Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
SYBTech
Încărcat de
Giggs0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
45 vizualizări16 paginiSYBTech - Syllabus - 2004-08 - VJTI
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentSYBTech - Syllabus - 2004-08 - VJTI
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
45 vizualizări16 paginiSYBTech
Încărcat de
GiggsSYBTech - Syllabus - 2004-08 - VJTI
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 16
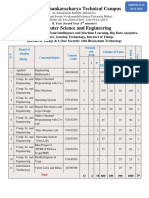
PROGRAMME: 101: B.
TECH (CIVIL ENGINEERING)
Sr. Course Code Course Title L P T Cr Evaluation ESE
No. weightage (Theory)
Hours
TWA MST ESE
Semester Three (2005-06)
1 200011 Applied. Mathematics I 3 1 4 7 15 10 75 3
2 301011 Geomatics-I 3 2 5 8 15 10 75 3
3 301020 Building Materials and Construction 3 0 3 6 15 10 75 3
4 301030 Fluid Mechanics 3 2 5 8 15 10 75 3
5 301040 Mechanics of Solids 5 0 5 10 15 10 75 3
6 301050 Concrete technology 3 2 5 8 15 10 75 3
7 301060 Construction Materials Laboratory 0 3 3 3 100 0 0
TOTAL 20 10 30 50
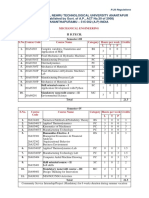
Semester Four (2005-06)
1 200012 Applied Mathematics II 3 1 4 7 15 10 75 3
2 301012 Geomatics- II 3 2 5 8 15 10 75 3
3 301070 Engineering Geology 4 2 6 10 15 10 75 3
4 301081 Building Planning & Graphics I 2 2 4 6 15 10 75 3
5 301091 Applied Hydraulics I 3 2 5 8 15 10 75 3
6 301101 Structural Analysis I 5 0 5 10 15 10 75 3
7 301110 Computer Aided Drafting 0 3 3 3 100 0 0 -
TOTAL 20 12 32 52
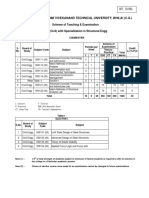
Semester Three (2006-07)
1 200011 Applied. Mathematics I 3 1 4 7 15 15 70 3
2 301011 Geomatics-I 3 2 5 8 15 15 70 3
3 301020 Building Materials and Construction 3 0 3 6 15 15 70 3
4 301030 Fluid Mechanics 3 2 5 8 15 15 70 3
5 301040 Mechanics of Solids 5 0 5 10 15 15 70 3
6 301050 Concrete technology 3 2 5 8 15 15 70 3
7 301060 Construction Materials Laboratory 0 3 3 3 100 0 0
TOTAL 20 10 30 50
Semester Four (2006-07)
1 200012 Applied Mathematics II 3 1 4 7 15 15 70 3
2 301012 Geomatics- II 3 2 5 8 15 15 70 3
3 301070 Engineering Geology 4 2 6 10 15 15 70 3
4 301081 Building Planning & Graphics - I 2 2 4 6 15 15 70 3
5 301091 Applied Hydraulics I 3 2 5 8 15 15 70 3
6 301101 Structural Analysis I 5 0 5 10 15 15 70 3
7 301110 Computer Aided Drafting 0 3 3 3 100 0 0 -
TOTAL 20 12 32 52
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 1 of 16
200011 : Applied Mathematics I
Detailed Syllabus
1 Laplace Transforms
Function of bounded variation. Laplace transforms of standard functions such as1, t n eat, sinat, cosat, sinhat,
coshat, erf(t), Linear property of Laplace- Transform. First shifting theorem, second shifting theorem,
L {tn f(t)}, L {f (t)}, L {f(t)/t} L{ ot f(u) du}, L {dn / dtn f(t)}
Change of scale property:
Unit step functions, Heaviside, Dirac delta functions, Periodic functions and their Laplace Transforms.
Inverse Laplace Transform using linear property, theorems, partial fractions and convolution theorem.
Application to solve ordinary differential equations with one dependent variable.
2 Matrices
Types of matrices. Adjoint ( Adjugate) of a matrix. Inverse of a matrix. Elementary transformations of matrix,
rank of a matrix. Reduction to a normal form.
Partitioning of matrix. System of Homogeneous and non-homogeneous equations, their consistency and
solution. Eigen values and Eigen vectors of square matrix, Cayley Hamiltons theorem and functions of square
matrix.
3 Fourier series and integrals
Orthogonal and orthonormal functions, Expression for a function in a series of orthogonal functions. Dirchlet's
Conditions. Fourier series of Periodic function with period 2 and 2l, Dirchlets theorem, Even and Odd
functions. Half range expansions, Parsevals relations. Complex form of Fourier series. Fourier integral.
