Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
EE 452-Power Electronics-Nauman Ahmad Zaffar
Încărcat de
Sheikh Asher0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
40 vizualizări4 paginisdadjlsajdls
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentsdadjlsajdls
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
40 vizualizări4 paginiEE 452-Power Electronics-Nauman Ahmad Zaffar
Încărcat de
Sheikh Ashersdadjlsajdls
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 4
The image part with relationship ID
rId1 was not found in the file.
Lahore University of Management Sciences
EE452 Power Electronics
Fall 2016-17
Instructor Nauman Ahmad Zaffar
Room No. 9-313A
Office Hours TBD
Email nauman.zaffar@lums.edu.pk
Telephone X8311
TA TBD
TA Office Hours TBD
Course URL (if any)
Course Basics
Credit Hours 4
Lecture(s) Nbr of Lec(s) Per Week 2 Duration 75 min each
Recitation (per week) Nbr of Lec(s) Per Week 1 Duration 50 min
Lab (per week) Nbr of Lec(s) Per Week 1 Duration 170 min
Course Distribution
Core N
Elective Y
Open for Student Category Electrical Engineering, Computer Science, Physics
Close for Student Category
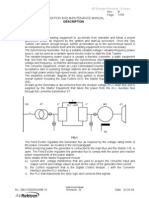
COURSE DESCRIPTION
This is the first course in Power Electronics. Students will learn about specific areas of application and the reasons Power
Electronics is becoming popular in areas traditionally occupied by analog electronics. The course will cover applications in
conversion and control of power using Power semiconductor devices, physics of their structure and operation and passive
components in power circuits. Students will also learn the principles governing the operation of converters, different
standard topologies, applications in power systems, motor drives, and applications in renewable energy sources.
COURSE PREREQUISITE(S)
EE340 Devices and Electronics
COURSE OBJECTIVES
1. Understand large signal behavior of devices and applications in high power circuits
2. Get hands-on experience on development of components and circuits within reasonable power limits
3. Understand form and function of fundamental converter topologies and their application
4. Design of practical converters/circuits based on specific needs
Learning Outcomes
1. Understand the need, use and limitations of Power Electronics
2. Appreciate the linkage of Power Electronics with electromagnetics, circuits, devices, electronics, feedback, control,
power systems, machines and emerging application areas like renewables, smart grids and high frequency
applications.
3. Understand the factors affecting choice of devices in power electronics
The image part with relationship ID
rId1 was not found in the file.
Lahore University of Management Sciences
4. Learn various topologies that are prevalent and be able to extend the design to develop practical circuits based on
application specifications
Grading Breakup and Policy
Assignment(s): N/A
Home Work: 06 10%
Quiz(s): 7-8 10%
Class Participation: N/A
Attendance: N/A
Labs: 12 15%
Midterm Examination: 01 25%
Project: 10%
Final Examination: Comprehensive 30%
Course Learning Outcomes
EE352: The students should be able to:
CLO1: Understand and analyze the behavior of non-ideal power switching devices.
CLO2: Understand, analyze and design converters for operation in steady state CCM.
CLO3: Understand, analyze and design converters for operation in steady state DCM.
CLO4: Understand and analyze low frequency power electronic conversion in single phase and three phase converters.
CLO5: Understand and apply the principles of electromagnetic induction in power circuits and use it to design magnetic elements.
CLO6: Apply the knowledge in lab environment working as a group.
Relation to EE Program Outcomes
EE-452 CLOs Related PLOs Levels of Learning Teaching Methods CLO Attainment checked in
CLO1 PLO1 Cog3 Instruction, Tutorial, Assignments Midterm, Final
CLO2 PLO3 Cog3 Instruction, Tutorial, Assignments Midterm, Final
CLO3 PLO3 Cog3 Instruction, Tutorial, Assignments Midterm, Final
CLO4 PLO2 Cog3 Instruction, Tutorial, Assignments Midterm, Final
CLO5 PLO3 Cog3 Instruction, Tutorial, Assignments Final
CLO6 PLO5 Psycho 3 Instruction, Labs Lab Exam
Examination Detail
Yes/No: Yes
Combine/Separate: Combined
Midterm
Duration: 03 hrs
Exam
Preferred Date: During Mid-week
Exam Specifications: Closed book, closed notes, 1 A4 double sided, hand written help sheet, calculators
Yes/No: Yes
Combine/Separate: Combined
Final Exam
Duration: 03 hrs
Exam Specifications: Closed book, closed notes, 1 A4 double sided, hand written help sheet, calculators
COURSE OVERVIEW
Week Topics Recommended Readings Objectives/Application
Introduction: Mohan: Chapter 1
1. - Review of concepts Erickson: Chapter 1
- Application examples
The image part with relationship ID
rId1 was not found in the file.
