Documente Academic
Documente Profesional
Documente Cultură
Wind Load 45
Încărcat de
lincah marpaungDrepturi de autor
Formate disponibile
Partajați acest document
Partajați sau inserați document
Vi se pare util acest document?
Este necorespunzător acest conținut?
Raportați acest documentDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
Wind Load 45
Încărcat de
lincah marpaungDrepturi de autor:
Formate disponibile
4.2.3 Force Coefficients C4.2.
3 Force Coefficients
The force coefficient for a set of Force coefficients COg are obtained
frames shall be calculated by from Figure 4.1 (see C4.2.1.1) or
Appendix 4.A A single value is obtained
Cr= COg / e (4.2) for each axis of the structure. This value
is the maximum force coefficient for the
.where component of force acting normal to the
frames for all horizontal wind angles.
COg is the force coefficient for the set of Although the wind direction is nominally
frames given in Figure 4.1, and considered as being normal to the set of
e is the solidity ratio calculated in frames' under consideration, the maximum
accordance with 4.2.4. force coefficient occurs when the wind is
not normal to the frames (see C4.2.6.1
Alternately, Cr may be determined and 4A.1). The angle at which the
using Appendix 4.A maximum force coefficient occurs varies
with the dimensions of the structure, the
Force coefficients are defined for solidity, number offrames, and frame
wind forces acting normal to the frames spacmg.
irrespective of the actual wind direction.
A method to estimate this angle is
given in the Appendix 4.A, which also
provides Cr values for a larger range of
SF/B and e values than Figure 4.1.
The force coefficients CDg were
developed for use on the gross area (i.e.,
- envelope area) of the structure as used by
the British wind loading standard
(Willford/Allsop). These are converted
to force coefficients which are applied to
solid areas as used in ASCE 7 by
Equation 4.2.
The force coefficients CDg were
developed from wind tunnel tests for
structures with a vertical aspect ratio
(ratio of height to width perpendicular to
the flow direction) of four. Although
4-7
S-ar putea să vă placă și
- A Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryDe la EverandA Heartbreaking Work Of Staggering Genius: A Memoir Based on a True StoryEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (231)
- The Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)De la EverandThe Sympathizer: A Novel (Pulitzer Prize for Fiction)Evaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (121)
- Grit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceDe la EverandGrit: The Power of Passion and PerseveranceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (588)
- Devil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaDe la EverandDevil in the Grove: Thurgood Marshall, the Groveland Boys, and the Dawn of a New AmericaEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (266)
- The Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingDe la EverandThe Little Book of Hygge: Danish Secrets to Happy LivingEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (399)
- Never Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItDe la EverandNever Split the Difference: Negotiating As If Your Life Depended On ItEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (838)
- Shoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeDe la EverandShoe Dog: A Memoir by the Creator of NikeEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (537)
- The Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerDe la EverandThe Emperor of All Maladies: A Biography of CancerEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (271)
- The Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeDe la EverandThe Subtle Art of Not Giving a F*ck: A Counterintuitive Approach to Living a Good LifeEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (5794)
- The World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyDe la EverandThe World Is Flat 3.0: A Brief History of the Twenty-first CenturyEvaluare: 3.5 din 5 stele3.5/5 (2259)
- The Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersDe la EverandThe Hard Thing About Hard Things: Building a Business When There Are No Easy AnswersEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (344)
- Team of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnDe la EverandTeam of Rivals: The Political Genius of Abraham LincolnEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (234)
- The Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreDe la EverandThe Gifts of Imperfection: Let Go of Who You Think You're Supposed to Be and Embrace Who You AreEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (1090)
- Hidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceDe la EverandHidden Figures: The American Dream and the Untold Story of the Black Women Mathematicians Who Helped Win the Space RaceEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (895)
