetic
or other selective drugs, or
certain foods and beverages
With significant overdose,
potentially lethal
Isocarboxazid 10 mg bid 30–60 mg Causes orthostatic hypotension
Phenelzine 15 mg tid 45–90 mg Causes orthostatic hypotension
Selegiline, 6 mg once/day 12 mg Can cause application site reac-
transdermal tions and insomnia
Tranylcypromine 10 mg bid 30–60 mg Causes orthostatic hypotension
Has amphetamine-type stimu-
lant effects and modest abuse
potential
THE SECTION Psychiatric Disorders
MERCK MANUALS FOR HEALTHCARE
SUBJECT
TOPIC
Mood Disorders
Depressive Disorders
ONLINE MEDICAL LIBRARY PROFESSIONALS
ANTIDEPRESSANTS—Continued
Therapeutic
Drug Starting Dose* Dosage Range Precautions
SSRIs . Causes discontinuation symp-
toms if stopped abruptly (less
likely with fluoxetine)
Citalopram 20 mg once/day 20–40 mg Lower potential for drug
interactions because it has
less effect on CYP450
isoenzymes
Escitalopram 10 mg once/day 10–20 mg Same as for citalopram
Fluoxetine 10 mg once/day 20–60 mg Has very long half-life
Less likely to cause discontinu-
ation symptoms
The only antidepressant proven
effective in children
Fluvoxamine 50 mg once/day 100–200 mg Can cause clinically significant
elevation of theophylline,
warfarin, and clozapine blood
levels
Has potential for interactions
between its active metabo-
lites and HCAs, carba-
mazepine, antipsychotics, or
type IC antiarrhythmics; has
CYP450 profile similar to
fluoxetine
Paroxetine 20 mg once/day 20–50 mg Has potential for interactions
between its active metabo-
lites and HCAs, carba-
mazepine, antipsychotics, or
type IC antiarrhythmics; has
CYP450 profile similar to
fluoxetine
25 mg CR 25–62.5 mg CR May cause the most weight
once/day gain among SSRIs
Sertraline 50 mg once/day 50–200 mg Of SSRIs, has highest
incidence of loose stools
Serotonin-norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors Causes discontinuation symp-
toms if stopped abruptly
Duloxetine 20 mg bid 60–120 mg Modest dose-dependent
increase in systolic and dias-
tolic BP
May cause mild urinary hesi-
tancy in males
Less potential for drug-drug
interactions because it has
less effect on CYP450
THE SECTION Psychiatric Disorders
MERCK MANUALS FOR HEALTHCARE
SUBJECT
TOPIC
Mood Disorders
Depressive Disorders
ONLINE MEDICAL LIBRARY PROFESSIONALS
ANTIDEPRESSANTS—Continued
Therapeutic
Drug Starting Dose* Dosage Range Precautions
Venlafaxine 25 mg tid 75–375 mg Modest dose-dependent
increase in diastolic BP
Dual norepinephrine and
5-HT reuptake effect at about
150 mg
37.5 mg XR 75–225 mg XR Rarely, increase in systolic BP
once/day (not dose-dependent)
If stopped, should be tapered
slowly
Less potential for drug-drug
interactions because it has
less effect on CYP450
Serotonin modulators (5-HT2 blockers)
Mirtazapine 15 mg once/day 15–45 mg Causes weight gain and
sedation
Has fewer sexual adverse
effects than SSRIs and
serotonin-norepinephrine
reuptake inhibitors
Nefazodone 100 mg once/day 300–500 mg May cause liver failure
Has fewer sexual adverse
effects than SSRIs and
serotonin-norepinephrine
reuptake inhibitors
Trazodone 50 mg tid 150–300 mg May cause priapism
May cause orthostatic
hypotension
Norepinephrine-dopamine-reuptake inhibitor
Bupropion 100 mg bid 200–450 mg Contraindicated in patients
150 mg SR who have bulimia or who are
once/day seizure-prone
150 mg XL May interact with HCAs,
once/day increasing the risk of seizures
May cause dose-dependent
recent memory loss
*All drugs are given orally except for transdermal selegiline.
