Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Lateral Drift Compatibility Analysis Using Finite Element Method Input Data & Design Summary
Încărcat de
Tri Angga Dio SimamoraTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Lateral Drift Compatibility Analysis Using Finite Element Method Input Data & Design Summary
Încărcat de
Tri Angga Dio SimamoraDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
PROJECT : PAGE :
CLIENT : DESIGN BY :
JOB NO. : DATE : REVIEW BY :
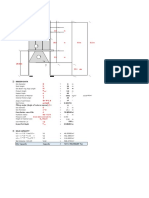
Lateral Drift Compatibility Analysis using Finite Element Method
INPUT DATA & DESIGN SUMMARY
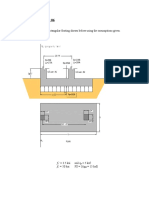
STORY HEIGHTS Habove = 14 ft, (4.3 m)
H= 14 ft, (4.3 m), continued top & bot
Hbelow = 16 ft, (4.9 m)
AXIAL LOAD, ASD PDL = 20 kips, (89.0 kN)
D D D
PLL = 18 kips, (80.1 kN)
EXPECTED STORY DRIFT D= 4.2 in, (107 mm)
(ASCE 7-16/10 12.12.5 )
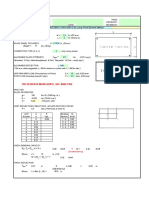
GRAVITY VERTICAL MEMBER INFORMATION
A= 17.6 in2 E = 29000 ksi, (199948 MPa)
` ( 114 cm2) G = 11154 ksi, (76903 MPa)
I= 341 in4
( 14193 cm4)
ANALYSIS
DETERMINE JOINT DEFLECTIONS AND SECTION DESIGN FORCES
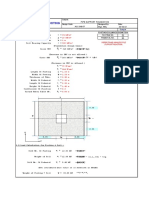
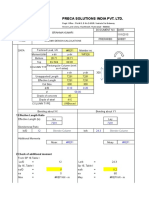
JOINT DEFLECTIONS UNDER D ONLY THE DESIGN MEMBER SECTION FORCES UNDER D ONLY
Note X (in) Y (in) q (deg) Note V (k) P (k) M (ft-k)
N1 0 0 0.496192 N2 -33.09 0.000 225.24
N2 0 0.0000 -1.007175 N3 33.09 0.000 238.00
N3 4.2 0.0000 -0.932621
N4 4.2 0.0000 0.457379
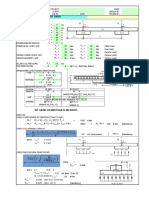
Pu = 1.2 PDL + 1.0 PLL = 42.00 kips, SD level
Mu = (PDL + PLL) D + M = 251.30 ft-kips, SD level
Vu = V = 33.09 kips, SD level
Note: The governing case is always that only the design vertical member has Story Drift and other stories no drift, since the other
story at same direction drifts, including PD effects, will reduce the section forces of design vertical member. The opposite story
drifts are not Expected Deformation, because Expected Deformation can not be developed from Linear Modes Analysis
after CQC or SRSS.
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Lateral Drift Compatibility Analysis Using Finite Element Method Input Data & Design SummaryDocument1 paginăLateral Drift Compatibility Analysis Using Finite Element Method Input Data & Design Summaryjorge01Încă nu există evaluări
- Finite Element Column Design AnalysisDocument9 paginiFinite Element Column Design Analysisciptastrada japek selatanÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Design Is Adequate.: Column Deformation Compatibility Design Using Finite Element Method Input Data & Design SummaryDocument1 paginăThe Design Is Adequate.: Column Deformation Compatibility Design Using Finite Element Method Input Data & Design SummaryCiprian Stelea100% (1)
- Columna de SotanoDocument40 paginiColumna de SotanoMed SbitiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Timber Circular Columns 1Document4 paginiTimber Circular Columns 1John SmithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basement Column Design AnalysisDocument4 paginiBasement Column Design AnalysisErielle AngelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Combined Footings 06: Design The Combined Rectangular Footing Shown Below Using The Assumptions GivenDocument6 paginiCombined Footings 06: Design The Combined Rectangular Footing Shown Below Using The Assumptions GivenjurieskÎncă nu există evaluări
- Column Supporting DiscontinuousDocument40 paginiColumn Supporting DiscontinuousRohan JaiswalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ring FoundationDocument4 paginiRing Foundationjorge01100% (2)
- Caisson Design ProjectDocument2 paginiCaisson Design Projectjorge01Încă nu există evaluări
- EC4 English PDFDocument23 paginiEC4 English PDFSever KawaÎncă nu există evaluări
- API 650 Storage Tank HRD - SubDocument7 paginiAPI 650 Storage Tank HRD - SubBimal DeyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Precast Prestressed Concrete Girder Bridge - Design ExampleDocument37 paginiPrecast Prestressed Concrete Girder Bridge - Design Examplerammiris100% (1)
