Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Pranav 1
Încărcat de
DesignTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Pranav 1
Încărcat de
DesignDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Annexure-I
Production Capacity
Sr. Name of product Quantity (MT/month)
No. Existing Proposed Total
1. PNTOSA (Para nitro toluene 0.00 250 400
ortho sulphonic acid)
2. DASDA (4-4 Diamino Stilbene 10
2-2 diSulphonic Acid )
3. DNSDA (4-4 Dinitro stilbene 0.00 140
2-2 disulphonic acid)
4. NASDA (4-amino 4-nitro 0.00
stilbene 2-2 disulphonic acid)
Total 10 390 400
List of Raw Materials
Sr. Name of Raw Materials Quantity
No. MT/MT
1. PNTOSA
PNT 0.65
Oleum 23% 1.53
2. DASDA
DNSDA 2.12
Iron Powder 1.50
Acetic Acid 0.01
Spent sulfuric acid 0.75
3. DNSDA
PNTSA 1.80
Soda Ash 0.10
C.S. Lye(48.3%) 1.73
Spent Sulphuric acid 0.75
4. NASDA
DNS (67%) 1.87
NaSH(30%) 2.00
HCl 0.20
NaCl 4.00
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 1
Annexure - II
Manufacturing Process
1. P.N.T.O.S.A.
Manufacturing Process
Sulphonation
In closed vessel P.N.T. and Oleum 23% with water is taken, under no
pressure after stirring of these materials, it is transferred in open vessel
called dumping. Then it is taken in notch for filtration of the above materials.
The material now called P.N.T.O.S.A. output of spent acid comes out during
this process.
Chemical Reaction
Mass Balance
Mass balance of PNTOSA
Input KG KG Output
PNT 653
Sulphonation of PNT
Oleum 23% 1525
2178
Water 1250 Drowing of
sulphonated mass
3428
2147 Spent acid (50‐52%)
Filltration
1281 PNTOSA wat cake
Finished product
(1000 KG 100% PNTOSA)
Total 3428 3428
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 2
2. D.A.S.D.A.
Manufacturing Process
Reduction
In reduction process, water and D.N.S.D.A. is taken into open reduction
vessel then it is heated up to certain temperature. Iron Powder is added as
per requirement. Then the material is filtered in Filter press and the whole
solution is now called isolation solution.
Isolation
In this process, isolation solution is taken in open vessel and then Hydro
Chloric Acid (HCl) is added gradually as per requirement and spent acid is
added as per requirement and transferred to open notch. After this process
vacuum is given to the material. Then the material is centrifuged in
centrifuge. The material ready is called D.A.S.D.A. (cake form).
Chemical Reaction
Mass Balance
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 3
Mass balance of DASDA
Input KG KG Output
DNSDA 2120
Water 7500
Reduction
Iron Powder 1500 2125 Iron slude for Disposal
Acetic Acid 5
9006
Spent sulfuric acid 750 Acidification
9056
Filltration 7750 Effluent
1000 Drying loss
DASDA Drying
1000 DASDA
Total 11875 11875
3. D.N.S.D.A.
Manufacturing Process
Oxidation
In this process, first water is taken into open vessel then P.N.T.O.S.A. and
caustic soda lye is added gradually as per requirement at the same time,
Oxygen is also added gradually as per requirement spent acid charged then
this solution is transferred to MEE process to removal of water. After
removing water material is transferred to ANF1 & ANF2 to obtain Di nitro
(D.N.S.D.A.).
The recovered water from MEE again recycle back to use in process
(oxidation)
Chemical Reaction
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 4
Mass Balance
Mass balance of DNSDA
Input KG KG Output
PNTSA 1795
Water 7460
Soda Ash 75 Oxidation
C.S. Lye(48.3%) 1725
Spent Sulphuric acid 750
11805
Concentration by 6000 Cond.water Back to Process
evaporation
9295
Soda Ash 25 Crystallization
9320
Filltration 4340 Effluent
DNSDA Wet 1490 DNSDA wet cake
Cake(1000 KG 100% (1000 KG 100% DNSDA)
Total 11830 11830
4. N.A.S.D.A.
Manufacturing Process
Partial Reduction
In partial reduction process, DNSDA is taken into open reduction vessel then
it is heated up to certain temperature. NaSH is added as per requirement.
