Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Individual Assignment 1 s1 20172018 PDF
Încărcat de
syak0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
48 vizualizări1 paginăTitlu original
individual_assignment_1_s1_20172018.pdf
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
48 vizualizări1 paginăIndividual Assignment 1 s1 20172018 PDF
Încărcat de
syakDrepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 1
FACULTY OF MECHANICAL AND MANUFACTURING ENGINEERING
THERMODYNAMICS I
(BDA20703)
INDIVIDUAL ASSIGNMENT 1
Instruction: Answer all questions, submit this assignment during the next class.
Q1 What are the difference between a thermodynamics open
system and a closed system?
*You need to sketch both systems, and differentiate them
in terms of boundary, and energy that crossing the
boundaries (as work and heat).
Q2 a) What is the difference between gage pressure,
atmospheric pressure and absolute pressure?
b) What is the differences between intensive and
extensive properties?
c) What do you understand about isothermal, isobaric,
adiabatic, isometric, and isochoric process?
d) What is the difference between specific weight and
specific gravity?
e) What is Pascals law? Give a real-world example of
a system using this law and sketch it. Figure Q4
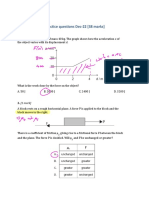
Q5 The absolute pressure of manometer shown in Figure Q5
Q3 A double-U manometer with a pressure gauge is is 270 kPa. If the specific gravity of oil is 0.82 and specific
connected to a gasoline pipe as shown in Figure Q3. If the gravity of kerosene is 0.75. Determine the local
reading of the pressure gage is 570 kPa, determine the
atmospheric pressure in bar.
gage pressure of the gasoline inside the pipe line.
Figure Q3
Figure Q5
Q4 Figure Q4 shows a manometer is attached to a tank of gas
in which the pressure is greater than that of the
surroundings. The manometer liquid is mercury, with a
density of 14 g/cm3. The difference in mercury levels in
the manometer is 3 cm. Atmospheric pressure is 98 kPa.
Calculate the gauge and absolute pressure (in kPa) of the
gas.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Mechanical EngineeringDocument12 paginiMechanical Engineeringanjaiah_19945100% (1)
- Bearing Capacity - 2Document36 paginiBearing Capacity - 2EICQ/00154/2020 SAMUEL MWANGI RUKWAROÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fiber Optic CommunicationDocument181 paginiFiber Optic CommunicationECE HoD PSNCET100% (1)
- Physics Questions - CorrelationDocument2 paginiPhysics Questions - CorrelationPamPeñeraSanchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lead CreepDocument11 paginiLead CreepEamonnSlatteryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Trihedron TNB Frame PDFDocument43 paginiTrihedron TNB Frame PDFAneelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Stress StrainDocument8 paginiSimple Stress StrainJames Ortega33% (3)
- Wetico Water Tank 70m Shell Ultimate ChecksDocument2 paginiWetico Water Tank 70m Shell Ultimate ChecksChristian Paul SanguyoÎncă nu există evaluări
- KeerthanaDocument120 paginiKeerthanagokiÎncă nu există evaluări
- M9 Experiment Lab ReportDocument5 paginiM9 Experiment Lab ReportShageenth Hashmeesh Sandrakumar100% (2)
- Grassmann NumbersDocument4 paginiGrassmann NumbershyriusenÎncă nu există evaluări
- EME4403 Finite ElementDocument25 paginiEME4403 Finite ElementAmmar muhammadÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unified Model For Gas - Liquid Pipe Flow Via Slug Dynamics - Part 1 - Model DevelopmentDocument8 paginiUnified Model For Gas - Liquid Pipe Flow Via Slug Dynamics - Part 1 - Model DevelopmentleofrazaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Compressible Fluids: 2004 Faith A. Morrison, All Rights ReservedDocument5 paginiCompressible Fluids: 2004 Faith A. Morrison, All Rights ReservedcoffewhoreÎncă nu există evaluări
- States of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetDocument2 paginiStates of Matter Kinetic Theory of Matter Thermal Expansion WorksheetChua Hui LinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade XI SCIENCE - Holiday Homework & WorksheetsDocument19 paginiGrade XI SCIENCE - Holiday Homework & WorksheetsReeja MathewÎncă nu există evaluări
- ExerciseDocument4 paginiExerciseAshebirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Example-1: Soil Mechanics-I Examples On Chapter-4Document12 paginiExample-1: Soil Mechanics-I Examples On Chapter-4Lami0% (1)
- PHD Application Research Proposal TemplateDocument2 paginiPHD Application Research Proposal TemplateZÄDsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Machine Dynamics Belt Friction Lab ReportDocument6 paginiMachine Dynamics Belt Friction Lab ReportnewbuieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cohen-Tannoudji - Quantum Mechanics, Vol.1Document887 paginiCohen-Tannoudji - Quantum Mechanics, Vol.1elke_hk100% (15)
- Introduction - 3 Topics: Flight Dynamics-I Prof. E.G. Tulapurkara Chapter-1Document6 paginiIntroduction - 3 Topics: Flight Dynamics-I Prof. E.G. Tulapurkara Chapter-1alysonmicheaalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Astm G38-01R13Document9 paginiAstm G38-01R13shuli liÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pressure Loss CalculationsDocument28 paginiPressure Loss CalculationsAgus ManggalaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Note Sad DangDocument16 paginiNote Sad DangEverton LimaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Projectile Motion: (Item No.: P2131100)Document6 paginiProjectile Motion: (Item No.: P2131100)oğuz hamurculuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Constant Head Permeability Test in Sand: University of Texas at ArlingtonDocument8 paginiConstant Head Permeability Test in Sand: University of Texas at ArlingtonSalihin MasriÎncă nu există evaluări
- More Mechanics Practice Questions Dec-22 JT AnswersDocument13 paginiMore Mechanics Practice Questions Dec-22 JT AnswersAnmol SINGHIÎncă nu există evaluări
- ITER Btech Syllabus Mechanical (3rd and 4th Year)Document56 paginiITER Btech Syllabus Mechanical (3rd and 4th Year)gate_guy100% (1)
- The Reality of Virtual Environments: Jean-Christian DelannoyDocument3 paginiThe Reality of Virtual Environments: Jean-Christian DelannoyHany ElGezawyÎncă nu există evaluări