Lahore University of Management Sciences
- Classification of Power processors
- Elements of Power Electronics
Switch Realization Mohan: Chapter 2
- Types of switches Erickson: Chapter 4
- Overview of Power semiconductor devices
- Comparison
2.
- Driver circuits Mohan: Chapter 20
Power Diodes
- Structure
- Switching characteristics
Power Mosfets Mohan: Chapter 22
3. - Switching characteristics
- Operating limitations and safe operating areas
Thyristors Mohan: Chapter 23
- Basic Structure
- I-V characteristics and device operation
- Switching characteristics
4.
IGBTs Mohan: Chapter 25
- Basic Structure
- I-V characteristics and device operation
- Switching characteristics
Steady State Converter Analysis Erickson: Chapter 2
- Inductor Volt-Sec Balance
- Capacitor Amp-Sec Balance
5.
- CCM Analysis
- Converter Analysis (Buck, Boost, Cuk, etc.)
- Ripple estimation and design
DCM Analysis of converters Erickson: Chapter 5
6. - Conduction mode boundary Mohan: Chapter 7
- Converter Examples: Boost, etc.
Converter Circuits: Form and Function Erickson: Chapter 6
7. - Canonical cell model
- Circuit Manipulation
Midterm
Transformer Isolation Erickson: Chapter 6
- Full Bridge, Half Bridge, Push-Pull and Flyback
converters
8.
- Boost Derived converters
- Isolated SEPIC and Cuk converters
- Switch Stress and Utilization
AC-DC converters: Mohan: Chapter 5
- Rectifiers
9.
- 1-f and 3-f rectifiers
- Inductive Load
Phase controlled rectifiers: Mohan: Chapter 6
10. - Use of Thyristors
- 3-f converters
Power and Signals in Non-Linear Circuits: Mohan: Chapter 3
11.
- Basic magnetic theory Erickson: Chapter 16
The image part with relationship ID
rId1 was not found in the file.
Lahore University of Management Sciences
- Electric Circuits
- Power and Harmonics in Non-sinusoidal systems
Magnetics: Erickson: Chapter 13
- Magnetic Circuits
12. - Transformer modeling
- Loss Mechanisms
- Eddy Currents
Inductor Design Erickson: Chapter 14
13. - Filter Inductor Design
- Multiple winding magnetics design
Transformer Design Erickson: Chapter 15
- Basic Constraints and design process
14.
- Example designs
- AC Inductor Design
Textbook(s)/Supplementary Readings
Textbook:
rd
Power Electronics Converters Applications and Design by Ned Mohan, Undeland, Robbins, 3 Edition, John Wiley and Sons,
2003
Fundamentals of Power Electronics by Erickson and Maksimovic, 2nd Edition, Oxford University Press, 2005
Supplementary Reading:
Labs (1+n weeks simulation + performance)
1. Switching characteristics of Devices Power Diodes and Power Mosfets
1+1 weeks
AC DC Conversion: SCRs and Phase Controlled Rectifiers Characteristics, Half wave 1+2 weeks
2.
controlled rectification, R-L Load, Full Bridge Rectification
DC-DC Conversion: Buck Converter Design, Simulation and Implementation of CCM and 1+1 weeks
3.
DCM operation. Effect of parasitics
DC AC Conversion: Inverter Design, Simulation and Implementation of Square wave with 1+1 weeks
4.
