Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
EJB
Încărcat de
Isha Shan0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
50 vizualizări2 paginiEJB stands for enterprise JavaBeans and is widely-adopted server side component architecture for J2EE. It enables rapid development of ission-critical application that are versatile, reusable and portable across middleware. There are three kinds of enterprise beans: 1. Session beans, 2. Entity beans, and 3. Message-driven beans.
Descriere originală:
Drepturi de autor
© Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentEJB stands for enterprise JavaBeans and is widely-adopted server side component architecture for J2EE. It enables rapid development of ission-critical application that are versatile, reusable and portable across middleware. There are three kinds of enterprise beans: 1. Session beans, 2. Entity beans, and 3. Message-driven beans.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
50 vizualizări2 paginiEJB
Încărcat de
Isha ShanEJB stands for enterprise JavaBeans and is widely-adopted server side component architecture for J2EE. It enables rapid development of ission-critical application that are versatile, reusable and portable across middleware. There are three kinds of enterprise beans: 1. Session beans, 2. Entity beans, and 3. Message-driven beans.
Drepturi de autor:
Attribution Non-Commercial (BY-NC)
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca DOC, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 2
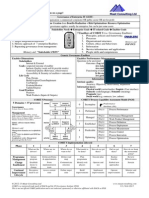
1. What is EJB?
EJB stands for Enterprise JavaBeans and is widely-adopted server side component
architecture for J2EE. It enables rapid development of ission-critical application that
are versatile, reusable and portable across middleware while protecting IT investment
and preventing vendor lock-in.
2. What is session Facade?
Session Facade is a design pattern to access the Entity bean through local interface
than accessing directly. It increases the performance over the network. In this case we
call session bean which on turn call entity bean.
3. What is EJB role in J2EE?
EJB technology is the core of J2EE. It enables developers to write reusable and
portable server-side business logic for the J2EE platform.
4. What is the difference between EJB and Java
beans?
EJB is a specification for J2EE server, not a product; Java beans may be a graphical
component in IDE.
5. What are the key features of the EJB technology?
1. EJB components are server-side components written entirely in the Java
programming language
2. EJB components contain business logic only - no system-level programming
& services, such as transactions, security, life-cycle, threading, persistence,
etc. are automatically managed for the EJB component by the EJB server.
3. EJB architecture is inherently transactional, distributed, portable multi-tier,
scalable and secure.
4. EJB components are fully portable across any EJB server and any OS.
5. EJB architecture is wire-protocol neutral--any protocol can be utilized like
IIOP, JRMP, HTTP, DCOM, etc.
6. What are the key benefits of the EJB technology?
1. Rapid application development
2. Broad industry adoption
3. Application portability
4. Protection of IT investment
7. How many enterprise beans?
There are three kinds of enterprise beans:
1. session beans,
2. entity beans, and
3. message-driven beans.
8. What is message-driven bean?
A message-driven bean combines features of a session bean and a Java Message
Service (JMS) message listener, allowing a business component to receive JMS. A
message-driven bean enables asynchronous clients to access the business logic in the
EJB tier.
9. What are Entity Bean and Session Bean?
Entity Bean is a Java class which implements an Enterprise Bean interface and
provides the implementation of the business methods. There are two types: Container
Managed Persistence (CMP) and Bean-Managed Persistence (BMP).
Session Bean is used to represent a workflow on behalf of a client. There are two
types: Stateless and Stateful. Stateless bean is the simplest bean. It doesn't maintain
any conversational state with clients between method invocations. Stateful bean
maintains state between invocations.
10. How EJB Invocation happens?
Retrieve Home Object reference from Naming Service via JNDI. Return Home Object
reference to the client. Create me a new EJB Object through Home Object interface.
Create EJB Object from the Ejb Object. Return EJB Object reference to the client.
Invokebusiness method using EJB Object reference. Delegate request to Bean
(Enterprise Bean).
