Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Haskel Gas Booster Booklet 4-30-16
Încărcat de
chrisofoma100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
284 vizualizări35 paginiHaskel Gas Booster Booklet 4-30-16
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentHaskel Gas Booster Booklet 4-30-16
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
100%(1)100% au considerat acest document util (1 vot)
284 vizualizări35 paginiHaskel Gas Booster Booklet 4-30-16
Încărcat de
chrisofomaHaskel Gas Booster Booklet 4-30-16
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca PDF sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 35
en Accudyne Industries brand
Pressure on Demand
Pneumatic and Hydraulic Driven
Gas Boosters
Why Use a Haskel Gas Booster
Haskel pneumatic and hydraulic driven ges boosters offer a lexible and efficient source for delivering high pressure gases.
®
Oxygen or High Purity Cleaning: Haskel boosters are noted for ther cleanliness and can handle pure gases
‘such as oxygen without risk of any contamination. (Special cleaning required — atvise factory) Haskel's oxygen cleaned
products are cerified per Mil Spec 1330, Refer to the Knowledge Library Link on the Haskel website, www.haskel.com, for
the Oxygen Usage -Best Fractice Guide
MulttStaging Capability: For nigner low rates and pressures, beyond tne capability ota single gas booster, on2 or
more boosters of the same ratio may be plumbed in parallel and then in series with one or more boosters cf the same rato.
High Flow Rates at High Pressures: When high flow rates at high pressures are needed, the booster can
cchargo a receiver to an even higher prassure love, thus storing a voluma of gas available for rapid rolease at a constant
pressure through a pressure reducing vawe.
Cost Savings: Mostindustrial gases are commonly delivered at pressures of 2000 — 2,600 psi n steel cylinders. the
{as isto be used well below the supply pressure, the pressurized supply is easily piped ané controlled to the point of use
with simple valving. However, ifthe end use requires the gas to be used at higher pressures than the supply it will have
tobe boosted. Ges Boosters can utiize al the gas from a supply source such es cylinders, and boost the ges to whatever
pressures jand flows) are required by the application; thus utilizing al the gas volume trom the supply source.
Ifthe application requires a pressure greater than common supply cylinder pressures, a booster can often be justified not only
because of utilization ofthe gas, butalso because itwif eliminate the need to purchase the gas in special higher pressure more
costly supply cylinders such as 3,600 or 6,000 psi O
Pneumatic Driven Gas Booster Features
*Reliable, easy to maintain, compact and robust
*No heat, flame or spark risk
‘Infinitoly variable eyciing spood and output
Pneumatic driven models do not require electrical connection
*Easy to apply automatic controls,
‘*No limit or adverse affect to continuous stop/start applications
+ Seal systems designed for long working life
*Noairine lubricator required
‘* Hydrocarbon free separation between ait and gas sections
Pressures to 29,000 psi (2690 bar}
Built-in cooling {mostmodels)
+ Standard & custom systems available
* Suitable for most gases
* Single, double acting, and two-stage models,
‘*Abiltyto stall at any predetermined pressure and hold the
‘xed pressure without consuming power or generating heat.
O
Introduction to Pneumatic Driven Gas Boosters
Theory of Operation
Haskel Gas Boosters consistof a large area reciprocating air
‘rive piston directly coupled by a connecting rod to a small
area gas piston. The gas piston operatas in a high pressure gas
barrel section. Each ges barrel end cap contains high pressure
inlet and outlet check valves. Varying applications require many
\ifferent booster and horse power |HP) combinations. Haskel
an assist with HP and Cooling requirements and provide
circuity assistance on the following issues: PID Control -
teview and advisement, electrical control, and heat exchanger,
recommendations. General HPU recommencations and guidelines
are available from Haskel drawing 87100-TAB. The air drive
section includes 2 eyciing spool and pilot vals that provide
continuous reciprocating action when airis supplied to the air
rive inlet The ratio between the area ofthe air drive piston and
the gas driven piston is indicated by the number in the model
‘éescription and approximates the maximum pressure the gas
booster is capable of generating.
Isolation ot te gas compression chambers from the air crive
section is provided by three sets of dynamic seals, The intervening
‘two chambers are ventedto atmosphere. This design prevents air
4érivo cantamination from antoring the gas straam.
Haskel gas boosters are used for boosting most all
commonly available industrial gases. However, the gas
should be “Dry Gas", Ino moisture content) Some gases
camnot be pumped with standard boosters, e.g pure Oxygen
or Hydrogen. Depending on the gas and application, 2.9. Dy
as Seal applications, same boosters wil require special
seals, materials of construction, venting, special clesning
ano otter considerations. Knowing the specitic gas is aiso
necessary to determine gas compressibility at the desired
pressure. Compressibilty isa factor used in calculating flow
rates at dfforont prossuras or filling times into a vossol.
Gas booster compressors are suitable for transfer and
pressurization of:
1. Nitrogen (N2)
2 Helium(He)
3. Breathing Air (N202)
4. Nitrous Oxide (N20)
5. Carbon Dioxide (C02)
& Noon (Ne)
7. Argon (Ar)
4 Oxygen (02)*
8 Sulphur Hexefluoride (SF®)
10. Carbon Monoxide (C)**
Cooling is provided by routing the cold exhausted drive air through
an indwvidual jacket surrounding the gas barrel.
Check valves also allow for the equalization of upstream and
downstream pressure prior to boosting therefore the gas booster
only needs to “raise” the upstream pressure to the required
pressure and does not nave to raise ittrom atmospheric pressure.
Operating temperatures for Gas Booster
‘There are two distinct sections: the air drive section and the cas,
barrel section.
Air Drive Section- Standard Air Drive Seals should perform
reliably within 2 temperature range of (25°F to 150°F} [-4°C to
85°C). Lower temperatures will cause air/gas leakage; higher
temperatures reduce seal lite. Haskel recommends 2 minimum
Class 4 air quality per1S0 857311 standards. For operation at
extremely low temperatures, consutttactory.
Gas Barrel Section- Low temperatures normally have little
effect on the operation of standard parts and seais. The
hestfrom the compressing gas helps ta balance outan
acceptable temperature.