resonant filter and PWM inverter with LP filter
5. D
C Motor Drive Optional extra lab 1+1 weeks
6. C ourse Project: Design, Simulation and Implementation of Application Specific PE converter 03 weeks
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- EE 452-Power ElectronicsDocument4 paginiEE 452-Power ElectronicsWA Q ASÎncă nu există evaluări
- LUMS EE340 Devices and Electronics Course OverviewDocument4 paginiLUMS EE340 Devices and Electronics Course OverviewSalaarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 452 Power ElectronicsDocument4 paginiEE 452 Power Electronicskibrom atsbha100% (1)
- EE 353-Electrical Power Systems-Farhan MahmoodDocument5 paginiEE 353-Electrical Power Systems-Farhan MahmoodMuhammad shahbazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Components and DevicesDocument6 paginiElectronic Components and DevicesSelvam MÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE340L Devices and Electronics LabDocument5 paginiEE340L Devices and Electronics LabMinahil NaumanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Birla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Work Integrated Learning Programmes Digital LearningDocument5 paginiBirla Institute of Technology & Science, Pilani Work Integrated Learning Programmes Digital Learningsudha mallikÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE-110L Circuit Analysis LabDocument6 paginiEE-110L Circuit Analysis LabԹԾւժ ՊևջիձլÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eee-103 Module - 1Document96 paginiEee-103 Module - 1AhmodÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline Fall-2021Document5 paginiCourse Outline Fall-2021Ahad MunawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EES512 Course OutlineDocument7 paginiEES512 Course OutlineDildar Khan BhatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EF-132 IE Basic Electrical Engineering CourseDocument6 paginiEF-132 IE Basic Electrical Engineering CourseGul sher BalochÎncă nu există evaluări
- Advanced Semiconductor Devices SyllabusDocument4 paginiAdvanced Semiconductor Devices SyllabusShubhi SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE-378 (Hardware Based) - SNHDocument100 paginiEEE-378 (Hardware Based) - SNHAkram HossenÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 528 (PHY 537) - Semiconductor Device Fundamentals - Nauman ButtDocument4 paginiEE 528 (PHY 537) - Semiconductor Device Fundamentals - Nauman ButtZeeshan RazaÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE F111 Handout II Sem 2023-2024Document3 paginiEEE F111 Handout II Sem 2023-2024Prinshu RawatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline Winter-2023Document5 paginiCourse Outline Winter-2023Abdul SamadÎncă nu există evaluări
- EEE F111 Electrical Sciences Handout I-Sem - 2023 - 2024Document3 paginiEEE F111 Electrical Sciences Handout I-Sem - 2023 - 2024KAUSHIK KADIUMÎncă nu există evaluări
- III-IV Syllabus 22 SeriesDocument30 paginiIII-IV Syllabus 22 SerieschoogandunÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction to Analog IC Design SyllabusDocument5 paginiIntroduction to Analog IC Design SyllabusBernard EbarleÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE2002 Analog Electronics - OBTLDocument8 paginiEE2002 Analog Electronics - OBTLAaron TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BSCS2 - A, B, C Course Out LineDocument3 paginiBSCS2 - A, B, C Course Out LineAtta RandhawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electronic Devices and CircuitsDocument3 paginiElectronic Devices and Circuitsjimfinch512Încă nu există evaluări
- Course Out-LineDocument24 paginiCourse Out-LinemandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Course HandoutDocument2 paginiPower Electronics Course HandoutHarsh GroverÎncă nu există evaluări
- Institute of Industrial Electronics Engineering, (Pcsir) KarachiDocument11 paginiInstitute of Industrial Electronics Engineering, (Pcsir) KarachiQuratulain AnwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE3010 Electrical Devices and Machines - OBTLDocument6 paginiEE3010 Electrical Devices and Machines - OBTLAaron TanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ELECTRÓNICA DE POTENCIA - Es.enDocument5 paginiELECTRÓNICA DE POTENCIA - Es.enAndrew Israel QÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Electrical Engineering: Course Clos, Plo Mapping, 12 Weeks Course Breakup and Assessment ToolsDocument2 paginiDepartment of Electrical Engineering: Course Clos, Plo Mapping, 12 Weeks Course Breakup and Assessment ToolsNOOR UR AIN ZAFARÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE-305 Power Electronics (3-3-4) (Elective) : Contact Hours: Credit HoursDocument4 paginiEE-305 Power Electronics (3-3-4) (Elective) : Contact Hours: Credit HoursAwais KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Science K Scheme PDFDocument10 paginiBasic Science K Scheme PDFvdvikram066Încă nu există evaluări
