Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
NCP SPH 5
Încărcat de
jay5ar5jamorabon5tor0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
48 vizualizări3 paginiasasa
Titlu original
NCP_SPH_5
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentasasa
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
48 vizualizări3 paginiNCP SPH 5
Încărcat de
jay5ar5jamorabon5torasasa
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOCX, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
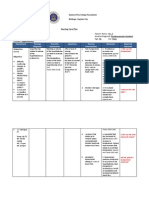
NURSING CARE PLAN
ASSESSMENT DIAGNOSIS PLANNING INTERVENTIONS RATIONALE EVALUATION
Objective: Deficit fluid volume At the end of the Weight px regularly Changes in weight
- Sudden weight loss r/t fluid loss to shift, no signs of provide
subcutaneous tissue dehydration will be information in fluid
- Decreased urine noted imbalance and the
output adequacy of fluid
volume
- (+) dry skin replacement
- (+) dry mucous Monitor intake and 1.040 indicates
membranes output. Note urine severe
color, and measure hypovolemia and
- Muscle weakness specific gravity as kidney
indicated involvement. Note:
Administration of
MgSO4 may cause
transient increase
increase in output
Monitor Blood These changes of
pressure and Pulse v/s are associated
Rate with fluid volume
loss and/or
hypovelemia
Check on dietary Proper nutrition
intake of proteins decreases
and calories incidence of
prenatal
hypovolemia and
hypoperfusion.
Intake of 80100 g
NURSING CARE PLAN
of protein may be
required daily to
replace losses.
Place px on strict This enhances
regimen of bedrest; placental and renal
encourage lateral perfusion, reduces
position adrenal activity,
and may lower BP
Increase fluid intake Fluid replacement
as needed treats
hypovolemia, yet
must be given
cautiously to
prevent overload
Encourage to avoid To prevent further
food that cause dehydration
dehydration such as
coffee and tea
Monitor serum uric Elevated levels,
acid and creatinine especially of uric
levels, and BUN acid, indicate
impaired kidney
function,
worsening of
maternal condition,
and poor fetal
outcome
Administer platelets Patients with HELLP
as indicated syndrome awaiting
NURSING CARE PLAN
delivery of the
fetus may benefit
from transfusion of
platelets when
count is below
20,000
Watched out for Observe further
further signs of signs of
dehydration dehydration that
may also lead to
hypovolemia
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Multiple Physical Injuries Secondary To Vehicular AccidentDocument31 paginiMultiple Physical Injuries Secondary To Vehicular AccidentJane Arian BerzabalÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Aneurism Case StudyDocument10 paginiNCP Aneurism Case StudyJean Paul Espinosa CrisologoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Colonic Carcinoma Case StudyDocument23 paginiColonic Carcinoma Case StudyGlaiza Claire Am-amlan OlayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Choking: by Jawad AhmedDocument25 paginiChoking: by Jawad Ahmedjawad_ahmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care PlanDocument13 paginiNursing Care Planyumiko0% (1)
- Upper Gastrointestinal BleedingDocument32 paginiUpper Gastrointestinal BleedinglicservernoidaÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Document4 paginiNCP-Case Presentation (CHF)Jessamine EnriquezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Head InjuryDocument2 paginiHead InjuryPheiyi WongÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case PresentationDocument6 paginiCase PresentationYrrem UbaganÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Book PolypDocument30 paginiCase Book PolypMARIAN RODRIGUEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- Complications in PregnancyDocument36 paginiComplications in PregnancyJADE PATEGAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaDocument6 paginiPa Tho Physiology of PneumoniaPaula YoungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ca CHN Copar ReviewDocument23 paginiCa CHN Copar Reviewapril punzalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- HemorrhoidsDocument15 paginiHemorrhoidspologroÎncă nu există evaluări