‘Maximum average acceptable temperature 115°C (240°F}.
Figure 1: Example
oF Single sage,
4 Connecting Red
5. haus Ne
1. Hagh PrecareBeral
7. Boosar Olt
8. Chat Vale
9. Soocr nat
10. cooing act
12 Aircyag Vato
14 Aira Por
15. per & Lower Caps
12 VertPor rather
11. Hydrogen
(nae
12.Methane(cHay"*
13. Ethylene (C2Ha)"*
18. Natural Gas (CH4)**
(ofl centaits fch eatin of 02 8 N2)
Note: Liquefied gases (propane. C02. nitrous oxide. halons. et.) cax be boested as aliquid or gas ia controlled applications.
* Oxygen (02-maxinum safe working pressure 345 bar (S000 psi}
“For these gases (10-15), the gas booster mustbe operated in a safe and well ventilated area end vert/s)piped to controled environment.
3
Pneumatic Driven Gas Booster Configurations
Dow ain nase protested acy sn age nse oO
‘Two stage models are used for high gas compression ratios.
ss Motel AG Model AG
Single Stage Single Acting StnmestageStgle Actas
osc tannin vain
nie Smrmeem C)
Cooling Fins
Model AGT MotelacT Mode! AGD-4feeding into Model AGT-x/x
‘Two Stage, Cooling Fins Two Stage, Cooling Jackets
Bhue=Compressed Air Yollow=Exhaus! Dive Alt Green=Gas Media
PSI ‘0.0708 Koon
scrn 0.0283 | cu. Metersmin,
Inches BA Willinatars Oo
AG.SDHigh-ratie gas AGT-30/15- Two stage Som 0.483 Kilograms
booster. sinale stane, 12s booster single airhead,
single acting cooling jacket
Selecting a Pneumatic Driven Gas Booster
Ar driven gas boosters have seven significant operating
parameters that determine their selection for any application.
‘These are as follows:
1. Maximum discharge pressure?
2.Alowrate
a Isitconstant?
i. Whatis flowrate required?
b lsitfilling a vessel?
i. Whatis vessel size (water volume}?
ii Whats fill time required?
3. Supply
2 Isit at constant prassure?
bb leit decrossing?
i. Whatis initial prossuro?
ii Whatis the minimum pressure?
4. Air drive pressure available?
5. Air drive volume available?
6. Wnatis the gas?
7. What's the application?
‘The selection ofthe proper booster for any application starts
with determining which booster “series” will provide the
‘amount offlow end pressure required. The ability af the booster
to generate pressure is a function of te drive pressure,
‘multiplied by the nominal booster ratio. The abiity to generate
flovrisa function of the quantity of air available to drive it, the
displacement per cycle of the booster, and volumetric efficiency.
Within each booster series, there are standard materials of
‘construction available. For applications involving aggressive
gases, such as Hydrogen, Helium and C02, some material
substitutions are required.
Single Acting Single Stage “AG” boosters provide economical
Model Number Contiguration
8 - AGT - 1575 - Cc -
bene" ender oe
gle Sage, Single Aa
‘means of boosting prassure for testing or small components and
similar applications where volume is small and efficiency is not
‘important. Control of maximum outlet pressure is accomplished
with the use of an air drive pressure regulator. Maximum outiet
pressureis drive area ratio multiplied by air pressure.
‘Double Acting Single Stage “AGD" boosters notenly pump twice the
volume afa Single Acting, Single Stage Booster per eycie, but also
require less circrive since theinlet ges pressure isassising the air drive
in each diecton, prvicinga substantial portion ortne required diving
{orce. These models provice eticientmeans of boestng large volumes.
of gas tlow to medum compression ras. Maximum outlet pressure
is crive area ratio times air drive pressure PLUS gas suppl pressure.
‘Two-Stage “AGT” boosters pravide efficient means of boosting
to 2 high gas comprossion ratio since the ratio per stago i low.
‘Maximum outlet pressure with these models is dive arza ratio
‘multiplied by air ative pressure plus supply pressure mutiplied
by the area ratio ofthe two gas pistons.
Since these models have interconnected gas pistons, they
‘multiply supoly pressure during the “interstage” stroke by the
area ratio ofthe two gas pistons. If supply prascure is too high,
the booster may have “interstage stall” at an outlet pressure
‘substantially less than that obtainable on the “output” stroke.
This limitation does nat apply if outlet pressure isless than the
“maximum supply” times the area ratio ofthe two ges pistons.
Remember, this condition only applies to two stage models.
‘Specific performance information for your application may be
obtained by referring to the Sample Performance Chart on page
8 ofthis catalog, or froma Haskel distributor. To locate a Haskel
distributor near you, view the Distribution link on our wabsite at
www.taskel.com, or contact Hastel direct.
28881
contol: sirine ster, reg wgouge end manual tarytop
Mectarisal ove suurernataect® at
‘Ecsra lotmesseaton ‘or snes
“are way eying apooitor seven
‘hag Soca mealies oro sares ona Sets pump
ae low pameabiy sel forcoe gue savine
low pameabity seis for Cot gurservion
Eaee'ivce ing weohenin ore Se esecpame
‘are purge nt pl eet singles mosee
‘Vere purge wt Spt reetior 250 €or canes
ive eearngandoeroston orgas sectors
Seer
Model Selection Chart
AB-102
6-182
sez
AaD14
AgD-5
43030
A022
ASDs0
apa
i
-
.
i
i
280.78
o-02
ps2
asta
AgTans
ASTI
asrws2
AST 10
AGT 1/90
AST 1980
2B
to
1
ss) 310
75087
so on
1075
750517
oo 1380
as 1651
soc 2090
a0
cr)
50
som 6
so00 3
co a
so 35
088
som 6
oma
‘00088
om 18
mw
pvmsar arose
[stn roe
100
100
ATM
aT™
100
10
200
250
10
20
AM
am
W
35
”
[vs ATM 16 ATM)
B
B
100
W
W
u
w
35
7
Maximum Rated Gas Outlet
hhorteas
0
10 2
1s
ss 310
7s 517
so om
na 75
som 108
om 1380
sm 1651
som 200
m0 1
no
m
soos
soo as
mm
som a5
vsom0 13
200 om
von 7
‘som 1094
som 126
10
so 35
2m om
soa
som om
a wah?
