Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Fluid Mechanics
Încărcat de
jimrDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Fluid Mechanics
Încărcat de
jimrDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
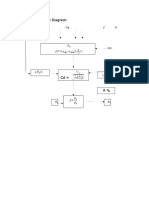
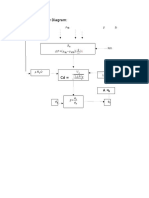
Water flowing through an 8-cm-diameter pipe enters a porous section, as in Fig. P3.
10, which
allows a uniform radial velocity vw through the wall surfaces for a distance of 1.2 m. If the
entrance average velocity V1 is 12 m/s, find the exit velocity V 2 if:
(a) vw = 15 cm/s out of the pipe walls
(b) vw = 10 cm/s into the pipe
(c) What value of vw will make V2 = 9 m/s?
Given A w = π Dp λ
2
π Dp
Ap = Qw = Aw vel w
4
A p vel 1 = Qw + A p vel 2
Dp vel1 - 4 λ vel w
Dp
vel2
π D p λ vel w
Q w
:= Find (vel 2 ,Qw ,A w ,Ap)
Aw π Dp λ
2
Ap π Dp
4
m 15 cm
D p :=8cm λ :=1.2m vel 1 := 12 vel w :=
s -10 s
D p vel 1 - 4 λ velw 3.0 m
vel 2 (velw ) := vel2 vel 2 (velw ) =
Dp 18.0 s
cm m
vel w :=400 ϖ2 :=9 Given vel 2 (velw ) = ϖ2
s s
vel w :=Find (vel w )
cm
vel w = 5.00
s
P3.10.xmcd 9/3/2010 Page 1
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- Fundamentals of Aerodynamics Reviewer Part 2Document39 paginiFundamentals of Aerodynamics Reviewer Part 2AngeloRofelTabundaNava50% (18)
- Project 4 Ethylene OxideDocument12 paginiProject 4 Ethylene OxideNhan Nguyen Van100% (4)
- III Examen Parcial FS0310 I 2023Document4 paginiIII Examen Parcial FS0310 I 2023Jose Murillo VargasÎncă nu există evaluări
- AME 3253 Aerodynamics Practice v03.0Document3 paginiAME 3253 Aerodynamics Practice v03.0jfishryanÎncă nu există evaluări
- ME2121 Finals ReviewDocument4 paginiME2121 Finals ReviewSherman LiamÎncă nu există evaluări
- P2.22 Heat TransferDocument2 paginiP2.22 Heat TransferjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2Ps2B-.85 High Pressure Oxygen Comressor: FeaturesDocument2 pagini2Ps2B-.85 High Pressure Oxygen Comressor: FeaturesCastile100% (1)
- DM Plant Design CalculationDocument196 paginiDM Plant Design CalculationAbhi100% (1)
- PETE 411 Well Drilling: Surge and Swab PressuresDocument40 paginiPETE 411 Well Drilling: Surge and Swab PressuresBendali MehdiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mecânica de Fluidos - Algumas Expressões: P P P M KG CM DineDocument4 paginiMecânica de Fluidos - Algumas Expressões: P P P M KG CM DineJúlia MariaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pacitor: Types of Capacitors and Their Capacitance Parallel Plate CapacitorDocument55 paginiPacitor: Types of Capacitors and Their Capacitance Parallel Plate CapacitorParthuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Coupling of Elasticity, Flow and Material BalanceDocument29 paginiCoupling of Elasticity, Flow and Material BalanceDicky AlviansyahÎncă nu există evaluări
- PETE 411 Well Drilling: Surge and Swab PressuresDocument40 paginiPETE 411 Well Drilling: Surge and Swab PressuresSohaib RashidÎncă nu există evaluări
- Thermodynamic Lesson 3Document5 paginiThermodynamic Lesson 3kelebekkÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solución Parcial Mecánica de FluidosDocument5 paginiSolución Parcial Mecánica de FluidosIñigoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mechanics of Fluids: V. KrishnaDocument13 paginiMechanics of Fluids: V. KrishnaAditya RaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Rientra Duct FlowAirS2012slidesDocument45 paginiRientra Duct FlowAirS2012slideso_mars_2010Încă nu există evaluări
- Alternating Current - 3Document5 paginiAlternating Current - 3noi KlÎncă nu există evaluări
- 351 F 22 Exam EquationsDocument1 pagină351 F 22 Exam EquationsEdaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture-12: P-N JunctionDocument24 paginiLecture-12: P-N Junctionksooryakrishna1Încă nu există evaluări
- Solution 678850Document8 paginiSolution 678850pradeep143789654Încă nu există evaluări
- ECU103 Lecture 06Document30 paginiECU103 Lecture 06sanicyril7Încă nu există evaluări