Then the material is filtered in centrifuge and filtered material is called
N.A.S.D.A.
Chemical Reaction
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 5
SO3 H
O2 N CH C NO 2
NaSH HCl
HO 3S
36.47
C14H10S2N2O 10 56.06
430 SO 3H
H
H 2N CH C NO2
NaCl SO2
58.44 64 HO3 S
C14H12S2O8
400
Mass Balance
Mass balance of NASDA
Input KG KG Output
DNSDA (67%) 1865
NaSH(30%) 2000
Water 2800
HCl 200 Reation
NaCl 4000
Catalyst ‐1 10
Catalyst ‐2 10
10885
Filltration 8885 Efflunet
2000 NASDA Wet cake
Drying
(1000 kg 100% bases)
Total 10885 10885
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 6
Annexure-IIIA
Water Consumption
Sr. Description Water Requirement KLD
No.
Existing Proposed Total After
addition Expansion
I Domestic Use 1.0 4.0 5.0
II Green belt 2.0 3.0 5.0
III Industrial:
1 Process 3.5 51.5 55
2 Cooling 5.0 45.0 50
3 Boiler 5.0 35.0 40
4 Washing 10.0 10.0 20
Total Industrial 23.5 141.5 165
Total (I+II+III) 26.5 148.5 175
Less recycle - -- 42
Fresh water requirement 26.5 -- 133
Waste Water Generation
Sr. Description Waste Water Generation KLD
No.
Existing Proposed Total After
addition Expansion
I Domestic 1.0 3.0 4.0
II Green belt - - -
III Industrial:
1 Process 3.0 42.0 45.0
2 Cooling 1.0 9.0 10.0
3 Boiler 1.0 3.0 4.0
4 Washing 10.0 10.0 20.0
Total Industrial 15.0 64.0 79.0
Total (I+II+III) 16.0 67.0 83.0
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 7
Water Balance Diagram
Total water consumption= All units are in KLD
175 KLD (133 Fresh water +
42 recycle)
Domestic Process Washing Utilities Greenbelt
5.0 55 20 90 5.0
17 Acid
from RM
4.0 to
soak pit
Spent Volume
H SO4 51
21 Cooling Boiler
50 40
13.0 Acid for 6
sale Drying Bleed off Blow
Loss 10.0 down
45
8.0 Acid For 4.0
captive use
Primary ETP
Total Effluent (20 + 10 + 4) = 34
1.5 MT salt MEE 1.5 system loss
45.0
42 condensate -
reuse
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 8
Annexure-IIIB
Wastewater Treatment Process
Process Description of ETP (Low COD Effluent)
Raw effluent from plant is collected into Collection Tank cum neutralization
tank by gravity. The acid / alkali solution is being dosed into this tank to
neutralize the effluent. The neutralized effluent is transferred to Primary
Settling Tank by effluent transfer pumps, where polyelectrolyte is added as a
coagulation aid. The clarified effluent from Primary Settling Tank is transferred
to Anaerobic Reactor, where complex organic matter will be digested and
converted into CH4 in absence of Oxygen. Over flow of this reactor will be sent
to Aeration Tank for further COD and BOD reduction. In Aeration tank
Microorganism (Bacteria) will decompose organic waste and convert into CO2
and H2O. This process needs Air from outside, so Blower will be provided for
sufficient Oxygen requirement. Overflow of this tank will be sent to secondary
clarifier for Active sludge separation. Here microbes will be settled at bottom of
tank and again charged into Aeration tank. Overflow of this tank is collected
into Holding Tank by gravity. The effluent from Holding Tank is transferred to
Sand Filter to remove TSS and is passed to Activated Carbon Filter, to remove
the color and polish the effluent. The outlet of Activated Carbon Filter is
pumped into underground NEPL drainage by means of HDPE pipe laid from
Pranav Chemicals to NEPL Chamber.
