Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
PDGF
Încărcat de
Xenish BhandariDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PDGF
Încărcat de
Xenish BhandariDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
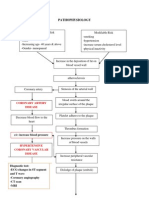
PDGF : released by activated platelets(locally adherent), disrupted endothelial cells, and
infiltrating macrophages promotes migration of SMs from media into the intima and increase SMCs
proliferation. Platelets also release TGF-beta which is chemotactic for SMCs and induces interstitial
collagen production.
........
fibroblast are found infrequently in the tunica intima of blood vessels and are not significantly
involved in atherosclerosis pathogenesis.
....
Vascular smooth muscle cells(VSMC) are directly responsible for the synthesis of new collagen
and extracellular matrx
Endothelial Cell Injury is due to hyperlipidemia and chronic hemodynamic stress.>>>>
this leads to increased expression of surface vascular cell-adhesion molecules (VCAM)>>>>that allow
adherence and migraton of monocytes and T lymphocytes into the intima>>>>the infiltrating
leukocytes and dysfunctional endothelium release cytokines and growth factor.( eg
PDGF,FGF,endothelin-1, interleukin-1) that promote migration and proliferation of VSMC from
media within intima.
VSMC are also stimulated to synthesize extracellular matrix proteins (eg collagen,
elastin,proteoglycans) that form the fibrous cap typical of mature atheroma.
COMPLICATONS :the likely hood of plaque rupture or other acute plaque change has more to do
with plaque stability than plaque size.
plaque stability depends upon mechanical strength of overlying fibrous cap.
during chronic inflammatory progression of an atheroma, the fibrous cap is continually being
remodeled. the balance of collagen synthesis and degredation determine the mechanical
strength of the cap.
activated macrophages in the atheroma contribute to collagen degredation by secreting
metalloproteinases.thus a high degree of ongoing intimal inflammation can destabilize the
mechainical integrity of plaque through release of the metallopreoteinases.
.........
macrophage also produce matrix metalloproteinases and tissue factors that degrade the
extracelular matrix,causing the formation of a large, soft lipid-rich core with thinning of the fibrous
cap. such vulnerable plaques have an increased propensity for rupture.
.
ATHEROMAS :start as early as 2nd decade with formation of fatty streak and intimal thickening
..........
fatty streak : presents as minimally raised yellow spots in the inner surface of vessels, these
are the earliest lesions in the progression to atherosclerosis and can be seen as early as the
second decade of life.with advancing age, the chronic inflammatory process initiated by
endothelial injury transitions from fatty streaks within the intima (composed mainly of
lipid-laden foam cells) into atherosclerotic plaques, such as fibrous cap atheromas and
fibrous plaques
...........................................................................................................
subendothelial collagen and subendothelial glycosaminoglycan form subendothelial fibrous
cap over the central core of an atherosclerotic plaque.
........
thin fibrous cap, rich lipid core and active inflammation all correlate with decrease plaque
stability.
.........
more advance lesion develop lipid-rich necrotic core and regions of calcification.
......
Abs to oxidized LDL have been detected in human serum and localize to atherosclerotic
plaque.
titer of this rises following acute coronary event.
although they play a role in atherosclerosis development , they do not act as growth
factors for SMc
.......
total coronary artery calcium content correlate modestly with coronary artery
atherosclerotic plaque burden.
but the presence of intraplque calcium could be consistent with either acute coronary
syndrome or with gradual occlusion without mycardial necrosis.
.
Isolated systemic hypertension is due to decrease in compliance of aorta and its major
branches with progressoin
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Abdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Atherosclerosis FINALDocument23 paginiAbdominal Aortic Aneurysm and Atherosclerosis FINALErica P. ManlunasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calcium ScanDocument3 paginiCalcium ScanStepyn SalvadorÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2023 Article 1906Document24 pagini2023 Article 1906Oeij Henri WijayaÎncă nu există evaluări
- HemiplegiaDocument31 paginiHemiplegiaislam1111Încă nu există evaluări
- Forks Over KnivesDocument12 paginiForks Over Knivesfarnorton50% (2)
- PHD Thesis On Coronary Artery DiseaseDocument5 paginiPHD Thesis On Coronary Artery Diseasebdg9hkj6100% (1)
- Abstract Book INAACCDocument83 paginiAbstract Book INAACCrodtobingÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ismail's Undergraduate ThesisDocument82 paginiIsmail's Undergraduate ThesisAbiola IbrahimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aztor Cme NewDocument59 paginiAztor Cme NewSheikh Sharfuddin RajeevÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cardiac PathophysiologyDocument36 paginiCardiac Pathophysiologykim suhoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ερωτήσεις διάφορεςDocument108 paginiΕρωτήσεις διάφορεςyiafkaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atherosclerosis PathophysiologyDocument12 paginiAtherosclerosis PathophysiologyHuman ResourcesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lec10 CV PathologyDocument75 paginiLec10 CV PathologymanuelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Journal of Food Biochemistry - 2022 - Rana - Health Benefits of Polyphenols A Concise ReviewDocument24 paginiJournal of Food Biochemistry - 2022 - Rana - Health Benefits of Polyphenols A Concise ReviewGustavoTorresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grape Seed Extract: Having A Potential Health BenefitsDocument11 paginiGrape Seed Extract: Having A Potential Health BenefitsGabriel GursenÎncă nu există evaluări
- HCVD Cad Cva InfarctionDocument2 paginiHCVD Cad Cva InfarctionPamela DomingoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Siriraj Stroke ScoreDocument3 paginiSiriraj Stroke ScoreHendy SetiawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Roseday EZ Webinar SlidesDocument35 paginiRoseday EZ Webinar SlidesPragnesh ShahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heart DiseasesDocument73 paginiHeart DiseasesturbomurboÎncă nu există evaluări
- Enzyme 20pagesDocument20 paginiEnzyme 20pagesEddie Optin100% (2)
- Exercise For Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Treatment From Molecular To Clinical Part 1Document320 paginiExercise For Cardiovascular Disease Prevention and Treatment From Molecular To Clinical Part 1Diego CardosoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pathology of Blood VesselsDocument80 paginiPathology of Blood VesselsiqiqiqiqiqÎncă nu există evaluări
- Therapy FINAL PDFDocument102 paginiTherapy FINAL PDFManushi HenadeeraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tip-Tv: Program Supplement CT: Cardiac ApplicationsDocument47 paginiTip-Tv: Program Supplement CT: Cardiac ApplicationsvitapabloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Human Biology (4HB0) Paper 02Document14 paginiMark Scheme (Results) Summer 2015: Pearson Edexcel International GCSE in Human Biology (4HB0) Paper 02Joseph LAU [11D]Încă nu există evaluări
- Panvascular Disease - Diagnosis and Management: SciencedirectDocument9 paginiPanvascular Disease - Diagnosis and Management: SciencedirectAndikaputra Brahma WidiantoroÎncă nu există evaluări
- Report Heart AttackDocument20 paginiReport Heart AttackLucía Andújar RodríguezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparison of Myocardial Ischemia During Intense Mental Stress Using Flight SimulationDocument7 paginiComparison of Myocardial Ischemia During Intense Mental Stress Using Flight Simulationluis11256Încă nu există evaluări
- Acute Coronary Syndrome 2022Document38 paginiAcute Coronary Syndrome 2022Anonymous100% (1)
- Stress and Physiological ResponseDocument11 paginiStress and Physiological ResponseCampbell BellÎncă nu există evaluări