Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Gerunds and Infinitives
Încărcat de
yolandagarciamorenoDescriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Gerunds and Infinitives
Încărcat de
yolandagarciamorenoDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
GERUNDS AND INFINITIVES
GERUNDS
El gerundio es la forma verbal terminada en ing que, adems de utilizarse para la formacin de
tiempos de continuo, tiene otros usos:
GERUNDIO COMO SUJETO
Cuando un verbo funciona como sujeto de la oracin, este verbo se pondr en gerundio (para
hablar de acciones en general)
e.g. Breaking up a relationship is never easy
Smoking is very unhealthy
GERUNDIO COMO CD
Hay muchos verbos que van seguidos de gerundio. Los ms comunes son:
ADMIT ADVISE ANTICIPATE APPRECIATE AVOID COMPLETE CONSIDER DELAY
DENY DETEST DISCUSS DISLIKE ENJOY FINISH FORGET HATE IMAGINE KEEP
LIKE LOVE MENTION MIND MISS POSTPONE PRACTICE PREFER QUIT RECALL
RECOLLET RECOMMEND REGRET REMEMBER RESENT RESIST RISK STOP
SUGGEST TOLERATE UNDERSTAND
e.g. I enjoy swimming
We discussed holding the wedding at home
GERUNDIO DETRAS DE DETERMINADAS EXPRESIONES O FORMAS VERBALES
I cant help laughing at him
I cant stand waiting in queues
Theres / its no use crying over spilt milk
That car isnt worth buying
Helen isnt used to driving on the left.
I look forward to seeing you again
David couldnt get used to living in a city.
John has given up smoking
Lets go swimming!
Your car needs cleaning (need + -ing = sentido pasivo)
GERUNDIO DETRAS DE PREPOSICION
Cuando una preposicin va seguida de un verbo, este normalmente se pondr en gerundio:
e.g. He apologized for not paying the bill
Lucy doesnt like his way of thinking
INFINITIVES
El infinitivo es otra forma invariable del verbo. Puede ir precedida de to o no. Si no lo lleva se
llama BARE INFINITIVE. Sin embargo, aqu vamos a hablar de los que van con to
INFINITIVO COMO SUJETO
Cuando un verbo funciona como sujeto de la oracin, este verbo se pondr en infinitivo (para
hablar de acciones concretas)
e.g. To live alone is not very good for you now
INFINITIVOS COMO CD VERBOS SEGUIDOS DE TO+ INFINITIVO
Hay muchos verbos que van seguidos de infinitivo con to. Los ms comunes son:
AFFORD AGREE APPEAR ARRANGE ASK BEG CARE CHOOSE CLAIM CONSENT
DECIDE DEMAND DESERVE EXPECT FAIL FORGET HESITATE HELP HOPE
LEARN MANAGE MEAN NEED OFFER PLAN PERSUADE PREPARE PRETEND
PROMISE REFUSE REGRET REMEMBER SEEM STRUGGLE SWEAR THREATEN
VOLUNTEER WAIT WANT WISH
e.g. Angela promised to arrive on time.
They decided not to take the car.
INFINITIVO DETRAS DE VERBOS QUE LLEVAN CI
Estos verbos llevan un nombre o un pronombre entre el primer verbo y el infinitivo.
e.g. Alan told me to call him at 7.00
I permitted my daughter to take the car
Harry warned me not to drive too fast
She wants you to do the shopping.
Verbos de este tipo son:
ADVISE ALLOW ASK BEG CAUSE CHALLENGE CONVINCE DARE ENABLE
ENCOURGE EXPECT FORBID FORCE HIRE INSTRUCT INVITE NEED ORDER
PERMIT PERSUADE REMIND REQUIRE TEACH TELL URGE WANT WARN
Algunos verbos frasales y ciertas expresiones van seguidas de infinitive con to.
e.g. The whole affair turned out to be an embarrassment.
We were about to leave, so hurry up
Helen made up her mind to buy a house
Its up to you to decide
INFINITIVO DETRAS DE ADJETIVOS Y ADVERBIOS
e.g. This text is difficult to understand
The car went too fast to see the traffic lights.
VERBOS SEGUIDOS DE INFINITIVO SIN TO
1. Modales y semi-modales:
e.g. We should leave soon
The boys will have to travel on Tuesday
2. Verbos auxiliaries:
e.g. Did you see the accident?