- Two Story Moment FrameDocument264 paginiTwo Story Moment FrameFranklyn GenoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- High-Rise Structural Embedded Design Based On 2019 CBC/2018 IBC Design CriteriaDocument1 paginăHigh-Rise Structural Embedded Design Based On 2019 CBC/2018 IBC Design CriteriaPhạm Quốc ViệtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 5Document9 paginiHomework 5Ashfaq H KaziÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wall Pier Design Based On 2016 CBC & 2018 IBC Input Data & Design SummaryDocument2 paginiWall Pier Design Based On 2016 CBC & 2018 IBC Input Data & Design SummaryCesar Romero VilchezÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. Power Requirement/Design Horsepower A. Force Required: ComputationDocument8 paginiI. Power Requirement/Design Horsepower A. Force Required: Computationjaynard_alejandrinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Design Is Inadequate, See AnalysisDocument1 paginăThe Design Is Inadequate, See AnalysisZiyad MonierÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design FootingsDocument9 paginiDesign FootingsRupesh KhandekarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slab Punching Design Based On ACI 318-19: Project: Client: Design By: Job No.: Date: Review byDocument2 paginiSlab Punching Design Based On ACI 318-19: Project: Client: Design By: Job No.: Date: Review byAndy BenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Exercises Problem No. 4 V - BeltsDocument4 paginiExercises Problem No. 4 V - BeltsAriel GamboaÎncă nu există evaluări
- BRBFDocument5 paginiBRBFtonyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design Calculation For Raising PlateformDocument15 paginiDesign Calculation For Raising PlateformAbdul Hameed100% (1)
- Seismic Analysis: CategoryDocument7 paginiSeismic Analysis: CategoryAnil kumar RÎncă nu există evaluări
- P (KN) (Pmax) (Pmax) : Structurepoint - Spcolumn V6.00 (TM) - Licensed To: Dungbv, Tedis. License Id: - XXXXXDocument3 paginiP (KN) (Pmax) (Pmax) : Structurepoint - Spcolumn V6.00 (TM) - Licensed To: Dungbv, Tedis. License Id: - XXXXXHoàngTrầnÎncă nu există evaluări
- Project Job Ref.: Col ColDocument4 paginiProject Job Ref.: Col ColDyesa G. BeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- N111 - Outrigger Parking - FinalDocument5 paginiN111 - Outrigger Parking - FinalcheeseonglawÎncă nu există evaluări
- A Wind AnalysisDocument7 paginiA Wind AnalysisGustavo Huesca RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Base PlateDocument4 paginiDesign of Base PlateBenjun Balbin100% (5)
- Spandrel Beam Analysis Hot-Rolled W-Shape AISC 2005 SpecificationDocument8 paginiSpandrel Beam Analysis Hot-Rolled W-Shape AISC 2005 SpecificationmohammedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Structural Glass Design FEMDocument1 paginăStructural Glass Design FEMErick Santiago CubillosÎncă nu există evaluări
- ANCHORED Sheet Pile WallDocument11 paginiANCHORED Sheet Pile WallFranklyn GenoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Perancangan Alat Pemindah Lanjut - 02: Marchellino Alexander Leimena 3 DEB (211322013)Document15 paginiPerancangan Alat Pemindah Lanjut - 02: Marchellino Alexander Leimena 3 DEB (211322013)NurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rigid Footing Moment CapacityDocument1 paginăRigid Footing Moment CapacityJUAN MANUEL ALFARO RODRIGUEZÎncă nu există evaluări
- c1Document1 paginăc1iwanguna71Încă nu există evaluări
- Structural Glass Design FEMDocument1 paginăStructural Glass Design FEMBoy BangusÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2 Seismic Performance of Adobe BuildingsDocument2 pagini2 Seismic Performance of Adobe Buildingsbasabi12Încă nu există evaluări
- Slab Design 2 Way IsDocument5 paginiSlab Design 2 Way IsPirpasha UjedeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Two-way slab design analysis and reinforcement detailsDocument5 paginiTwo-way slab design analysis and reinforcement detailsKamran AliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daniel Tian Li: Grade Beam Design Based On ACI 318-02Document2 paginiDaniel Tian Li: Grade Beam Design Based On ACI 318-02mdalgamouniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Binder 1Document87 paginiBinder 1K KARTHIKÎncă nu există evaluări
- Elements of Soil Mechanics, 8th Edition Example 7.4Document15 paginiElements of Soil Mechanics, 8th Edition Example 7.4renishkavukattÎncă nu există evaluări
- Input Data & Design Summary: Steel Stair Design Based On AISC-ASD 9thDocument48 paginiInput Data & Design Summary: Steel Stair Design Based On AISC-ASD 9thrupesh417Încă nu există evaluări