4 Vector calculus
Scalar and vector point functions. Directional derivative Curl and Divergence, Consecervative, Irrotational and
Solenoidal field. Line integral and its properties, Grrens theorem, Stokes theorem, divergence theorem and its
applications
Recommended Books:
Higher Engineering Mathematics, Dr B S Grewal, Khanna Publications
A text book of Applied Mathematics, P N & J N Wartikar, Pune Vidyarthi Griha
Advanced Engineering Mathematics, Erurin Kreyszig, Wiley Eastern Limited
Engineering Mathematics for Semester III, T Veerrajan, Tata McGraw Hill
Matrices, A R Vasishtha
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 2 of 16
301011 : Geomatics I
Detailed Syllabus
1 Introduction
Various types of surveying- based on methods and instruments, classifications, uses and necessity of geodetic
surveying, photographic, astronomy and hydrographic surveying
Diagonal scale, various types of venires, micrometers on surveying instruments, principles of surveying
Chain surveying, instruments required for linear measurement, minor instruments for setting out right angle
2 Leveling and contouring
Definitions, technical terms, different types of levels such as dumpy, quickset, precise, auto
Temporary and permanent adjustments of dumpy and auto level
Different methods of leveling, reduction of levels, problems
Difficulties in leveling work, corrections and precautions to be taken in leveling work
Contour definitions, contour interval, equivalent, uses and characteristics of contour lines, direct and indirect
methods of contouring
Running a level line, L section, cross section, methods of interpolation
Grade contour- definition, use, setting out in field
Computation of volume by trapezoidal and prismoidal formula, volume from spot levels, volume from contour
plan
3 Plane table surveying
Definitions, uses and advantages, temporary adjustments
Different methods of plane table surveying
Two point problem
Errors in plane table survey, use of telescopic alidade
4 Traverse Surveying
Compass: Bearings- different types, compass prismatic, surveyor, whole circle, reduced bearings, Local
Attraction
Theodolite:- Various parts and axis of transit, technical terms, temporary and permanent adjustments of a
transit, horizontal and vertical angles, methods of repetition and reiteration
Different methods of running a theodolite traverses, Gales traverse table, balancing of traverse by Bow-Ditchs
transit and modified transit rules
Problems on one-plane and two-plane methods, omitted measurements
Precautions in using theodolite, errors in theodolite survey
Use of theodolite for various works such as prolongation of a straight line, setting out an angle
5 Setting out works
General horizontal and vertical control, setting out of foundation plan for load bearing and framed structure,
batter board, slope and grade stakes, setting out with theodolite
Setting out of sewer line, culvert, use of laser for works
Setting out center line for tunnel, transfer of levels to underground work
Project / route survey for bridge, dam and canal
Checking verticality of high rise structures
6 Areas
Area of a irregular figure by Trapezoidal rule, average ordinate rule, Simpsons 1/3 rule, various co ordinate
methods
Planimeter: types of planimeter including digital planimeter, area of zero circle, use of planimeter
Practicals:
Use of Amslar polar planimeter for finding the area of irregular figures and certifying it by using Digital
Planimeter
Use of optical theodolite / Electronic theodolite for measurement of horizontal and vertical angles
Theodolite traverse, Gales traverse table
A two day project on theodolite traversing and plane table detailing,
Use of optical theodolite / Electronic theodolite for one plane and two plane methods
Simple and compound leveling by using Dumpy / Auto Level, booking methods
Methods of plane tabling:- Radiation . Intersection and Traversing
Setting out a simple foundation plan in the field
Recommended Books:
Surveying and Leveling, Vol I & II, Kanetkar & Kulkarni, Pune Vidyarthi Griha, Pune
Surveying and Leveling, N N Basak, Tata McGraw Hill
Surveying, R Agor, Khanna Publishers
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 3 of 16
301020 : Building Materials and Construction
Detailed Syllabus
1 Introduction
Types of structures framed, load bearing and composite, suitability and economic aspects of each type
2 Building materials
Classification of Building materials, requirements of building materials and products, functional, aesthetical and
economic
Study of properties of materials: physical, mechanical, chemical, biological, aesthetical and other complex
properties like durability, reliability, compatibility, and economic characteristics
3 Surface finishes
Pointing: types, plastering: materials and types, painting, Building facia,
Materials and products based on mineral binders, gypsum, lime, plaster of paris, cement, hydraulic lime, mortars
and concrete, gypsum-concrete products.
Paints and Varnishes: types and uses
4 Masonry Construction
Structural Clay products, Classification, Common clay brick, face bricks and tiles, ceramic tiles, paving blocks
Brick masonry, stone masonry and block masonry
5 Doors and windows
Types, materials used, manufacture of doors and windows, fixtures
Grill work materials used, manufacture
Metal and metal alloys: Products made of ferrous and non ferrous metals, Aluminum alloys, Types and Uses,
Anticorrosive treatment
Glass Types and uses
Wood varieties and uses, defects in timber, preservative treatments, and wood composites.
5 Floors and roofs
Floors types of floors, floor finishes, suitability
Roofs materials used, types, wooden and steel trusses, roof coverings, roof drainage
Synthetic Polymer resins and resins based materials, floor covering, wall facing, heat insulating and sound
proofing plastics, water proofing and sealing resins, Method of Fixing.
6 Excavation and foundations
Excavation in soils and rocks, shoring and strutting, dewatering
Simple foundations like isolated, strip, continuous and raft, Pile Foundation
7 Concrete construction
Batching and mixing, transportation and placing, curing
Pre-cast concrete advantages, suitability, manufacturing storage curing and erection methods for pre-cast
components
Formwork design of simple form work, materials for formwork, centering and staging, scaffolding
8 Damp proofing and water proofing materials and methods
Bitumen, tars and asphalt: Properties and uses
Recommended Books:
Building Construction, B.C. Punmiya
Building Construction, Mackay, Vol I to VII
Building Drawing, M G Shah, C M Kale, S Y Patki, Tata McGraw Hill
Services in Building Complex, V K Jain, Khanna Publishers
Engineering Materials, Rangwala
Materials of Construction, Ghosh, Tata McGraw Hill Publications
Relevant IS Codes
National Building Code
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 4 of 16
301030 : Fluid Mechanics
Detailed Syllabus
1 Properties of Fluid:
Mass density, specific weight, specific gravity, specific volume, vapour pressure, compressibility, elasticity,
surface tension, capillarity; Newtons law of viscosity, classification of fluids, dynamic viscosity and kinematics
viscosity, variation of viscosity with temperature; Basic concept applicable to fluid mechanics.
2 Fluid Statics
Measurement of Pressure:
Pressure variation in a static fluid, PASCALs law, Units and scales of pressure measurement Atmospheric
pressure, Absolute Pressure, Gauge Pressure and Vacuum Pressure, Hydrostatic Paradox.
Piezometer,U-Tube Manometer, Single Column Manometer,U-Tube Differntial Manometer , Inverterd U-Tube
Differntial Manometer, Micromanometers. Mechanical Pressure Gauges.
Hydrostatic force on plane and curved surface:
Total Pressure and Center of Pressure, Pressure Diagram, Total Pressure on Plane Surfaces and Depth of
Center of Pressure, Total Pressure on Curved Surfaces, Practical applications of Total Pressure and Center of
Pressure
Buoyancy and Flotation:
Buoyant force, Buoyancy and Center of Buoyancy, Archimedes Principle, Principle of Floatation
Metacentre and Metacentric Height, Equilibrium of Floating bodies and Submerged bodies
Evaluation of Metacentric Height Theoretical Method and Experimental Method
Oscillation of Floating Body
Fluids in Relative Equilibrium:
Static fluid subjected to uniform linear acceleration
Liquid containers subjected to constant horizontal acceleration and constant vertical acceleration, Liquid
containers subjected to constant rotation
3 Fluid Kinematics
Fluid flow Methods of analysis of fluid motion, Streamlines, Pathlines, Streaklines and Streamtubes.