She would like to help me
3. Let/ Make + objeto + bare infinitive
e.g. He made me feel bad
My mother didnt let me go to the party
PERO, cuando ponemos en pasiva una frase con MAKE, hemos de ponerle TO
e.g. They made the pupil do his homework
The pupil was made to do his homework
El verbo LET no tiene pasiva; en su lugar se pone TO BE ALLOWED TO
e.g. I let my son borrow the car
My son was allowed to borrow the car
4. Los verbos de los sentidos (SEE HEAR WATCH NOTICE FEEL) pueden ir con:
- GERUNDIO: implica que la accin est incompleta
e.g. I saw the plane falling (lo vi mientras estaba cayendo, pero no vi donde cayo)
- INFINITIVO SIN TO: implica que vimos u omos una accin completa
e.g. I saw the plane fall (lo vi en el suelo)
OJO!: el verbo SMELL se suele emplear solo en GERUNDIO
e.g. I could smell something burning
VERBOS + GERUNDIOS / INFINITIVOS SIN CAMBIO DE SIGNIFICADO
Algunos verbos pueden ir seguidos tanto de gerundio como de infinitive SIN QUE CAMBIE
SU SIGNIFICADO. Si el verbo esta en un tiempo de continuo, se suele preferir el infinitivo.
Los mas comunes son:
ADVISE ALLOW BEGIN CEASE CONTINUE HATE INTEND LIKE LOVE
PERMIT PREFER RECOMMEND START
1. Con ADVISE, ALLOW, PERMIT Y RECOMMEND:
- Si se menciona el nombre o pronombre se pone infinitivo, pero si no lo hay debe usarse el
gerundio:
e.g. I advised him to sell the car
I advised selling the car
- Despues de INTEND, es mas frecuente el infinitive:
e.g. I intend to move house in the summer
- PREFER + infinitive es mas frecuente cuando estamos pensando en una ocasion particular
e.g. I prefer to go to the pool today
VERBOS + GERUNDIO / INFINITIVO CON CAMBIO DE SIGNIFICADO
STOP
He stopped smoking last year
He stopped to smoke a cigarette
REGRET
I regret wasting so much money
I regret to tell you that he has died
REMEMBER
I remember taking the suitcase
Please remember to take the suitcase before you leave
FORGET
I will never forget visiting The Tower of London
David always forgets to visit his grandmother
TRY
Please try to help me if you can
He t
S-ar putea să vă placă și
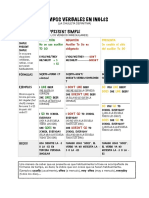
- Tiempos Verbales Presente InglésDocument5 paginiTiempos Verbales Presente InglésnadiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fonética InglesaDocument4 paginiFonética InglesaAntonio MolinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Translation Booklet 4 Week 16Document8 paginiTranslation Booklet 4 Week 16ALBERTOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preferencias Would Rather - Would PreferDocument10 paginiPreferencias Would Rather - Would PreferDennisse PérezÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Big FourDocument65 paginiThe Big FourAnonymous hYfyUHlhÎncă nu există evaluări
- Doblar Consonantes en Inglés - Aprende Inglés SilaDocument8 paginiDoblar Consonantes en Inglés - Aprende Inglés Silanico ryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Resumen de Gramatical InglesDocument17 paginiResumen de Gramatical InglesYazminÎncă nu există evaluări
- Expresiones Con GET PDFDocument2 paginiExpresiones Con GET PDFBebéDoNascimento100% (1)
- Lista de Phrasal Verbs para Aprobar El B1 - Academia Puerta RealDocument9 paginiLista de Phrasal Verbs para Aprobar El B1 - Academia Puerta RealMartha MendozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lista de Phrasal VerbsDocument25 paginiLista de Phrasal VerbsdecoletiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Tenses Usage ExplainedDocument1 paginăPast Tenses Usage ExplaineddaveturnerspainÎncă nu există evaluări
- English VI - Guide 8 - Writing and SpeakingDocument30 paginiEnglish VI - Guide 8 - Writing and SpeakingJulieth LaraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjetivos CalificativosDocument3 paginiAdjetivos CalificativosJonatan CondeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ingles Basico - Modulo 1Document12 paginiIngles Basico - Modulo 1Ayi ButtnerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conditional Sentences PDFDocument3 paginiConditional Sentences PDFj.t.LLÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerunds and Infinitives - Teoría y EjerciciosDocument5 paginiGerunds and Infinitives - Teoría y EjerciciosRosanna BellaubiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vicios de La Redaccion PresentacionDocument56 paginiVicios de La Redaccion PresentacionLopez MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ejercicios de REPHRASING II Intermediate AdvancedDocument63 paginiEjercicios de REPHRASING II Intermediate Advancedbrisa100% (1)
