Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Orthopaedic Terminology: Classifications of Fractures & Dislocation
Încărcat de
Nurul Shahira MaswahTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Orthopaedic Terminology: Classifications of Fractures & Dislocation
Încărcat de
Nurul Shahira MaswahDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Orthopaedic Terminology
Classifications of Fractures & Dislocation
Fracture (#) Structural break in the continuity of a bone, epiphyseal plate, or a
cartilaginous joint surface.
#/dislocation # of a bone which is also dislocated from its normal position in a
joint.
Dislocation The complete & persistent displacement of bone from its normal
position at the joint surface.
Subluxation Incomplete or partial dislocation, in that one bone forming a joint
is displaced only partially from its normal position.
Sprain-ligament Joint injury to a ligament, varying in degree from being stretched
rupture to being ruptured (torn), while the continuity of the ligament
remains intact.
Strain Overstretching of muscle fibers caused by overexercising or
overexerting some part of the musculature; results in sore,
painful, & sometimes stiff muscles.
Classification of Fractures
Open versus Closed
Closed # A # that does not produce an open wound of the skin but does
result in loss of continuity of bone subcutaneously.
Open # A # in which one of the fragments has broken through the skin &
Compound # in which there is loss of continuity of bone internally.
General Appearance
Avulsion # Tearing away of a part; a # of a part of bone where the pull of a
strong ligamentous or tendinous attachment tends to forcibly pull
the fragment away from the rest of the bone at the time of injury.
Bursting # Multiple fragments, usually at the end of a bone; classically, the
first cervical vertebra.
Butterfly # Comminuted or segmental # in which the central fragment is
shaped like a butterfly with wings outstretched.
Chip # # of a small fragment, usually at the articular margin of a condyle.
Comminuted # # with more than two fragments; lines of # that may be transverse,
oblique, spiral, or T &Y shaped.
Complete # # in which the bone is completely broken.
Incomplete # # in which the bone is buckled or cracked but the continuity is not
destroyed; occurs in young bones in which the cortex is broken on
one side & only bent on the other.
NK2053 Terapi Carakerja Disfungsi Fizikal 1
Semester 1 Sesi 2015-2016
SC.Chai
Compression # Crumbling or smashing of a cancellous bone by forces acting
parallel to the long axis of bone; applied particularly to vertebral
body #.
Depressed # Usually used when describing skull or articular surface #, with the
fragment being displaced below the overall level of the skull or
articular surface.
Displaced # Fragments are moved away from each other.
Double # Segmental # of a bone in two places.
Epiphyseal # Involves the cartilaginous growth plate of a bone; also referred to
as epiphyseal slip #, Salter #, & Salter-Harris #.
Fatigue # Stress # occurring as the result of excessive physical activity in a
short period of time in normal bone or chronic stress in
weakened bone.
Fissure # Crack in one cortex (surface) only of a long bone.
Greenstick # Incomplete, angulated # with a partial break.
Impacted # # in which fragments are compressed by force of original injury;
one fragment of bone driven into another.
Inflammatory # Pathological # of bone weakened by inflammation.
Infraction # Small radiolucent line seen in pathological #, most commonly
resulting from metabolic problems.
Linear # Lengthwise # of bone; implies that there is no displacement.
Multiple # Two or more lines of # in the same bone.
Neoplastic # Pathological # of bone weakened by neoplasia (abnormal tissue
growth).
Oblique # Slanted # of the shaft of long bone.
Occult # Hidden # (undetected by radiograph), generally occurring in areas
of the ribs, tibia, metatarsal, & navicula.
Pathologic # Spontaneous #; occurs as a result of a disease & not trauma.
Secondary # Pathological # of bone weakened by disease.
Segmental # Several large # fragments in the same bony shaft.
Spiral # One in which # line is spiral-shaped; torsion #.
Stellate 3 # with central point of injury, from which radiate numerous
fissures.
Stress # Gradual # caused by repeated or prolonged stress.
Subperiosteal # A # in which the bone but not the periosteal tube is broken;
uncommon, usually the result of a direct blow.
Torus # Usually noted in children; a stable, incomplete # in which one
cortical surface appears to be wrinkled by compression forces &
the opposite cortex may or may not be infracted by tension forces;
also called lead pipe #.
Transverse # Line of # across the shaft at right angles to the axis of bone.