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (894)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (587)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (265)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2219)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (119)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- TAXATION LAW TITLEDocument6 paginiTAXATION LAW TITLEJose Maria Jude DuremdesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Marketing Systems Analytics Director in Boston MA Resume Sean PrestonDocument3 paginiMarketing Systems Analytics Director in Boston MA Resume Sean PrestonSeanPrestonÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scd Hw2 Nguyễn Thị Hoài Liên Ielsiu19038Document4 paginiScd Hw2 Nguyễn Thị Hoài Liên Ielsiu19038Liên Nguyễn Thị HoàiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Griffin Chap 11Document34 paginiGriffin Chap 11Spil_vv_IJmuidenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Ratio Analysis and Working Capital ManagementDocument26 paginiFinancial Ratio Analysis and Working Capital Managementlucky420024Încă nu există evaluări
- Randy Gage Haciendo Que El Primer Circulo Funciones RG1Document64 paginiRandy Gage Haciendo Que El Primer Circulo Funciones RG1Viviana RodriguesÎncă nu există evaluări
- LPP Mod 2Document27 paginiLPP Mod 2ganusabhahit7Încă nu există evaluări
- Starting A Caf or Coffee Shop BusinessDocument11 paginiStarting A Caf or Coffee Shop Businessastral05Încă nu există evaluări
- En (1119)Document1 paginăEn (1119)reacharunkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nike's Winning Ways-Hill and Jones 8e Case StudyDocument16 paginiNike's Winning Ways-Hill and Jones 8e Case Studyraihans_dhk3378100% (2)
- Resilia OverviewDocument25 paginiResilia OverviewNoor Kareem100% (1)
- PDFDocument14 paginiPDFBibhuti B. Bhardwaj100% (1)
- Steelpipe Sales Catalogue 4th Edition May 12Document61 paginiSteelpipe Sales Catalogue 4th Edition May 12jerome42nÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamic Cables Pvt. LTD.: WORKS ORDER-Conductor DivDocument2 paginiDynamic Cables Pvt. LTD.: WORKS ORDER-Conductor DivMLastTryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Max232 DatasheetDocument9 paginiMax232 DatasheetprincebahariÎncă nu există evaluări
- SHS Entrepreneurship Week 2Document12 paginiSHS Entrepreneurship Week 2RUSSEL AQUINO50% (2)
- Customer Sample Report BSR For S4hanaDocument79 paginiCustomer Sample Report BSR For S4hanaHarpy AhmedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Taos Museum of Southwestern Arts and CraftsDocument11 paginiTaos Museum of Southwestern Arts and Craftssourovkhan0% (1)
- Bills of ExchangeDocument31 paginiBills of ExchangeViransh Coaching ClassesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Quality Audit Report TemplateDocument3 paginiInternal Quality Audit Report TemplateGVS RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lesson 6 Internal ControlDocument24 paginiLesson 6 Internal ControlajithsubramanianÎncă nu există evaluări
- Financial Statement of A CompanyDocument49 paginiFinancial Statement of A CompanyApollo Institute of Hospital Administration100% (3)
- H4 Swing SetupDocument19 paginiH4 Swing SetupEric Woon Kim ThakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ais 9 ImDocument117 paginiAis 9 ImSimonNisjaPutraZai100% (1)
- PNV-08 Employer's Claims PDFDocument1 paginăPNV-08 Employer's Claims PDFNatarajan SaravananÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cabanlit - Module 2 SPDocument2 paginiCabanlit - Module 2 SPJovie CabanlitÎncă nu există evaluări
- Jama Bandi RecordsDocument4 paginiJama Bandi RecordsImran KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- COBIT 5 Foundation Exam Revision On A PageDocument1 paginăCOBIT 5 Foundation Exam Revision On A PageSergiö Montoya100% (1)
- Ch03 - The Environments of Marketing ChannelsDocument25 paginiCh03 - The Environments of Marketing ChannelsRaja Muaz67% (3)
- Deloitte Supply Chain Analytics WorkbookDocument0 paginiDeloitte Supply Chain Analytics Workbookneojawbreaker100% (1)