- Essay in EnglishDocument8 paginiEssay in EnglishgilmoltoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Curso de Om Personal EnglishDocument29 paginiCurso de Om Personal EnglishJesus Ruiz de CastillaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diferencia Entre Los Verbos DO y MAKE en Inglés PDFDocument3 paginiDiferencia Entre Los Verbos DO y MAKE en Inglés PDFHectorDiazÎncă nu există evaluări
- Interacción Inicial en Inglés PDFDocument50 paginiInteracción Inicial en Inglés PDFoswald martinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- El Preterito Perfecto Simple. El Preterito Indefinido. NIVEL A2Document6 paginiEl Preterito Perfecto Simple. El Preterito Indefinido. NIVEL A2Hamid Hussain Kalathingal Thodi100% (1)
- Nouns AdjetiveDocument52 paginiNouns AdjetiveMónica González50% (2)
- Summary TensesDocument7 paginiSummary TensesLiliana MimizaÎncă nu există evaluări
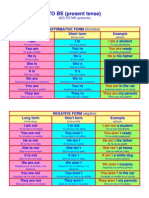
- To Be (Present Simple Tense)Document5 paginiTo Be (Present Simple Tense)msdv63100% (1)
- Countable NounsDocument9 paginiCountable NounsLili MoralesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spagnolo ContrastivaDocument28 paginiSpagnolo ContrastivaAnonymous KHQBqn1qÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepositions Place and MovementDocument14 paginiPrepositions Place and MovementtemplarioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive VoiceDocument6 paginiPassive VoiceGabriela GarciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Idioms 1Document616 paginiIdioms 1Angel Ernesto Hernandez SierraÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Passive VoiceDocument3 paginiThe Passive VoiceMatias Alfredo VillagraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerunds and Infinitives PDFDocument2 paginiGerunds and Infinitives PDFQuel MenorcaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cuadro de Subjuntivo e IndicativoDocument4 paginiCuadro de Subjuntivo e IndicativoLuciaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3-Jacinto Rivera de Rosales - El Método Transcendental. Su Desarrollo en El Fichte de JenaDocument29 pagini3-Jacinto Rivera de Rosales - El Método Transcendental. Su Desarrollo en El Fichte de JenaNombre FalsoÎncă nu există evaluări
- English 1-First Grammar and Vocabulary TextDocument34 paginiEnglish 1-First Grammar and Vocabulary TextMMnI82100% (1)
- Uso de Gerundios e InfinitivosDocument3 paginiUso de Gerundios e Infinitivosrudeboy100% (2)
- Personal PronounsDocument3 paginiPersonal PronounsEli SanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema 19 - Los CondicionalesDocument17 paginiTema 19 - Los CondicionalesAlejandro JiménezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Los Verbos Modales PerfectosDocument10 paginiLos Verbos Modales PerfectosVane HidalgoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reported SpeechDocument6 paginiReported SpeechsweetlormurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Passive VoiceDocument4 paginiPassive Voiceednasugo100% (1)
- Ficha Indicativo Vs Subjuntivo Parte 1Document1 paginăFicha Indicativo Vs Subjuntivo Parte 1Irina SuredaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Personal Pronouns and Verb To BeDocument2 paginiPersonal Pronouns and Verb To BeTío Alex Catalán100% (1)
- Oraciones CondicionalesDocument8 paginiOraciones CondicionalesvallinskiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prueba de Examen GESDocument6 paginiPrueba de Examen GESMaritrini CuencaÎncă nu există evaluări
- In - On - AT - Aprende Cuándo Usar Las Preposiciones de Tiempo y Lugar - Aprobar El CAEDocument12 paginiIn - On - AT - Aprende Cuándo Usar Las Preposiciones de Tiempo y Lugar - Aprobar El CAERomina CaceresÎncă nu există evaluări
- Prepositions of Movement or DirectionDocument5 paginiPrepositions of Movement or DirectionJaquelineMartinezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Como Hacer Preguntas en InglesDocument4 paginiComo Hacer Preguntas en InglesRodolfo AlvaradoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Get AdjectiveDocument3 paginiGet AdjectivewilliamIIÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lengua Examen 2Document2 paginiLengua Examen 2Ant_and_RaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ise I Examination. EsquemaDocument3 paginiIse I Examination. EsquemaAlba Chumilla MorenoÎncă nu există evaluări
- AdjetivosDocument7 paginiAdjetivosMónica GalpÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tema 20 - Estilo Directo e Indirecto (Reported Speech)Document20 paginiTema 20 - Estilo Directo e Indirecto (Reported Speech)Alejandro Jiménez100% (1)
- BIEN y BUENO Diferencias de UsoDocument3 paginiBIEN y BUENO Diferencias de UsoacaromcÎncă nu există evaluări