- ME 203, Circuits and Electronic Devices (Fall 2022)Document4 paginiME 203, Circuits and Electronic Devices (Fall 2022)M HarisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Voltage, Current and Impedance Are Valid. at Intermediate Frequencies, The Analysis Needs Inclusion of An AdditionalDocument2 paginiVoltage, Current and Impedance Are Valid. at Intermediate Frequencies, The Analysis Needs Inclusion of An Additionalashish6789Încă nu există evaluări
- Basic ScienceDocument9 paginiBasic SciencekirankumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- The University of Lahore: Linear Circuit Analysis Winter 2021Document6 paginiThe University of Lahore: Linear Circuit Analysis Winter 2021Asif HanifÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Distribution and Utilization - Updated2020 - Spring 2021Document4 paginiPower Distribution and Utilization - Updated2020 - Spring 2021Ahad MunawarÎncă nu există evaluări
- BE STheory Outline Fall2022 20221028Document4 paginiBE STheory Outline Fall2022 20221028Abubakar SajidÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 301 Electric Circuit Theory AnalysisDocument6 paginiEE 301 Electric Circuit Theory AnalysissavithaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Drives U1Document67 paginiPower Electronics Drives U1Ruvenderan SuburamaniamÎncă nu există evaluări
- TDU Course Syllabus EMTPDocument8 paginiTDU Course Syllabus EMTPPheap SophanÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE-260 Electrical Machines Course OutlineDocument5 paginiEE-260 Electrical Machines Course OutlinehamzaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 401068-Chapter 0Document9 pagini401068-Chapter 0LUFFYDRAGON D.MONKEY.Încă nu există evaluări
- Eeef111 EsDocument2 paginiEeef111 EsYash BhardwajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curriculum ModifiedDocument3 paginiCurriculum ModifiedSakthivel MÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Plan and Evaluation Plan: Analog Electronics (3-1-0) 4Document2 paginiCourse Plan and Evaluation Plan: Analog Electronics (3-1-0) 4Tarun VenkatÎncă nu există evaluări
- CMR Institute of Technology, Bangalore: Link To Detailed SyllabusDocument6 paginiCMR Institute of Technology, Bangalore: Link To Detailed SyllabusChithra Manivelan0% (1)
- PHY319 - Electronics Practical I: ParticularsDocument5 paginiPHY319 - Electronics Practical I: ParticularsEddie Rio CokerÎncă nu există evaluări
- De La Salle University: Course Syllabus AY 2015 - 2016Document8 paginiDe La Salle University: Course Syllabus AY 2015 - 2016Karl BelasaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEE Course CLOs-2k16Document2 paginiBEE Course CLOs-2k16Syed Zubair ZahidÎncă nu există evaluări
- EC0206 Linear Integrated CircuitsDocument6 paginiEC0206 Linear Integrated Circuitsmani_vlsiÎncă nu există evaluări
- EECE 1311 Electric CircuitsDocument6 paginiEECE 1311 Electric CircuitsMad lolÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Principles Power ElectDocument67 paginiPower Electronics Principles Power Electkibrom atsbhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHE F311 Kinetics and Reactor DesignDocument2 paginiCHE F311 Kinetics and Reactor DesignshreyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrical Sciences CourseDocument3 paginiElectrical Sciences CourseNikunj SharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course Outline EE 434Document3 paginiCourse Outline EE 434Ali SafdarÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE701OE - R18 - IV Yr I Sem EDC Handbook-2021-22Document29 paginiEE701OE - R18 - IV Yr I Sem EDC Handbook-2021-22katta040Încă nu există evaluări
- Power Electronics Digital NotesDocument181 paginiPower Electronics Digital NotesnagarajanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction To Electrical EngineeringDocument4 paginiIntroduction To Electrical Engineeringmanyabhat2812Încă nu există evaluări
- 6 Semester: Institute of Engineering & ManagementDocument40 pagini6 Semester: Institute of Engineering & ManagementManohar PÎncă nu există evaluări
- Circuits, Matrices and Linear Vector SpacesDe la EverandCircuits, Matrices and Linear Vector SpacesEvaluare: 5 din 5 stele5/5 (1)
- CHEM 101 Atomic StructureDocument40 paginiCHEM 101 Atomic StructureSheikh AsherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chaeat SheetDocument3 paginiChaeat SheetSheikh AsherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saturation-Mode Operation Will Be Maintained Up To The Point That VD Exceeds VG by That Is, UntilDocument2 paginiSaturation-Mode Operation Will Be Maintained Up To The Point That VD Exceeds VG by That Is, UntilSheikh AsherÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE 320 (CS 320) - Computer Organization and Assembly - Jahangir IkramDocument4 paginiEE 320 (CS 320) - Computer Organization and Assembly - Jahangir IkramSheikh AsherÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANTH 100 - Introduction To Cultural Anthropology - Anjum Alvi & Lukas WerthDocument12 paginiANTH 100 - Introduction To Cultural Anthropology - Anjum Alvi & Lukas WerthSheikh AsherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Saturation-Mode Operation Will Be Maintained Up To The Point That VD Exceeds VG by That Is, UntilDocument2 paginiSaturation-Mode Operation Will Be Maintained Up To The Point That VD Exceeds VG by That Is, UntilSheikh AsherÎncă nu există evaluări
