Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
3prep - FirstTerm-UnitTwo
Încărcat de
Kamal NaserTitlu original
Drepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
3prep - FirstTerm-UnitTwo
Încărcat de
Kamal NaserDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Kamal Science 01115671119
3Prep- FirstTerm-UnitTwo
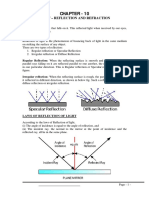
Light Energy-Mirrors & Lenses
Types of Mirrors:
1- Flat Mirrors
2- Spherical Mirrors:-
(a) Concave Mirrors
(b) Convex Mirrors
Give a reason For Answer
1-Convex mirror is To show the path
placed in front of the behind the car。
driver。
2- Concave mirror is To reflect light in front
used in the front lights of the car。
of car。
3-Lenses are used in To study the
telescopes。 planets。
3- Lenses are used To examine the
In microscopes。 microscopic objects 。
4- Lenses are used in To treat the
making medical impairments of vision.
glasses。
The Properties of the image of the objects
formed by the Plane Mirror:
1- Upright 2- Equal to the object
2- Laterally inverted ( Reversed)
3- Virtual (Cannot be received on a screen)
4- The distance of the object to the mirror
= the distance of the image to the mirror
5- The straight line connecting the object and
its image is perpendicular to the mirror
surface。
Laws of the Reflection of light:
First Law:
Angle of incidence = Angle of reflection
Second Law:
The incident light ray,the reflected light ray
and the normal line all lie in the same plane
perpendicular to the reflecting surface。
Concepts Concerning Reflecting of light:
Reflection of light:
The bouncing of the incident light ray in the
same medium when it strikes a reflecting
surface。
The Incident Ray The Reflected Ray
It is the light ray It is the light ray
that: falls on that: bounces from
the reflecting surface the reflecting surface
Angle of Incidence Angle of Reflection
It is the angle It is the angle
between the incident between the reflected
light ray and the light ray and the
normal line. normal line.
The Spherical Mirror:
It is a mirror that its reflecting surface is a
part of a hollow sphere.
Concave Mirror Convex Mirror
Converging Diverging
Its reflecting surface Its reflecting surface
Is a part of the inner Is a part of the outer
surface of the sphere surface of the sphere
Center of Mirror Curvature:
It is the center of the sphere that the mirror is
considered a part of it.
The Center of the The Center of the
Curvature of the Curvature of the
Concave Mirror Convex Mirror
In front of the behind the
reflecting surface reflecting surface
The Radius of Curvature of the Mirror(r):
It is the radius of the sphere that the mirror is
a part of it.
The Pole of the Mirror
(P):
The point that is in the middle
Of the reflecting surface of the
Mirror.
The Principal axis of the mirror( CP):
The straight line that passes by the pole of the
mirror and its center of curvature.
The Secondary axis of the mirror:
Any straight line that passes by the center of
curvature of the mirror and any point on its surface
except the pole of the mirror.
The Focal Length of the concave mirror:
It is the distance between the focus of the concave
mirror and its pole.
The relation between the focal length and the
radius of curvature:
Focal Length = Radius of Curvature /2
F=R/2
The Rules to determine the direction of the
reflecting light rays incident on the concave mirror:
Case(1) The incident light It reflects passing
ray parallel to the through the focus.
principal axis
Of the mirror
Case(2) The incident light It reflects parallel
ray passing to the
through the focus Principal axis.
of the mirror
Case(3) The incident light It reflects back on
ray passing itself.