Types of fluid flow Steady and unsteady flow, Uniform and non-uniform flow, Laminar, Transitional and
Turbulent flow Reynolds number, Reynolds Experiment, Rotational and Irrotational flow, Subcritical , Critical
and Supercritical flow, Compressible and Incompressible Flow , One , Two and Three dimensional
Circulation and vorticity, Velocity potential and Stream function, Flow net
4 Fluid Dynamics
Eulers equation, Bernoullis equation, Energy correction factor
5 Flow Measuring Devices
Measurement of discharge- Venturi meter, Orifice meter, Nozzle meter, Bend meter, Rotometer.
Measurement of velocity-Pitot tube.
Orifice - Classification, Flow through a Reservoir Opening i.e. Orifice, Trajectory of free jet, Hydraulic
Coefficients, Experimental determination of hydraulic coefficient, Small and large orifice, Time of emptying a
tank with orifice
Mouthpieces-Classification, External cylindrical mouthpiece, Convergent divergent mouthpiece,
Bordas mouthpiece
Notches and Weirs -Discharge over a rectangular notch and a triangular notch, Velocity of approach, End
contractions, Cippoletti Notch, Discharge over a stepped notch, Time of emptying a tank with notch or weir,
Ventilation of weir, Proportional Weir or Sutro Weir
6 Compressible flow:
Basic equations of flow (elementary study), Mach number, Mach cone,
Area Velocity relationship, Stagnation Properties
7 Ideal fluid flow
Uniform flow, source and sink, doublet, free vortex.
List of Experiments:
Hydrostatics Calibration of Flowmeter
Measurement of viscosity Calibration of Orifices
Study of Pressure Measuring Devices Calibration of Mouthpieces
Stability of Floating Body Calibration of Notches
Hydrostatics Force on Flat Surfaces/Curved Calibration of Weirs
Surfaces Flow Visualisation -Ideal Flow
Bernoullis Theorem
Recommended Books:
Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics, Dr. P.M. Modi and Dr. S.M. Seth, Standard Book House
Theory and Applications of Fluid Mechanics, K. Subramanya, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing co. Ltd.
Fluid Mechanics, Dr. A.K. Jain, Khanna Publishers
Engineering Fluid Mechanics, K.L. Kumar, S.Chand & Company Ltd
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 5 of 16
301040 : Mechanics of Solids
Detailed Syllabus
1 Axial Force, Shear Force and Bending moment Diagram
Axial force, shear force and bending moment diagrams for statically determinate beams and frames.
2 Simple Stress & Strain
Definitions of Stress, Strain, Modulus of elasticity, Modulus of Rigidity, Bulk Modulus, Yield stress, Ultimate
stress, Factor of safety, Shear stress, Poisson ratio, Bars of varying sections, Stress due to self weight. Composite
sections, Temperature stresses.
3 Theory of Pure Bending
Flexure formula for straight beams, moment of inertia, product of inertia and polar moment of inertia of plane
areas, principal axes of inertia, moments of inertia about principal axes, Transfer theorem, flitched beams.
Unsymmetrical bending. Flexural stresses due to bending in two planes for symmetrical sections, bending of
unsymmetrical sections.
4 Shear Stress in Beams
Distribution of shear stress across plane sections, shear connectors. Shear center of thin walled sections such as
angle, tee, channel and I sections.
5 Simple theory of torsion
Torsion of circular shafts solid and hollow, stresses in shaft when transmitting power, close-coiled helical
springs under axial load.
6 Bending moment combined with axial loads
Application to members subjected to eccentric loads, core of a section, problems on chimneys, retaining walls
etc., involving lateral loads.
7 Stresses and strains in thin cylindrical and spherical shells under internal pressure.
8 Principal stresses
General equations for transformation of stress, principal planes and principal stresses, maximum shear stress,
determination using Mohrs circle, principal stresses in beams, principal stresses in shafts subjected to torsion,
bending and axial thrust, concept of equivalent torsional and bending moments.
Recommended Books:
Mechanics of Materials, E. P. Popov, Prentice Hall of India Pvt. Ltd..
Mechanics of Materials, Timoshenko & Gere, Tata McGraw Hill Book Publishing Co. Ltd..
Engineering Mechanics, Timoshenko & Young, Tata McGraw Hill Book Publishing Co. Ltd..
Mechanics of Structures, S.B. Junnarkar, Charotar Publishers.
Mechanics of Materials, James M. Gere, Brooks/Cole.
Strength of Materials, G.H. Ryder, MacMillan.
Mechanics of Materials, Peter & Singer, McGraw Hill.
Strength of Materials, Schaums Outline Series, William A. Nash, McGraw Hill Book Co.
Mechanics of Materials, Beer & Johnston, McGraw Hill Books Publishing Co. Ltd..
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 6 of 16
301050 : Concrete Technology
Detailed Syllabus
1 Properties of Ingredients:
Properties of coarse and fine aggregates and their influence on concrete, types of cement and their use, physical
properties of 33 Grade, 43 Grade, 53 Grade ordinary Portland cement, Portland pozzolana cement, rapid
hardening Portland cement, hydrophobic cement, low heat Portland cement and sulphate resisting Portland
cement as per relevant I.S. codes
Stone types and properties, preservative treatments, stone aggregates.
2 Grades of concrete:
Concrete for ordinary work, light weight concrete, high density concrete, workability, durability and strength
requirements, effect of w/c ratio, acceptability criteria, laboratory testing of fresh and hardened concrete.
3 Concrete mix design:
Mix design for compressive strength by I.S. methods, road note method and British method, mix design for
flexural strength.
4 High performance concrete:
Constituents of high grade concrete, various tests and application of high performance concrete.
5 Admixtures:
Plasticizers, retarders, accelerators and other admixtures, test on admixtures, chemistry and compatibility with
concrete.
6 Ready mix concrete: requirements of ready mix concrete, transit mixer details, mix design of RMC.
7 Concrete for repairs and rehabilitation of structures:
Polymer concrete, fiber reinforced concrete, polymer impregnated concrete, polymer modified cement concrete
and Ferro cement, different tests.
8 Non-Destructive testing of concrete:
hammer test, ultrasonic pulse velocity test, load test, carbonation test, half cell potentio-meter, corrosion of steel,
core test and relevant provision of I.S. codes.
List of experiments:
Effect of w/c ratio o workability (slump cone, compaction factor, V-B test, flow table)
Effect of w/c ratio on strength of concrete,
Mix design in laboratory
Non destructive testing of concrete some applications (hammer, ultrasonic)
Secant modulus of elasticity of concrete & indirect tensile test on concrete.