NK2053 Terapi Carakerja Disfungsi Fizikal 2
Semester 1 Sesi 2015-2016
SC.Chai
Portion of Bone Involved
Apophyseal # Avulsion # of an apophyseal where there is strong tendinous
attachment.
Articular # # involving joint surface.
Condylar # # of any round end of a hinge joint.
Cortical # # involving cortex of bone.
Diacondylar # Transcondylar # (line across the condyle).
Extracapsular # # that occurs near, but outside, the capsule of a joint, especially
the hip.
Intra-articular # # within a joint cavity, usually involving the joint surface.
Intracapsular # # within a joint the capsule of a joint.
Periarticular # # near but not involving a joint.
Subcapital # # just distal to the head of a ball joint, as described in femoral or
humeral neck #.
Tuft # # of the distal phalanx (tuft) of any digit.
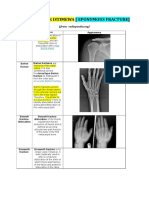
Position & Alignment of Fragments (Classic & Descriptive Names)
Anatomical neck # # in the area of tendinous attachments, true neck of humeral
metaphysic.
Surgical neck # # in area below the anatomic neck of the humerus.
Bartons # Dorsal dislocation of carpus on radius with associated # of the
dorsal articular surface of radius; deformity similar to Colles #.
Colles # # through the distal radial epiphyis within to inch of the
articular surface with dorsal displacement & angulation of the
distal fragment, producing a silver fork deformity; generally
associated with a # of the ulnar styloid.
Galeazzis # # of the distal radius, with distruption of the distal radioulnar
articulation; Dupuytrens #.
Monteggias # Isolated # of proximal/3 of ulna, with either posterior or anterior
dislocation of radial head allowing angulation & overriding of
ulnar fragments
Radial head # # of the most proximal part of the radius.
Reverse Bartons # Volar displacement of carpus on radius, with associated # of volar
articular surface of radius.
Smiths # Reverse Colles #, with distal fragment displaced & angulated
volarly.
Bennetts # Dorsal subluxation or dislocation of thumb metacarpal on greater
multangular with associated avulsion # of the volar articular
surface of the metacarpal.
Boxers # Volarly angulated impacted # of the neck of the 5th and/or 4th
metacarpal, caused by striking closed fisted hand on hard object.
Mallet # Avulsion # of the dorsal base of the distal phalanx of any digit
that includes insertion of extensor apparatus, thus allowing distal
segment to drop into flexion.
Rolandos # # at the base of the 1st metacarpal.
NK2053 Terapi Carakerja Disfungsi Fizikal 3
Semester 1 Sesi 2015-2016
SC.Chai
Teardrop # Avulsion #, in the shape of a teardrop, of the anterior lip of a
cervical vertebral body.
Wedge # Anterior compression # of any vertebra; most common in the
dorsal spine.
Femoral neck # Transcervical # through midportion of femoral neck.
Intertrochanteric # # along a line joining the greater & lesser trachanters.
Subtrochanteric # Transverse # of femur just below the lesser trochanter.
March # Stress # of metatarssal caused by excessive marching.
Classification of Dislocations
General Dislocations
Congenital Dislocation that exists at birth.
dislocation
Habitual dislocation Dislocation that repeatedly recurs; usually congenital.
Recurrent Repetitive dislocation with or without adequate trauma.
dislocation
Monteggia # of the ulna with a radial head dislocation.
#/dislocation
Perilunate A dislocation of all carpals shifted posteriorly, leaving the lunate
dislocation in proper position.
Boutonniere Deformity following injury to the extensor hood mechanism;
deformity appear after lateral bands displace volarly around the PIPJ. This
may result from a dislocation that has been reduced, but the
deformity itself is not a true dislocation.
Bennetts dislocation Dislocation of the 1st metacarpal-carpal joint.
Gamekeepers Rupture of the ulnar collateral ligament of the MCPJ with
dislocation associated subluxation or dislocation.
NK2053 Terapi Carakerja Disfungsi Fizikal 4
Semester 1 Sesi 2015-2016
SC.Chai
Musculoskeletal Diseases & Related Terms
Tissue Diseases
Bone Diseases
Osteoarthritis Chronic multiple degenerative joint disease; inflammation of
bone & joint.