- CASE STUDY PheumoniaDocument5 paginiCASE STUDY PheumoniaEdelweiss Marie CayetanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Newest Research Paper The Challenges of Student Nurses in Their Clinical Skills Development Using Digital Technology. UwuDocument50 paginiNewest Research Paper The Challenges of Student Nurses in Their Clinical Skills Development Using Digital Technology. UwuMaryan SubaldoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Document11 pagini4th Yr. Med Cardio Module Question - Copy-1Sheda BondÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Pancreatitis - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyDocument18 paginiAcute Pancreatitis - Practice Essentials, Background, PathophysiologyInês BipÎncă nu există evaluări
- Operating RoomDocument13 paginiOperating RoomrichardÎncă nu există evaluări
- Anatomy and Phsyiology of MeningococcemiaDocument2 paginiAnatomy and Phsyiology of MeningococcemiaKevin Comahig100% (1)
- CholecysitisDocument165 paginiCholecysitisCholo Miguel C. RamirezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Management of OliguriaDocument14 paginiManagement of OliguriaAhmed El-MalkyÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisDocument12 paginiNCP Poststreptococcal GlomerulonephritisScarlet ScarletÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter-25 Kidney Function Tests: January 2017Document14 paginiChapter-25 Kidney Function Tests: January 2017DrFarah Emad AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute and Chronic Pancreatitis ShirleyDocument6 paginiAcute and Chronic Pancreatitis ShirleyVictor AladejanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathophysiology MaiaDocument2 paginiPathophysiology Maiajia88Încă nu există evaluări
- Case Study ReportDocument23 paginiCase Study Reportapi-290866384Încă nu există evaluări
- Epidemiology and Pathophysiology of Colonic Diverticular DiseaseDocument8 paginiEpidemiology and Pathophysiology of Colonic Diverticular DiseaseAnonymous Hz5w55Încă nu există evaluări
- Atun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableDocument2 paginiAtun Maricris Jorre Ca2 Au Legarda Leadership Managemet Research DownloadableCharissa Magistrado De LeonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jose Paulo D. Verances, RNDocument5 paginiJose Paulo D. Verances, RNpauloverancesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Osteosarcoma-Ana and PhysiologyDocument4 paginiOsteosarcoma-Ana and PhysiologyNeirfla WassabiÎncă nu există evaluări
- DM Case StudyDocument21 paginiDM Case StudyBern TolentinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- DB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaDocument5 paginiDB31 - Pathophysiology of Diabetes Mellitus and HypoglycemiaNeil Alcazaren かわいいÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Fracture Concept MapDocument1 paginăBone Fracture Concept MapJette Charmae OlboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingDocument6 paginiRle Module Rle Unit Week: Bachelor of Science in Nursing: Rle NCM 105 - Psychiatric NursingAllisson BeckersÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hildegard Peplau's Interpersonal Relations 101Document85 paginiHildegard Peplau's Interpersonal Relations 101Ynaffit Alteza Untal100% (1)
- Abruptio Placenta. Final OutputDocument15 paginiAbruptio Placenta. Final OutputCharles Loriaga Cruz IIÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP CvaDocument4 paginiNCP CvaMariquita BuenafeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Men in NursingDocument2 paginiMen in NursingMark JosephÎncă nu există evaluări
- 403 Full PDFDocument10 pagini403 Full PDFKuroto YoshikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDocument2 paginiNursing Care Plan (NCP) : Date and Time Nursing Diagnosis Short - Term and Long - Term OutcomesDeanne Carla DalilisÎncă nu există evaluări
- NCP GeDocument14 paginiNCP GeSuluhTriUtomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Glomerulonephritis 10Document5 paginiGlomerulonephritis 10Eden Jay Calija AgoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course in The WardDocument4 paginiCourse in The WardNejie Zarrah DiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Philippine Nursing Organizations Org Name DescriptionDocument8 paginiPhilippine Nursing Organizations Org Name DescriptionShehada Marcos BondadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acute Head InjuryDocument5 paginiAcute Head InjuryRitesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- X. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveDocument6 paginiX. Nursing Care Plan: ObjectiveRenea Joy ArruejoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Inflammatory Bowel Disease .. Last EditDocument22 paginiInflammatory Bowel Disease .. Last EditRashed ShatnawiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Uremic EncephalophatyDocument48 paginiUremic EncephalophatySindi LadayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example Case StudyDocument7 paginiExample Case StudyTerrena Lyn BlackmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Approach To Pleural EffusionDocument46 paginiApproach To Pleural EffusionBaskoro Tri LaksonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cerebrovascular Disease (Bleed)Document25 paginiCerebrovascular Disease (Bleed)Margaret Jenaw JenawÎncă nu există evaluări
