Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Molluscum Contagiosum MC Water Warts: Viral Infection Skin
Încărcat de
kenDescriere originală:
Titlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Molluscum Contagiosum MC Water Warts: Viral Infection Skin
Încărcat de
kenDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
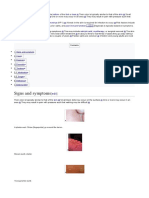
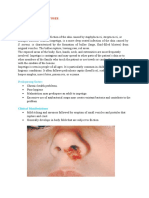
Molluscum contagiosum (MC), sometimes called water warts, is a viral infection of the skin that
results in small, raised, pink lesions with a dimple in the center.[1] They may occasionally be itchy or
sore.[1] They may occur singly or in groups.[1] Any area of the skin may be affected, with abdomen,
legs, arms, neck, genital area, and face being most common.[1] Onset of the lesions is around 7
weeks after infection.[3] It usually goes away within a year without scarring.[1]
MC is caused by a poxvirus called the molluscum contagiosum virus (MCV).[1] The virus is spread
either by direct contact including sexual activity or via contaminated objects such as towels.[4] The
condition can also be spread to other areas of the body by the person themselves.[4] Risk factors
include a weak immune system, atopic dermatitis, and crowded living conditions.[2] Following one
infection, it is possible to get reinfected.[9] Diagnosis is typically based on the appearance.[3]
Prevention includes hand washing and not sharing personal items.[6] While treatment is not
necessary some may wish to have the lesions removed for cosmetic reasons or to prevent
spread.[7] Removal may occur with freezing, opening up the lesion and scraping the inside, or laser
therapy.[7] Scraping the lesion can however result in scarring.[9] The medication cimetidine by mouth
or podophyllotoxin cream applied to the skin may also be used.[7]
Approximately 122 million people globally were affected by molluscum contagiosum as of 2010
(1.8% of the population).[8] It is more common in children between the ages of one and ten years
old.[2] The condition has become more common in the United States since 1966.[2] MC is not a reason
to keep a child out of school or daycare
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Molluscum MedscapeDocument35 paginiMolluscum MedscapeAninditaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moluskum KontagiosumDocument10 paginiMoluskum KontagiosumAtika JuliÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Dangers of Faecal Incontinence in The At-Risk PatientDocument6 paginiThe Dangers of Faecal Incontinence in The At-Risk PatientRicardo BalauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moluscum ContagiosuDocument17 paginiMoluscum ContagiosuEveline YÎncă nu există evaluări
- MolluscumDocument11 paginiMolluscumAstari Pratiwi NuhrintamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxoplasmosis WikiDocument36 paginiToxoplasmosis WikiUnggul YudhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- VitiligoDocument11 paginiVitiligoNirmal BhowmickÎncă nu există evaluări
- Signs and Symptoms: Wart Bottom Foot Toes SkinDocument3 paginiSigns and Symptoms: Wart Bottom Foot Toes SkinIana CovaliovÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum Contagiosum Causes and SymptomsDocument1 paginăMolluscum Contagiosum Causes and Symptoms79lalalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MycosisDocument3 paginiMycosisMartin Ponce de León100% (1)
- Vitiligo skin condition causes patches of white skinDocument14 paginiVitiligo skin condition causes patches of white skinMalte SersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum Contagiosum (EScholarship)Document7 paginiMolluscum Contagiosum (EScholarship)Try Wahyudi Jeremi LoLyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impetigo: Signs and SymptomsDocument3 paginiImpetigo: Signs and Symptomspragna novaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum Contagiosum: What Is It?Document2 paginiMolluscum Contagiosum: What Is It?rendyprimanandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum Contagiosum and WartsDocument8 paginiMolluscum Contagiosum and WartscefalalgiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 8-Hal 1-3Document3 pagini8-Hal 1-379lalalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Folliculitis, Furunculosis...Document8 paginiFolliculitis, Furunculosis...Coral Srinivasa RamaluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum ContagiosumDocument1 paginăMolluscum Contagiosumshailesh284Încă nu există evaluări