- Lecture1-Notes 2 PDFDocument5 paginiLecture1-Notes 2 PDFalagarg137691Încă nu există evaluări
- Rectilinear Kinematics Erratic Motion PDFDocument28 paginiRectilinear Kinematics Erratic Motion PDFJubillee MagsinoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lecture 5: Wind Power Estimation Weibull & Rayleigh DistributionsDocument32 paginiLecture 5: Wind Power Estimation Weibull & Rayleigh DistributionsDanielK TetteyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Solution 867900Document11 paginiSolution 867900sujinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Notes 06 Gauss LawDocument8 paginiNotes 06 Gauss LawCaio CamposÎncă nu există evaluări
- E - Gr11 - Physics Test - Chapters Mechanical Properties Fluids QpkeyDocument4 paginiE - Gr11 - Physics Test - Chapters Mechanical Properties Fluids QpkeyMuhammad bilal KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Final 2007 With SolutionsDocument9 paginiFinal 2007 With Solutionsjwangofango7485Încă nu există evaluări
- Electric Potential of A Charge Distribution.: Today's AgendaDocument30 paginiElectric Potential of A Charge Distribution.: Today's AgendaÖzgür BOZAÎncă nu există evaluări
- Isothermal Gas Expansion: P V T P V TDocument4 paginiIsothermal Gas Expansion: P V T P V Twolfofphysics08IPMP01Încă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 AKDocument14 paginiChapter 2 AKSan jayÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cheat SheetDocument2 paginiCheat Sheethome44366Încă nu există evaluări
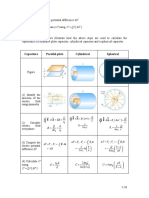
- Formula Sheet + Charts Must Be Returned A3er The ExamDocument19 paginiFormula Sheet + Charts Must Be Returned A3er The ExamRaphael ErfeÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ph1FCAT04 OJEAD120C08 100619 SOLUTION PDFDocument4 paginiPh1FCAT04 OJEAD120C08 100619 SOLUTION PDFmehul pantÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electric Potential of A Charge Distribution.: Today's AgendaDocument13 paginiElectric Potential of A Charge Distribution.: Today's AgendaSimlindile NgobelaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sistema Cerrado Gas Ideal: V P P V P VDocument2 paginiSistema Cerrado Gas Ideal: V P P V P VSaul OsmarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 6Document7 paginiChapter 6William LeiteÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cep PRC II 20 C 860Document44 paginiCep PRC II 20 C 860ImdadÎncă nu există evaluări
- 35 8. (A, D) When The Small Particle Moving With Velocity VDocument1 pagină35 8. (A, D) When The Small Particle Moving With Velocity VTomislav CarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sodapdf-Merged 4Document5 paginiSodapdf-Merged 4harshrajclass9brollno.21Încă nu există evaluări
- R R Q KQ F: Formula Sheet. Electricity and Magnetism, Coulomb's Law and Electric FieldsDocument3 paginiR R Q KQ F: Formula Sheet. Electricity and Magnetism, Coulomb's Law and Electric Fieldskishore_sailuxÎncă nu există evaluări
- Chapter 2 Maxwell's Equations and Plane EM WavesDocument22 paginiChapter 2 Maxwell's Equations and Plane EM Waves123 georgeÎncă nu există evaluări
- 04 Problem Solving Strategies CapacitorsDocument1 pagină04 Problem Solving Strategies CapacitorsSagir Musa SaniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Finite Volume Method For One DimensionalDocument26 paginiFinite Volume Method For One Dimensionalscience1990Încă nu există evaluări
- StudenttextDocument16 paginiStudenttextapi-195130729Încă nu există evaluări
- Compressible Flow Through Nozzles and Diffusers: V DT V D V VDocument14 paginiCompressible Flow Through Nozzles and Diffusers: V DT V D V VCamilo SantacruzÎncă nu există evaluări
- Vector Space PDFDocument26 paginiVector Space PDFShashi KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- Repaso CPU 2022Document21 paginiRepaso CPU 2022Ledesma LópezÎncă nu există evaluări
- LU CapacitorDocument5 paginiLU CapacitorMahadi HasanÎncă nu există evaluări