through the
center of the
mirror
The Formation of the images on a convex mirror:
Always Smaller & Upright & Virtual
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Science Pp3 - Unit 2Document37 paginiScience Pp3 - Unit 2EmadElDinEzzatÎncă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Light ReflectionDocument28 paginiGrade 10 Light ReflectionAnne MalobagoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NoteDocument10 paginiChapter 10 Light Reflection and Refraction NoteJay Maki100% (1)
- Light Reflection and Refraction images by convex concave r explainedDocument11 paginiLight Reflection and Refraction images by convex concave r explainedSeetha SenthilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Sci+Document19 paginiLight Reflection and Refraction Class 10 Notes Sci+Sahil GuptaÎncă nu există evaluări
- CH 1 PhysicsDocument18 paginiCH 1 Physicsraj chopdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Chapter'sDocument24 paginiLight Chapter'sPratik ChavanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 SCIENCE - PhysicsDocument59 paginiClass 10 SCIENCE - PhysicsRamya L NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Science 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Document6 paginiScience 10 Quarter 2 Module 4Jess Anthony Efondo100% (4)
- Padhle 10th - Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument37 paginiPadhle 10th - Light - Reflection & Refractionved bhaskerÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection of LightDocument17 paginiReflection of LightNishant SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection and Refraction of Light Chapter 10 NOTESDocument4 paginiReflection and Refraction of Light Chapter 10 NOTESTechnical AyushÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection of LightDocument11 paginiReflection of Lightlohitha charyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optics 10-PhysicsDocument6 paginiOptics 10-PhysicsTapas BanerjeeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1Document19 pagini10 Science Notes 10 Light Reflection and Refraction 1GAURAV K SHARMAÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3rd Term s2 PhysicsDocument25 pagini3rd Term s2 PhysicsAdelowo DanielÎncă nu există evaluări
- PhysicsX PDFDocument124 paginiPhysicsX PDFcitsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Course of Lectures Contemporary Physics: Part2 : Lecture 1Document64 paginiCourse of Lectures Contemporary Physics: Part2 : Lecture 1Dana SatybaldyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument3 paginiLight Reflection and RefractionUtsav BhavsarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 9 - Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument48 paginiChapter 9 - Light - Reflection and Refractionsekhsayan0102Încă nu există evaluări
- Class 10 - Chapter 10Document52 paginiClass 10 - Chapter 10Ramya L N100% (1)
- Reflection Mirrors 2022 2023Document92 paginiReflection Mirrors 2022 2023Jeon ManobanÎncă nu există evaluări
- LIGHT Physics Form 4Document11 paginiLIGHT Physics Form 4Amrita KaurÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Chapter LightDocument25 paginiPhysics Chapter LightNurliyana Zairul AfendiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection and Refraction - CBSE - XDocument7 paginiReflection and Refraction - CBSE - Xvidyamane23100% (1)
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument2 paginiLight - Reflection and Refractionanilpatel39Încă nu există evaluări
- Light - Reflection and Refraction 10th Phy PDFDocument10 paginiLight - Reflection and Refraction 10th Phy PDFManeeshAkhandJyoyi100% (1)
- Class 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision NotesDocument51 paginiClass 10 Science Chapter 10 Revision Notesved bhaskerÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesDocument78 paginiThe Learners Demonstrate An Understanding of The Images Formed by The Different Types of Mirrors and LensesWarren Dela CernaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light - Reflection & RefractionDocument31 paginiLight - Reflection & RefractionsagarÎncă nu există evaluări
- P3507 Lec 6 7 2023Document6 paginiP3507 Lec 6 7 2023Keketso ThathoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Reflection NotesDocument8 paginiLight Reflection NotesSuperParthz GAMING100% (2)
- Light Reflection Guide in 40 CharactersDocument72 paginiLight Reflection Guide in 40 CharactersTrendi Printing ServicesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light Reflection and Refraction GuideDocument38 paginiLight Reflection and Refraction Guidejatinder kohliÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light: Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument15 paginiLight: Light - Reflection and RefractionShabir KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics ProjectDocument10 paginiPhysics ProjectPranav PatilÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument4 paginiLight - Reflection and RefractionRounak BasuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 - LightDocument35 paginiChapter 10 - LightMadhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision NotesDocument35 paginiChapter 10 - Light Reflection and Refraction Revision Notesprateeksahu1111Încă nu există evaluări