The sludge collected at bottom of primary settling tank is sent to Sludge
drying beds. Filtered water from Sludge Drying Beds percolates to Collection
tank from where it is again treated in Neutralization Tank for further treatment.
List of units of ETP with their size are given in below table.
Process Description of ETP (High COD Effluent)
Raw effluent coming from process is collected separately into Collection
Tank cum neutralization tank by gravity. Alkali solution is being dosed into this
tank to neutralize the effluent. The neutralized effluent either settled in settling
tank of filter out from filter press. The clear neutral effluent is transferred to
Multiple effect evaporator (MEE), followed by agitated thin film dryer to
separate the water and solid present in effluent.
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 9
Recovered water and condensate coming from MEE will be collected in
specified tanks and recovered water will be used for consecutive batch of
oxidation and reduction. In the same way collected steam condensate will be
used back in boiler.
Solid separated from effluent will be sent to M/ s Saurastra Enviro Project
for land filling.
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 10
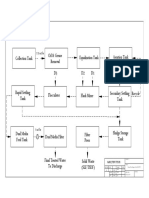
Flow Diagram of ETP
13
13 Filter press
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 11
Annexure-IV
Hazardous waste detail
Sr. Type of Category of Quantity Disposal facility
No. Waste waste as Existing Total after
per expansion
MT/month
HWM Rules MT/month
2016
1. Process waste 26.1 25 300 Collection, Storage,
(Iron sludge) Transportation &
Disposal at TSDF
approved by the board.
2. ETP Sludge 35.3 1.5 22.5 Collection, Storage,
Transportation &
Disposal at TSDF
approved by the board.
3. Used Oil 5.1 50 Lit/Year 200 Collection, Storage,
Lit/Year Transportation &
Disposal by selling to
Registered Reprocesses
or Reuse at lubricant.
4. Discarded 33.1 45 2.25 Collection, Storage,
container/Liner Nos/month 1.5 Decontamination
220
Nos/month
5. Spent Acid 36.3 62.5 325 Sale to
1) sunflex chemical Ind.
2)Gayatri Chemicals Ind.
6. Evaporation 35.3 20 57.5 Collection, Storage,
Residue Transportation &
Disposal at TSDF
approved by the board.
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 12
Annexure-V
Details of Stacks
Sr. Stack Stack Fuel Fuel APC Probable
No. attached to Height consumpt measures emission
(m) ion rate
Flue Gas Stack
Existing
1. Steam Boiler 12 Coal 2.44* Cyclone PM<150 mg/NM3
(1.5 tonne) MT/day Separator + SO2<100 ppm
Multi cyclone NOx<50 ppm
2. Hot Air 12 Coal --
Generator for
Spin Flash
Dryer
3. Steam Boiler 30 Coal Dust Collector
for MEE (4 & Bag Filter
TPH)
Proposed
2. D.G. set 11 Diesel 35 Lit/hr - PM<150 mg/NM3
SO2<100 ppm
NOx<50 ppm
Process Gas Stack
Existing
1. Spin Flash 11 - - In built PM<150 mg/NM3
Dryer Cyclone
followed by
bag filter
Proposed
1. Spin Flash 11 - - In built PM<150 mg/NM3
Dryer (4 nos.) Cyclone
followed by
bag filter
* Fuel will be increased from 2.44 TPD to 22.0 TPD because working
hours will be increased in the same boiler.