- MeaslesDocument4 paginiMeaslesMohammad Yordan GandaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- VitiligoDocument4 paginiVitiligoAbi ZakiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB (Short For TubercleDocument14 paginiTuberculosis, MTB, or TB (Short For TubercleRakhi RameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measles - WikipediaDocument46 paginiMeasles - WikipediaMuhammad MuslimÎncă nu există evaluări
- ChickenpoxDocument84 paginiChickenpoxraymondabaduÎncă nu există evaluări
- AIDS: A Disease of the Human Immune System Caused by HIVDocument225 paginiAIDS: A Disease of the Human Immune System Caused by HIVbharatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 183-Review Article-757-1-10-20220406Document4 pagini183-Review Article-757-1-10-20220406Cok DevitiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum Contagiosum (EScholarship)Document5 paginiMolluscum Contagiosum (EScholarship)Imha MikanersandsmashblastÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dengue InglésDocument2 paginiDengue InglésGohan MiguelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hematological Malignancy Types & TreatmentDocument4 paginiHematological Malignancy Types & TreatmentSrinivas LaishettyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acne Vulgaris: Acne, Also Known As Acne Vulgaris, Is A Long-TermDocument1 paginăAcne Vulgaris: Acne, Also Known As Acne Vulgaris, Is A Long-TermOkti WiratuljannahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cutaneous Leishmaniasis: Clinical Manifestations and DiagnosisDocument18 paginiCutaneous Leishmaniasis: Clinical Manifestations and DiagnosisAndréia GomesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum ContagiosumDocument4 paginiMolluscum ContagiosumOrang KalonganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of Malignant Cutaneous Wounds in Oncologic PatientsDocument6 paginiManagement of Malignant Cutaneous Wounds in Oncologic Patients郭品君Încă nu există evaluări
- Monkeypox symptoms, causes, transmissionDocument3 paginiMonkeypox symptoms, causes, transmissionElle VernezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epidemiology: Aureus and GABHS 10% of The Time. Methicillin-Resistant S Aureus (MRSA) HasDocument8 paginiEpidemiology: Aureus and GABHS 10% of The Time. Methicillin-Resistant S Aureus (MRSA) HasPutra YdpaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum Contagiosum: Dermatology Patient EducationDocument3 paginiMolluscum Contagiosum: Dermatology Patient EducationOrang KalonganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum Contagiosum - An Update: ReviewDocument3 paginiMolluscum Contagiosum - An Update: ReviewArdi WidiatmikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum Contagiosum Andrew N PitzpatrickDocument5 paginiMolluscum Contagiosum Andrew N PitzpatrickHel DaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tuberculosis, MTB, or TB (Short For TubercleDocument22 paginiTuberculosis, MTB, or TB (Short For TubercleKriti AgrawalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Measles (Rubeola) Rubeola Red Spot: Dr. Eman Khammas Alsadi Community Medicine LecturerDocument34 paginiMeasles (Rubeola) Rubeola Red Spot: Dr. Eman Khammas Alsadi Community Medicine Lecturereman khammasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Molluscum ContagiosumDocument2 paginiMolluscum ContagiosumArdi WidiatmikaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tetanus 1Document7 paginiTetanus 1Mohammad Yordan GandaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Is AnDocument2 paginiCoronavirus Disease 2019 (COVID-19) Is AnSadhak AarushÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxoplasmosis - A Global ThreatDocument8 paginiToxoplasmosis - A Global ThreatDr-Sadaqat Ali RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- C R o W E, M A R K A - Moluscum Contagiosum. Diakses Dari: - Pada Tanggal 27 Desember 2016Document22 paginiC R o W E, M A R K A - Moluscum Contagiosum. Diakses Dari: - Pada Tanggal 27 Desember 201679lalalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- The COVIDDocument6 paginiThe COVIDK59 Sơn Thị Thu HiềnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jurnal 3 MoluskumDocument2 paginiJurnal 3 MoluskumFausiah Ulva MÎncă nu există evaluări
- SsssDocument5 paginiSsssputeri nashuha100% (1)
- Noma امجد حمزة عبد حسينDocument8 paginiNoma امجد حمزة عبد حسينSaif HaiderÎncă nu există evaluări
- Candidiasis (Brut)Document6 paginiCandidiasis (Brut)Ilyes FerenczÎncă nu există evaluări