- Her Body and Other Parties: StoriesDe la EverandHer Body and Other Parties: StoriesEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (821)
- Elon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureDe la EverandElon Musk: Tesla, SpaceX, and the Quest for a Fantastic FutureEvaluare: 4.5 din 5 stele4.5/5 (474)
- The Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaDe la EverandThe Unwinding: An Inner History of the New AmericaEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (45)
- The Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)De la EverandThe Yellow House: A Memoir (2019 National Book Award Winner)Evaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (98)
- On Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealDe la EverandOn Fire: The (Burning) Case for a Green New DealEvaluare: 4 din 5 stele4/5 (73)
- Legends & Lairs - Giant LoreDocument66 paginiLegends & Lairs - Giant LoreGary DowellÎncă nu există evaluări
- Homework 1 Tarea 1Document11 paginiHomework 1 Tarea 1Anette Wendy Quipo Kancha100% (1)
- DLP in EmpowermentDocument13 paginiDLP in EmpowermentTek Casonete100% (1)
- Antonov 225 - The Largest - Airliner in The WorldDocument63 paginiAntonov 225 - The Largest - Airliner in The WorldFridayFunStuffÎncă nu există evaluări
- DGA Furan AnalysisDocument42 paginiDGA Furan AnalysisShefian Md Dom100% (10)
- Mathematical Method For Physicists Ch. 1 & 2 Selected Solutions Webber and ArfkenDocument7 paginiMathematical Method For Physicists Ch. 1 & 2 Selected Solutions Webber and ArfkenJosh Brewer100% (3)
- Wireless Communications: ImportantDocument1 paginăWireless Communications: Importantlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Regulatory Statements: Federal Communications Commission Notice (FCC - United States)Document1 paginăRegulatory Statements: Federal Communications Commission Notice (FCC - United States)lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4620 - Manual 89Document1 pagină4620 - Manual 89lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Specifications: GeneralDocument1 paginăProduct Specifications: Generallincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Product Specifications and Regulatory InformationDocument1 paginăProduct Specifications and Regulatory Informationlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- RF Exposure Content: FCC Equipment Authorization IDDocument1 paginăRF Exposure Content: FCC Equipment Authorization IDlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4620 - Manual 2Document1 pagină4620 - Manual 2lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- How Do I Reset The Access Point and Router Settings Back To Factory Settings?Document1 paginăHow Do I Reset The Access Point and Router Settings Back To Factory Settings?lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Troubleshooting: Common Problems and Solutions Technical SupportDocument1 paginăTroubleshooting: Common Problems and Solutions Technical Supportlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4620 - Manual 83Document1 pagină4620 - Manual 83lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Common Problems and Solutions: My Mifi 4620L Just Powered Off Without My Pressing The Power Button. Why?Document1 paginăCommon Problems and Solutions: My Mifi 4620L Just Powered Off Without My Pressing The Power Button. Why?lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Port Ranges: Hide Links As Necessary To Open and Close The Port Definition Panel So You Can Define The Ports ForDocument1 paginăPort Ranges: Hide Links As Necessary To Open and Close The Port Definition Panel So You Can Define The Ports Forlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- First Steps: ImportantDocument1 paginăFirst Steps: Importantlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Port Forwarding Custom Applications DMZDocument1 paginăPort Forwarding Custom Applications DMZlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 158Document1 paginăWind Load 158lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- 4620 - Manual 82Document1 pagină4620 - Manual 82lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 162Document1 paginăWind Load 162lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 161Document1 paginăWind Load 161lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
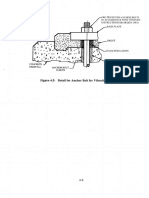