‘sD 18
orygen
150
1050
20
600
WA
NA
0
20
NA
150
Hydrogen
eS 8 BRR
$88 8 8 8 8
600
NA
r2sa
NA
e000
NA
NA
A
NA
NA
NA
sos
soon
10
wa
3000
Wa
Wa
wa
a0
WA
oo
NA
WA
NA
NA
wa
m
WA
me
a
NA
oo
m8
2
020
oo
134
4a
1Pe
1Pa
mPa
Pe
ore
Pa
imps
wore
2s
amps
isPaPe
AP aie
TPatfs
Poste
1sPaste
soFeiPs
soFeiPs
sores:
cores:
TePesPs
‘mo PasPs
worais
Pais
15Pat2Ps
‘OPaHPs
sopeiPs
corasrs
saPai2Ps
areas
0
132
02
31
138
a
2
18
2
2
103
m8
m8
vt
2
ry
132
132
nz
12
LEGEND: Ps = Gas Supply Pressure, Pa = Drive Pressure, Po = Outlet Pressure
| exe |g NPTBothPote| 2511)
2103 |" NPT Both Pots | 304)
| meeoungeaie
toro | sameaeeciene | 27(12)
‘een
08 aia
|x | mia)
sos sito
| 195 | mi
zu 35110)
| 90 | mua
108) syrseentieene | 40081
| 49 we weparentam pe 4420)
9632) ometron ve wer | 4420)
3183 | Se NFTeomrons | 31/14)
irae net
sus) oie ne | 35110
420 car | 222)
meeoungeate
ma peer fc) 201
toro [erie neazer? | 38107
mo eA] sx
Forveritom rere 2 | 391)
s9tza|
aia
s9(22)
sa
ast
203) cer desse | aire
jzus) SEES | ana
‘meray
zns) Gee | an
fee eae
cuewremen | 109
10.8 (fewer parent soon) 39118)
(12 Wearerensass| a0
Macinun | Min.cst Maximem Rated Gas Outlat Stati Owtet| Piston
ce oe oe be
PaIG | BAR
AGT-/75 jsreese sree] 100 | 7 | 15000 | 1008 ima ‘45 |1e000| 1094 | 75 Pats Ps] 02 la ro le
Astanfo|sreme| crmer| ron | 7 | rsan0 | rose | som | ses |reono| mss |saPasisP4 31 | soe ‘memmeaes seca [17
= ASts075|sreeme| sree] 1m | 7 | 1sm0 | root | smo 315 so) wot |7sPes2sPy a1 | sue Messer 20a)
& asrsene Jee come on | 7 | mo, | ooo [smo | ate [mm | azo | eoroszes| 2 |rorn| remit |asiza
2 psrzanm|snene| ome] son | 7 | rome [tox |e | a6 |rso| rot |sPeo3P4 02 rxn SERENATA oe
3 eorsana}rone] mex] uo | 7 | om | ws |son 9 [ro] me | arose 02 sha)
AGT-62/102|eF0000r) weomer| 10) | 7 | 15000 | 1038 sm | ‘5 /16000) 1034 j100 Pos16 Ps 31 (ae mere 118)
asr-eznea vm | 7 | zom| tam | NA WA |reno} oe neororasr} ox | suo SERRE oz
AST en ro | 7 | amg.) rma | ma | wa | NA) WA heoPosz5P} 21 | sue JERR at
ago | 90] 21 Jama fama] so | 21 | ao | 2 | NA) WA rsPaiPs| am sie) seeTeMreR axis
aaso2 | 0 | 2 Jarmfam| aw | 21 | so | 2 | NA) WA| 2Petes | 200 | szr7) Mrvereemvon liz)
aagozzs| om | 55 atm |aTM| so | 55 | a0 55 | NA| WA) 28Pe4?s| 125 | 2048 | vrMTBeIMom 59(71)
aco. | sto | 245 | so | as | sooo | a4 | som | a5 |so00| 245 | r4Paso | 207 ass) meres hans]
ss |e|a aaa sl|ak scs | s [eee
aso-a | ao | 20 | so | 35 | axoo | ooo |smo | x5 |sxn| 345 | ones? | 62 (1018) vevermenecuenr 12155
scoso| ammo | 176 | so | as [ammo | tom |omm| ow | WA WA | toPeste| 24 |at2 wren smc
iE exctan [arom owmce] ae | 17 | 200 | ame fame) ma | wal WA JoePeosry 7 oe gure ane
B ercrsoo|imese| mum | 2s | 17 | soo | vas | smo | 306 |WA| WA |soPotoPs| 7 | ses | merenuzwer ze
sorucojemem| mee | 2s | 17 | suo, | sas |som | sxe [amo | 270 [oopeeziPg 122 2103, armani 18)
s
Becta x | 17 | ono | ea |smo | a6 | Wa | WA JonPesa3y 122/203), seamen 268)
& sAGr-s009 2 | 17 | 9mp,)..ga0 |som | s45 |omo| ozo | coPes2Ps] 02 1010, urarmare 1115)
£ wore 25 | 17 | 2moo | 137 | NA) WA] NA | WA jeoPoH25Pp a1 | S08 | wrwrriran 12168)
— o> [ogy eo [rs |x| ua ua bean at |r wg rer
1uaso-315 63 | asomo | 2e13 | NA | NA | WA | WA | st5PasP=| 353 | 57. a9 net trons 58I70)
|. o-stage ode Supp pressure so med by ractorx ar dro (Pat avi itertage Stal
irate pressreoxcandeMeximur Ta stag rescire and euppyerocvaresimatanauay exceedepresur link atove thong ineaMintrtge ef valvesotat
thsomessre.
Port information and Addivonal Notes.
2 Ar Dive let Port= 12° FUPT lM” 853)" Modes
© Reler pages 19-7 dmensonel devinge a limos
4 Zipsmnimun are esa a uns
Moimum revels i yagelmen cepAG-23 AGT ACD ps AS Be AS Sees Sic
{Sapam ve pes ret en nod 840, A0T series socrm
©. Grsrosersryraer preston mtb spate cero een yoge exon
i Est wosoge Get bose htsnoxmun eval tispesurnaved scone aso, magrsenes | 40.CEM
‘tows Inerstege Stal: Retr the KrowedgeLiarynkon he Haskel webste,
raw haselcom or adetaleeexlanton. eter topogee 18 2r dimensional srowing ofall moda.