CR = continuous release; CYP450 = cytochrome P450 system; HCAs = heterocyclic antidepres-
sants; 5-HT = 5-hydroxytryptamine (serotonin); MAOIs = monoamine oxidase inhibitors; SR =
sustained release; XL = extended release; XR = extended release.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- RisperdalDocument2 paginiRisperdalAdrianne Bazo100% (1)
- Lamictal (Lamotrigine)Document1 paginăLamictal (Lamotrigine)E100% (1)
- PIX4D Simply PowerfulDocument43 paginiPIX4D Simply PowerfulJUAN BAQUEROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cross Talk Details and RoutingDocument29 paginiCross Talk Details and RoutingRohith RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clevo W940tu Service ManualDocument93 paginiClevo W940tu Service ManualBruno PaezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti Depresan1Document39 paginiAnti Depresan1Akmal SafwanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antidepressants Drug SnigDocument18 paginiAntidepressants Drug SnigSnigdha MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychopamacology PresentationDocument131 paginiPsychopamacology Presentationsalmalissu0Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study 2 de Guzman Miguel Paulo P. NCMHDocument2 paginiDrug Study 2 de Guzman Miguel Paulo P. NCMHMark Angelo SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychopharmacology Presentation1Document25 paginiPsychopharmacology Presentation1Juliax ClintonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Table 56-2 - Medications Used in Treatment of Depression - SupDocument2 paginiTable 56-2 - Medications Used in Treatment of Depression - SupDragutin PetrićÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Choose AntidepressantDocument30 paginiHow To Choose AntidepressantAfnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Student Psychopharmacology - PPTX 2015-16 John WDocument98 paginiMedical Student Psychopharmacology - PPTX 2015-16 John WDr TNTÎncă nu există evaluări
- JOURNAL READING-Epilepsy-RidhaDocument22 paginiJOURNAL READING-Epilepsy-RidhaUlul Azmi AdnanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study 1 (Done)Document3 paginiDrug Study 1 (Done)Otaku MiyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Panic Disorde4rs THDocument10 paginiPanic Disorde4rs THDragutin PetrićÎncă nu există evaluări
- TramadolDocument3 paginiTramadolKaren Viviene Aberilla CincoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnP - PsychopharmacologyDocument37 paginiAnP - PsychopharmacologyNicole JohnsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorDocument4 paginiEffectiveness Indicated by A Reduction in Psychotic BehaviorGwyn RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingDocument1 paginăDrug Study: Sedation, Dizziness/vertigo, Headache, Hypotension Sweating, Nausea, VomitingRoland YusteÎncă nu există evaluări
- DepressionDocument2 paginiDepressionAhmad SyahmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beers Criteria HandoutDocument3 paginiBeers Criteria Handoutapi-647779956Încă nu există evaluări
- Psychotropic Drugs in Dermatology: FR-Utilización de Psicofármacos en DermatologíaDocument3 paginiPsychotropic Drugs in Dermatology: FR-Utilización de Psicofármacos en DermatologíaNilson Morales CordobaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antidepressant DrugsDocument11 paginiAntidepressant Drugssuresh patilÎncă nu există evaluări
- 02 - 19 - Psychiatric Care of Cardiac PatientDocument23 pagini02 - 19 - Psychiatric Care of Cardiac PatientIndrias SalisaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychopharmacology 1Document7 paginiPsychopharmacology 1RajP01Încă nu există evaluări
- Appi Focus 20200048Document16 paginiAppi Focus 20200048agus sanjayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PsychopharmacologyDocument50 paginiPsychopharmacologyapi-3703352Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study: TramadolDocument6 paginiDrug Study: TramadolShara Lailanie A. AzisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)Document2 paginiLexapro (Escitalopram Oxalate)EÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Therapy For Obsessive-Compulsive DisorderDocument6 paginiDrug Therapy For Obsessive-Compulsive Disorderpsique.reflexivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntidepressantsDocument84 paginiAntidepressantsGiovanna AlguÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prozac (Fluoxetine) 40mgDocument1 paginăProzac (Fluoxetine) 40mgEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument4 paginiDrug StudyDean Angelo BarrientosÎncă nu există evaluări