Study of admixtures & their effect on workability and strength of concrete.
Modulus of rupture of concrete.
Permeability test on concrete
Tests on polymer modified mortar / concrete
Tests on fiber-reinforced concrete
Flexture test on beam (central point load and two point load) (plotting of load deflection curve and finding value
of E)
Recommended Books:
Plain & reinforced concrete, Vol. I, O.P. Jain & Jaikrishna,
Concrete technology, theory and practice, M.S. Shetty.
Properties of concrete, Neville, El, Society & Pub.
Relevant I.S. codes.
Special Publication of ACI on Polymer concrete and FRC.
Proceedings of International Conferences on Polymer Concrete and FRC.
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 7 of 16
301060 : Construction Materials Laboratory
Detailed Syllabus
Following experimentss to be performed as per relevant IS standards:
Physical properties of Cement :
Consistency,
compressive strength,
initial & final setting time,
soundness.
Bricks:
water absorption
compressive strength
Wood:
Tension
Compression
Tiles:
transverse test
water absorption test
Steel:
Tension test on mild steel bars (stress-strain) behavior, Young's modulus determination)
Test on tour steel bar ( tension,bend & rebend)
Test on cast iron (transverse, tension)
Shear test on mild steel bar / cast iron bar
Torsion test on mild steel, cast iron bar
Brinell hardness test
Rockwell hardness test
Izod impact test / charpy test
Aggregates:
sieve analysis
crushing value
shape test
impact test
abrasion test
crushing test
Los angels abrasion test
soundness test
Bitumen:
Penetration test
Ductility test
Softening point test
Viscosity test
Flash & fire point test
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 8 of 16
200012 : Applied Mathematics- II
Detailed Syllabus
1 Statistics
Review of measures of central tendency, measure of variation and probability, Discrete and continuous Random
variable Binomial, Poisson and Normal distribution. Random sampling, sampling distribution, Standard error,
Central limit theorem. Estimation of parameters, point estimation, interval estimation, confidence internal.
Testing of Hypothesis, Large sample and small sample tests. t test and F test, Chi-square test
Correlation and regression, Coefficient of correlation and Rank correlation, Regression analysis. Curve fitting,
method of least square
Statistical quality control and control charts
Analysis of variance
2 Numerical Methods
Solutions of systems of linear algebric equations. Gauss Elimation, Gauss Jordan, Crouts (LU) method, Gauss
Seidal and jacobi iteration
Differential equation ,Taylor Series method, Picard method, Rungakutta method, Euler method
Recommended Books:
Mathematical Statistics, Kapur & Saxena
Statistics, Schaums Series
Numerical Methods for Engineers, S K Gupta
Introductory methods of numerical analysis, S S Sastry
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 9 of 16
301012 : Geomatics- II
Detailed Syllabus
1 Curves
Definitions of different terms, necessity of curves and types of curves
Simple circular curves and compound curves, office and field work, linear methods of setting out of curves
Angular methods for setting out of curves, two theodolite and Rankine deflection angle methods
Reverse and transition curves, their properties and their advantages, design of transition curves, shift, spiral
angle
Composite curves office and field work, setting out of curve by angular method, composite curve problems
Vertical curves definitions, geometry and types, tangent correction and chord gradient methods, sight distance
on a vertical curve, difficulties in setting out curves and solutions for the same
2 Modern surveying instruments
Electronics in surveying, general principles used in the instruments
Auto levels, self compensating instrument , Digital Level
Electronic distance measurements - types, principles, applications of Total Station in surveying, corrections for
field observations
Electronic digital theodolite types, uses and applications, concept of total station
Use of computer in survey work for level computation and plotting contour plan
3 Tacheometric surveying
Principles and uses, advantages, stadia formula, different methods of tacheometer, subtense bar method, location
details by tacheometer, stadia diagram and tables, error and accuracy in tacheometry survey work
4 Global Positioning System (G.P.S)
G.P.S. Segments: Spaces Segment, Control Segment, User Segment
Features of G.P.S. Satellites, Principle of Operation
Surveying with G.P.S.: Methods of observations, Absolute Positioning, Relative Positioning, differential G.P.S.,
Kinematics of G.P.S.
G.P.S. Receivers: Navigational Receivers, Surveying Receivers, Geodetic Receivers,
Computation of Co- ordinates:- Transformation from Global to Local Datum , Geodetic Coordinates to map co-
ordinates , G.P.S. Heights and mean sea level Heights
Applications of G.P.S.
5 Remote Sensing:
Electromagnetic remote sensing process
Physics of radiant energy: Nature of Electromagnetic radiation, Electromagnetic spectrum
Energy Source and its Characteristics
Atmospheric influences: Absorption, Scattering
Energy interaction with Earth Surfaces: Spectral reflectance Curve
Image Acquisition: Photographic sensors, Digital Data, Earth Resource satellites, Image resolution
Image Interpretation
Application of Remote Sensing
6 Geographical Information System:
Information systems, spatial and non- spatial information, geographical concept and terminology, advantages of
GIS, Basic component of GIS
Commercially available GIS hardware and Software
Field data, statistical data, maps, aerial Photographs, satellite data, points , lines, and areas features, vector and
raster data, data entry through keyboard, digitizer and scanners, preprocessing of data rectification and
registration , interpolation techniques
Practicals:
To find the constants of a tacheometer and to verify field distances
A project for preparing L section and cross section, block contouring and tacheometric survey
Height and distance problems in tacheometric surveying
Study of satellite images and its interpretation
Determination of horizontal, sloping and vertical distance between any two points by using Total Station
Geo-registration of map and its digitization by using suitable GIS software.
Map editing, vector and raster analysis of digitized map by using suitable GIS software
Collection of field data like point data, line data and area data by using surveying and mapping GPS receiver
Recommended Books:
Surveying and Leveling, Vol I & II, III, B.C.Punmiya , Laxmi Publication
Surveying and Leveling, N N Basak, Tata McGraw Hil
Surveying, R Agor, Khanna Publishers
Concepts and Techniques of Geographical Information System, Lo C.P.Yeung A K W, Prentice Hall India
Introduction to Geographical Information System, Kang-tsung Chang, Tata mcGraw Hill
Remote sensing and Geographical information sysytem, K. Anjali Rao , BS Publications
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 10 of 16
301070 : Engineering Geology
Detailed Syllabus
1 Introduction
Branches of geology useful to civil engineering, importance of geological studies in various civil engineering
projects
2 General geology
Internal structure of the earth & use of seismic waves in understanding the interior
Agents modifying the earth surface, study of weathering & its significance in physical & engineering properties
of rocks like strength & water tightness, durability etc.
