Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Yhghgjjjhjh
Încărcat de
tayan10 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări3 paginihyutnh
Titlu original
yhghgjjjhjh
Drepturi de autor
© © All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
TXT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documenthyutnh
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca TXT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
0 evaluări0% au considerat acest document util (0 voturi)
11 vizualizări3 paginiYhghgjjjhjh
Încărcat de
tayan1hyutnh
Drepturi de autor:
© All Rights Reserved
Formate disponibile
Descărcați ca TXT, PDF, TXT sau citiți online pe Scribd
Sunteți pe pagina 1din 3
5.
3 Synchronizing Slave Clocks with SFC48 "SNC_RTCB"
Definition: Synchronizing Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real time clocks) you synchronize all the
slave clocks on a bus segment. Successful synchronization is only possible when
SFC48 is called on a CPU whose real-time clock was assigned the master clock
function for at least one bus segment. You assign the relevant parameters with
STEP 7.
The system synchronization of the slave clocks (cyclic after the selected
synchronization interval has elapsed) is independent of SFC48 calls.5.3
Synchronizing Slave Clocks with SFC48 "SNC_RTCB"
Definition: Synchronizing Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real time clocks) you synchronize all the
slave clocks on a bus segment. Successful synchronization is only possible when
SFC48 is called on a CPU whose real-time clock was assigned the master clock
function for at least one bus segment. You assign the relevant parameters with
STEP 7.
The system synchronization of the slave clocks (cyclic after the selected
synchronization interval has elapsed) is independent of SFC48 calls.5.3
Synchronizing Slave Clocks with SFC48 "SNC_RTCB"
Definition: Synchronizing Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real time clocks) you synchronize all the
slave clocks on a bus segment. Successful synchronization is only possible when
SFC48 is called on a CPU whose real-time clock was assigned the master clock
function for at least one bus segment. You assign the relevant parameters with
STEP 7.
The system synchronization of the slave clocks (cyclic after the selected
synchronization interval has elapsed) is independent of SFC48 calls.5.3
Synchronizing Slave Clocks with SFC48 "SNC_RTCB"
Definition: Synchronizing Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real time clocks) you synchronize all the
slave clocks on a bus segment. Successful synchronization is only possible when
SFC48 is called on a CPU whose real-time clock was assigned the master clock
function for at least one bus segment. You assign the relevant parameters with
STEP 7.
The system synchronization of the slave clocks (cyclic after the selected
synchronization interval has elapsed) is independent of SFC48 calls.g Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real time clocks) you synchronize all the
slave clocks on a bus segment. Successful synchronization is only possible when
SFC48 is called on a CPU whose real-time clock was assigned the master clock
function for at least one bus segment. You assign the relevant parameters with
STEP 7.
The system synchronization of the slave clocks (cyclic after the selected
synchronization interval has elapsed) is independent of SFC48 calls.5.3
Synchronizing Slave Clocks with SFC48 "SNC_RTCB"
Definition: Synchronizing Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real tg Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real time clocks) you synchronize all the
slave clocks on a bus segment. Successful synchronization is only possible when
SFC48 is called on a CPU whose real-time clock was assigned the master clock
function for at least one bus segment. You assign the relevant parameters with
STEP 7.
The system synchronization of the slave clocks (cyclic after the selected
synchronization interval has elapsed) is independent of SFC48 calls.5.3
Synchronizing Slave Clocks with SFC48 "SNC_RTCB"
Definition: Synchronizing Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real tg Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real time clocks) you synchronize all the
slave clocks on a bus segment. Successful synchronization is only possible when
SFC48 is called on a CPU whose real-time clock was assigned the master clock
function for at least one bus segment. You assign the relevant parameters with
STEP 7.
The system synchronization of the slave clocks (cyclic after the selected
synchronization interval has elapsed) is independent of SFC48 calls.5.3
Synchronizing Slave Clocks with SFC48 "SNC_RTCB"
Definition: Synchronizing Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real tg Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real time clocks) you synchronize all the
slave clocks on a bus segment. Successful synchronization is only possible when
SFC48 is called on a CPU whose real-time clock was assigned the master clock
function for at least one bus segment. You assign the relevant parameters with
STEP 7.
The system synchronization of the slave clocks (cyclic after the selected
synchronization interval has elapsed) is independent of SFC48 calls.5.3
Synchronizing Slave Clocks with SFC48 "SNC_RTCB"
Definition: Synchronizing Slave Clocks
Synchronizing slave clocks refers to the transmission of the date and time from the
master clock of a bus segment (for example, the S7-400 K-bus, MPI, or S7
backplane bus) to all clock slaves of the bus segment.