Sample Gas Booster Flow Rate Performance (SCFM)
Flow and Pressure Performance:
‘Sample performance shown below is used for general reference only, consuit Haskel Technical Sales or your Haskel Representative for
specie pertarmanc infomation. Cabie Meters Per Minute = SCFM 0.0282
cia ere
a
aga | 2% | | wo | ae aston | | oo
B| | m | 4 5 | to
Blas ae | ze 2) &
aT 2 | 120 | wo | 16 ATO | | 1200
| @ |G | of 2 | wo
vc | | bm | te | 51 = | owe | as | 2 1 |e] we
AGI) 30 | am | too | “& AGD-1c2 |e | $000 | tooo | 13 DE 7 | 90
| io de | a 3 fas| fms | ats =|
soo] S$) Be | 1g aco | BE | ae | ene | | WP
fo | to | iam | 28 = fom | tom | 7 =| 2
S| ts | bm | & 8 | tam | tam | 18 3 | Be
ags0 ) 35 | om | 40 | 3 AGD-1S2H1 fp | 7000 | teom | 15 manze 0 | 200
B | mo fm | 32 2m |‘ | 2 te | i
age2 | 3 | tow | foo | 3 aes | 3 | fe | v2 © sname2e | | om
% | Soo | Sno | ii Bo 2 | om | de ie | im
Poe eae Bm | im | @ | wo
AG75 ) 30 | tom | ono | 12 ABT Ae | 35 | eo | 100 | 21 aie | 30
2) oe | BS lm) se § | 8
% | too tn | ae Bom | jm | ae 3 | so
oo) | Sao ton | SS & ie | im | 2 |
AG-102 | 32 | 2000 | emo | 4 Ast 70! 4 | ts | 2000 | 19 a J | 500
% | aoa | tao | 28 Sao | som | ba ® | ae
B | fon | ae | cua] @ | se | ito |S van | 3 | te
AG-152 | 20 | 3e00 | amo | 23 AGT1482) ge | 200 | 2400 3 sehsn 78 | 1200
B | ioe | 1am | 12 Sim | im | 2 & | fo
| soo fo | 22 = me | im | 42 & | a
AG-233 | 30 | e000 | 20000 | 24 acT 42) 3 | ize | 4000 | 26 Pete 78 | 1800
tS tome 3m | to
46-303 | fo | Yeu | Zac | as AGTAS/0/ 3 a saspis | 7 | ao
‘| tra | 20m | 32 2 & | ‘0
Se gr | a 2.8 \8
sors] | | we | 11 agrasiso] 2 | 28 wotau | 2 | 2
Sim Bs a| 2 e| @
sons | 2] S| | 8 acrasns| & | uctaa | = | 8
B\2 o| sé S| i 3| 3
2) i fm | ie Sm =|
voc7 | % | $% | am | 8 agransa] | asta | |
2) st 23 2| 8
& | ie | Bm | ate 3 |e 3 |
poor | | 180 0) BY persons] BB! easrwm | 3 | #8
© | zo | | 403 Sire | 0
ooas| Bie |e | RL sare] Bie wsraom | 2 | ie
| S| tee | 3 3 Se | oo
soon | 2 | 220 80/23 porsanad Bm sacra |B | He
so | eo 0 | oe 3 me | oo
S| im | 37 2 8 a | iam
gos | fa | Yeto | ‘oo | ter ABTs2I82| 3 | 9 waasosts | $e | ooo
5 | os | dm | ae | fom
& | So Se | St i) Se
acom |B] 72 | m0] 2 cream] & | wacrxaars| 32 | 282
S| Be | & | 2 | itso
eseno (Qa Ar Dive Qnty 2 | joo
Pa= Air Drive Pressure Po= Gas Outlet Pressure 406-25 oe
8 Supply Pressure a.
8 Outlet Faw Fate
©
Alternative Gas Booster and System
Hydrogen
Booster
Model
Nunber
ora
am
8718s
Specialty Ges Bocster Models
exon | iydogen oxygia
Bootor | Bort: Brsor
Model | Mate ods!
tumor | Number unter
sez ABT880
9 astasns | 205
ac7 | zane porauto | eo
sors | zoca0 aotaors | se
acco | vas | oneo | agtsane| 20
asso | soon AsT-n02
acez | ros | erara | astra
ac% | rma | oeaoo | acT-azro
aseioa |_oxar2 astaanee
toa | ze | omer acrenezh} 2010
1620 or) |
om saco2 | soo
‘80-15 | e218 saco28 | ane
cp | 220 sasoo28
aco7 | sus7 | ame | saeDs | ona
p00 | som taco- | e200
aspis | zen | ames | eacom | ee
spa | res | ames | eaco-an | soa
spe | soso | ames | easo-10
‘spso | sos ‘pers | ams |
Aspe | 2mm | somo | axctsno | samo
so75 | size | sour | sxsr-ac0| sz
AgD-io2| nme sAST-400
sasraoeo| som
acre | 27 sacteuico
acrans| sie | amee | uaco.ais
acT-p0| sams | ame | WAT)
15316
sre
AaT-1e2 x07
Acr-1sn) amar | ese
Models
Inert Gas Booster System Models
Standard | Oxygen
Systom | System
Modo! | Model
Numer | Numer
was | one | ezean
AGA
AGT
gts
AG30
AG50
Age2
G75
6-102
AG.152
AG-233,
Ag-03
ago-rs | eccor | sz
ago-s | seas | ans
aco-7 | sxior | a0s2s
aac-14 | ocso2 | eos
Ago-rs | cso | aosar
acoso | soe | saa
ag-s2 | sos | ansa
ast-so
Ago-e2 | sos | axsao
ae0-7s | cso | mean
asD-102
-aso-1s2 | soa
‘ncr-+ | ocooe | oxsat
astans| seo | msm
asta0| 5363 | s8
AGT
AQT-4/e2| o84s1
asT-w-n| 2008 | 2868
standard
Oxygen
Syston
‘Nol
‘Number
AGT-1950
AcT-1975) sama | so7a0
AgT-ws0
acrours| som | somo
agree | 208 | ssis0
agTsa02
acrsanse) aoe
Acta
AgT-sais2| ast
AGTaz/s2H| 8012
sAGD1
axon2 | cons | ocesa
ene2e | sone | sca
eacn228
arods | oss | oas
eean4 | aosio | cosa
saapco | aos | scar
easpeo | aro
aAGD-I50
sacs | oss | axaas
acr.sc0 | asia | oxo
wacr-wen] sues | sc
wagr-1weo] soso | axse0
wacr-syeo| soit | ase
eacr-onns
as0-315
TaGr
13315
Inert Gas Booster Systems
Haskel’s ability to incorporate and interface electronic contiols into systems provides precise compression and control of gases. O
Standard system components are:
1 Booster with External Pilot Modification to enable use of external
components to start/stop the booster.