- Pre-Te"Sioned Anchor Bolts in Accordance ''NTH Vendor'S Instructions or Design Dwg. Ase PlateDocument1 paginăPre-Te"Sioned Anchor Bolts in Accordance ''NTH Vendor'S Instructions or Design Dwg. Ase Platelincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Ultimate Strength Design Ultimate Tensile Capacity 3-5 Uniform Building Code IUBC)Document1 paginăUltimate Strength Design Ultimate Tensile Capacity 3-5 Uniform Building Code IUBC)lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Design (CCD) Approach For Fastening To ConcreteDocument1 paginăDesign (CCD) Approach For Fastening To Concretelincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 157Document1 paginăWind Load 157lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 159Document1 paginăWind Load 159lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 156Document1 paginăWind Load 156lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 152Document1 paginăWind Load 152lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 150Document1 paginăWind Load 150lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- E:ti V: Tape - Base PL Grout, A. Bolt A.Bolt Sleeve - T.O. ROUGH Concrete Tape - A. BOLTC-. - '. - / Basepl - GroutDocument1 paginăE:ti V: Tape - Base PL Grout, A. Bolt A.Bolt Sleeve - T.O. ROUGH Concrete Tape - A. BOLTC-. - '. - / Basepl - Groutlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 154Document1 paginăWind Load 154lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- Wind Load 151Document1 paginăWind Load 151lincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
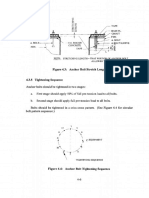
- Figure 4.1: Sleeve Used For Alignment Purposes: Concrete - GroutDocument1 paginăFigure 4.1: Sleeve Used For Alignment Purposes: Concrete - Groutlincah marpaungÎncă nu există evaluări
- LLB IV Sem GST Unit I Levy and Collection Tax by DR Nisha SharmaDocument7 paginiLLB IV Sem GST Unit I Levy and Collection Tax by DR Nisha Sharmad. CÎncă nu există evaluări
- Preprints201808 0216 v1Document15 paginiPreprints201808 0216 v1Baptista Jaime MilioneÎncă nu există evaluări
- Biology Concepts and Applications 9th Edition Starr Solutions ManualDocument9 paginiBiology Concepts and Applications 9th Edition Starr Solutions Manualscarletwilliamnfz100% (31)
- Cs09 404 Programming Paradigm (Module 1 Notes)Document24 paginiCs09 404 Programming Paradigm (Module 1 Notes)Rohith BhaskaranÎncă nu există evaluări
- Sample Database of SQL in Mysql FormatDocument7 paginiSample Database of SQL in Mysql FormatsakonokeÎncă nu există evaluări
- E34-1 Battery Charging and Dishcharging BoardDocument23 paginiE34-1 Battery Charging and Dishcharging BoardGanesa MurthyÎncă nu există evaluări
- Study of Bond Properties of Concrete Utilizing Fly Ash, Marble and Granite PowderDocument3 paginiStudy of Bond Properties of Concrete Utilizing Fly Ash, Marble and Granite PowderLegaldevil LlabsÎncă nu există evaluări
- Goodman Aula 1 e 2Document17 paginiGoodman Aula 1 e 2Danilo TetÎncă nu există evaluări
- Festival Implementation PlanDocument5 paginiFestival Implementation Planapi-318058589Încă nu există evaluări
- VERITAS NetBackup 4 (1) .5 On UnixDocument136 paginiVERITAS NetBackup 4 (1) .5 On UnixamsreekuÎncă nu există evaluări
- Minimization Z Z Z Z Maximization Z Z : LP IPDocument13 paginiMinimization Z Z Z Z Maximization Z Z : LP IPSandeep Kumar JhaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Veris Case StudyDocument2 paginiVeris Case StudyPankaj GargÎncă nu există evaluări
- VHP Series Five P9394Gsi S5: With Esm2 and Empact Emission Control SystemDocument2 paginiVHP Series Five P9394Gsi S5: With Esm2 and Empact Emission Control SystemGabrielito PachacamaÎncă nu există evaluări
- Erectus Ever Found Within The Boundaries of China. The Two Fossil Teeth Unearthed WereDocument6 paginiErectus Ever Found Within The Boundaries of China. The Two Fossil Teeth Unearthed WereenerankenÎncă nu există evaluări
- User Manual - Wellwash ACDocument99 paginiUser Manual - Wellwash ACAlexandrÎncă nu există evaluări
- I. Matching Type. Write Letters Only. (10pts) : Adamson University Computer Literacy 2 Prelim ExamDocument2 paginiI. Matching Type. Write Letters Only. (10pts) : Adamson University Computer Literacy 2 Prelim ExamFerrolinoLouieÎncă nu există evaluări
- Omegas Prezentacija 01Document20 paginiOmegas Prezentacija 01Predrag Djordjevic100% (1)
- Formula BookletDocument2 paginiFormula BookletOm PatelÎncă nu există evaluări
- Fish Siomai RecipeDocument12 paginiFish Siomai RecipeRhyz Mareschal DongonÎncă nu există evaluări
- WP05 - ACT 01 - Development 1909Document53 paginiWP05 - ACT 01 - Development 1909ramesh9966Încă nu există evaluări
- (Guide) Supercharger V6 For Everyone, Make Your Phone Faster - Xda-DevelopersDocument7 pagini(Guide) Supercharger V6 For Everyone, Make Your Phone Faster - Xda-Developersmantubabu6374Încă nu există evaluări
- Applications of Remote Sensing and Gis For UrbanDocument47 paginiApplications of Remote Sensing and Gis For UrbanKashan Ali KhanÎncă nu există evaluări
- CivilCAD2014 English Rev1Document443 paginiCivilCAD2014 English Rev1Nathan BisÎncă nu există evaluări
- Plant Gardening AerationDocument4 paginiPlant Gardening Aerationut.testbox7243Încă nu există evaluări