Description
With SFC48 "SNC_RTCB" (synchronize real t
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (400)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (345)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (74)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- Mastering Sap S4hana 1709Document617 paginiMastering Sap S4hana 1709yakar55592% (38)
- Peterbilt Conventional Trucks Operators Manual After 1 07 SupplementalDocument20 paginiPeterbilt Conventional Trucks Operators Manual After 1 07 Supplementalmichael100% (44)
- Beauty Parlour Manangement SystemDocument47 paginiBeauty Parlour Manangement SystemShivani GajÎncă nu există evaluări
- Building Management Systems For Pharma, Healthcare & Life SciencesDocument12 paginiBuilding Management Systems For Pharma, Healthcare & Life Sciencesdubaisrinivasulu100% (1)
- 590 Safety ManualDocument54 pagini590 Safety ManualTaz Juan G100% (2)
- DVC RpuDocument28 paginiDVC RpupujFierros100% (1)
- Signature Analysis and Computer ForensicsDocument11 paginiSignature Analysis and Computer ForensicsAnindya Nandi100% (1)
- Motorized Screw JackDocument19 paginiMotorized Screw JackPushpendra Kumar33% (3)
- JETPRO DM-wind (English Small)Document2 paginiJETPRO DM-wind (English Small)Royal Kasepuhan IndonesiaÎncă nu există evaluări
- OptiX RTN 980 Product IntroductionDocument24 paginiOptiX RTN 980 Product IntroductionRafael LessaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 5Document21 paginiChapter 5Yoomif TubeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45CMV Series Manual en v1.1Document77 pagini45CMV Series Manual en v1.1Kamran CarayevÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021 Campus Selection Process & EligibilityDocument1 pagină2021 Campus Selection Process & EligibilityNishant KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Blaupunkt True Wireless Earphone BTW-Lite - ManualDocument17 paginiBlaupunkt True Wireless Earphone BTW-Lite - ManualKiran KissanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antec 1200 ManualDocument11 paginiAntec 1200 ManualmhtradeÎncă nu există evaluări
- House Guide TemplateDocument8 paginiHouse Guide TemplatewandolyÎncă nu există evaluări
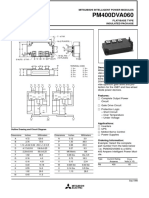
- PM400DVA060: Mitsubishi Intelligent Power ModulesDocument6 paginiPM400DVA060: Mitsubishi Intelligent Power ModulesDiego GrisalesÎncă nu există evaluări
- BR4144A.8 英 (conector)Document1 paginăBR4144A.8 英 (conector)Victor GuzmanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Iso 25964 2 201 PDFDocument19 paginiIso 25964 2 201 PDFLetícia MirandaÎncă nu există evaluări
- SANOG35 Tutorial Programming and Python For Network Engineers PDFDocument138 paginiSANOG35 Tutorial Programming and Python For Network Engineers PDFPhuwanart PhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Do Teenagers Really Need A Mobile PhoneDocument2 paginiDo Teenagers Really Need A Mobile Phonetasya azzahraÎncă nu există evaluări
- K.Surya Rao: Curriculum VitaeDocument6 paginiK.Surya Rao: Curriculum Vitaenaveen_spy122Încă nu există evaluări
- Embedded Web TechnologyDocument3 paginiEmbedded Web TechnologySneha Nagaruru0% (1)
- Tnms SNMP Nbi - Operation GuideDocument90 paginiTnms SNMP Nbi - Operation GuideAdrian FlorensaÎncă nu există evaluări
- TI RTOS Workshop Installation Guide Rev4.00Document12 paginiTI RTOS Workshop Installation Guide Rev4.00asdfÎncă nu există evaluări
- DEFA 800 Serie Installations ManualDocument20 paginiDEFA 800 Serie Installations ManualWendy Mon De ValderramaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pumper March 2011 IssueDocument108 paginiPumper March 2011 IssuePumper MagazineÎncă nu există evaluări
- Summer 2016 Model Answer Paper PDFDocument24 paginiSummer 2016 Model Answer Paper PDFDeepali Bhaskar KarandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nguyenvanthinh BKC13107 N01Document35 paginiNguyenvanthinh BKC13107 N01Văn thinh NguyenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Concord 4 Quick Install GuideDocument12 paginiConcord 4 Quick Install Guidebill080808Încă nu există evaluări