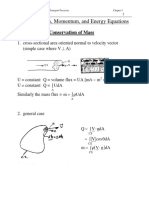
- Chapter 5 Mass, Momentum, and Energy EquationsDocument38 paginiChapter 5 Mass, Momentum, and Energy EquationsShailesh BhanushaliÎncă nu există evaluări
- 2021-2022-1st Sem RRR AERODYN3 - LP 2 of 6 UpdatedDocument28 pagini2021-2022-1st Sem RRR AERODYN3 - LP 2 of 6 Updatedsean buenaventuraÎncă nu există evaluări
- CapacitorDocument37 paginiCapacitorAshok PradhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- Clase 11 Fisica ModernaDocument2 paginiClase 11 Fisica ModernanoelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Boundary LayerDocument3 paginiBoundary LayerPatrick Joseph RoblesÎncă nu există evaluări
- Physical Work 3Document25 paginiPhysical Work 3ScribdTranslationsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Electrostatics - 2: XerciseDocument17 paginiElectrostatics - 2: XerciseAshu MishraÎncă nu există evaluări
- Mathcad - Headbox wall@EL 764.00-MX Vertical DowelsDocument1 paginăMathcad - Headbox wall@EL 764.00-MX Vertical Dowelssaurabh bansalÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Flow DiagramDocument1 paginăInformation Flow DiagramLouie Shaolin LungaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Information Flow DiagramDocument1 paginăInformation Flow DiagramLouie Shaolin LungaoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capacitors: Q E K R R VDocument5 paginiCapacitors: Q E K R R VAlex NbÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dynamics Tutorial II (2016-17) - Answers 1 A) : DZ DXDocument2 paginiDynamics Tutorial II (2016-17) - Answers 1 A) : DZ DXSayan MandalÎncă nu există evaluări
- CE6101 Behaviour of Cam ClayDocument14 paginiCE6101 Behaviour of Cam ClayGan Chin PhangÎncă nu există evaluări
- Aerodynamics Formula OverviewDocument2 paginiAerodynamics Formula OverviewAmmar BegenÎncă nu există evaluări
- Tables of Weber Functions: Mathematical Tables, Vol. 1De la EverandTables of Weber Functions: Mathematical Tables, Vol. 1Încă nu există evaluări
- Discharge From A Water ReservoirDocument4 paginiDischarge From A Water ReservoirjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM 414 Engineering Stress AnalysisDocument4 paginiSM 414 Engineering Stress AnalysisjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Internal Surface Roughness of PipeDocument3 paginiInternal Surface Roughness of PipejimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design of Proposed PipelineDocument2 paginiDesign of Proposed PipelinejimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of Materials - EX23Document3 paginiStrength of Materials - EX23jimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Temperature EffectsDocument2 paginiTemperature EffectsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Air Flow in Galvanized Iron PipeDocument2 paginiAir Flow in Galvanized Iron PipejimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM 406 Engineering Stress AnalysisDocument2 paginiSM 406 Engineering Stress AnalysisjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P520 Strength of MaterialsDocument3 paginiP520 Strength of MaterialsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM324 Stress Analysis Using Strain GagesDocument2 paginiSM324 Stress Analysis Using Strain GagesjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Strength of MaterialsDocument2 paginiStrength of MaterialsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- SM325 Stress Analysis Using Strain GagesDocument2 paginiSM325 Stress Analysis Using Strain GagesjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P4-24 Proposed Power PlantDocument2 paginiP4-24 Proposed Power Plantjimr0% (1)
- P593 Strength of MaterialsDocument2 paginiP593 Strength of MaterialsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Entropy of A SystemDocument1 paginăEntropy of A Systemjimr100% (1)