2 Aciustable Air Pilot Svtch (inlet) —used to stop the booster when supply z i G@
Dressure fals to adusted setpoint. 5)
3. Adjustable Remoteset Air Plat Switch (outlet —used to stop the booster
when outlet pressure reaches adjusted set point.
4 Pressure Gauge indicetes outlet boosted pressure
5, Pressure Gauge indicates inlet gas pressure supply
6.Gas Fiter used to stop any ingested contamination from @
centering the booster (e.¢. while changing out a gas supply bottle) aysoeyinicy |
7 Roll Bar Frame inot shown) used for mounting booster and 1% Ws),
‘ther components. ae
‘8, Air Filter - inline filter { 20-40 micron) for maintaining air drive quality.
9 Adjustable Air Regulator used to set the Air Drive Pressure
(6-10psiman)
‘10, Air Pressure Gauge indicates the Air Drive Pressure
I, Manual On/Off Vaive and Speed Control Valve used to adjust
cycling speed that the booster cycles
12 Ral Valve used protetne booster & ther components
fromoverpressunzaion
12, Ajutabe Renotset Plot Requltorused to asus the set
paintorthe Remeteset ir Pict Sten
‘14. Pressure Gauge used to indicate the Adjustable Remoteset
equator adjusted ressure oO
15 lterstage Coler-atute & stellcocer used reduce the
baosed gas temperature (part he voeste)
20039 System Shown Above
Charging Systems
Charging systems provide a fast efficient and economical method of charging, or “topping up” gas pressures. Charging units ensure
‘tat tne optimum use is made of commercial botved gases down to as ow as 150 psi or vaporized liquid (cryogenic) supplies wnile
producing pressures as high as 39,000 psi depending on gas type. Units are standard or custom-built ina variety of configurations,
samples of which are ilustrated here.
26968 Oxygen Booster System 26968 Sampo Porformanco
‘oxygen booster systems for iting oxygen cinders. an ertcient, sare ana ‘Onypen GasPressue psi] _ONV9eVOulet
economical system for oxygen handling sere se
‘Ai Div PSL
(A) Outlet stall max gas outlet pressure is: Air drive psix 30 Plus 2x gas inlet psil
(8) interstage stal (Max gas inlet pressure is ar drive psix 15 ifoutletexceeds air
drive psix20. ifitdoes not, max gas inlets air drive psi x20)
(c) Iless air now is available, outlet gas retes will d2crease about in propartion
Performan sedon nested ir rive PSIO 8 SM
Charging Booster ScubAmp
‘includes cylinder mounting bracket. ‘With the use of a ScubAmp, existing air compressor systems can stay
O Nea neo sen et ore
vant
i
i ae i Aka well
a ISSR} AEE
a A RT naar Mn
i we
Gas Transfer, Test Console Controlled
& Charging Carts Test Systems
‘ype! gatesused are Test console housing pneumatic
02, Nz, He, Ar & Air used Gas Booster selected tomest
foruarste, charging, test parameters ofthe customers
testing, calibration or specification. Ove pressures can be
tocloperefon produced up 32,000 psig
Natural Gas Vehi Gaz Cylinder Test Rigs
oe
‘System with Storage
eee
Hy¢rostate and eyinder steteh
test rigs for inspection end
testing ofall gas cylinder and
pressure vessels, including
‘xyger, nitrogen, carbon dioxide
‘and holon bots.
aa]
12
Hydraulic Driven Gas Boosters
For flow rates thattypically go beyond the capability ot pnematic driven boosters.
Haskel's gas booster product line began with hydraulic driven gas booste's. Their gas compression technology has been proven
in critical applications such as Fuel Cell/ Hydrogen, Photovoltaic, Semiconductor, Specialty Gases, and more.
Capable of boosting a variaty of gases, Haskols broad rango of Hydraulic Drivon Gas Boostors offer complate‘toxiilty for your
(gas compression and transfer needs. The key design elements incorporated in tnis range are based on the Haske! technology
that has been combined with cutting edge hycraulic drive contralto provide a complete solution, from plug-in electrical supply to
reliable gas output pressure and flow.