- PharmatherapyDocument21 paginiPharmatherapyiiout346Încă nu există evaluări
- Drugs For Anxiety and InsomniaDocument10 paginiDrugs For Anxiety and InsomniaApple MaeÎncă nu există evaluări
- AntidepressantsDocument27 paginiAntidepressantsMourian AmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti DepresanDocument58 paginiAnti Depresanrayinda mamahitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medicines and Falls - Guidance On Causes and Risks: (Version 1 - July 2015)Document4 paginiMedicines and Falls - Guidance On Causes and Risks: (Version 1 - July 2015)Dr. Asif RahmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CC Rubie Ann G. Tillor: IM: (Schizophrenia)Document11 paginiCC Rubie Ann G. Tillor: IM: (Schizophrenia)Rubie Ann TillorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psych DrugsDocument3 paginiPsych DrugsSwarna BanikÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 2 Drugs Used in PsychiatryDocument6 pagini5 2 Drugs Used in PsychiatryJoseph NyirongoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Depressant Drugs: Presented by L.Nithish Shankar Ii Year Mbbs KGMCDocument17 paginiAnti-Depressant Drugs: Presented by L.Nithish Shankar Ii Year Mbbs KGMCÑiťhišh Śhankąŕ LóganáthánÎncă nu există evaluări
- Depressive-Disorders SheetDocument2 paginiDepressive-Disorders SheetCrystal MarloweÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3.1 Pharmacology Lecture Part-II 2023Document53 pagini3.1 Pharmacology Lecture Part-II 2023Talha TariqÎncă nu există evaluări
- DTR (2nd Set)Document7 paginiDTR (2nd Set)Fionah RetuyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study (Tofranil J Zoloft)Document2 paginiDrug Study (Tofranil J Zoloft)alteahmichaella.mintuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antidepressant DrugsDocument55 paginiAntidepressant Drugsmaheen aurangzaib100% (2)
- Quetiapine - Drug StudyDocument3 paginiQuetiapine - Drug StudyJeran Henrich BusobusoÎncă nu există evaluări
- MDD Study GuideDocument5 paginiMDD Study GuideTop VidsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Student Psychopharmacology - PPTX 2015-16 John WDocument99 paginiMedical Student Psychopharmacology - PPTX 2015-16 John WMrLarry DolorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amitriptyline of My Pharmacology TaskDocument6 paginiAmitriptyline of My Pharmacology TaskRika ChisakaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychopharma 1Document7 paginiPsychopharma 1Mitchee Zialcita100% (1)
- PowerPoint AntidepressantsDocument29 paginiPowerPoint AntidepressantsRaeika GanjiÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH19-25 PharmaDocument20 paginiCH19-25 Pharmakwon nanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CNS II Drug NotesDocument4 paginiCNS II Drug NotesErin YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intro To PsychopharmacologyDocument8 paginiIntro To Psychopharmacologyprettykiran7Încă nu există evaluări
- Anxiety Disorders - TreatmentDocument16 paginiAnxiety Disorders - TreatmentFAMED RESIDENTS CESMEDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 6 Drugs Acting On The CNS and PNSDocument43 paginiUnit 6 Drugs Acting On The CNS and PNSTherese Margarette SantiagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anti-Depressants: WWW - Bradfordvts.co - UkDocument23 paginiAnti-Depressants: WWW - Bradfordvts.co - UkHemantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psychotropic Medications Questions You Should Ask Your 37th Psychiatric Consultation William R. Yee M.D., J.D., Copyright Applied for October 16th, 2022: 3rd editionDe la EverandPsychotropic Medications Questions You Should Ask Your 37th Psychiatric Consultation William R. Yee M.D., J.D., Copyright Applied for October 16th, 2022: 3rd editionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcDe la EverandMedical Encyclopedia XXL: Prof. J.P. Schadé, M.D., Ph.D. D.Sc.hcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Shipko's Informed Consent For SSRI AntidepressantsDe la EverandDr. Shipko's Informed Consent For SSRI AntidepressantsEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (2)