- Design of Single and Group Pile FoundationsDocument98 paginiDesign of Single and Group Pile FoundationsWai Yann ZawÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC Pier TabaDocument19 paginiRC Pier TabaMitiku AregieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind On SiloDocument7 paginiWind On SiloHgagselim SelimÎncă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Design: 1.20 M 17.3 KN/M 25 Deg 0 Kpa 1.2 M SquareDocument1 paginăFoundation Design: 1.20 M 17.3 KN/M 25 Deg 0 Kpa 1.2 M SquareKS LeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Analysis For Building With H 60 FT, Based On 2018 IBC/ASCE 7-16 Input DataDocument10 paginiWind Analysis For Building With H 60 FT, Based On 2018 IBC/ASCE 7-16 Input DataOmar RubioÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steel Road PlateDocument1 paginăSteel Road Platejklo12Încă nu există evaluări
- Steel ColumnDocument8 paginiSteel ColumnLeeCH LeeCHÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cantliver Beam DesignDocument87 paginiCantliver Beam DesignShivaranjan HJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Slab Design 2 Way IsDocument3 paginiSlab Design 2 Way IsRam LangheÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fire Engine - Loading Appendix - G - 293Document46 paginiFire Engine - Loading Appendix - G - 293Shivaranjan HJÎncă nu există evaluări
- Steelstair DesignDocument6 paginiSteelstair DesignKenneth EdraÎncă nu există evaluări
- GTG Beam Formwork DesignDocument32 paginiGTG Beam Formwork DesignshihabÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basement Column Design Analysis and Capacity CheckDocument3 paginiBasement Column Design Analysis and Capacity CheckPhanithÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basement Column Supporting Lateral Resisting Frame Based On CBC 2001/ ACI 318-05 Input Data & Design SummaryDocument28 paginiBasement Column Supporting Lateral Resisting Frame Based On CBC 2001/ ACI 318-05 Input Data & Design SummaryFranklyn GenoveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsDe la EverandSolution Manual for an Introduction to Equilibrium ThermodynamicsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estehmanisanget 1Document2 paginiEstehmanisanget 1Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAD Code120Document2 paginiSAD Code120Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estehmanis 3Document2 paginiEstehmanis 3Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estehmanis 2Document2 paginiEstehmanis 2Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAD Code127Document2 paginiSAD Code127Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAD Code Phyler 02123345Document2 paginiSAD Code Phyler 02123345Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAD Code122Document2 paginiSAD Code122Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAD Code117Document2 paginiSAD Code117Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Estehmanis 2Document2 paginiEstehmanis 2Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- RC Pier-F (Box & Girder)Document36 paginiRC Pier-F (Box & Girder)robynson banik100% (6)
- SAD Code115Document2 paginiSAD Code115Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- SAD Code Phyler 02123345Document2 paginiSAD Code Phyler 02123345Tri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Box Girder Super Structure1Document74 paginiBox Girder Super Structure1Hemant Sonawadekar100% (2)
- Marshall Mix DesignDocument2 paginiMarshall Mix DesignTakdir Satria NandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 50/20 POST TENSIONED CONCRETE MIX DESIGNDocument86 pagini50/20 POST TENSIONED CONCRETE MIX DESIGNTri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Box Girder Super Structure1Document74 paginiBox Girder Super Structure1Hemant Sonawadekar100% (2)
- Concrete Design Mix Calculator Ver 2 00 ManipalDocument2 paginiConcrete Design Mix Calculator Ver 2 00 ManipalTri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concrete Design Mix Calculator Ver 2 00 ManipalDocument2 paginiConcrete Design Mix Calculator Ver 2 00 ManipalTri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Replacement Bridge Design ProjectDocument64 paginiReplacement Bridge Design ProjectTri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reinforcing Bar Area Chart for Various Bar Sizes and SpacingsDocument3 paginiReinforcing Bar Area Chart for Various Bar Sizes and SpacingsTri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- StructuresBuild Software ListDocument2 paginiStructuresBuild Software ListTri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Design For Low-Profile Solar Photovoltaic Arrays On Flat Roof, Based On SEAOC PV2-2012 Input Data & Design SummaryDocument2 paginiWind Design For Low-Profile Solar Photovoltaic Arrays On Flat Roof, Based On SEAOC PV2-2012 Input Data & Design SummaryTri Angga Dio Simamora100% (1)