Applications
‘Hydrogen Filling Stations
‘Charging high-pressure gas cylinders and receivers
‘Gas assisted plastic injection molding
Hydraulic accumulator charging
‘charging airbag storage vessels
‘Missile and satelite launch and guidance systems
= Componenttesting
‘Lasor cutting and wolding
+ Oilfield high volume gas testing
‘= Automotive hoses and component gas testing
“Hot isostatic pressing
‘Inert/specialty gas transfer
Biogas charging
‘Extending pressure
Gas blanketing
O
Designs
Single-Stage Double Acting Model=
+ Available in7 models with flow rates to 400 sofm and
maximum supply and outlet pressures to 16,000 pai
+ Designed for high flow end low-to medium compression
ratios
‘Two-Stage Models
* Available in 8 models with flow rates to 45 scfm. Maximum
‘Supply pressure 6000 psig. Maximum outlet pressure to
16000 psig
‘+ Modular construction for easy gas section maintenance
‘+ Adapts to muttple units in parallel or in series driven by
Hydraulic Driven Gas Booster ‘eas somo sabres
Model Number Configuration
100 HGT 6- 85/50 - Options! Features (nemnenygreyianey
EX
Hasta dletrbutor or system bntograion
WJ WJ WJ tJ WJ * Mot arta * Renta operat station
* ietpresurecntal op + Heater bydauic serait
tao Sarak
I
Qesat + Temes ontobon © Mise stomibaponse
‘ Ll
a Fe vere eatenceseute mrt der tet
wo Las Giana meer inne oem
ey cnt cucunyeaneemaueoucce ay
oe
+ Stainless Steeytonel gas berrel construction
* Gil Free, gas section non-tubricated operation
* Integrated cooling barrels on each gas section
‘Isolation between hydraulic and gas sactions to
prevent contamination,
Gn. and 10in. stroke models
+ Proximity switch control to automate cycling
‘= Able to accept high supply pressures
Benefits
+= Capable of flow rates up to 8x higher than air driven models
* Modular construction for easy gas section maintenance
+ Willnot rust like ather carbon stee! manufactured units
= Non-contaminating gas compression
* Minimizes gas temperature rise trom compression
* Suitable for ultra pure gas compression
+= Broad range of flows and pressures,
+ Smooth stroke diraetion changeover and cyclo rato control
+ Mutple gas boosters can be driven by one power source
+ Steady state cycle control ta maximize seal ife
* High efficiency for continuous operation
13
Een Pos Gat Outer ProccurefPS)
tocpowerpurbased on Max. hy Pressure 2000 sig CPM Clas Far Min. (18a 120 cers, 29mex 10 srs)
sae Supply Pressure 31 Gae Carer Fw Re SCAM)
Hydraulic Drives Gas Booster Specifications ‘Sample Perfonmance
‘Sopp Pressure |SupplyPressure| Duwet Pressure | Maximem | Displacement cyte |cycles
Minimum | Maximun Maximum | Compression asa es ee eae
ato
soowepe-vs | so | as | 10 | 127 | 1 | a7] 6 an | sim | 25 | 270 | 250 | 00) 25 | ots
az | son | s600| 25 | 2
212 | 160 | zo00| 25 | 20
220 | m0 | woo] 25 | a5
sooHspe-115 | 50 | 3s | 260 | 19 | 270 | wo) 6 isi | sie | 25 | 209 | 25 | 1900! 25 | a7
217 | v0 | z00| 25 | 195
te | soo | z000| 25 | 441
ooHsne-s | io | 7 | ow | s13 | oso | ae | 6 tor | veo | 25 | 274 | 80 | s00| 25 | sao
2as | 10 | a7s0| 25 | 169
272 | sa | eoo| 25 | 72
193 | vam | enoo| 25 | 374
ooHane-s | roo | 7 | amo | azo | 1360] m0 | ao | esr | 2s | 240 | 100 | so00| 25 | sa4
272 2=00 | woon| 25 | 733
21 | | so | 13 | 0
vanes | so | ae | 10 | 127 | 130 | v7 | 6 rie | ve | ie | 434 | 5 | too) 8 | 777
ass | 20 | woo] i | m1
242 | ono | zs00| 10 | ovo
vorspioes | oo | 7 | owo | a3 | eso | ae] 6 re | 2a | ag | 229 | 1200 | s200) 19 | tat
aot 130 | ano| 12 | 9
395 200 | sano| 18 | 705
veonepio-so | soo | 7 | 9000 1200 | ao | 6 oe ff aim |e | St tae | oe as,
2 zoo |iter| 2 | wa
‘20 | zoo |taat| 12 | tr
is 20 | za| | 30
vnorosases| so | as | veo | rz | eso | ae | noe te | ao | | at w/a) no
2s bo |stno| 2 | 7
zi | to | so| a | wo
mo | to | 5m0| a | ws
vncrowaso| so | as | veo | rr |e | as | coe | xo | | 22 12 | am] | us
moto || 2 | ms
i a0 |am| | 2
zi 30 | am| a | 21
rmerasises| so | as | zen | uo |eso | as | se os | ams | | BI 90 am) Bt
Bs oo |amo| m | a3
rerosiss0| so | as | ze0| 1 |r| oo | mw | wo | | M2 Jem) es
mos 20 || 2 | ns
mon || | ts
rooeTeaséo | 00 | 7 | oom | sis |issio| so | 20 ss | aos | as | 22 | Om) | 8
ar ro |tom| a | 27
ms | ts | o| i | ae
Ss | zo || 1s | 92
raweroscim| so | as | veo | ra |e | ae | we | on | soo | w | SF) Sa) | 2
3 zo || 1 | eo
weave |stoo| te | 22
otto || ts | 21
raeriosesa) so | se | reo | 127 |r| eo | so | oo | umm | oo | ye |e) | me
20 | amo| te | 00
ait | 30 | mo| 12 | 8
at oo | amo| 8 | uz
raniereseco| oo | 7 | emo | a jis] oo | a | sx | w | ey OB | am Be
too |ttar| | ae
14. peFERTOPAGES20-25,OR DIMENSIONAL DRAVINGS OF AU MODES
Applications for Pneumatic and Hydraulic Driven
Gas Boosters and Gas Booster Systems
oO General Applications
Condenser LeakDetection crc Recovery + Oxygen Boosting
‘Gas Transfer Circuit Broakars + Loat Detection Systems ‘Fual Celis; Mobile, Portable and Stationary
‘Aircraft Jacking + Charging Gas Suspensions Power Vaive Actuation/Hold Dump Valves Closed
* Heliconter Pop Floats * Missile Test Systems ‘Gas Assisted injection Molding |GAIN)
‘ Autociaving - Low Pressure *Coolingwith Helium m Plot Plants +*Gas Chargngfor Aircraft Tre Ifation
* Hot isostatic Presses * Nitrogen nection for Molding Machines _* Pressure Testng of Hydraulic Systems-— Skycrol