- LISTERIOSISDocument15 paginiLISTERIOSISCedric VillalbaÎncă nu există evaluări
- PATIENT EDUCATION Hepatic Encephalopathy PDFDocument1 paginăPATIENT EDUCATION Hepatic Encephalopathy PDFAgung Prasetyo0% (1)
- Chelsea Amman Pku Case StudyDocument37 paginiChelsea Amman Pku Case Studyapi-365955738Încă nu există evaluări
- Hirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsDe la EverandHirschsprung’s Disease, A Simple Guide To The Condition, Diagnosis, Treatment And Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsDe la EverandA Simple Guide to Parathyroid Adenoma, Diagnosis, Treatment and Related ConditionsÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutDe la EverandA Study of the Lack of Hiv/Aids Awareness Among African American Women: a Leadership Perspective: Awareness That All Cultures Should Know AboutEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- Saint Paul University PhilippinesDocument3 paginiSaint Paul University Philippinesjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- St. Paul University Philippines: Professional Regulation Commission Work PlanDocument3 paginiSt. Paul University Philippines: Professional Regulation Commission Work Planjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)Document4 paginiNursing Practice Test/Exam About Communicable Diseases (NLE 1-20)jay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- NMAT USA Supplementary Handout December 2012Document2 paginiNMAT USA Supplementary Handout December 2012jay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Nursing Care PlanDocument2 paginiFamily Nursing Care Planjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- BP Monitoring CardDocument1 paginăBP Monitoring Cardjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- St. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health SciencesDocument2 paginiSt. Paul University Philippines: School of Nursing and Allied Health Sciencesjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- St. Paul University Philippines: Work Plan (Cluster 3)Document2 paginiSt. Paul University Philippines: Work Plan (Cluster 3)jay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nmat Usa November 22 2014 Supplementary HandoutDocument2 paginiNmat Usa November 22 2014 Supplementary Handoutjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Maternal and Child Health Nursing Ii: Krishan Soriano, MSNDocument130 paginiMaternal and Child Health Nursing Ii: Krishan Soriano, MSNjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- MCHN Must READDocument56 paginiMCHN Must READjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Effects On Lab Test ResultsDocument18 paginiEffects On Lab Test Resultsjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Family Care PlanDocument5 paginiFamily Care Planjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pay-For - Performance: Prepared By: PR10MS212 PR10MS234Document16 paginiPay-For - Performance: Prepared By: PR10MS212 PR10MS234jay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- J Psychiatry. 2007 52 (1) :14-21. Available From: (Document1 paginăJ Psychiatry. 2007 52 (1) :14-21. Available From: (jay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elective Course IIDocument21 paginiElective Course IIjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Asessment DengueDocument11 paginiPhysical Asessment Denguejay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beliefs: Bereavement Practices RitualsDocument5 paginiBeliefs: Bereavement Practices Ritualsjay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self-Administered QuestionnaireDocument1 paginăSelf-Administered Questionnairejay5ar5jamorabon5torÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science - The Human BodyDocument31 paginiScience - The Human BodyHarshil PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Frog Dissection HomeworkDocument4 paginiFrog Dissection Homeworkaibiaysif100% (1)
