Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pathophysiology of Chronic Glomerulonephritis: Legend
Încărcat de
Georich NarcisoTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pathophysiology of Chronic Glomerulonephritis: Legend
Încărcat de
Georich NarcisoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
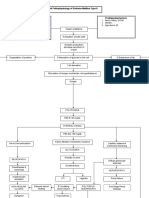
Pathophysiology of Chronic Glomerulonephritis
PRIMARY CAUSES SECONDARY CAUSES
Unknown SLE, Good pastures,
Direct glomerular Infection
damage
Inflammation
Damage to the glomerular
membrane Lodging of antigen-antibody
complexes in the glomerular
membrane
Fibrosis, scarring, sclerosis
of the glomerulus
Release of inflammatory Pain and
mediators
tenderness
on the back
Decrease in glomerular
Hyperpermeability of the Renal failure
filtration rate
glomerular membrane
Fatigue, difficulty of
Sodium and water breathing, anemia,
Increased urinary retention nausea and vomiting
frequency, proteinuria,
albuminuria, hematuria
Diuretics
Decreased urinary output,
Edema, Hypertension
Dark frothy urine Angiotensin Converting
Enzyme Inhibitors,
Amgiotensin II receprotr
Congestive heart failure, blockers for hypertension
Pulmonary edema
LEGEND:
Causes
Diet modifications: low
salt, low fat, low protein Disease process
diet. Fluid restrictions as
Reaction/compensation
advised
Signs and symptoms
Complications
Treatment and management
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Nursing Care Plan for Hypertension ManagementDocument5 paginiNursing Care Plan for Hypertension Managementbhavana100% (1)
- NCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingDocument3 paginiNCP Hyperbilirubinemia Staff NursingVerajoy DaanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study SummaryDocument7 paginiDrug Study SummaryKateLayaogÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample (Concept Map)Document1 paginăSample (Concept Map)NMDNMSSDÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisDocument9 paginiPathophysiology (Book-Based) : CystitisIrish EspinosaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Congenital Heart Defects in BabiesDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Congenital Heart Defects in BabiesMarlon CruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hypovolemic Shock Concept MapDocument1 paginăHypovolemic Shock Concept MapJM AsentistaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CebUN Drug Study for HypothyroidismDocument4 paginiCebUN Drug Study for HypothyroidismGwyn RosalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydronephrosis Fred LuceDocument69 paginiHydronephrosis Fred LuceKMÎncă nu există evaluări
- DRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Document11 paginiDRUG STUDY (Preeclampsia)Jobelle AcenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMADocument3 paginiCommon Side Effects of Oxytocin Include:: CNS: Maternal: COMAann camposÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisDocument4 paginiManage Preterm Labor with Bed Rest and TocolysisYeni PuspitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pre Term Case OlieDocument10 paginiPre Term Case OlieKimsha ConcepcionÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeDocument2 paginiNCP - Activity Intolerance & Excess Fluid VolumeCindy MariscotesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study Pedia WardDocument2 paginiDrug Study Pedia WardCayanne ChuaÎncă nu există evaluări
- N. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Document32 paginiN. Bacalso Ave., Cebu City Philippines: Page 1 of 32Joule PeirreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Midyr Case Study NewDocument18 paginiMidyr Case Study NewAndres Ham Samson BernabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of the urinary tractDocument8 paginiPathophysiology of the urinary tractMarjorie CarganillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Individual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisDocument26 paginiIndividual Case Study Acute GlomerulonephritisBatrisyia HalimsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument2 paginiDrug Studymegreen GamingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study SARAHDocument2 paginiDrug Study SARAHirene Joy DigaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Assessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationDocument6 paginiAssessment/ Cues Nursing Diagnosis Background Knowledge Goal and Objectives Nursing Interventions and Rationale EvaluationimnasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Albendazole - Drug Information PDFDocument7 paginiAlbendazole - Drug Information PDFjjjkkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study Benign Tumors of The Uterus: MyomaDocument3 paginiCase Study Benign Tumors of The Uterus: MyomaToto RyanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study..Document36 paginiCase Study..Michael G. CorreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Non-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The AmericasDocument2 paginiNon-Modifiable Factor Modifiable Factor: South-East Asia, Eastern, Mediterranean, Western Pacific, and The Americaschristian quiaoitÎncă nu există evaluări
- ICS Pedia WardDocument8 paginiICS Pedia Wardsweet061991Încă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument8 paginiDrug StudyzenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Analysis and Interventions Pyschopathology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorDocument1 paginăCase Analysis and Interventions Pyschopathology: Predisposing Factor Precipitating FactorSydelle GravadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study Quinine SulfateDocument7 paginiDrug Study Quinine SulfateKathlyn_Matic_6376Încă nu există evaluări