‘Automotive Air Bag Vessel Filing * Cryostat Testing (Nitrogen and Argon) —-—_—* Gas Pressure and Leak Testing
= Hein Cock Prox aur testa * Nitrogen Accumulator Cnarging + Super Creal Flu Extraction
* Blow Moing * Die Cushion Gyinger Charging Gas Reciam -Low Pressure
“Boost Pressures from N2/02 Generators» Oxygen Life Support Batles ‘Testing Brake Calipers
+ Breathing Air Systems ‘Escape Chute Charging-Co2 Charging __* Cylinder Hydro Test
+ Later Cutting (Ar, N2,02, Ho)
Preumaic Driven Gas Boosters for
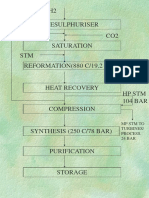
Hydrogen Applications
Hydrogen Applications
Prosu
Hastel Manutactures the most extensive range of gas handling tena
‘solutions for gas rarsfe orboostng applications, including ‘AG-82 | 1000 | 421@ 4800 80979
Hydrogen. Hydrogen use products include Pneumatic or as7s | 1500 | 381@so00 1990
Hydrauic Driven Sas Beosters, Diaphragm Compressors, and ‘asi | 2000 | s02@ 12000 ax901
BuTech High Pressure Valves andFitings,thatare Hydrogenated gan, | 459 | gas@e7i0 21992
1» over 20000 sg. asp-s | 500 | wss@r700 81983
CO fates. acps0 | 750 | s1z@s160 oxs0e
* Hydrogen Fueling & Filing Stations aso | 750 | wes 80985
‘Hydrogen Compression, Storage & Transfer Asb-2 | 900 | s97@s800 81980
Fue call: Mobile, Portable & Stationary SSE GEES RSE ea Oe
‘Boosting H2 Generator Out Pressure enasr_ | mee | 207m riese0 || Toner
styeoven Punteaton ast-mns | 100 | 2es@rsi0 | 250044000 | staee
= seanfeaca panies
PTA manufacture actiaez | 250 | sa@soo0 25009000 | angst
See ye AGT1s30 | 500 | s8e@s400 4g009,000 | sta92
cpabouins enet/ aia ieee actasys | 250 | 254@7250 | 4onnzc00| 20002
- Hiyiropenatin eacions AGts075 | soo | 270@7250 9.eouz,c00| sta9
+ Cyne fling for storage rom H2 generation Ea ico cn sce Acc eee
RAD lab gas distribution actams2 | 260 | 193@ 13750 4oonns.c00 | aea08
Power generation lused asa contart) aaT-eznsz | 1000 | se0@ v4s00 | 9eoors,00| stos7
+ Semiconductor manufacturing {fase ps Ove Press an 8 SCFM (P10 st)
eAso-4 | 160 | oav@sc | 5000 | e720
aasvo | 70 | wasesio | 500 | a0
aaso-s0 | 1000 | s47@sem 900 | i185,
aact-wao | soo | m@sem) son | a7220
sast-iwoo | 250 | ssr@oom aco | izes
aaat-ayeo | tooo | to@ssoo | oo | siz
ose on 10s ive Presuran 6 SCFM F-10525)
15
Selecting Your Accessories
Haskel can either provide accessories separately or supply them fied to form 2 complete package suited to your apolication
‘Additionally, Heskel can fit customer nominated accessories. Our accessories catalog is available and our techricel supportteam is,
alvays ready to advise you on the most suitable choice of accessories for your application,
Aull range of high-pressure regulators, valves, switchas and ancillary equisment is avaiable to suit all
our gas boosters.
+ Air pilot switches
+ Air pilot valves
* Regulating reiet valves
* Directional control and
release valves
+ Hydraulic accumulators, gas
‘and tubing
‘Plenum chambers
Port adapters
«Pressure Regulators
Gauge snubbers
receivers and storage cylinders sFiters
16
Regulating Relief and Back
Preseure Centre! Valves
Provide over pressure protection on any
high pressure low flow gas or liquid systen.
(See system accessory catalog.)
Gas Receivers
Gas receivers in 10,000 ané
20,000 psi series. Eleven models
‘from 20 to 897 cu in. displacements
{See system accessory catalog.)
Stainless Steel Check Valves
‘Constructed throughout of 316 series
‘stainless steel for high corrosion resistance.
= APTFE semi soft seat forhigher
contamination tolerance withoutleekage.
‘The PTFE initially deflects a sight amount
then the ball or poppet to come to rest against
‘the motal soatso the PTFE dose nothave to
absorb the fullload of the high pressure.
‘High pressure valves, fitings
«Stainless stesl check valves
+ Intensiiers with integral checks
for cycling
* Capillary type gauge snutbers
Please ask for your copy of our
latest accessories brochure
ee
Air Pilot Switches
‘These pressure switches produce a pneumatic
signal up to 150 psi at any sensing pressure within
‘their adjustmentrange,
ters
+5 Microns
+6000 psi, 30,000 psi 2medels,
1a" NPT and 1/4" 8 tube
+83. or paper elements
Directional Control and
Release Valves
Directional Control valves are basically a family
with common characteristics and benefts.
They are seated poppet or ball design for
virally zero leakage at high pressures with
low viscosity fluids.
Intensifiers
Intensifers with integral ehecks for cycling
All stainless steel in high pressure
wetted section.
Pneumatic Driven
° Gas Booster
Dimensional
Drawings
Air Drive Inlet Port = ¥” FNPT all the Models
Gas Booster Model: 4AG-25
Gas Booster Model: AG-7
622388)
238i 28m) a 238m
Gas Booster Models: AG-15, AG-30, AG-50, AG-75
ea
Gas Booster Models: AG-62, AG-102, AG-152
aT enn 107672}
382 mn
09a {oer} ASME PORT cxsourer ont
ery aoepeont
S88 - Lessa en
gen mm - + azemmienm
18
Gas Booster Models: AG-233
O - it i so petmn
\
sosapea
esiencinny SENATOR xs omneroort
at Bt - seompeon ourasvous
Gas Booster Models: AG-303
Baan + [—tsameen
ssn
civngasomy OETPCRT f cxsounerroet
Sie onl
Han ont
: sa _- was
O eons Boel ssh prem +
sone wournenoise
Gas Booster Models: AGD-1.5
8m
L esanpteomy , sseemceem,
20m 8mm
O . , suspen
sani 19am)
a2 a
13422 item saneest © aR
L ameperen
20
Gas Booster Models: AGD-4
sessed
sate ml
cevmpesnn) —— SSSOUETPONT casero
Lose m | ir ie!