- Nephron Game - Questions and InstructionsDocument7 paginiNephron Game - Questions and InstructionsRubi Ann100% (1)
- Justification For MonetizationDocument3 paginiJustification For MonetizationCharina Balunso100% (1)
- Isolated Glomerular Diseases Associated With Recurrent Gross HematuriaDocument17 paginiIsolated Glomerular Diseases Associated With Recurrent Gross HematuriaMay PingolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Case Presentation: Patient Chart - Mary JohnsonDocument12 paginiCase Presentation: Patient Chart - Mary Johnsonivoneeh_16100% (1)
- Cardinal Manifestetions of Renal DiseaseDocument61 paginiCardinal Manifestetions of Renal Diseasekirubel deribÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Anatomy & Physiology: NotesDocument5 paginiRenal Anatomy & Physiology: NotesTawhid ZihadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dr. Didik Fetal Urogenital Anomalies Fetal Urogenital Anomalies PDFDocument25 paginiDr. Didik Fetal Urogenital Anomalies Fetal Urogenital Anomalies PDFJTÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1 s2.0 S0085253822010171 MainDocument15 pagini1 s2.0 S0085253822010171 MainJack JackÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3627 10770 1 PBDocument11 pagini3627 10770 1 PBsandra mayoemiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal Ultrasound Renal Ultrasound Basic Principles of Ultrasound ExaminationDocument41 paginiRenal Ultrasound Renal Ultrasound Basic Principles of Ultrasound ExaminationSav GaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 FinalDocument10 paginiRESPIRATORY SYSTEM 1 FinalJann ericka JaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Contoh Soal KMB Ujikom 1Document34 paginiContoh Soal KMB Ujikom 1RobbyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Proteinuria in Adults - A Diagnostic Approach - September 15, 2000 - American Family PhysicianDocument7 paginiProteinuria in Adults - A Diagnostic Approach - September 15, 2000 - American Family PhysicianSi vis pacem...100% (1)
- Tetada Kalimasad1Document16 paginiTetada Kalimasad1Rasaraj Ramon Castaneda100% (2)
- Marjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsDocument8 paginiMarjorie A. Carganilla BSN 3-2 Pathophysiology of Urinaryy Tract Infection Precipitating FactorsMarjorie CarganillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- THE EFFECTIVENESS OF INTRADIALYSIS STATIC BIKE EXERCISE TOWARD FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY IN HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS OkeeDocument5 paginiTHE EFFECTIVENESS OF INTRADIALYSIS STATIC BIKE EXERCISE TOWARD FUNCTIONAL CAPACITY IN HEMODIALYSIS PATIENTS OkeeriadesnitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Farmacologia DMDocument15 paginiFarmacologia DMedalveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dame HandbookDocument284 paginiDame Handbooktcalith100% (1)
- 4 - Management of SAM Without Complications OTC - Part I 2015-04-07Document87 pagini4 - Management of SAM Without Complications OTC - Part I 2015-04-07Angel LambanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Test Bank For Pathophysiology 6th Edition Jacquelyn L BanasikDocument5 paginiTest Bank For Pathophysiology 6th Edition Jacquelyn L BanasikJesus Carter97% (30)
- Estimated Glomerular Filtration RateDocument5 paginiEstimated Glomerular Filtration Rateseno adi pÎncă nu există evaluări
- Renal AssessmentDocument12 paginiRenal AssessmentAnonymous LnWIBo1GÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2016 - Long-Term Donor Outcomes After Pure Laparoscopic Versus Open Living Donor NephrectomyDocument7 pagini2016 - Long-Term Donor Outcomes After Pure Laparoscopic Versus Open Living Donor Nephrectomynarutota181Încă nu există evaluări
- Nursing Case Study (Final) - ArchieDocument23 paginiNursing Case Study (Final) - ArchieArchie Astorga100% (2)
- Cctarget Multical-Pc400 1907801rev02 CiblescalibrantDocument6 paginiCctarget Multical-Pc400 1907801rev02 CiblescalibrantSivaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sistem Urinaria: Dr. AL-MUQSITH, M.SiDocument43 paginiSistem Urinaria: Dr. AL-MUQSITH, M.SiAndrey DwiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mind Map: Amino Acid MetabolismDocument1 paginăMind Map: Amino Acid MetabolismAbbey Ayala100% (1)
- Pathophysiology of Kidney Diseases: CKF (Chronic Kidney Failure), Characteristics in ChildrenDocument3 paginiPathophysiology of Kidney Diseases: CKF (Chronic Kidney Failure), Characteristics in ChildrenAcademic JournalÎncă nu există evaluări