Geological action of river, wind & glaciers, erosion; transport & depositional landforms created by them
Volcanism- central type & fissure type, products of volcanoes
Earthquakes- earthquake waves, construction and working of seismographs, earthquake zones of India
Geological aspects for earthquake resistant structures
3 Mineralogy
Methods of mineral identification, physical properties of minerals, rock forming minerals, megascopic
identification of common primary & secondary minerals, study of common ore minerals - as prescribed under
Practicals
4 Petrology
Study of igneous, sedimentary rocks, distinguishing properties between igneous, sedimentary and metamorphic
rocks to identify them in field
Igneous petrology- mode of formation, textures, structures etc., Hatchs scheme of classification, study of
common igneous rocks
Sedimentary petrology- mode of formation, textures, characteristics of shallow water deposits like lamination,
bedding, current bedding etc., classification of secondary rocks, types, residual deposits, true clastic deposits,
chemically formed and organically formed deposits, commonly occurring sedimentary rocks
Metamorphic petrology- mode of formation, agents and types of metamorphism, metamorphic minerals, rock
cleavage, structures & textures in metamorphic rocks, classification, commonly occurring metamorphic rocks
5 Structural geology
Structural elements of rocks- dip, strike, outcrop patterns, unconformities, outliers & inliers, study of joints,
faults and folds, importance of structural elements in engineering operations
6 Stratigraphy
Principle of stratigraphy & co-relation, geological time scale, physiographic divisions of India- study of
formations occurring in peninsular India
7 Geological investigations
Preliminary geological investigations & their importance to achieve safety & economy of the projects,
supporting case histories of dams and tunnel projects in Maharashtra state
Methods of surface & sub-surface investigations- trial pits, trenches, drill holes, geological logging, inclined drill
holes, resistivity method & seismic methods
Use of aerial photographs & satellite imageries in civil engineering projects
8 Ground water
Sources & zones, water table, unconfined & perched aquifers, springs
Factors controlling water bearing capacity of rocks, pervious & impervious rocks, cone of depression & its use
in civil engineering
9 Geology of dam and reservoir site
Importance of geological conditions while selecting the type of dam, ideal geological conditions for dam and
reservoir site, favorable & unfavorable conditions in different types of rocks in presence of various structural
features, precautions to be taken to counteract unsuitable conditions, significance of faults, folds, crushed zone,
dykes & fractures on the dam site and treatment giving to such structures, tail channel erosion
10 Tunneling
Importance of geological considerations while choosing sites and alignment of the tunnel
Ideal site conditions for tunneling, geological conditions to be avoided
11 Stability of hill slopes
Land slides, their types, causes and preventive measures for landslides
12 Building stones
Geological factors controlling properties of good building stones, consideration of common rocks as building
stones, study of different building stone from various formation in Indian peninsula, geological factors
controlling location of quarries, quarrying methods and quarrying operations
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 11 of 16
Practicals:
Study of physical properties of the minerals
Identification of minerals- crystalline, crypto-crystalline and amorphous silica & their varieties, Orthoclase,
Microcline, Plagioclase, Muscovite, Biotite, Hornblende, Asbestos, Augite, Olivine, Tourmaline, Garnet,
Natrolite, Actinolile, Calcite, Dolomite, Gypsum, Beryl, Bauxite, Graphite, Galena, Pyrite, Hematite,
Magnetite, Chalcopyrite, Chromite, Corundum, Talc, Fluorite, Kyanite
Identification of rocks Igneous: Granite and its varieties, Synite, Dionite, Gabbro, Pegmatite, Porphyry,
Dolerite, Rhyolite, Pumice, Trachyte, Basalt and its varieties, Volcanic Breccia, Volcanic Tuffs. Sedimentary:
Conglomerate, Breccia, Sandstone & its varieties, Shales, Limestone, Melliolite, Laterite, Slate, Phyllite, Mica,
Schists, Hornblende schists, Granite gneiss & its varieties, Augen gneiss, Marbles & quartzite
Structural geological maps
Study of core samples, percentage recovery, RQD, core logging.
Recommended Books:
A Text Book of Engineering Geology, Dr R B Gupte
A Text Book of Engineering & General Geology, Parbin Singh
A Text Book of Engineering Geology, Dr Kesavalu
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 12 of 16
301081 : Building Planning & Graphics I
Detailed Syllabus
1 Principles of modular planning, Architectural Planning , massing & composition, Concept of built environment
& its application in Planning, Recommendations of National Building Organisation
2 Planning of Buildings such as:
Building For Residence: Bungalows, Row Houses, Hostels, Apartment Houses
Building for Education: Schools, College, Libraries
Buildings for Health: Hospitals, Health Centers, Dispensaries, Maternity Homes, Sanatoriums
Industrial Structures
Buildings for Entertainment: Theaters, Cinema Hall, Club House, Sport Clubs
Other Structures: Offices, Hotels, Rest Room
3 Preparation of constructional details and drawings of foundations, floors, roofs flat and pitched, doors and
windows, staircases, plumbing items, columns, beams and slabs
4 Staircase: Types, size and location, layout, design considerations, materials for stair case construction
5 Perspective Drawing: One point Perspective and Two Point perspective
6 Town planning : Objectives and principles, master plan, Road Systems, Zoning, Green Belt, Slums , D.C.Rules
7 Recommended Books:
Building Drawing, M G Shah, C M Kale, S Y Patki, Tata McGraw Hill
Building Drawing , Y.S.Sane
Civil Engineering Drawing, M Chakraborty
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 13 of 16
301091 : Applied Hydraulics - I
Detailed Syllabus
1 Laminar Flow
Laminar flow through: circular pipes, annulus and parallel plates. Stokes law, Measurement of viscosity.
2 Turbulent Flow:
Reynolds experiment, Transition from laminar to turbulent flow. Definition of turbulence, scale and intensity,
Causes of turbulence, instability, mechanism of turbulence and effect of turbulent flow in pipes. Reynolds
stresses, semi-empirical theories of turbulence, Prandtls mixing length theory, universal velocity distribution
equation. Resistance to flow of fluid in smooth and rough pipes, Moodys diagram.