- Carnot CycleDocument1 paginăCarnot CyclejimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P4-10 ThermodynamicsDocument1 paginăP4-10 ThermodynamicsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P4-12 ThermodynamicsDocument2 paginiP4-12 ThermodynamicsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P4-11 ThermodynamicsDocument1 paginăP4-11 ThermodynamicsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P9.19 ThermodynamicsDocument1 paginăP9.19 ThermodynamicsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P8.19 ThermodynamicsDocument1 paginăP8.19 ThermodynamicsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P9.15 ThermodynamicsDocument2 paginiP9.15 ThermodynamicsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P6 37Document1 paginăP6 37jimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P6.16 ThermodynamicsDocument2 paginiP6.16 ThermodynamicsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P7.52 ThermodynamicsDocument1 paginăP7.52 ThermodynamicsjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- P1.6 Electrical Engineering Using MATHCADDocument2 paginiP1.6 Electrical Engineering Using MATHCADjimrÎncă nu există evaluări
- Housewarmer LP Gas Heater ManualDocument48 paginiHousewarmer LP Gas Heater ManualGrover GatewoodÎncă nu există evaluări
- 002 Tacr enDocument233 pagini002 Tacr enhandaru dwi yunantoÎncă nu există evaluări
- British Pneumatic HandbookDocument96 paginiBritish Pneumatic HandbookAliArababadiÎncă nu există evaluări
- Dimensionless NumberDocument14 paginiDimensionless NumberSarang KumarÎncă nu există evaluări
- E3sconf Icenis2019 14009Document8 paginiE3sconf Icenis2019 14009agungtiyo21Încă nu există evaluări
- Ch-6 Vapor Power and Refrigeration CycleDocument23 paginiCh-6 Vapor Power and Refrigeration CycleKhurram SattarÎncă nu există evaluări
- P 4750319Document16 paginiP 4750319Yaroslav KulykÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sliding Side Door SleevesDocument20 paginiSliding Side Door SleevesSlim.B100% (3)
- Sheet 2 Properties of Pure SubstancesDocument2 paginiSheet 2 Properties of Pure SubstancesZainhumÎncă nu există evaluări
- Cement Balanced Plug TechniqueDocument2 paginiCement Balanced Plug TechniquezapspazÎncă nu există evaluări
- GA 37 VSD 125 Psi Air CooledDocument1 paginăGA 37 VSD 125 Psi Air CooledRobby Ardi NugrohoÎncă nu există evaluări
- Calibration PDFDocument289 paginiCalibration PDFRaj ManovaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viscosity MeasurementDocument8 paginiViscosity MeasurementRiomin AlemaniaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Waterpumps WPDocument25 paginiWaterpumps WPPradyumna Keshari NahakÎncă nu există evaluări
- DB 05 AirCond 130204Document33 paginiDB 05 AirCond 130204Nguyen Huu TriÎncă nu există evaluări
- MagnetosDocument339 paginiMagnetosrobertocadenaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Particulate MatterDocument7 paginiParticulate MatterelyasilahÎncă nu există evaluări
- Pneumatic ClutchDocument29 paginiPneumatic ClutchAarav Shah100% (1)
- ME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsDocument19 paginiME6301 Engineering ThermodynamicsJeevanandam ShanmugaÎncă nu există evaluări
- AC Servicing Guide enDocument22 paginiAC Servicing Guide enaiigee100% (1)
- Qus Ans Matter in Our SorroundingsDocument7 paginiQus Ans Matter in Our SorroundingssabirafrinÎncă nu există evaluări
- Capability Dl&tocument For Process Platforms PDFDocument72 paginiCapability Dl&tocument For Process Platforms PDFSunil SinghÎncă nu există evaluări
- Lessons LearnedDocument13 paginiLessons LearnedBilaljafraniÎncă nu există evaluări
- Viscometer-Group 7Document25 paginiViscometer-Group 7Camille Millondaga100% (1)
- H H. W W W 358.9628.D - .H 6.31533.W D.: AGA Flow Orifice Calculation RoutinesDocument24 paginiH H. W W W 358.9628.D - .H 6.31533.W D.: AGA Flow Orifice Calculation RoutinescincaohijauÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sonatrach - Training - Manual - Tuga - 5001paDocument841 paginiSonatrach - Training - Manual - Tuga - 5001paalaeddine chahdane100% (2)