- NCP - ERDocument5 paginiNCP - ERAnnelore ArcayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug StudyDocument6 paginiDrug StudyAisha LakibulÎncă nu există evaluări
- MYOMA PathoDocument1 paginăMYOMA Pathobsn2011100% (1)
- Nursing Care Plan for a Patient with Multiple Bruises and Difficulty BreathingDocument3 paginiNursing Care Plan for a Patient with Multiple Bruises and Difficulty BreathingLeogalvez BedanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophy NCADocument1 paginăPathophy NCAKaren ValdezÎncă nu există evaluări
- OPD Case Study SummaryDocument35 paginiOPD Case Study SummaryMicah MagallanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AnatomyDocument6 paginiAnatomyKadulum100% (1)
- Case CHFDocument10 paginiCase CHFAgnes Erlita Distriani Patade50% (2)
- Drug-Study NCPDocument5 paginiDrug-Study NCPMURILLO, FRANK JOMARI C.Încă nu există evaluări
- St. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LDocument2 paginiSt. Anthony's College Nursing Department Patient Care Plan for S.LAirme Raz AlejandroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanDocument6 paginiChronic Renal Failure Nursing Care PlanRuva Oscass JimmyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP DM and HCVDDocument3 paginiNCP DM and HCVDMAYBELINE OBAOB100% (1)
- Drug Action, Contraindications, Adverse Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsDocument14 paginiDrug Action, Contraindications, Adverse Effects and Nursing ConsiderationsArdel LabadaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ceftriaxone IM Drug StudyDocument5 paginiCeftriaxone IM Drug StudyCastillo MikaellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Drug Study CISPLATINDocument1 paginăDrug Study CISPLATINIrish Jane Gallo100% (1)
- Assessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesDocument20 paginiAssessing Nursing Diagnoses and Expected OutcomesZamranosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Generic Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsDocument2 paginiGeneric Name & Brand Name Mechanism of Action Indications and Drug Rationale Contraindications Common Side Effects Nursing ConsiderationsMary Shine GonidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderDocument1 paginăAnatomy and Physiology of The GallbladderRojanisa Baculi RomathoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Hypercalcemia Prepared By: Carbonilla, Leda GraceDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Hypercalcemia Prepared By: Carbonilla, Leda Graceshielamaygo05100% (1)
- SCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Obstructive JaundiceDocument1 paginăSCHEMATIC DIAGRAM Obstructive JaundiceJan Niño EstrellaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Asian College of Science and Technology College of Nursing Drug StudyDocument7 paginiAsian College of Science and Technology College of Nursing Drug StudynizabangxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Name of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesDocument4 paginiName of Drug Classification of Drug Mechanism of Action Indication Contraindications Side Effects Nursing ResponsibilitiesNemo Del RosarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Manage uterine contractions and bleeding with MetherginDocument2 paginiManage uterine contractions and bleeding with MetherginOtan Cuison100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of GI Bleeding from Bleeding PolypsDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of GI Bleeding from Bleeding PolypsGinoTevesÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCVDDocument5 paginiHCVDkhrizaleehÎncă nu există evaluări
- PP Insect Bite 2007 (Print)Document16 paginiPP Insect Bite 2007 (Print)Ali RumiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Physiology of GlomerulonephritisDocument1 paginăPa Tho Physiology of GlomerulonephritisJhaziel BermejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2Document7 paginiPathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus Type 2jnrue_aerith96% (28)
- Renal Anatomy and DiseaseDocument10 paginiRenal Anatomy and DiseaseGlen David Efrenson SupangaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophy - Nephrotic SyndromeedDocument1 paginăPathophy - Nephrotic Syndromeedianecunar100% (1)
- How To Treat Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 paginăHow To Treat Chronic GlomerulonephritisGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- NMAT2005Document29 paginiNMAT2005Mbatutes100% (3)
- 5 Nursing Diagnosis For GlomerulonephritisDocument2 pagini5 Nursing Diagnosis For GlomerulonephritisGeorich Narciso67% (3)
- How To Treat Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument1 paginăHow To Treat Chronic GlomerulonephritisGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 23chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument18 pagini23chronic GlomerulonephritisGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Youth and Pure LivingDocument10 paginiYouth and Pure LivingGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology of Chronic Glomerulonephritis: LegendDocument1 paginăPathophysiology of Chronic Glomerulonephritis: LegendGeorich Narciso50% (4)
- NMATDocument34 paginiNMATBHUSHAN80% (5)
- Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument5 paginiChronic GlomerulonephritisLabs MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Chronic GlomerulonephritisDocument2 paginiWhat Is Chronic GlomerulonephritisjingymickeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- ScholarshipDocument5 paginiScholarshipGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan for Pneumonia PatientDocument15 paginiNursing Care Plan for Pneumonia PatientGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ivy 2Document1 paginăIvy 2Georich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Scholarship Application EssaysDocument2 paginiSample Scholarship Application EssaysGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scholarship Package:: Doktor!" in Cooperation With Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office (PCSO) and Several StateDocument1 paginăScholarship Package:: Doktor!" in Cooperation With Philippine Charity Sweepstakes Office (PCSO) and Several StateGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Study PneumoniaDocument13 paginiCase Study Pneumonialavparedes93% (44)