Osteoarthropathy A condition of increased bone formation at the joints; sometimes
used to refer to osteoarthritis.
Osteoarthrosis Chronic arthritis, usually mechanical, not caused by
inflammatory process.
Osteoarticular Pertaining to or affecting bones & joints.
Osteochondritis Inflammation of both bone and cartilage.
Osteochandroma Begine bone and cartilage tumoron surface of bone.
Osteochondrosarcoma Bone & cartilage sarcomatous tumors.
Osteochondrosis Disease of children in which one or more growth ossification
centers degenerate or become necrosed or inactive, followed by
regeneration & usually deformity.
Osteogenesis Condition in which bones are abnormally brittle & subject to #;
imperfecta inherited, but metabolic etiology unknown.
Osteolysis Dissolution of bone.
Osteomalacia Softening of bones resulting from mineral loss; may result from
vitamin D (or calcium & phosphorus) deficiency.
Osteomyelitis Inflammation of bone marrow, cortex, tissue, & periosteum; can
be caused by any organism, but usually bacteria.
Osteonecrosis Death of bone tissue.
Osteoneuralgia Nerve pain in bone.
Osteopathy Any disease process of bone.
osteophyte Bony excrescene or osseous outgrowth, usually found around the
joint area of bone.
Osteoporosis Abnormal rarefaction of bone resulting from a failure of
osteoblasts to lay down bone matrix; caused by age, disuse,
trauma, or neurologic or other disease (osteopenia).
Osteosarcoma Sarcoma containing osseous tissue.
Osteosclerosis Hardening or abnormal denseness of bone; eburnation; osteitis
ossificans.
Osteosis Formation of bony tissue with filtration of connective tissue
within bone
osteosynovitis Inflammation of synovial membranes & neighboring bones.
Osteothrombosis Blood clots or plugging of veins of bone.
NK2053 Terapi Carakerja Disfungsi Fizikal 5
Semester 1 Sesi 2015-2016
SC.Chai
Cartilage Tumors (Affecting Bone)
Chondroma Cartilage tumor
Chondrosarcoma Sarcoma in which cancer cells are making cartilage.
Other Tumors
Fibrosarcoma Malignant tumor of bone composed mostly of malignant
fibroblasts.
Giant cell tumor Tumor of bone composed of many giant cells, occasionally
malignant.
Miscellaneous Latin & English Terms
Aseptic necrosis Osteonecrosis (bone death) caused by vascular insult, usually at
the end of a bone. In adults, the most common symptom-
producing aseptic necrosis occurs in femoral head (avascular
necrosis); in children, it is called epiphyseal ischemic necrosis or
epiphyseal aseptic necrosis.
Bone infarct Area of bone where blood supply is interrupted.
Myelofibrosis Replacement of bone marrow by fibrous tissue.
Nonsuppurative Term used for tuberculosis of bone.
osteomyelitis
Progressive Neuromuscular dystrophy associated with general wasting;
diaphyseal dysplasia abnormal formed shafts of long bones; Engelmanns disease.
Slipped capital A gradual or sudden movement of the femoral head toward a
femoral epiphysis posterior & medial direction; usually occurs in obese preteenage
children; Frohlichs adiposogenital dystrophy.
Heberdens nodes Cartilaginous & bony enlargement of the DIPJs.
Kienbocks disease Aseptic necrosis of affecting lunate or ilium.
Pagets disease Osteitis deformans, a disease of excess bone removal &
replacement with deformity; seen in older people.
Perthes disease Aseptic necrosis of the hips in children.
Potts disease Osteomyelitis; tuberculosis of the spine.
Sudecks atrophy Atrophy secondary to minor trauma; spotty osteoporosis;
sudecks disease.
NK2053 Terapi Carakerja Disfungsi Fizikal 6
Semester 1 Sesi 2015-2016
SC.Chai
Muscle Diseases
Myasthenia gravis Syndrome of attcks of muscle weakness that is episodic &
reversible; Erb-Goldflam disease.
Myatrophy Muscle wasting.
Myoasthenia Amyosthenia; lack of muscle strength.
Myopathy Any disease of muscles.
Myositis Inflammation of a voluntary muscle; for example, 1) myositis
ossificans, a bony ossification of muscle; & 2) myositis ossificans
progreesiva, a terminal process in which muscle becomes
calcified.