3 Boundary Layer Analysis:
Assumption and concept of boundary layer theory. Boundary-layer thickness, displacement, momentum &
energy thickness, laminar and Turbulent boundary layers on a flat plate; Laminar sub-layer, smooth and rough
boundaries. Local and average friction coefficients. Separation and Control.
4 Flow Past immersed bodies:
Drag and lift ,Types of drag , Drag on a sphere, cylinder ,flat plate and Airfoil, Karman Vortex Street, effect of
free surface and compressibility on drag .Development of lift on immersed bodies ,Lift ,Magnus Effect and
Circulation, lift characteristics of airfoils , polar diagram.
5 Dimensional Analysis and Hydraulic Similitude:
Dimensional homogeneity, Rayleigh method, Buckinghams Pi method and other methods. Dimensionless
groups. Similitude, Model studies, Types of models. Application of dimensional analysis and model studies to
fluid flow problem.
6 Introduction to Open Channel Flow
Comparison between open channel flow and pipe flow, geometrical parameters of a channel, classification of
open channels, classification of open channel flow, Velocity Distribution of channel section.
7 Uniform Flow
Continuity Equation ,Energy Equation and Momentum Equation ,
Characteristics of uniform flow , Chezys formula , Mannings formula
Factors affecting Mannings Roughness Coefficient n .
Most economical section of channel. Computation of Uniform flow
Normal depth .
8 Non-Uniform Flow
Specific energy, Specific energy curve, critical flow, discharge curve Specific force Specific depth , and Critical
depth .Channel Transitions .
Measurement of Discharge and Velocity Venturi Flume, Standing Wave Flume , Parshall Flume ,Broad
Crested Weir.
Measurement of Velocity- Currentmeter , Floats, Hot-wire anemometer.
9 Gradually Varied Flow
Dynamic Equation of Gradually Varied Flow, Classification of channel bottom slopes , Classification of surface
profile, Characteristics of surface profile. Computation of water surface profile by graphical, numerical and
analytical approaches. Direct Step method, Graphical Integration method and Direct integration method.
10 Hydraulic Jump
Theory of hydraulic jump, Elements and characteristics of hydraulic jump in a rectangular Channel, length and
height of jump, location of jump, Types ,applications and location of hydraulic jump. Energy dissipation and
other uses, surge as a moving hydraulic jump. Positive and negative surges.
11 List of Experiment
Length of establishment of flow Uniform Flow
Velocity distribution in pipes Velocity Distribution in Open channel flow
Laminar Flow Venturi Flume
Flow Visulisation Standing Wave Flume
Studies in Wind Tunnel Gradually Varied Flow
Boundary Layer Hydraulic Jump
Flow around an Aerofoil / circular cylinder Flow under Sluice Gate
Recommended Books
Hydraulics and Fluid Mechanics, Dr. P.M. Modi and Dr. S.M. Seth, Standard Book House
Theory and Applications of Fluid Mechanics, K. Subramanya, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing co. Ltd.
Fluid Mechanics, Dr. A.K. Jain, Khanna Publishers
Fluid Mechanics and fluid pressure Engineering, D. S. Kumar, F.K. Kotharia and sons.
Open channel Flow , K. Subramanya, Tata McGraw Hill Publishing co. Ltd.
Open channel Hydraulics , Ven Te Chow , Tata McGraw Hill Publishing
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 14 of 16
301101 : Structural Analysis - I
Detailed Syllabus
1 General theorems : Theorems relating to elastic structures, Principle of virtual work, Strain energy in elastic
structures, complementary energy, Castiglianos theorem, Bettis and Maxwells reciprocal theorems.
2 Deflection of statically determinate structures: Deflection of determinate beams by Double integration
Macaulays, Moment area and Conjugate beam methods, Principle of virtual work (unit load method) and
Castiglianos theorem, Deflection of determinate pin jointed trusses and rigid jointed frames by principle of
virtual work (unit load method) ,Starin Energy and Castiglianos theorem.
3 Influence lines for statically determinate structures : Influence lines for cantilever, simply supported beam,
overhanging beam and pin jointed trusses, criteria for maximum shear force and bending moment under moving
loads for simply supported beams, absolute maximum bending moment
4 Elastic arches : determination of normal thrust, shear force and bending moment for parabolic and segmental
three hinged arches, Influence lines for normal thrust, shear force and bending moment for three hinged
parabolic arch.
5 Suspension bridges : Suspension cable with three hinged stiffening girder, influence line diagrams for horizontal
tension in the cable, shear force and bending moment at any section of the stiffening girder.
6 Struts : struts subjected to axial loads, concept of buckling, Eulers formula for strut with different support
conditions, Eulers and Rankines design formulae. Structs subjected to eccentric and lateral loads, struts with
initial curvature.
Recommended Books:
Basic Structural Analysis, C.S. Reddy., Tata McGraw Hill Publishing Co. Ltd.
Theory of Structures, Timoshenko & Young, Tata McGraw Hill Book Publishing Co. Ltd.
Intermediate Structural Analysis, C. K. Wang, McGraw Hill Publishing Co.
Structural Mechanics Vol I & II, Junnarkar S.B., Charotar Publisher.
Elementary Structural Analysis, Norries & Wilbur, McGraw Hill Publishing Co.
Structural Analysis, Laursen, H.I., McGraw Hill Publishing Co.
Structural Analysis, Bhavikatti, Vikas Publishers.
Structural theorems and their application, B.G. Neal, Pergaman Press.