- Grade 10 Subject-Science CHAPTER - 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument9 paginiGrade 10 Subject-Science CHAPTER - 10 Light - Reflection and Refraction Notesluv manotÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch#14 Spherical Mirrors and Lenses: Name DefinitionsDocument4 paginiCh#14 Spherical Mirrors and Lenses: Name DefinitionsZeeshanMahdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionDocument12 paginiChapter - 10 (A) Light and ReflectionSuhani GosainÎncă nu există evaluări
- Folio Physics Chapter 5: Light: Name: Nor Nadia Mohd Azam Class: 4 Ibn Khaldun Teacher'S Name: en - Zai HousneyDocument16 paginiFolio Physics Chapter 5: Light: Name: Nor Nadia Mohd Azam Class: 4 Ibn Khaldun Teacher'S Name: en - Zai Housneynornadeeya_94Încă nu există evaluări
- Phy. 8.chap 5. EngDocument11 paginiPhy. 8.chap 5. EngAmaan V NÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2Document9 paginiUnit 2Mohamed AbdelghanyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Light - Reflection and Refraction NotesDocument9 paginiLight - Reflection and Refraction NotesRaviraj Desai100% (2)
- Light Reflection and RefractionDocument3 paginiLight Reflection and RefractionΛkashÎncă nu există evaluări
- 10 TH Class NotesDocument27 pagini10 TH Class NotesPavana Kumar KallakuriÎncă nu există evaluări
- OpticsDocument63 paginiOpticsJesrel Austria Vidal SarmientoÎncă nu există evaluări
- The Law of ReflectionDocument11 paginiThe Law of ReflectionJeremy ChaiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsDocument19 paginiPhysics Notes For Class 12 Chapter 9 Ray Optics and Optical InstrumentsAsamÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection and Refraction of LightDocument19 paginiReflection and Refraction of LightShalom LogosÎncă nu există evaluări
- Third Term E-Learning Note: Subject: Physics Class: Ss2 Scheme of Work Week TopicsDocument29 paginiThird Term E-Learning Note: Subject: Physics Class: Ss2 Scheme of Work Week TopicsHASSAN OLUMIDEÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 25 Physics 2 TatulianDocument28 paginiChapter 25 Physics 2 TatulianKarissa JanisseÎncă nu există evaluări
- Reflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionDocument11 paginiReflection: Light - Reflection and RefractionmathclubÎncă nu există evaluări
- Written Report in OpticsDocument9 paginiWritten Report in OpticsJhun Lerry Manalo TayanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Formation of Image LDocument24 paginiFormation of Image LTel BiscochoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Optigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationDe la EverandOptigal's Q & A for the NOCE: National Opticianry Certification Exam Questions - Basic CertificationÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Chemical Basis For Life and BiochemistryDocument39 pagini3 Chemical Basis For Life and BiochemistryKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 1-D MotionDocument62 pagini1-D MotionKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Questions On Mirrors and LensesDocument29 paginiQuestions On Mirrors and LensesKamal Naser100% (2)
- 3prep FirstTerm Unit 2 LensesDocument12 pagini3prep FirstTerm Unit 2 LensesKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Unit 2 Chemical Basis of Life ReviewDocument2 paginiUnit 2 Chemical Basis of Life ReviewKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kamal Science 01115671119 3Prep-First Term-Unit One Physical QuantitiesDocument2 paginiKamal Science 01115671119 3Prep-First Term-Unit One Physical QuantitiesKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3Prep-First Term-Revising Units (1-4)Document16 pagini3Prep-First Term-Revising Units (1-4)Kamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 9.3-Analysis of A Chemical FormulaDocument27 pagini9.3-Analysis of A Chemical FormulaKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- B1.2.19 Distance and Displacement WorksheetDocument1 paginăB1.2.19 Distance and Displacement WorksheetKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3prep First Term Revision Unit TwoDocument28 pagini3prep First Term Revision Unit TwoKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3Prep-FirstTerm-Unit4-Reproduction & Species ContinuityDocument9 pagini3Prep-FirstTerm-Unit4-Reproduction & Species ContinuityKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3Prep-The First Term-Unit 3-The UniverseDocument5 pagini3Prep-The First Term-Unit 3-The UniverseKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3prep - First Term-Unit 4-Lessson 2Document8 pagini3prep - First Term-Unit 4-Lessson 2Kamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kamal Science 01115671119 3Prep-First Term-Unit One Physical QuantitiesDocument2 paginiKamal Science 01115671119 3Prep-First Term-Unit One Physical QuantitiesKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Intelligence Community and Classified InformationDocument22 paginiIntelligence Community and Classified InformationKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Prep-First Term - ScienceDocument6 pagini3 Prep-First Term - ScienceKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ch. 7 - IntelligenceDocument7 paginiCh. 