Myospasm Muscle spasm
Myotonia Increased muscular irritability & contractility with decreased
power of relaxation; tension & tonic spasm of muscle.
Muscular dystrophy A group of degenerative disorders of muscle resulting in atrophy
& weakness; Erbs disease.
Muscle atrophy A general loss of muscle from various causes; muscle wasting.
Muscle spasm Sudden contraction of muscle, usually in reflex response to
stimulus from external source, for example, back spasm caused
by a herniated disk.
Muscle contracture A condition of fixed resistance to passive stretch of a muscle
resulting from fibrosis of the tissues supporting the muscles or the
joints, or from disorders of the muscle fibers.
NK2053 Terapi Carakerja Disfungsi Fizikal 7
Semester 1 Sesi 2015-2016
SC.Chai
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Musculoskeletal Radiography Trauma and Fracture ClassificationDocument63 paginiMusculoskeletal Radiography Trauma and Fracture ClassificationNurliana NingsihÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interpretasi Foto TulangDocument35 paginiInterpretasi Foto TulanganwarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jenis Fraktur IstimewaDocument14 paginiJenis Fraktur IstimewaUllya AisyafitriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fractures: Types, Complications, and ManagementDocument26 paginiFractures: Types, Complications, and Managementsm - kardmÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fracture Classification: DR - Banna Kiran KumarDocument68 paginiFracture Classification: DR - Banna Kiran KumarBanna Kiran KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Actures & DislocationsDocument16 paginiActures & Dislocationssabina_grapiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clavicle Fracture (Broken Collarbone) : AnatomyDocument5 paginiClavicle Fracture (Broken Collarbone) : AnatomyAan AlawiyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bimbingan Muskuloskeletal CoassDocument224 paginiBimbingan Muskuloskeletal CoassMichael AndhitoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compilation Notes Pathology - FractureDocument5 paginiCompilation Notes Pathology - FractureDionne Jillian SyÎncă nu există evaluări
- TARGET 200 PLUS Orthopaedics GuideDocument21 paginiTARGET 200 PLUS Orthopaedics GuideTMC PGI GENER MICKOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basics of Orthopedic RadiologyDocument94 paginiBasics of Orthopedic RadiologyandreÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSK Week 2 Catatan Ko KoresDocument10 paginiMSK Week 2 Catatan Ko KoresFirmanHidayatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types and Patterns of Bone FracturesDocument30 paginiTypes and Patterns of Bone FracturesAryo WibisonoÎncă nu există evaluări
- J Orthop Trauma 2007 21 (5) 352Document3 paginiJ Orthop Trauma 2007 21 (5) 352Andrés KnubelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fractures & OrthopaedicsDocument10 paginiFractures & OrthopaedicsPriya SreeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sudden Trauma: Overlying Skin IntactDocument4 paginiSudden Trauma: Overlying Skin IntactSuha AbdullahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radiology ReviewDocument48 paginiRadiology ReviewriddhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fracture and Joint Injuries-General FeaturesDocument19 paginiFracture and Joint Injuries-General Featuresngurah123456789Încă nu există evaluări
- Salter Chapter XVDocument16 paginiSalter Chapter XVSamuel Pola Karta SembiringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traumas of Spine and Pelvis. Done By:moldir Akynbay 17-40-01Document25 paginiTraumas of Spine and Pelvis. Done By:moldir Akynbay 17-40-01Moldir AkynbayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Principles-Of-FracturesDocument95 paginiPrinciples-Of-Fracturesbyanfqha1Încă nu există evaluări
- Spine and MusculoDocument116 paginiSpine and MusculoKomang Soniananda Pradnyana PutriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jharkhand Raksha Shakti UniversityDocument23 paginiJharkhand Raksha Shakti UniversityniteshÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degenerative Disease: Lecture By: M.K. SastryDocument42 paginiDegenerative Disease: Lecture By: M.K. SastryAnonymous 5IUoLwGSdÎncă nu există evaluări
- The ElbowDocument10 paginiThe ElbowKatalinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Bone Fractures and Clinical ManifestationsDocument10 paginiTypes of Bone Fractures and Clinical ManifestationsFryam BellsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perioperative of ORIFDocument27 paginiPerioperative of ORIFSometwo C. Hangal91% (11)