+ antngasn)—L ration) + trdeeg | arte
espn i mt
Gas Booster Models: AGD-7
‘oxngsien}
Bree
25m)
rampoamm | IS NETIORT citar
L annTbem
s2ie(0e ssn!
saszieerTent
scent
£95 06m) ts mst ot xs ouersont
wowmnerase ss9npsen t+ sanity
“019m een) tsapiten|
ssn etem =
28 STS
Gas Booster Models: AGD-14
sot retont : farsa ee
ssp)
stant exscueront
voarmeness ote Sent J
23a en] S ssingeremy +
sang tem}
Gas Booster Models: AGD-32, AGD-62, AGD-102, AGD-152
2atep on ; tsar
pe
aterm | SHENTON cas ounersone
sehen
{ss pheni =-636n67 m+
Gas Booster Models: AGT-4
sesongrom sissies
Ll
eon 1805 od
sean veueoes [Fat
Sings om +
Tstepitean)
21
Gas Booster Models: AGT-7/15, AGT-7/30
26.5 in 4 em nest
sola
aia
nag ame] sa
am Stem)
Gas Booster Models: AGT-15/30, AGT-15/50, AGT-15/75,
AGT-30/50, AGT-30/75
sa femes ‘sree
cxsounervont ae
foo
seni =| asso ae
maar + sian om) +
Gas Booster Models: AGT-14/32, AGT-14/62
sump ae soaen peat
erent ~
21m ont
2103 6m) J
Lassa =
onan
Gas Booster Models: AGT-32/62, AGT-32/102, AGT-32/152
AGT-62/102, AGT-62/152, AGT-62/152H
atapmstont
siaapeomn
satnpartens
‘stnpeestan
wowmgraues- > susegiron)
oi aa peaten
ce 853m ETRE nel 45650 [115.5 mn]
astetiten seasnptetim
23
i
to
aH
24
Gas Booster Models: 8AGD-2.8, 8AGD-2.8H
+ ss PS oo a
25
26
Gas Booster Model: 8AGD-5
Gas Booster Model: 8AGD-14
Gas Booster Models: 8AGD-30, 8AGD-60
O = . asthe ne
27
Gas Booster Model: 8AGT-5/14
Gas Booster Model: 8AGT-5/30
28
Gas Booster Models: 8AGT-14/30, 8AGT-14/60
O Gas Booster Model: 8AGT-30/60
29
Gas Booster Model: 8AGT-60/150
Gas Booster Model: 14AGT-125/315
30
Gas Booster Model: 14AGD-125, 14AGD-315
31
Hydraulic Driven
Gas Booster
Dimensional
Drawings
Hydraulic Connections:
120H0D10, 120 HGTIOmodele: tin SAE female perts(2) rated at 2900 psi max.
{100HGDE, 1OHGTO models 1/2 in SAE female pots (2 rated at 3500 psi max.
Gas Connections:
129HOD10, 120 HETI0, 1004606, 1O0HT@ modele ratoe:
$0, Min SAE femal pr het, 5 M/PEuTech Pri pars each dl ctng singe two sage, Outetrated 160U0psg 120 senes, 130 psig 100 sere,
Inet orisos0 psig bath ses
5; linen pte nen part Cue pr aig sinew ope raed tsp cheba etptenpsbhowes
185, Jin AEtnale ote Nin SAE at) proach cing sng to gle 20 sg
“146, | in SAEfemsle port|init), im SAE louse (2 portseach di acting, single two stagel, rsted2250 psq
105, lin SAEfemale port, (2 ports each dhl acting, single tivo stage), rated 1880 psig
Gas Booster Model: 100HGD6-50, 100HGD6-85,
100HGD6-115, 100HGD6-145
32
Gas Booster Model: 100HGT6-85/50, 100HGT6-145/50
O —
© Gas Booster Model: 120HGD10-50, 120HGD10-85,
120HGD10-165
0 | Se
33
34
Gas Booster Model: 120HGT10-85/50, 120HGT10-165/85
Notes
a
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- GPDC and Other Charts For Packed ColumnsDocument12 paginiGPDC and Other Charts For Packed ColumnschrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hazard Identification Report FormDocument1 paginăHazard Identification Report FormchrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Climate Finance Inflows To South Africa (Mitigation Versus Adaptation)Document60 paginiClimate Finance Inflows To South Africa (Mitigation Versus Adaptation)chrisofoma100% (1)
- Distillation Tower Flooding More Complex Than You Think PDFDocument8 paginiDistillation Tower Flooding More Complex Than You Think PDFchrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Injection Molding MachineDocument3 paginiInjection Molding MachinechrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- MEOH Flow ChartDocument1 paginăMEOH Flow ChartchrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Comparative Studies of Gasoline Samples Used in Nigeria U.Z. Faruq, M. Runde, B.G. Danshehu, H.N. Yahaya, A.A. Zuru and A.B. MuhammadDocument6 paginiComparative Studies of Gasoline Samples Used in Nigeria U.Z. Faruq, M. Runde, B.G. Danshehu, H.N. Yahaya, A.A. Zuru and A.B. MuhammadchrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Android CodesDocument2 paginiAndroid CodeschrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.2 JKR 28 Vacuum Brick Production LineDocument5 pagini2.2 JKR 28 Vacuum Brick Production LinechrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2.1 JKR 28 Vacuum Brick Production LineDocument5 pagini2.1 JKR 28 Vacuum Brick Production LinechrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Euromktscan PlattsDocument16 paginiEuromktscan PlattschrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Abstract - Marathon Oil Company - Unloading Horizontal Gas WellsDocument1 paginăAbstract - Marathon Oil Company - Unloading Horizontal Gas WellschrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- T22 User ManualDocument67 paginiT22 User ManualchrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fee Payment Form - Application For Permanent ResidenceDocument1 paginăFee Payment Form - Application For Permanent ResidenceSlowfingerÎncă nu există evaluări
- RE StudioDocument41 paginiRE StudiochrisofomaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)