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 13
Annexure-VI
Noise level of existing plant
Sr. Location Noise level
No. dB(A)
1. Near Security Gate (Main Gate) 54
2. Administration Building Inside 50
3. Administration Building Outside 55
4. Administration Building Terrace 56
5. Nr Production Area 69
6. Nr Storage Area 64
7. ETP Area 65
M/s. Pranav Chemicals 14
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Etp For Dasda 2Document9 paginiEtp For Dasda 2DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Linear Mixing CalcDocument12 paginiLinear Mixing CalcClarence AG YueÎncă nu există evaluări
- VolumeDocument8 paginiVolumeSUNNY GUPTAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dispersion of Gases CalculationsDocument4 paginiDispersion of Gases CalculationsPeddy Nesa0% (1)
- 03 HRR Flame Height Burning Duration Calculations Sup1Document5 pagini03 HRR Flame Height Burning Duration Calculations Sup1Haris AbdulahÎncă nu există evaluări
- DistillationDocument12 paginiDistillationapi-3728602Încă nu există evaluări
- TANK Module Package: Sample PrintoutDocument20 paginiTANK Module Package: Sample PrintoutSIVAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dowtherm Vent CondenserDocument1 paginăDowtherm Vent Condensersushant_jhawerÎncă nu există evaluări
- STM Dosing and Feeding Systems For Air Pollution ControlDocument42 paginiSTM Dosing and Feeding Systems For Air Pollution ControlJoseph RileyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Basic Control Valve Sizing and SelectionDocument38 paginiBasic Control Valve Sizing and SelectionmohamedÎncă nu există evaluări
- PRICE LIST OF LUFF LUFFIYA COSMETICS 2019Document5 paginiPRICE LIST OF LUFF LUFFIYA COSMETICS 2019Sue2511Încă nu există evaluări
- Converter Atomic Percent To Weight PercentDocument6 paginiConverter Atomic Percent To Weight Percentdiegomez84Încă nu există evaluări
- Txy Diagram For Ethanol/Water at 760Mmhg: Model, Bubble Point Model, Dew Point Data, Bubble Point Data, Dew PointDocument3 paginiTxy Diagram For Ethanol/Water at 760Mmhg: Model, Bubble Point Model, Dew Point Data, Bubble Point Data, Dew PointjunomarsÎncă nu există evaluări
- 09 SpargerDocument17 pagini09 SpargerWeb LogueandoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stack Gas Specification: Project Name Client Location GeneralDocument6 paginiStack Gas Specification: Project Name Client Location Generalbudi utomoÎncă nu există evaluări
- CentrifugalCompressorPower SI UnitsDocument4 paginiCentrifugalCompressorPower SI UnitsReza GhanavatiÎncă nu există evaluări
- MicrofilterDocument17 paginiMicrofilterArrianne Jaye MataÎncă nu există evaluări
- AtfdDocument4 paginiAtfdDarshan PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Divinylbenzene Equipment DesignDocument20 paginiDivinylbenzene Equipment DesignMehul DeshpandeÎncă nu există evaluări
- ATFE Installation Costing for Xylene Distillation ProjectDocument27 paginiATFE Installation Costing for Xylene Distillation ProjectPrathmesh GujaratiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASME - Shell Thickenss Calculation MAIN SHELLDocument4 paginiASME - Shell Thickenss Calculation MAIN SHELLCoralPT WorldwideÎncă nu există evaluări
- Spray Nozzles Total STDDocument3 paginiSpray Nozzles Total STDDylan RamasamyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapor Line Sizing-Mpp6Document10 paginiVapor Line Sizing-Mpp6Nitin KurupÎncă nu există evaluări
- Nozzle Development For AerosolsDocument38 paginiNozzle Development For Aerosolsemre sönmezÎncă nu există evaluări
- Atomic mass and formula calculationsDocument4 paginiAtomic mass and formula calculationssristisekharÎncă nu există evaluări
- 단위 환산 표 및 열전달 계산 문서Document27 pagini단위 환산 표 및 열전달 계산 문서김종민Încă nu există evaluări
- Pump Selection SH BoilersDocument4 paginiPump Selection SH BoilersAnith kumar ReddyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vessel Heat LossDocument2 paginiVessel Heat LossakisdassasÎncă nu există evaluări