- Chronic Kidney DiseaseDocument2 paginiChronic Kidney DiseaseGerardLum100% (2)
- A Worry Free LIFEDocument4 paginiA Worry Free LIFEGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50 Item Psychiatric Nursing Exam IDocument11 pagini50 Item Psychiatric Nursing Exam Iɹǝʍdןnos98% (40)
- HDN1Document40 paginiHDN1jaep1965100% (1)
- UBCN Endorsement SlipDocument1 paginăUBCN Endorsement SlipGeorich NarcisoÎncă nu există evaluări
- School NursingDocument1 paginăSchool NursingGeordiza Narciso AmpongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rethinking Men and CodependencyDocument6 paginiRethinking Men and Codependencynmmng2011Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture5lecture5 160419133248Document35 paginiLecture5lecture5 160419133248Linh TinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogue of Medical Equipment and SuppliesDocument52 paginiCatalogue of Medical Equipment and SuppliesbobÎncă nu există evaluări
- CBDMT - Market and Business Intelligence - Pharmaceutical IndustryDocument1 paginăCBDMT - Market and Business Intelligence - Pharmaceutical IndustrycbdmtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Massive Transfusion in Trauma Guildelines PDFDocument18 paginiMassive Transfusion in Trauma Guildelines PDFChey Ochy Aprilia100% (2)
- Osimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung CancerDocument12 paginiOsimertinib or Platinum-Pemetrexed in EGFR T790M-Positive Lung CancerAdriana VladutuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Members of group 9: *Dương Tấn Phước *Nguyễn Văn Sang *Nguyễn Văn Phát *Nguyễn Tiến Phát *Hoàng Ngọc QuýDocument50 paginiMembers of group 9: *Dương Tấn Phước *Nguyễn Văn Sang *Nguyễn Văn Phát *Nguyễn Tiến Phát *Hoàng Ngọc QuýPhat NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Fear of PainDocument2 paginiA Fear of PainBabac Compass PashazadehÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chiro Guidelines WHODocument51 paginiChiro Guidelines WHOMinh MinhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epilepsy Emergencies - Status Epilepticus, Acute Repetitite Seizures, and Autoimmune EncephalitisDocument23 paginiEpilepsy Emergencies - Status Epilepticus, Acute Repetitite Seizures, and Autoimmune Encephalitisnight.shadowÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audiologists diagnose and treat hearing and balance issuesDocument5 paginiAudiologists diagnose and treat hearing and balance issuesm afiq fahmiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Overview On Peripheral Artery Disease - FinalDocument78 paginiOverview On Peripheral Artery Disease - FinalMITHAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental Health in The WorkplaceDocument20 paginiMental Health in The Workplacekepri balaidiklatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Art Therapy For People With Psychosis: A Narrative Review of The LiteratureDocument12 paginiArt Therapy For People With Psychosis: A Narrative Review of The LiteratureRafa RAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Septic Shock PathophysiologyDocument33 paginiSeptic Shock Pathophysiologytummalapalli venkateswara rao67% (3)
- Byagagaire - Xylazine Hydrochloride and Ketamine Hydrochloride Combinations For General Anaesthesia in SheepDocument182 paginiByagagaire - Xylazine Hydrochloride and Ketamine Hydrochloride Combinations For General Anaesthesia in SheepThamil ArasanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Access Cavity Preparation PDFDocument60 pagini3-Access Cavity Preparation PDFAllisyia MalauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Specialty Group Physicians LocationsDocument82 paginiSpecialty Group Physicians LocationsGuru NandeshwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Peroneal Nerve Palsy Following Acp TreatmentDocument3 paginiPeroneal Nerve Palsy Following Acp TreatmentLydwiNa JcÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2011 Joint Commission Tissue StandardsDocument24 pagini2011 Joint Commission Tissue StandardsPatient Safety MyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inspired to Raise the Bar: OxyHelp's Superior HBOT TechnologyDocument16 paginiInspired to Raise the Bar: OxyHelp's Superior HBOT TechnologySencer SoyluÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM Critical Care Medicine PDFDocument23 paginiDM Critical Care Medicine PDFArun Sahaya RajaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jawline Definition MovesDocument5 paginiJawline Definition Movesagonza70Încă nu există evaluări
- Principle and Applications of Pavlovian ConditioningDocument44 paginiPrinciple and Applications of Pavlovian ConditioningTheDetailerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Retinoblastoma - EyeWikiDocument11 paginiRetinoblastoma - EyeWikimay171989Încă nu există evaluări
- Pharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingDocument58 paginiPharmacology of Endocrine System-NursingRaveenmayiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument6 paginiNursing Care PlanNeza AgdalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mental BreakdownDocument33 paginiMental BreakdownTamajong Tamajong Philip100% (1)
- Gamma CameraDocument26 paginiGamma CameraNishtha TanejaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pulmonary Rehabilitation (S)Document79 paginiPulmonary Rehabilitation (S)liz100% (3)