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 15 of 16
301110 : Computer Aided drafting
Detailed Syllabus
1 To create CAD files and draw basic elements (lines, circles, arcs, curves and polygons) in the file
2 To manipulate elements in the file by using manipulation tools like: move, delete, copy, rotate, mirror and
extend, to change colours, styles, types and weights of existing elements, To use various view controls,
3 Terminology: extension line, dimension line, arrowhead, leader, diameter symbols, radius symbol, aligned and
unidirectional dimensioning
4 To draw title block, to print / plot drawing/s at different scales
5 To draw objects to an exact size and combining the same to create different shapes, To produce sectional
drawings, to create multi-view drawing using orthogonal projections
Second Year B. Tech- 2005-06(Civil Engg.) 16 of 16
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nitc Mechanical Btech Syllabus and CurriculumDocument110 paginiNitc Mechanical Btech Syllabus and Curriculumpikasoc1Încă nu există evaluări
- Civil Soe and Syllabus 2014-15 For Old Course PDFDocument104 paginiCivil Soe and Syllabus 2014-15 For Old Course PDFYogesh KherdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Programme: 101 - B.TECH. - CIVIL ENGINEERING: Semester SevenDocument50 paginiProgramme: 101 - B.TECH. - CIVIL ENGINEERING: Semester SevenGiggsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus: II YearDocument12 paginiSyllabus: II YearSheezan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Syllabus: II YearDocument12 paginiSyllabus: II YearSheezan KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assam Science and Technology University Guwahati: B.Tech Civil Engineering 3 SemesterDocument13 paginiAssam Science and Technology University Guwahati: B.Tech Civil Engineering 3 SemesterKF KF360Încă nu există evaluări
- Course Beyond SyllabusDocument21 paginiCourse Beyond SyllabuskarthiyuvenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Structure For M.Tech in Mechanical Engineering: Specialization: Machine DesignDocument10 paginiCourse Structure For M.Tech in Mechanical Engineering: Specialization: Machine DesignSandip BarikÎncă nu există evaluări
- DBATUDocument33 paginiDBATUSunil Rathod0% (1)
- Gujarat Technological University Mechanical EngineeringDocument5 paginiGujarat Technological University Mechanical EngineeringAsyPatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- SE Electrical Engg. 2019 PattDocument47 paginiSE Electrical Engg. 2019 PattPrathameshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Csvtu Syllabus Be Civil 3 SemDocument12 paginiCsvtu Syllabus Be Civil 3 SemMinendra Kumar ChandrakarÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.tech 4th Sem CE Final 2Document15 paginiB.tech 4th Sem CE Final 2Medalson RonghangÎncă nu există evaluări
- BTech Civil Scheme and Syllabi Subject To Approval of AcademDocument47 paginiBTech Civil Scheme and Syllabi Subject To Approval of Academdinesh_nitu2007Încă nu există evaluări
- Updated B.Tech 3rd & 4th Sem Structure & Syllabus JUT, RanchiDocument196 paginiUpdated B.Tech 3rd & 4th Sem Structure & Syllabus JUT, RanchiAbhishek 18CED31Încă nu există evaluări
- Latest Syllabus B.tech 3rd & 4th SyllabusDocument213 paginiLatest Syllabus B.tech 3rd & 4th SyllabusKanhai BouriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pandit Deendayal Petroleum University Gandhinagar School of Technology Course Structure For B Tech in Civil EngineeringDocument12 paginiPandit Deendayal Petroleum University Gandhinagar School of Technology Course Structure For B Tech in Civil EngineeringAJAY GELOTÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd YearDocument15 pagini2nd YearSaket ThakkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TS SBTET C-18 DCE III Sem SyllabusDocument120 paginiTS SBTET C-18 DCE III Sem SyllabusSrinivas NaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engg - 2-1 SEM CS & Syllabus - UG - R20Document21 paginiCivil Engg - 2-1 SEM CS & Syllabus - UG - R20Sobha Ranjith KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.Tech-4th-Sem-CE-final-2 2Document16 paginiB.Tech-4th-Sem-CE-final-2 2Bhaswat KashyapÎncă nu există evaluări
- CIVIL R20 Regulation SyllabusDocument40 paginiCIVIL R20 Regulation Syllabusvenkat gÎncă nu există evaluări
- CSE 3 NotesDocument15 paginiCSE 3 NotesCSE SSGIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE SyllaubusDocument32 paginiECE SyllaubusAkhilesh UppulaÎncă nu există evaluări
- R18B.tech - ECMI IIYearSyllabusDocument52 paginiR18B.tech - ECMI IIYearSyllabusShadow MonarchÎncă nu există evaluări
- SRM 15 PDFDocument55 paginiSRM 15 PDFjeyaprabha [prof./civil]Încă nu există evaluări
- Yeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering: (Accredited 'A' Grade by NAAC With A Score of 3.25)Document14 paginiYeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering: (Accredited 'A' Grade by NAAC With A Score of 3.25)Vedant MankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Urr18 Syllabi EceDocument114 paginiUrr18 Syllabi EceSri HarshaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Itm University Naya Raipur, Raipur: Bachelor of Technology)Document21 paginiItm University Naya Raipur, Raipur: Bachelor of Technology)Mufaddal ZakaviÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uet Lahore CourseDocument23 paginiUet Lahore CourseSufian AhmadÎncă nu există evaluări
- B.tech 2 1 Mechanical Engineering R20 Course Structure SyllabusDocument21 paginiB.tech 2 1 Mechanical Engineering R20 Course Structure SyllabusArun KÎncă nu există evaluări
- VNR Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering & Technology Hyderabad B.Tech. I Year (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) I Semester R19Document36 paginiVNR Vignana Jyothi Institute of Engineering & Technology Hyderabad B.Tech. I Year (Electrical and Electronics Engineering) I Semester R19Bhanuteja KorutlaÎncă nu există evaluări
- B - Tech Civil Batch 2011 PTU SyllabusDocument12 paginiB - Tech Civil Batch 2011 PTU SyllabusMohit Dev100% (1)
- Ece PDFDocument36 paginiEce PDFGnaneshwar KandukuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- BE Civil 2015 CourseDocument6 paginiBE Civil 2015 CourseVijay Muthekar0% (1)
- II B.tech - Mechanical Engineering R20 Course Structure SyllabusDocument48 paginiII B.tech - Mechanical Engineering R20 Course Structure SyllabusDr.KVSRIT PrincipalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engg - 1&2 YEARS CS & Syllabus - UG - R20Document76 paginiCivil Engg - 1&2 YEARS CS & Syllabus - UG - R20udayramakoteswarao.2410Încă nu există evaluări
- 3rd&4thsemsyllabus PDFDocument139 pagini3rd&4thsemsyllabus PDFVikash KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Year of Bachelor of TechnologyDocument18 paginiFirst Year of Bachelor of TechnologyGiggsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering: (Accredited 'A' Grade by NAAC With A Score of 3.25)Document14 paginiYeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering: (Accredited 'A' Grade by NAAC With A Score of 3.25)Yogesh KherdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 Sem ME Civil (Structure)Document11 pagini1 Sem ME Civil (Structure)Vijay YadavÎncă nu există evaluări