- Infectious DermatosesDocument41 paginiInfectious DermatosesJuma SammyÎncă nu există evaluări
- COVID-19 causes, symptoms, transmission and preventionDocument1 paginăCOVID-19 causes, symptoms, transmission and preventionAlbean DelojeroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Impetigo: A Bacterial Skin InfectionDocument13 paginiImpetigo: A Bacterial Skin InfectionTasya SyafhiraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Luka 2 PDFDocument6 paginiLuka 2 PDFBarryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Emergency Management - WikipediaDocument36 paginiEmergency Management - WikipediaLolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smallpox - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaDocument26 paginiSmallpox - Wikipedia, the free encyclopediaSatish Kumar DashÎncă nu există evaluări
- Toxoplasmosis Is A: Toxoplasma GondiiDocument16 paginiToxoplasmosis Is A: Toxoplasma Gondiidiana_iuliana_13Încă nu există evaluări
- Bio-Development Pharmaceuticals, Corp. (BDP) : Corporate Business PlanDocument11 paginiBio-Development Pharmaceuticals, Corp. (BDP) : Corporate Business PlanNOVA CHALLENGEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diseases: Infected With Scabies Again? Focus in Management in Long-Term Care FacilitiesDocument12 paginiDiseases: Infected With Scabies Again? Focus in Management in Long-Term Care FacilitiesGede AdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- VaalbaraDocument3 paginiVaalbarakenÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Kill The Nemean LionDocument1 paginăHow To Kill The Nemean LionkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- ShōtōkanDocument1 paginăShōtōkankenÎncă nu există evaluări
- CoronationDocument2 paginiCoronationkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Kill The Hind of KeryneiaDocument1 paginăHow To Kill The Hind of KeryneiakenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Demon SlayerDocument1 paginăDemon SlayerkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- RobertDocument2 paginiRobertkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Karijini National ParkDocument1 paginăKarijini National ParkkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- GeologyDocument1 paginăGeologykenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wipro Philippines medical allowance claim receiptsDocument1 paginăWipro Philippines medical allowance claim receiptskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Masashi KishimotoDocument1 paginăMasashi KishimotokenÎncă nu există evaluări
- How To Kill The Kalydonian BoarDocument2 paginiHow To Kill The Kalydonian BoarkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hero Saitama Fights Monsters in City ZDocument2 paginiHero Saitama Fights Monsters in City ZkenÎncă nu există evaluări
- NarutoDocument1 paginăNarutokenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Math CG - With Tagged Math Equipment 1 PDFDocument257 paginiMath CG - With Tagged Math Equipment 1 PDFsweetienedsÎncă nu există evaluări
- k1 Writing Monthly Exams Sept.28 0ct.1Document2 paginik1 Writing Monthly Exams Sept.28 0ct.1kenÎncă nu există evaluări
- 00 IntroductionDocument8 pagini00 IntroductionClimz AetherÎncă nu există evaluări
- CASES For Crim. Law Review 2020Document3 paginiCASES For Crim. Law Review 2020kenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peroneus LongusDocument1 paginăPeroneus LonguskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Special Power of AttorneyDocument2 paginiSpecial Power of AttorneykenÎncă nu există evaluări
- KissDocument1 paginăKisskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Law Review SyllabusDocument6 paginiCivil Law Review SyllabuskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- You've Got A New Submission To Job Applications Form 2!Document2 paginiYou've Got A New Submission To Job Applications Form 2!kenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peroneus LongusDocument1 paginăPeroneus LonguskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fibular ArteryDocument1 paginăFibular ArterykenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peroneus LongusDocument1 paginăPeroneus LonguskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interosseous CrestsDocument1 paginăInterosseous CrestskenÎncă nu există evaluări
- NamiDocument1 paginăNamikenÎncă nu există evaluări
- The TibiaDocument1 paginăThe TibiakenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roronoa ZoroDocument1 paginăRoronoa ZorokenÎncă nu există evaluări