- WTP CalculationsDocument10 paginiWTP CalculationsAngshuman Roy ChoudhuryÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sizing Column Distillation C-Factor MethodDocument20 paginiSizing Column Distillation C-Factor MethodCHANADASÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrochloric acid Regeneration of Cation Exchange Resin 225 HDocument8 paginiHydrochloric acid Regeneration of Cation Exchange Resin 225 HPravin BoteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strigle (1994) (014 103) PDFDocument90 paginiStrigle (1994) (014 103) PDFMiguel ReyesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Decanter FunctionDocument6 paginiDecanter FunctionJamil HytÎncă nu există evaluări
- NAC&SACDocument5 paginiNAC&SACEngr. Asif malikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Alpha Chemika PDFDocument208 paginiAlpha Chemika PDFMTech ProjectÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aa + BB +CC+DD RR A+ (B/a) B + (C/a) C + (D/a) D (R/a) R R - KC C C C N N (1-X) N N - (B/a) (N - N) N N - (C/a) (N - N) N N - (D/a) (N - N) C N /VDocument7 paginiAa + BB +CC+DD RR A+ (B/a) B + (C/a) C + (D/a) D (R/a) R R - KC C C C N N (1-X) N N - (B/a) (N - N) N N - (C/a) (N - N) N N - (D/a) (N - N) C N /VChemical EngineeringÎncă nu există evaluări
- Type k1 (Re 1) NP (Re 10 5) : Anchor 0.7 LaminarDocument3 paginiType k1 (Re 1) NP (Re 10 5) : Anchor 0.7 LaminarRobinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Heat Loss Example 4 4Document4 paginiHeat Loss Example 4 4WickyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit conversion program for engineering processesDocument9 paginiUnit conversion program for engineering processesAnubhav KhandelwalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Raw Gas Venturi Scrubber Design and SizingDocument2 paginiRaw Gas Venturi Scrubber Design and SizingDũng LêÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermal design of a 2-effect forward-feed evaporatorDocument4 paginiThermal design of a 2-effect forward-feed evaporatorAristya KurniawanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Desuperheater Boiler Feed Water RequirementDocument2 paginiDesuperheater Boiler Feed Water Requirementmehul10941Încă nu există evaluări
- Final Energy Balance-Vizag DT 9-6-18Document6 paginiFinal Energy Balance-Vizag DT 9-6-18SUBHOMOYÎncă nu există evaluări
- Hydrometer Test: King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals CE 353 Soil Mechanics LaboratoryDocument8 paginiHydrometer Test: King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals CE 353 Soil Mechanics Laboratoryprashanth palaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Control Valve Technical Specification Sheet Globe Service: GasDocument1 paginăControl Valve Technical Specification Sheet Globe Service: Gassiddhesh_guessÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finned Pipe Heat TransferDocument92 paginiFinned Pipe Heat TransferAnonymous JWI6rqtÎncă nu există evaluări
- Made by Date: Top BTM Condition Condition Braced ? SS Slenderness Status Lo LeDocument12 paginiMade by Date: Top BTM Condition Condition Braced ? SS Slenderness Status Lo LeT Satheesh KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- H2S Conversion CalcDocument2 paginiH2S Conversion CalcAnonymous oVRvsdWzfBÎncă nu există evaluări
- Parameter Symbol Value Data Obtained Form Design Intent UnitDocument8 paginiParameter Symbol Value Data Obtained Form Design Intent Uniteke23Încă nu există evaluări
- Metal Extraction Pump SpecsDocument2 paginiMetal Extraction Pump SpecsVenturindo SiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- L-CV-155-VA-24XX01 Nitrogen: ASME Sec VIII Div 1+ PED97/23/ECDocument1 paginăL-CV-155-VA-24XX01 Nitrogen: ASME Sec VIII Div 1+ PED97/23/ECevrim77Încă nu există evaluări
- Heat Exchanger Shell Id CalculationsDocument7 paginiHeat Exchanger Shell Id CalculationsmanojÎncă nu există evaluări
- Psuextension Particle Size 4mm MetricDocument8 paginiPsuextension Particle Size 4mm MetricRed RedÎncă nu există evaluări