- Verbo To BeDocument8 paginiVerbo To BeLuz BelénÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparatives and SuperlativesDocument3 paginiComparatives and Superlativesaitor100% (1)
- Pronombres INDEFINIDOS en Inglés Somebody, Anyone, EverythingDocument10 paginiPronombres INDEFINIDOS en Inglés Somebody, Anyone, EverythingYojansel Matos JavierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Diferencias Entre Say & Tell y PreposicionesDocument5 paginiDiferencias Entre Say & Tell y PreposicionesDe Alonso AlaiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Condicionales Con SIDocument2 paginiCondicionales Con SIMónica LozaÎncă nu există evaluări
- RephrasingDocument1 paginăRephrasingceliacabeÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRONOMBES EspañolDocument1 paginăPRONOMBES EspañolClaudio Martinez CuperÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerunds and Infinitive. EXPLANATIONdocxDocument4 paginiGerunds and Infinitive. EXPLANATIONdocxYOLANDA GARCIA MORENOÎncă nu există evaluări
- Gerunds and Infinitives - Teoría y EjerciciosDocument5 paginiGerunds and Infinitives - Teoría y EjercicioshenrysaloÎncă nu există evaluări
- Historia-Teoria-Traduccion Problemas Procedimientos y Tcnicas 20140912Document45 paginiHistoria-Teoria-Traduccion Problemas Procedimientos y Tcnicas 20140912Ivana FasanoÎncă nu există evaluări
- SabeeeDocument6 paginiSabeeeEmmanuel Quezada CarvÎncă nu există evaluări
- Teoria Especial Del ConocimientoDocument5 paginiTeoria Especial Del ConocimientoGenaro SeguraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Copia de Pastel Portfolio Green VariantDocument15 paginiCopia de Pastel Portfolio Green Variantcriolloestefania3006Încă nu există evaluări
- Tilde DiacriticaDocument3 paginiTilde DiacriticaErika Fabiola LobatonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lamotivacindelsignolingstico 111230055053 Phpapp01Document14 paginiLamotivacindelsignolingstico 111230055053 Phpapp01Nadejda VishnevskaiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenguaje FiguradoDocument2 paginiLenguaje FiguradoKike Valdizón FélixÎncă nu există evaluări
- Guia de AdjetivosDocument5 paginiGuia de AdjetivosLuisa JofreÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 de InglesDocument6 paginiLesson 6 de InglesClaudiaShimÎncă nu există evaluări
- MORFOLOGIADocument4 paginiMORFOLOGIAMARBELLAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latín 4º 20 - 21 TERCER TRIMESTRE PDFDocument80 paginiLatín 4º 20 - 21 TERCER TRIMESTRE PDFElena StrunilinaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Las Proposiciones SubordinadasDocument3 paginiLas Proposiciones SubordinadasAngelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Traduccion Contrastiva e InterpretativaDocument22 paginiTraduccion Contrastiva e InterpretativaClaudia JeriaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lenguaje y Comunicacin-EiaespecDocument16 paginiLenguaje y Comunicacin-EiaespecMa. Gabriela Cueva100% (1)
- Arcaismos 10Document3 paginiArcaismos 10Kelly Catherin Basante GuastarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Conceptualización de La Escritura y La Lectura Palem PronaleesDocument10 paginiConceptualización de La Escritura y La Lectura Palem Pronaleesmonx0311Încă nu există evaluări
- Uso de La Letra CDocument2 paginiUso de La Letra CElizabeth Valdivieso SifuentesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Centro Escolar Coronel Francisco Linares Guía de Lenguaje 3°Document20 paginiCentro Escolar Coronel Francisco Linares Guía de Lenguaje 3°Marcelo ChacónÎncă nu există evaluări
- Los SufijosDocument1 paginăLos SufijosMarta Aguarón EsquiroleaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Adjetivos y AdverbiosDocument12 paginiAdjetivos y AdverbiosomarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Latin ProfundizaciónDocument25 paginiLatin ProfundizaciónTom WolfyÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Bachillerato. Cuadro Clasificacion de La Oracion Compuesta.Document2 pagini2 Bachillerato. Cuadro Clasificacion de La Oracion Compuesta.Esther SimpsonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recursos EstilísticosDocument3 paginiRecursos EstilísticosNoemí Infantes MoreirasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Modelo de Análisis Sintáctico PDFDocument7 paginiModelo de Análisis Sintáctico PDFAlmudenaEscuderoCarbajoÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021-09-13 - PronombresDocument13 pagini2021-09-13 - Pronombresgoyola2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Patrones OrtográficoDocument3 paginiPatrones OrtográficoAraa LoqitaÎncă nu există evaluări