- Eng 210 Design Aid Ut2101401 Eng Pipe DesignDocument12 paginiEng 210 Design Aid Ut2101401 Eng Pipe DesignTri Angga Dio SimamoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- BEAMANAL - Single & Continuous Beam AnalysisDocument6 paginiBEAMANAL - Single & Continuous Beam AnalysistambokÎncă nu există evaluări
- ECE 4363 Syllabus Fall 2011Document8 paginiECE 4363 Syllabus Fall 2011Ref DocsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6600mgwa JKT Psi - FatDocument6 pagini6600mgwa JKT Psi - FatanandakoeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electromagnetic InductionDocument13 paginiElectromagnetic InductionRanjit SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Catalogo EngDocument88 paginiCatalogo EngbysakÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vendors ListDocument59 paginiVendors ListGoliBharggav100% (1)
- Temperature Instrument CalibrationDocument9 paginiTemperature Instrument CalibrationAllen DagsilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questionbank - DCN 8th Sem 1Document2 paginiQuestionbank - DCN 8th Sem 1tanuj125Încă nu există evaluări
- Foundation Earth ElectrodesDocument1 paginăFoundation Earth ElectrodesSandeep KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Scientific Notation CalculationsDocument32 paginiScientific Notation CalculationsMelanie Niña CullarÎncă nu există evaluări
- TLC 549Document19 paginiTLC 549Farhana ImronÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capital Budgeting Techniques and NPV AnalysisDocument38 paginiCapital Budgeting Techniques and NPV AnalysisKushÎncă nu există evaluări
- REHEAT-REGENERATIVE RANKINE CYCLE CalculatorDocument86 paginiREHEAT-REGENERATIVE RANKINE CYCLE CalculatorJustine SomentacÎncă nu există evaluări
- DSP ManualDocument43 paginiDSP ManualMaryam MuneebÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fast Formula GuideDocument96 paginiFast Formula GuideRinita BhattacharyaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omega: HHM30 Digital LCR MeterDocument12 paginiOmega: HHM30 Digital LCR Metervishalbharate123Încă nu există evaluări
- Nms 2nd UnitDocument30 paginiNms 2nd UnitjilikajithendarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Technical Specification PC 1060 I: Atlas Copco PowercrusherDocument4 paginiTechnical Specification PC 1060 I: Atlas Copco PowercrusheralmirÎncă nu există evaluări
- Bomin Paek and Alan Morse, Minjung Kim, & Hoyoon Jung, 2020. Sport Consumer Flow and Shopping Well-Being in Online ShoppingDocument16 paginiBomin Paek and Alan Morse, Minjung Kim, & Hoyoon Jung, 2020. Sport Consumer Flow and Shopping Well-Being in Online ShoppingRen SuzakuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Department of Education: Weekly Home Learning PlanDocument56 paginiDepartment of Education: Weekly Home Learning PlanJaneth Miguel SatrainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Some Probability NotesDocument2 paginiSome Probability Notesapi-179841211Încă nu există evaluări
- CAPE Chemistry Data BookletDocument5 paginiCAPE Chemistry Data BookletAnvitha PanyamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Introductory Chemistry 5th Edition Tro Solutions ManualDocument6 paginiIntroductory Chemistry 5th Edition Tro Solutions Manualjonathantruongylunfl100% (16)
- Chapter 3Document46 paginiChapter 3AnilKarwankarÎncă nu există evaluări
- 6.1 HWDocument3 pagini6.1 HWcocochannel2016Încă nu există evaluări
- Functional Specification Document (Template)Document11 paginiFunctional Specification Document (Template)Madiha Malik50% (2)
- Cost Object ControllingDocument2 paginiCost Object ControllingFranki Giassi MeurerÎncă nu există evaluări
- 17 PCS ResourceGuide Full Final1 PDFDocument68 pagini17 PCS ResourceGuide Full Final1 PDFMako ZoltanÎncă nu există evaluări
- DG 09 006-E 12-09 HELENOS IDocument61 paginiDG 09 006-E 12-09 HELENOS IBalu MÎncă nu există evaluări
- C Programming LanguageDocument41 paginiC Programming Languagekazi habibaÎncă nu există evaluări