- Valve CV Sizing Liquids GasesDocument24 paginiValve CV Sizing Liquids GasesRicardo RamosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dykewall CalculationDocument4 paginiDykewall CalculationVipul GandhiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dish End Weight CalculationDocument5 paginiDish End Weight CalculationAniket royÎncă nu există evaluări
- GA GAS HOLDER - 120MLD-Layout2Document1 paginăGA GAS HOLDER - 120MLD-Layout2epe civil1Încă nu există evaluări
- Densitas Komponen dan Viskositas pada Proses Pengolahan Jerami PadiDocument254 paginiDensitas Komponen dan Viskositas pada Proses Pengolahan Jerami PadiRifah Rizkiyah HasibuanÎncă nu există evaluări
- XSteam V2aDocument9 paginiXSteam V2aPRABU PERUMALÎncă nu există evaluări
- QC 011712Document2 paginiQC 011712nimrovÎncă nu există evaluări
- CYS01 ModelDocument1 paginăCYS01 ModelDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Log Sheet For GMDC BhavnagarDocument1 paginăLog Sheet For GMDC BhavnagarDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Evaporator Rapid DesignDocument2 paginiEvaporator Rapid DesignDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5 m3 STP BOMDocument12 pagini5 m3 STP BOMDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etp fOR Dasda PDFDocument6 paginiEtp fOR Dasda PDFDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical Storage Tank PDFDocument1 paginăVertical Storage Tank PDFDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical Reboiler PDFDocument1 paginăVertical Reboiler PDFDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vertical Storage TankDocument1 paginăVertical Storage Tankmiki156799Încă nu există evaluări
- EC (Electrode Coagulation) Collection Tank & Equalization (LTDS)Document1 paginăEC (Electrode Coagulation) Collection Tank & Equalization (LTDS)DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- ReadmeDocument1 paginăReadmeShraddha SrivastavaÎncă nu există evaluări
- P I DiagramDocument1 paginăP I DiagramDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Horizontal Storage TankDocument1 paginăHorizontal Storage TankDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Horizontal Heat Exchanger PDFDocument1 paginăHorizontal Heat Exchanger PDFDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- JFNLVMGF V (0JMS (8 ZLPH (PVFZP58 (Document16 paginiJFNLVMGF V (0JMS (8 ZLPH (PVFZP58 (DesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Offer For 65 KLD STP Plant BasedDocument12 paginiSubject Offer For 65 KLD STP Plant BasedDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Catalogue 2016 - Industrial ProductsDocument15 paginiProduct Catalogue 2016 - Industrial ProductsDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Etp fOR Dasda PDFDocument6 paginiEtp fOR Dasda PDFDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Recommendations for Oxygen ScavengerDocument2 paginiRecommendations for Oxygen ScavengerDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- MIT Environment 9-9-04Document2 paginiMIT Environment 9-9-04Dr. Ir. R. Didin Kusdian, MT.Încă nu există evaluări
- Tech. Spec. - Grease Contactor ReactorDocument12 paginiTech. Spec. - Grease Contactor ReactorDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- EnglishDocument8 paginiEnglishErUmeshGandhasÎncă nu există evaluări
- 293 Type of Agitator PDFDocument1 pagină293 Type of Agitator PDFDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- MSDS SSS 1303 Oxygen ScavengerDocument3 paginiMSDS SSS 1303 Oxygen ScavengerDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45 KLD Stp-ModelDocument1 pagină45 KLD Stp-ModelDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Subject Offer For 65 KLD STP Plant BasedDocument12 paginiSubject Offer For 65 KLD STP Plant BasedDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- 45 KLD Stp-ModelDocument1 pagină45 KLD Stp-ModelDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optimizing a Waste Water Treatment PlantDocument6 paginiOptimizing a Waste Water Treatment PlantDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