- R18 B.Tech 2-1 EEE SyllabusDocument16 paginiR18 B.Tech 2-1 EEE SyllabusSravan KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 21 - R20 - IIMid Nov-December-2023Document6 pagini21 - R20 - IIMid Nov-December-2023NADELLA Jhansi raniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Yeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering: (Accredited 'A' Grade by NAAC With A Score of 3.25)Document46 paginiYeshwantrao Chavan College of Engineering: (Accredited 'A' Grade by NAAC With A Score of 3.25)Yogesh KherdeÎncă nu există evaluări
- JNTUA B.tech Civil R15 SyllabusDocument187 paginiJNTUA B.tech Civil R15 Syllabusr.vani100% (1)
- R18B TECHCIVILENGG IIYearSyllabusDocument32 paginiR18B TECHCIVILENGG IIYearSyllabusmohammed shamsuddinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Code Title Contact Hrs/week Credits MarksDocument3 paginiCode Title Contact Hrs/week Credits MarksSourabh Alok SaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai (C.G.)Document11 paginiChhattisgarh Swami Vivekanand Technical University, Bhilai (C.G.)bhaskarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineerig R19 II Year Course Structure SyllabiDocument50 paginiCivil Engineerig R19 II Year Course Structure SyllabikoppolusrinivasuluÎncă nu există evaluări
- Revised Syllabus M.Chem Engg 2021Document35 paginiRevised Syllabus M.Chem Engg 2021Kajal MIshraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final BTech MechanicalDocument31 paginiFinal BTech MechanicalAniket GaikwadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gujarat Technological University Automobile EngineeringDocument4 paginiGujarat Technological University Automobile EngineeringvetocÎncă nu există evaluări
- Civil Engineering BE IVDocument12 paginiCivil Engineering BE IVkamalnitrrÎncă nu există evaluări
- B Tech Civil Batch 2011 Uploaded 16-07-13Document66 paginiB Tech Civil Batch 2011 Uploaded 16-07-13Girish Jain100% (1)
- BtechaDocument104 paginiBtechamathewsivin5266Încă nu există evaluări
- CSE 1st-2nd Sem Syllabus DCE-AKUDocument28 paginiCSE 1st-2nd Sem Syllabus DCE-AKUdheerajkumar8340563557Încă nu există evaluări
- Engineering Surveying: Theory and Examination Problems for StudentsDe la EverandEngineering Surveying: Theory and Examination Problems for StudentsEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (8)
- Experiment No.8Document5 paginiExperiment No.8Osama RashaydaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chute Design and Problems-Causes and SolutionDocument19 paginiChute Design and Problems-Causes and SolutionThakaneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Best Practices For Design of Slurry Flow DistributionsDocument11 paginiBest Practices For Design of Slurry Flow Distributionsfelipe muñozÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Boundary Layer SolutionDocument6 paginiThermal Boundary Layer Solutionmsnaghavi100% (3)
- Effect of Impeller Blades Number On The Performance of A Centrifugal PumpDocument10 paginiEffect of Impeller Blades Number On The Performance of A Centrifugal PumpPrasad GharatÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2018 Experimental and CFD Analysis of Solar Air Heater With Rectangular ShapedDocument5 pagini2018 Experimental and CFD Analysis of Solar Air Heater With Rectangular ShapedaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sound Generated AerodynamicallyDocument33 paginiSound Generated AerodynamicallyAbraham Benjamin Britto100% (1)
- Model Rocket Aerodynamics PDFDocument27 paginiModel Rocket Aerodynamics PDFDenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 4 EditedDocument15 paginiChapter 4 EditedfieraminaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modern Dispersion Technology: A Primer in DispersersDocument24 paginiModern Dispersion Technology: A Primer in Dispersersdevang asherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cherdron 1978 - J Fluid Mech - Asymmetric Flows and Instabilities in Symmetric Ducts With Sudden ExpansionsDocument24 paginiCherdron 1978 - J Fluid Mech - Asymmetric Flows and Instabilities in Symmetric Ducts With Sudden ExpansionsNandan SarkarÎncă nu există evaluări
- PaperM - 4346 MelihDocument10 paginiPaperM - 4346 MelihbensouiciÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluent Combustion AnalysisDocument31 paginiFluent Combustion AnalysisVignesh SambanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unsteady Heat Transfer Measurements in ADocument249 paginiUnsteady Heat Transfer Measurements in AM usman qureshiÎncă nu există evaluări
- GalindoDocument8 paginiGalindoSouhardya BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- FEDSM2012-72094: Study of Flow Controlling On LP Turbine at Different Reynolds NumberDocument11 paginiFEDSM2012-72094: Study of Flow Controlling On LP Turbine at Different Reynolds NumberKarthikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal Systems Design LabDocument40 paginiThermal Systems Design LabSyam Raju100% (1)
- Section 5B Rheology & HydraulicsDocument10 paginiSection 5B Rheology & HydraulicsLazharÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual TURBO 87Document334 paginiUser Manual TURBO 87ravennÎncă nu există evaluări
- Turbontachinery: of TheDocument149 paginiTurbontachinery: of TheAnoopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrodynamics of Gas Stirred Melts - Part I - Gas-Liquid CouplingDocument10 paginiHydrodynamics of Gas Stirred Melts - Part I - Gas-Liquid CouplingStephany CamacaroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prediction of Pressure Drop For Tubulent Flow in 90 BendsDocument3 paginiPrediction of Pressure Drop For Tubulent Flow in 90 BendsNakkolopÎncă nu există evaluări
- Moore (1974) Swab and Surge Pressures (Drilling Practices Manual)Document12 paginiMoore (1974) Swab and Surge Pressures (Drilling Practices Manual)James BourneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Turbulence, ME634, Lecture NotesDocument144 paginiIntroduction To Turbulence, ME634, Lecture NotesSreekar Gomatam100% (2)
- Gas Natural TransmisionDocument43 paginiGas Natural Transmisionangel3reyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Designing Criteria Siphonic Roof Drainage SystemDocument42 paginiDesigning Criteria Siphonic Roof Drainage SystemCzarSASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Explicacion K PDFDocument10 paginiExplicacion K PDFLeidy Renteria EstradaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computational Fluid DynamicsDocument73 paginiComputational Fluid Dynamicskevinmuri100% (2)
- Best Practices For Flushing GearboxesDocument3 paginiBest Practices For Flushing GearboxesElios TorreblancaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fluid Mechanics MCQSDocument46 paginiFluid Mechanics MCQSyaseenÎncă nu există evaluări