- Pediatria FrattureDocument12 paginiPediatria FrattureGaia TarantiniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Role of Imaging in Fractures - An Introduction: Dr. Muhammad Bin ZulfiqarDocument54 paginiRole of Imaging in Fractures - An Introduction: Dr. Muhammad Bin ZulfiqarCynthia AyuPermatasariÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bone Fracture": Jea N. Daligdig BSN-3Document7 paginiBone Fracture": Jea N. Daligdig BSN-3pjcolitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal Reading - Angga (English)Document31 paginiJournal Reading - Angga (English)angga andriyantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bedah Menejemen FrakkturDocument53 paginiBedah Menejemen FrakkturvitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sprain and DislocationDocument9 paginiSprain and Dislocationbhavesh jain100% (1)
- Imaging - Lecture 3 (Fractures)Document11 paginiImaging - Lecture 3 (Fractures)Adham MohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fracture TulangDocument55 paginiFracture TulangAnonymous HAbhRTs2TfÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wrist Injuries (BK)Document5 paginiWrist Injuries (BK)Malueth AnguiÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1nd Graduation Project, 1Document37 pagini1nd Graduation Project, 1fetacademymediaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bones of the Upper LimbDocument48 paginiBones of the Upper Limbhuzaifa arshadÎncă nu există evaluări
- FrakturDocument188 paginiFrakturSiti RaihanatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Forearm Fracture Types and TreatmentsDocument21 paginiForearm Fracture Types and TreatmentsAbdullah MatarÎncă nu există evaluări
- SYLLABUS Traumato DRAFTDocument91 paginiSYLLABUS Traumato DRAFTpapyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Pediatric Fractures Common Pediatric FracturesDocument67 paginiCommon Pediatric Fractures Common Pediatric FracturesJeane SuyantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bedah 2 - BimbelmantapDocument208 paginiBedah 2 - BimbelmantapDELLA DWIÎncă nu există evaluări
- FracturePPT UpdatedDocument108 paginiFracturePPT Updatedgaile pattugalanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Degenerative Spine DiseasesDocument10 paginiDegenerative Spine DiseasesmarizamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Types of Bone Fractures Classification GuideDocument8 paginiTypes of Bone Fractures Classification GuideApple PaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- OrthopaedicsDocument45 paginiOrthopaedicsZeinab HusseinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introduction of MSK ImagingDocument63 paginiIntroduction of MSK ImagingyeabsraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 2 - Fracture - IIDocument12 paginiLecture 2 - Fracture - IIAnkit LakshyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEDAH 2: Orthopaedic, Urologic, Digestive, and Oncology SurgeryDocument202 paginiBEDAH 2: Orthopaedic, Urologic, Digestive, and Oncology SurgerySelvi AristinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fractures and DislocationsDocument53 paginiFractures and Dislocationsagha_sajjad90Încă nu există evaluări
- 01 TraumaDocument37 pagini01 TraumaMajid KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- 05 Fractures of The Upper Extremity Part 2 - Dr. TanDocument75 pagini05 Fractures of The Upper Extremity Part 2 - Dr. TanMonique BorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSK Imaging MELLYA FIXDocument28 paginiMSK Imaging MELLYA FIXMELLYAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bedah 2 Batch 3 2018Document87 paginiBedah 2 Batch 3 2018Meiza Ihsan FakhriÎncă nu există evaluări
- Radioanatomy of The Extremities & Some of The MSK PathologiesDocument114 paginiRadioanatomy of The Extremities & Some of The MSK PathologiesTogodly 07Încă nu există evaluări
- Clinical Features and Diagnosis of FracturesDocument43 paginiClinical Features and Diagnosis of FracturesChenna Kesava100% (2)
- Adult Fractures and DislocationsDocument18 paginiAdult Fractures and DislocationsSamuel Pola Karta SembiringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Persiapan Operasi ORIFDocument38 paginiPersiapan Operasi ORIFamir hamzahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Self Care Training ManualDocument64 paginiSelf Care Training ManualNurul Shahira MaswahÎncă nu există evaluări