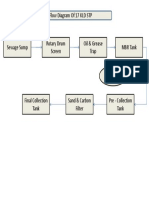
- 17 KLD STP FlowDocument1 pagină17 KLD STP FlowDesignÎncă nu există evaluări
- PolyacetalDocument16 paginiPolyacetalChakma SHIMULÎncă nu există evaluări
- Caramel OverviewDocument6 paginiCaramel OverviewPham Thi Cam TuÎncă nu există evaluări
- CarbofilDocument3 paginiCarbofilBranko FerenčakÎncă nu există evaluări
- PPTDocument28 paginiPPTRaj KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Experience With The Sealed Alcan Compact Degasser Acd PDFDocument10 paginiExperience With The Sealed Alcan Compact Degasser Acd PDFDebashis DashÎncă nu există evaluări
- General Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Document41 paginiGeneral Chemistry 1 - Week 1: Mr. Daryl Vince D. Romerosa - SST1Abcd Reyes100% (1)
- Alkyl Halides and AlcoholsDocument61 paginiAlkyl Halides and AlcoholscasÎncă nu există evaluări
- Antiseptics and Disinfectants GuideDocument38 paginiAntiseptics and Disinfectants GuideNora AboshanadyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Water Treatment in ChillersDocument14 paginiWater Treatment in ChillersabmopalhvacÎncă nu există evaluări
- Daftar Harga Generik dan Non-Generik dari PT Sapta Sari TamaDocument70 paginiDaftar Harga Generik dan Non-Generik dari PT Sapta Sari Tamanaelarizqi0% (1)
- Science 8 3RD Quater Exam ReviewerDocument6 paginiScience 8 3RD Quater Exam ReviewerCrafter CaptsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Engineering ChemistryDocument4 paginiEngineering ChemistrySaha naÎncă nu există evaluări
- Week 2A-Concetration of SolutionDocument72 paginiWeek 2A-Concetration of SolutionLuke BelmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- ASTM A1008 SpecificationDocument7 paginiASTM A1008 SpecificationramorusoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Royalene 301T TDSDocument1 paginăRoyalene 301T TDSMohamed BendoudouchÎncă nu există evaluări
- Health Care GuideDocument51 paginiHealth Care GuideM Zainuddin M SaputraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chile Wish List (Desmond Pilcher)Document8 paginiChile Wish List (Desmond Pilcher)Ogalde LuisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Un NoDocument64 paginiUn Noapi-127528443Încă nu există evaluări
- Formation of Zein Micro Phases in Ethanol-Water - Wang and Padua 2010Document5 paginiFormation of Zein Micro Phases in Ethanol-Water - Wang and Padua 2010Joeska HyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cylinder Salvage ReceptaclesDocument5 paginiCylinder Salvage ReceptaclesAlvaro Rojas AnzolaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Stoichiometry - 1: Concept of Gram AtomDocument36 paginiStoichiometry - 1: Concept of Gram AtomVijay KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- UHLF Liquid FertilizerDocument1 paginăUHLF Liquid FertilizerGrignionÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vapor Pressures: Appendix HDocument1 paginăVapor Pressures: Appendix HMeetu KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Titalon 6800GF-HT: Charpy Impact Strength (Notched)Document1 paginăTitalon 6800GF-HT: Charpy Impact Strength (Notched)katolokchokÎncă nu există evaluări
- C100E Resin PUROLITEDocument3 paginiC100E Resin PUROLITEmilaÎncă nu există evaluări
- 5124 w04 QP 1Document16 pagini5124 w04 QP 1mstudy123456Încă nu există evaluări
- A Detailed Lesson Plan in Chemical ReactionsDocument7 paginiA Detailed Lesson Plan in Chemical Reactionsgorio98% (52)
- Machining Processes GuideDocument21 paginiMachining Processes GuideVenkat Reddy YanamiÎncă nu există evaluări
- ٣٢٥ Molecular biology Sabah Linjawi ١Document13 pagini٣٢٥ Molecular biology Sabah Linjawi ١Zainab RaikÎncă nu există evaluări
- Note CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110Document40 paginiNote CHP 3 Material Science 281 Uitm Em110bino_ryeÎncă nu există evaluări