- Owner'S Manual: 2023 Chassis CabDocument444 paginiOwner'S Manual: 2023 Chassis CabDmitry DimasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lab Report Marketing Mansi 4Document39 paginiLab Report Marketing Mansi 4Mansi SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Data Bulletin Group Motor Installations:: Understanding National Electrical Code (NEC) 430.53 RequirementsDocument8 paginiData Bulletin Group Motor Installations:: Understanding National Electrical Code (NEC) 430.53 RequirementsshoaibÎncă nu există evaluări
- Provision of EPCI Services For EPCIC Sidayu Wellhead Platforms and Pipelines Sidayu Field DevelopmentDocument7 paginiProvision of EPCI Services For EPCIC Sidayu Wellhead Platforms and Pipelines Sidayu Field Developmentriandi100% (1)
- Plastics and Polymer EngineeringDocument4 paginiPlastics and Polymer Engineeringsuranjana26Încă nu există evaluări
- PEH Q3 Long QuizDocument1 paginăPEH Q3 Long QuizBenedict LumagueÎncă nu există evaluări
- Logic NotesDocument19 paginiLogic NotesCielo PulmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12/1/2014 Powder MetallurgyDocument29 pagini12/1/2014 Powder Metallurgysofyan sam0% (2)
- DudjDocument4 paginiDudjsyaiful rinantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Significance of GodboleDocument5 paginiSignificance of GodbolehickeyvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electricity NotesDocument35 paginiElectricity Notesapi-277818647Încă nu există evaluări
- Mockery Breed Murder Birds PDFDocument12 paginiMockery Breed Murder Birds PDFLautaro BojanichÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ali Erdemir: Professional ExperienceDocument3 paginiAli Erdemir: Professional ExperienceDunkMeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emw 2007 FP 02093Document390 paginiEmw 2007 FP 02093boj87Încă nu există evaluări
- Training Report On Self Contained Breathing ApparatusDocument4 paginiTraining Report On Self Contained Breathing ApparatusHiren MahetaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Main Girders: CrossDocument3 paginiMain Girders: Crossmn4webÎncă nu există evaluări
- FYP ProposalDocument11 paginiFYP ProposalArslan SamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 1 Chapter 9 ErosiondepositionDocument1 paginăLesson 1 Chapter 9 Erosiondepositionapi-249320969Încă nu există evaluări
- Lesson Plan in Science 9: I. ObjectivesDocument8 paginiLesson Plan in Science 9: I. ObjectivesmarichuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study The Effect of Postharvest Heat Treatment On Infestation Rate of Fruit Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera L.) Cultivars Grown in AlgeriaDocument4 paginiStudy The Effect of Postharvest Heat Treatment On Infestation Rate of Fruit Date Palm (Phoenix Dactylifera L.) Cultivars Grown in AlgeriaJournal of Nutritional Science and Healthy DietÎncă nu există evaluări
- Percent by VolumeDocument19 paginiPercent by VolumeSabrina LavegaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrowetting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDocument5 paginiElectrowetting - Wikipedia, The Free EncyclopediaDwane AlmeidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cisco 2500 Series RoutersDocument16 paginiCisco 2500 Series RoutersJull Quintero DazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cecilia-Puff-Tee-Final-OUSM-Designs-12 MESES A TALLA 8Document19 paginiCecilia-Puff-Tee-Final-OUSM-Designs-12 MESES A TALLA 8Jose SanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tugas Dikumpulkan Pada Hari Sabtu, 11 April 2020. Apabila Email Bermasalah Dapat Mengirimkan Via WA PribadiDocument4 paginiTugas Dikumpulkan Pada Hari Sabtu, 11 April 2020. Apabila Email Bermasalah Dapat Mengirimkan Via WA PribadiFebry SugiantaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Presentation On 4G TechnologyDocument23 paginiPresentation On 4G TechnologyFresh EpicÎncă nu există evaluări
- Amnaya Sutra (English)Document458 paginiAmnaya Sutra (English)Assam Bhakti SagarÎncă nu există evaluări