- BasketballDocument1 paginăBasketballNurul Shahira MaswahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Low Back PainDocument22 paginiLow Back PainNurul Shahira MaswahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Improving Writing Skills of Children with Learning Disabilities Using Word Processing and PredictionDocument13 paginiImproving Writing Skills of Children with Learning Disabilities Using Word Processing and PredictionNurul Shahira MaswahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Body Image QuestionaireDocument2 paginiBody Image QuestionaireNurul Shahira MaswahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ages and Stages Birth To FiveDocument35 paginiAges and Stages Birth To FiveNurul Shahira MaswahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Angah PunyaDocument1 paginăAngah PunyaNurul Shahira MaswahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Medscape DermatologyDocument38 paginiMedscape DermatologyAli KhalidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Microbes and Disease Mini TestDocument2 paginiMicrobes and Disease Mini TestNazma NoreenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Problems On Course 2ndDocument7 paginiProblems On Course 2ndالأغا محمد زكارنةÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnsefalitisDocument3 paginiEnsefalitisAnizha AdriyaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Pathophysiology of Otosclerosis: Review of Current ResearchDocument6 paginiThe Pathophysiology of Otosclerosis: Review of Current ResearchFelipeAsenjoÁlvarezÎncă nu există evaluări
- N"SF) VF) K Nufpg) DoDocument4 paginiN"SF) VF) K Nufpg) DoRajesh KoiralaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BadjokoDocument4 paginiBadjokoanderson mendesÎncă nu există evaluări
- ST English 8 No. 1Document4 paginiST English 8 No. 1Roylyn Joy CarlosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Genital Tract InfectionsDocument1 paginăGenital Tract InfectionsKatrina TaracatacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Meningitis - Introduction and ManagementDocument27 paginiMeningitis - Introduction and ManagementAmmo KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- BPOC in Medicina PrimaraDocument3 paginiBPOC in Medicina PrimaraAlina GheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dic 2015Document16 paginiDic 2015Sanaz NikiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Neurodermatitis (Lichen Simplex Chronic)Document26 paginiNeurodermatitis (Lichen Simplex Chronic)Yusran Ady FitrahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Epidemiology Rates TutorialDocument6 paginiEpidemiology Rates TutorialyunitaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Brain Cancer ScriptDocument2 paginiBrain Cancer Scriptapi-251981413Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter14 PDFDocument21 paginiChapter14 PDFsgw67Încă nu există evaluări
- KULIAH UMUM TANGGAL 4 JANUARI 2016 MENGENAI MULTIPLE CAUSE OF DAMAGE (MCODDocument1 paginăKULIAH UMUM TANGGAL 4 JANUARI 2016 MENGENAI MULTIPLE CAUSE OF DAMAGE (MCODJulia Jolanet Syafrianty AdamÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Death Struck YearDocument42 paginiA Death Struck Yearapi-543810353Încă nu există evaluări
- GiloyDocument2 paginiGiloyAdarsh SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sexual Health LeafletDocument2 paginiSexual Health LeafletdesbestÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gambaran Bakteriologis Lalat Dan Culicidae Ordo DiDocument9 paginiGambaran Bakteriologis Lalat Dan Culicidae Ordo DiJuliapertiwi264Încă nu există evaluări
- Industry Paper On The Activities of Amusement Parks and Theme Parks in The PhilippinesDocument14 paginiIndustry Paper On The Activities of Amusement Parks and Theme Parks in The PhilippinesHeina LyllanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Liver Function TestsDocument28 paginiLiver Function TestsDr. Ashish Jawarkar100% (2)
- English: Quarter 1 - Module 14Document12 paginiEnglish: Quarter 1 - Module 14Roxanne ManalotoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Animal Shelter Management GuideDocument20 paginiAnimal Shelter Management GuideAndres DavidÎncă nu există evaluări
- 12-Fancy Birds RearingDocument45 pagini12-Fancy Birds RearingAnonymous sBJu38BqÎncă nu există evaluări
- CHN ReviwerDocument1 paginăCHN ReviwerHeccie Duque-LarraquelÎncă nu există evaluări
- FNCPDocument10 paginiFNCPgracielue1120100% (1)
- Saccharomycesboulardiiprobiotic 131015101311 Phpapp01Document13 paginiSaccharomycesboulardiiprobiotic 131015101311 Phpapp01Dora FrătiţaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Oora200 Assessment 3 Bhima Devi Poudel Adhikari 220179000 MNP 3rd YearDocument17 paginiOora200 Assessment 3 Bhima Devi Poudel Adhikari 220179000 MNP 3rd Yearapi-522985556Încă nu există evaluări