- ACCT 100-Principles of Financial Accounting - Omair HaroonDocument7 paginiACCT 100-Principles of Financial Accounting - Omair HaroonUmar FarooqÎncă nu există evaluări
- MGMT 261 New CompressedDocument411 paginiMGMT 261 New CompressedSheikh AsherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Beidelman Ritual Kaguru Anthropos 1991 PDFDocument20 paginiBeidelman Ritual Kaguru Anthropos 1991 PDFSheikh AsherÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microelectronic Circuits Sedra Smith 6th Edition Solution Manual For INTERNATIONAL EDITIONDocument226 paginiMicroelectronic Circuits Sedra Smith 6th Edition Solution Manual For INTERNATIONAL EDITIONEliab60% (42)
- Data-Tech 2013 Hyundai Santa Fe Sport 2.4L GDI-Charging SystemDocument25 paginiData-Tech 2013 Hyundai Santa Fe Sport 2.4L GDI-Charging SystemRubenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Excitation Rectifier Transformers Selection and CalculationDocument7 paginiExcitation Rectifier Transformers Selection and CalculationAdis Kawe67% (3)
- GeneratorDocument55 paginiGeneratorVlad Iulian100% (3)
- Practical Viva Question CollectionDocument6 paginiPractical Viva Question CollectionAnonymous o4OUZfÎncă nu există evaluări
- 600 5 DA21 EngDocument168 pagini600 5 DA21 EngBoris MonroyÎncă nu există evaluări
- C9 A4xDocument2 paginiC9 A4xjojibaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Acs 1000 Technical CatalogDocument106 paginiAcs 1000 Technical CatalogMiguel LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2nd Year Short Question Answers From Within ChaptersDocument40 pagini2nd Year Short Question Answers From Within ChaptersZain ZuhabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calculation of Compact Amplitude-Integrated EEG TRDocument7 paginiCalculation of Compact Amplitude-Integrated EEG TRSamuel CardosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diode Detectors For RF Measurement: Part 1: Rectifier Circuits, Theory and Calculation ProceduresDocument116 paginiDiode Detectors For RF Measurement: Part 1: Rectifier Circuits, Theory and Calculation Proceduresashish_moudghilÎncă nu există evaluări
- EE6601-Solid State DrivesDocument11 paginiEE6601-Solid State DrivesBALAKRISHNANÎncă nu există evaluări
- Full Paper SonometerDocument6 paginiFull Paper SonometerCésar DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- SCR Applications - Electronic Circuits and Diagram-Electronics Projects and DesignDocument13 paginiSCR Applications - Electronic Circuits and Diagram-Electronics Projects and DesignOmar Cazor CidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Deecorp.: Thyristor-Thyristor ModulesDocument4 paginiDeecorp.: Thyristor-Thyristor ModulesAB Francisco JuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hve02.2 w018n System200 IndramatDocument128 paginiHve02.2 w018n System200 IndramatMiguel Macp100% (1)
- PandarosDocument9 paginiPandarosTempest_LÎncă nu există evaluări
- PS481000 5Document3 paginiPS481000 5buiquangsangÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2mu1000 00 6249b-10 - B - eDocument104 pagini2mu1000 00 6249b-10 - B - eVeerapandiyan KaliyasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Audit Criteria: AC7114/2S REV. MDocument27 paginiAudit Criteria: AC7114/2S REV. MRaja HoneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Customer-Production List Per BMK: INTERSCHALT Maritime Systems AG 22869 Schenefeld Tel.:+49 40 830330 Page 1 From 31Document31 paginiCustomer-Production List Per BMK: INTERSCHALT Maritime Systems AG 22869 Schenefeld Tel.:+49 40 830330 Page 1 From 31Богдан КендзерÎncă nu există evaluări
- Power Grids With Renewable EnergyDocument597 paginiPower Grids With Renewable EnergyvasikasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ee502 26Document19 paginiEe502 26Gopi RamÎncă nu există evaluări
- A330 Electrical Power System OverviewDocument118 paginiA330 Electrical Power System OverviewSohaib Aslam ChaudharyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sensores de Proximidad TelemecaniqueDocument40 paginiSensores de Proximidad TelemecaniqueAdri Cota CabreraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Smartpack Monitoring and Control Unit PDFDocument20 paginiSmartpack Monitoring and Control Unit PDFSohaib Omer SalihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bridge Rectifier CheggDocument2 paginiBridge Rectifier Cheggsal27adamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simulation of Parallel Resonance Condition in ElectricalDocument6 paginiSimulation of Parallel Resonance Condition in ElectricalyaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expt.3 ME2612L Individual Report Group 5Document15 paginiExpt.3 ME2612L Individual Report Group 5Dan Joshua EspinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Eecim02 Course MaterialDocument42 paginiEecim02 Course Materialsmahesh_1980Încă nu există evaluări
- Variable Power SupplyDocument27 paginiVariable Power SupplyRose Ann MarceloÎncă nu există evaluări