7 - IntelligenceKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- 3 Prep-First Term-Unit OneDocument9 pagini3 Prep-First Term-Unit OneKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Simple vs Past ContinuousDocument21 paginiPast Simple vs Past ContinuousKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Computer Assisted Learning - Analysis Through Multiple IntelligencesDocument31 paginiComputer Assisted Learning - Analysis Through Multiple IntelligencesKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- يوسف الصحفي -لغة إنجليزية- تفكير إبداعيDocument2 paginiيوسف الصحفي -لغة إنجليزية- تفكير إبداعيKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present Vs Present ContinuousDocument26 paginiSimple Present Vs Present ContinuousKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Web Traffic PDFDocument17 paginiWeb Traffic PDFKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Simple Present: QuestionsDocument29 paginiSimple Present: QuestionsKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- يوسف محمد الصحفي-عمليات العلم-انجليزيDocument3 paginiيوسف محمد الصحفي-عمليات العلم-انجليزيKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- يوسف محمد الصحفي-عمليات العلم-انجليزيDocument3 paginiيوسف محمد الصحفي-عمليات العلم-انجليزيKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Past Simple vs Past ContinuousDocument21 paginiPast Simple vs Past ContinuousKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Seo For Beggainers PDFDocument20 paginiSeo For Beggainers PDFKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Professionals Secrets PDFDocument37 paginiProfessionals Secrets PDFKamal NaserÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tulip Dress Pattern Multipage PDFDocument21 paginiTulip Dress Pattern Multipage PDFEvelina AnileveÎncă nu există evaluări
- Workman 2011 Children's CatalogDocument45 paginiWorkman 2011 Children's CatalogWorkman Extras0% (1)
- Ballroom Dance NotesDocument12 paginiBallroom Dance Notesmaelin dagohoyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Making A Technical PosterDocument22 paginiMaking A Technical Posters v k100% (2)
- Mixed Twnses English CourseDocument2 paginiMixed Twnses English CourseMorrieÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Cut Off List of Ete-Govt Diets, On 25/06/2010Document42 paginiFirst Cut Off List of Ete-Govt Diets, On 25/06/2010chetanprakashsharmaÎncă nu există evaluări
- What Is Poetry? PoetryDocument8 paginiWhat Is Poetry? PoetryJun HagonosÎncă nu există evaluări
- m006 Modal Test Junio 17Document2 paginim006 Modal Test Junio 17Alex Saca MoraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Crafts From India, Shilparamam, Crafts Village of Hyderabad, Shilparamam Crafts Village, IndiaDocument2 paginiCrafts From India, Shilparamam, Crafts Village of Hyderabad, Shilparamam Crafts Village, IndiavandanaÎncă nu există evaluări
- (Artigo) Zgorzelski, Andrzej. Is Science Fiction A Genre of Fantastic LiteratureDocument9 pagini(Artigo) Zgorzelski, Andrzej. Is Science Fiction A Genre of Fantastic LiteratureFelipe BenicioÎncă nu există evaluări
- ArchitectsDocument18 paginiArchitectsAnand RajÎncă nu există evaluări
- No. 6 Jehovah's "Loyal Love Is Better Than Life"Document2 paginiNo. 6 Jehovah's "Loyal Love Is Better Than Life"api-517901424Încă nu există evaluări
- The Alleged Anonymity of The Canonical Gospel - GathercoleDocument30 paginiThe Alleged Anonymity of The Canonical Gospel - GathercoleAle Monje100% (1)
- You Dian TianDocument5 paginiYou Dian TianWinda AuliaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Twisted Sisters Knit SweatersDocument16 paginiTwisted Sisters Knit SweatersInterweave55% (62)
- Pisces Kissing Style: Slow KisserDocument2 paginiPisces Kissing Style: Slow Kisserfadila batoulÎncă nu există evaluări
- Kunci Gitar Slank - Ku Tak BisaDocument6 paginiKunci Gitar Slank - Ku Tak BisaWilliamRayCassidyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Quarter 2-Performance Task 1Document1 paginăQuarter 2-Performance Task 1Clarence Ramos100% (1)
- Periodic Law LabDocument2 paginiPeriodic Law LabHarrison Lee80% (5)
- Lista Notas Ingles I - DerechoDocument6 paginiLista Notas Ingles I - DerechoMaria Jose Polanco UrreaÎncă nu există evaluări
- WWW Thisisclassicalguitar Com Francisco Tarrega Free Sheet MDocument11 paginiWWW Thisisclassicalguitar Com Francisco Tarrega Free Sheet Mpsk346Încă nu există evaluări
- Septic Tank and Soak Away PitDocument1 paginăSeptic Tank and Soak Away Pitcprein9360% (5)
- Flower Markets in JakartaDocument3 paginiFlower Markets in JakartaDIAS MARIAHQIBTIAH1006780281Încă nu există evaluări
- Soudal Soudaflex 40FC DataDocument2 paginiSoudal Soudaflex 40FC DatarekcahzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Celloidin EmbeddingDocument14 paginiCelloidin EmbeddingS.Anu Priyadharshini100% (1)
- Stair Details by 0631 - DAGANTADocument1 paginăStair Details by 0631 - DAGANTAJay Carlo Daganta100% (1)
- Literary Elements: Self-Learning KitDocument19 paginiLiterary Elements: Self-Learning KitRoMe LynÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rhythm Explored Jordan Rudess PDFDocument15 paginiRhythm Explored Jordan Rudess PDFKedma FrancielleÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tourism in TranscarpathiaDocument7 paginiTourism in TranscarpathiaТетяна МешкоÎncă nu există evaluări
- ¡YES, YOU SHOULD BELIEVE IN THE TRINITY (Ch. 7), Christina R. Darlington, 2013Document27 pagini¡YES, YOU SHOULD BELIEVE IN THE TRINITY (Ch. 7), Christina R. Darlington, 2013Dante A. UrbinaÎncă nu există evaluări